
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Headers and footers in Word are sections at the top and bottom margins of each page. They can contain additional information such as page numbers, document titles, dates, author names, and other identifying details. By default, the headers or footers on all pages are the same, but in certain scenarios, you can also insert different headers or footers on the first page, odd pages, or even pages. This article will demonstrate how to insert headers and footers into a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Insert Headers and Footers into a Word Document
- Add Different Headers and Footers for the First Page and Other Pages
- Add Different Headers and Footers for Odd and Even Pages
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Insert Headers and Footers into a Word Document in Python
To insert a header or a footer into a Word document, you first need to get them through the Section.HeadersFooters.Header and Section.HeadersFooters.Footer properties, and then add paragraphs to them to insert pictures, text, page numbers, dates, or other information.
The following are steps to add headers and footers in Word:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section using Document.Sections[] property.
- Add Header
- Get header using Section.HeadersFooters.Header property.
- Add a paragraph to the header using HeaderFooter.AddParagraph() method and set paragraph alignment.
- Add an image to the header paragraph using Paragraph.AppendPicture() method, and then set the text wrapping style and position of the image.
- Add text to the header paragraph using Paragraph.AppendText() method, and then set the font name, size, color, etc.
- Add Footer
- Get footer using Section.HeadersFooters.Footer property.
- Add a paragraph to the footer and then add text to the footer paragraph.
- Get the borders of the footer paragraph using Paragraph.Format.Borders property, and then set the top border style and space.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Get a specific section
section = document.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get header
header = section.HeadersFooters.Header
# Add a paragraph to the header and set its alignment style
headerParagraph = header.AddParagraph()
headerParagraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Left
# Add an image to the header paragraph and set its text wrapping style, position
headerPicture = headerParagraph.AppendPicture("Logo.png")
headerPicture.TextWrappingStyle = TextWrappingStyle.Square
headerPicture.VerticalOrigin = VerticalOrigin.Line
headerPicture.VerticalAlignment = ShapeVerticalAlignment.Center
# Add text to the header paragraph and set its font style
text = headerParagraph.AppendText("E-iceblue Co. Ltd."+ "\nYour Office Development Master")
text.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
text.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 10
text.CharacterFormat.Bold = True
text.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Blue()
# Get footer
footer = section.HeadersFooters.Footer
# Add a paragraph to the footer paragraph and set its alignment style
footerParagraph = footer.AddParagraph()
footerParagraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
# Add text to the footer paragraph and set its font style
text = footerParagraph.AppendText("Copyright © 2013 e-iceblue. All Rights Reserved.")
text.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
text.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 10
# Set the border of the footer paragraph
footerParagraph.Format.Borders.Top.BorderType = BorderStyle.Single
footerParagraph.Format.Borders.Top.Space = 0.05
# Save the result file
document.SaveToFile("HeaderAndFooter.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
document.Close()
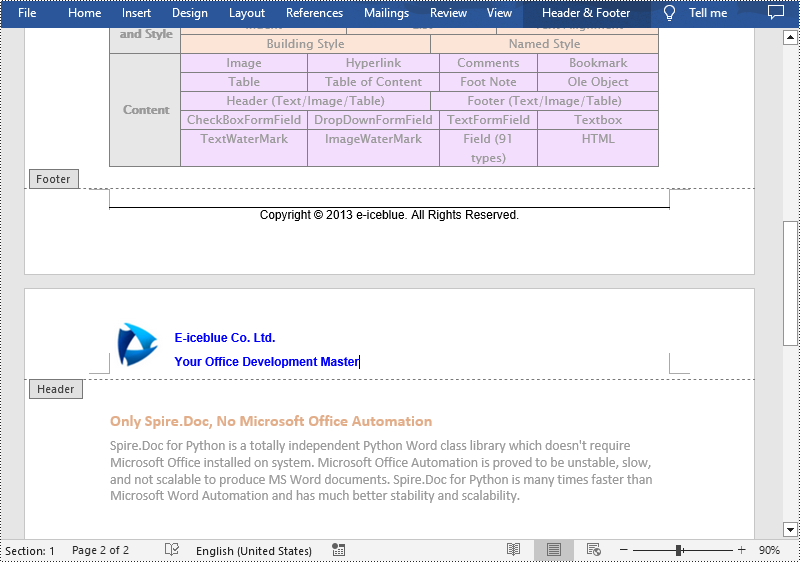
Add Different Headers and Footers for the First Page and Other Pages in Word in Python
Sometimes you may need to insert a header and footer only on the first page, or you may want the header and footer on the first page different from other pages.
Spire.Doc for Python offers the Section.PageSetup.DifferentFirstPageHeaderFooter property to enable a different first page header or footer. The following are the detailed steps to accomplish the task.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section using Document.Sections[] property.
- Enable different headers and footers for the first page and other pages by setting the Section.PageSetup.DifferentFirstPageHeaderFooter property to True.
- Get the first page header using Section.HeadersFooters.FirstPageHeader property.
- Add a paragraph to the first page header and then add an image to the header paragraph.
- Get the first page footer using Section.HeadersFooters.FirstPageFooter property.
- Add a paragraph to the first page footer and then add text to the footer paragraph.
- Set headers and footers for other pages. (There's no need to set this if you only need the header & footer for the first page.)
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Get a specific section
section = document.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Enable different headers and footers for the first page and other pages
section.PageSetup.DifferentFirstPageHeaderFooter = True
# Add a paragraph to the first page header and set its alignment style
headerParagraph = section.HeadersFooters.FirstPageHeader.AddParagraph()
headerParagraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Right
# Add an image to the header paragraph
headerimage = headerParagraph.AppendPicture("E-iceblue.png")
# Add a paragraph to the first page footer and set its alignment style
footerParagraph = section.HeadersFooters.FirstPageFooter.AddParagraph()
footerParagraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
# Add text to the footer paragraph and set its font style
text = footerParagraph.AppendText("Different First Page Footer")
text.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 11
# Set the header & footer for other pages. If you only headers & footers for the first page, don't set this.
para = section.HeadersFooters.Header.AddParagraph()
para.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Left
paraText = para.AppendText("A Professional Word Python API")
paraText.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
paraText.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_DeepPink()
para.Format.Borders.Bottom.BorderType = BorderStyle.Single
para.Format.Borders.Bottom.Space = 0.05
paragraph = section.HeadersFooters.Footer.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
paraText = paragraph.AppendText("E-iceblue Co. Ltd.")
paraText.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
paraText.CharacterFormat.Bold = True
paraText.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_DodgerBlue()
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("DifferentFirstPage.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
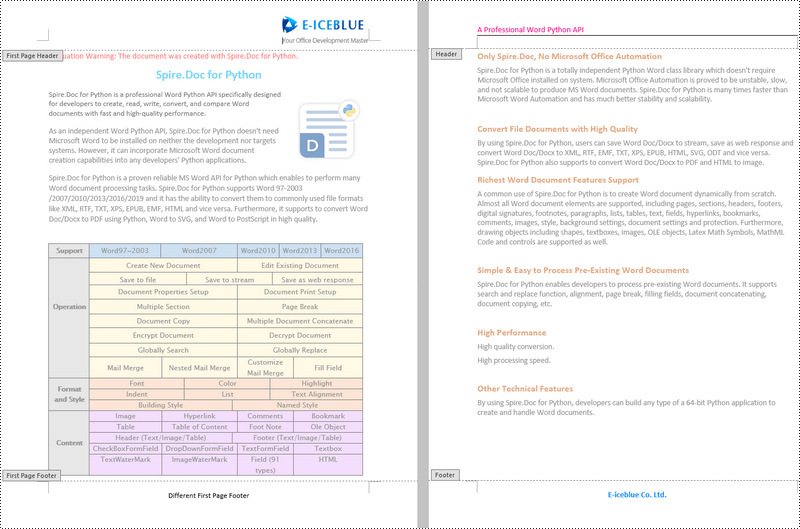
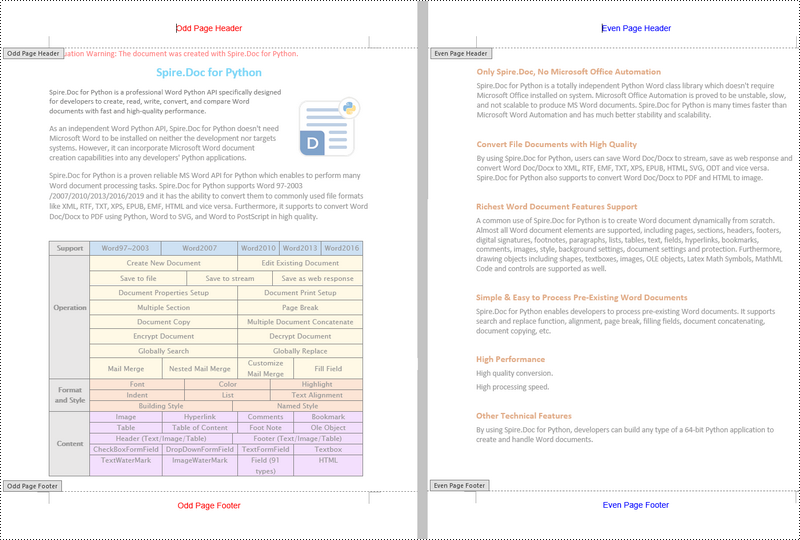
Add Different Headers and Footers for Odd and Even Pages in Word in Python
To have different headers and footers on odd and even pages, Spire.Doc for Python provides the Section.PageSetup.DifferentOddAndEvenPagesHeaderFooter property. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section using Document.Sections[] property.
- Enable different headers and footers for the odd and even pages by setting the Section.PageSetup.DifferentOddAndEvenPagesHeaderFooter property to True.
- Get the header and footer of odd pages using Section.HeadersFooters.OddHeader and Section.HeadersFooters.OddFooter properties.
- Add paragraphs to the header and footer of odd pages and then add text to them.
- Get the header and footer of even pages using Section.HeadersFooters.EvenHeader and Section.HeadersFooters.EvenFooter properties.
- Add paragraphs to the header and footer of even pages and then add text to them.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Get a specific section
section = document.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Enable different headers and footers for the odd and even pages
section.PageSetup.DifferentOddAndEvenPagesHeaderFooter = True
# Add headers and footers to odd pages
OHpara = section.HeadersFooters.OddHeader.AddParagraph()
OHtext = OHpara.AppendText("Odd Page Header")
OHpara.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
OHtext.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
OHtext.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
OHtext.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Red()
OFpara = section.HeadersFooters.OddFooter.AddParagraph()
OFtext = OFpara.AppendText("Odd Page Footer")
OFpara.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
OFtext.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
OFtext.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
OFtext.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Red()
# Add headers and footers to even pages
EHpara = section.HeadersFooters.EvenHeader.AddParagraph()
EHtext = EHpara.AppendText("Even Page Header")
EHpara.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
EHtext.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
EHtext.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
EHtext.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Blue()
EFpara = section.HeadersFooters.EvenFooter.AddParagraph()
EFtext = EFpara.AppendText("Even Page Footer")
EFpara.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
EFtext.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
EFtext.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
EFtext.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.get_Blue()
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("OddAndEvenHeaderFooter.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Setting an appropriate background is a crucial step when creating visually captivating and impactful PowerPoint presentations. The background serves as the foundation upon which your content is displayed, and choosing the right background can greatly enhance the overall aesthetic and effectiveness of your slides. Whether you are presenting at a business meeting, educational seminar, or social event, a well-designed background can engage your audience and effectively convey your message. In this article, we will explain how to set background color or picture for PowerPoint slides in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
- Set a Background Color for a PowerPoint Slide in Python
- Set a Gradient Background for a PowerPoint Slide in Python
- Set a Background Picture for a PowerPoint Slide in Python
- Set a Background for a Slide Master in PowerPoint in Python
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Set a Background Color for a PowerPoint Slide in Python
Adding a background color for a PowerPoint slide is very simple. You just need to set the fill mode of the slide's background as a solid fill and then set a color for the slide’s background. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific slide using Presentation.Slides[index] property.
- Access the background of the slide using ISlide.SlideBackground property.
- Set the type of the slide's background as a custom type using SlideBackground.Type property.
- Set the fill mode of the slide’s background as a solid fill using SlideBackground.Fill.FillType property.
- Set a color for the slide’s background using SlideBackground.Fill.SolidColor.Color property.
- Save the result presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
ppt = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
ppt.LoadFromFile("Input.pptx")
# Get the first slide
slide = ppt.Slides[0]
# Access the background of the slide
background = slide.SlideBackground
# Set the type of the slide's background as a custom type
background.Type = BackgroundType.Custom
# Set the fill mode of the slide's background as a solid fill
background.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
# Set a color for the slide's background
background.Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_PaleTurquoise()
# Save the result presentation
ppt.SaveToFile("Solidbackground.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
ppt.Dispose()
Set a Gradient Background for a PowerPoint Slide in Python
Adding a gradient background is a little complex. You need to set the fill mode of the slide’s background as a gradient fill and then set the gradient stops and colors. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific slide using Presentation.Slides[index] property.
- Access the background of the slide using ISlide.SlideBackground property.
- Set the type of the slide's background as a custom type using SlideBackground.Type property.
- Set the fill mode of the slide’s background as a gradient fill using SlideBackground.Fill.FillType property.
- Set gradient stops and colors for the slide’s background using SlideBackground.Fill.Gradient.GradientStops.AppendByColor() method.
- Set the shape type and angle for the gradient fill.
- Save the result presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
ppt = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
ppt.LoadFromFile("Input.pptx")
# Get the first slide
slide = ppt.Slides[0]
# Access the background of the slide
background = slide.SlideBackground
# Set the type of the slide's background as a custom type
background.Type = BackgroundType.Custom
# Set the fill mode of the slide's background as a gradient fill
background.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Gradient
# Set gradient stops and colors
background.Fill.Gradient.GradientStops.AppendByColor(0.1, Color.get_LightCyan())
background.Fill.Gradient.GradientStops.AppendByColor(0.7, Color.get_LightSeaGreen())
# Set the shape type of the gradient fill
background.Fill.Gradient.GradientShape = GradientShapeType.Linear
# Set the angle of the gradient fill
background.Fill.Gradient.LinearGradientFill.Angle = 45
# Save the result presentation
ppt.SaveToFile("Gradientbackground.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
ppt.Dispose()
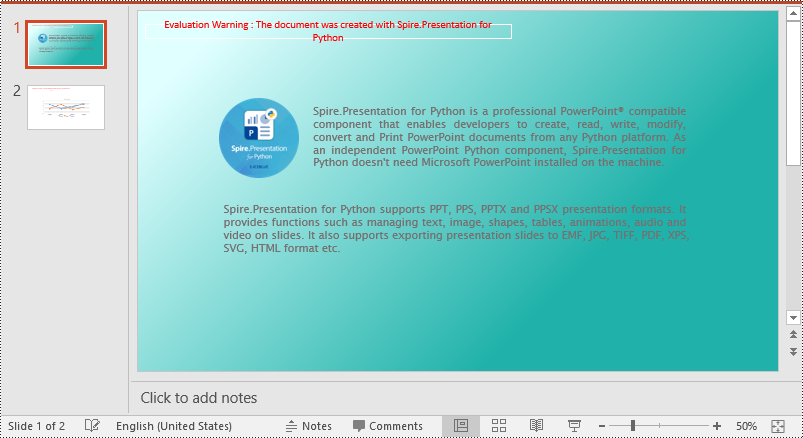
Set a Background Picture for a PowerPoint Slide in Python
To add a background picture for a PowerPoint slide, you need to set the fill mode of the slide's background as a picture fill, then add a picture to the image collection of the presentation and set it as the slide’s background. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific slide using Presentation.Slides[index] property.
- Access the background of the slide using ISlide.SlideBackground property.
- Set the type of the slide's background as a custom type using SlideBackground.Type property.
- Set the fill mode of the slide’s background as a picture fill using SlideBackground.Fill.FillType property.
- Add an image to the image collection of the presentation using Presentation.Images.AppendStream() method.
- Set the image as the slide’s background using SlideBackground.Fill.PictureFill.Picture.EmbedImage property.
- Save the result presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
ppt = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
ppt.LoadFromFile("Input.pptx")
# Get the first slide
slide = ppt.Slides[0]
# Access the background of the slide
background = slide.SlideBackground
# Set the type of the slide's background as a custom type
background.Type = BackgroundType.Custom
# Set the fill mode of the slide's background as a picture fill
background.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Picture
# Add an image to the image collection of the presentation
stream = Stream("background.jpg")
imageData = ppt.Images.AppendStream(stream)
# Set the image as the slide's background
background.Fill.PictureFill.FillType = PictureFillType.Stretch
background.Fill.PictureFill.Picture.EmbedImage = imageData
# Save the result presentation
ppt.SaveToFile("Picturebackground.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
ppt.Dispose()
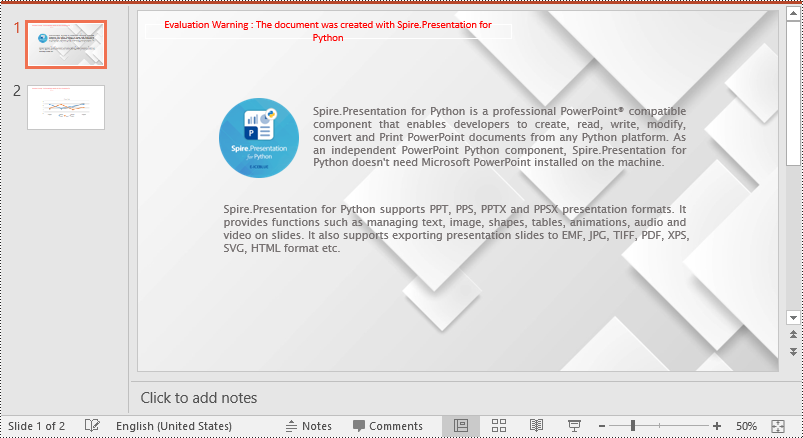
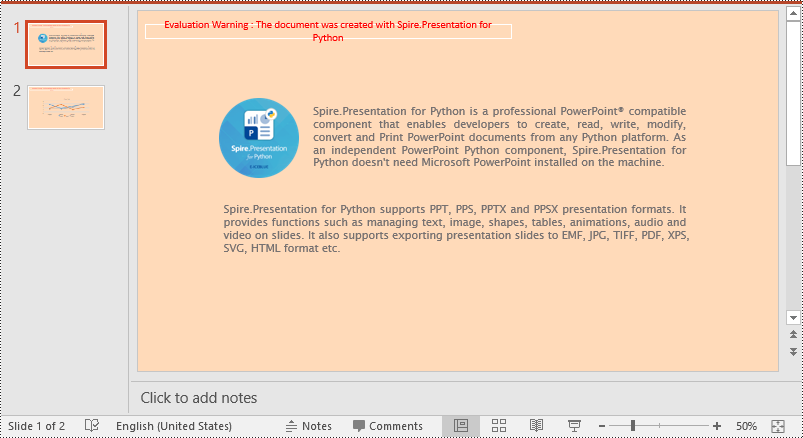
Set a Background for a Slide Master in PowerPoint in Python
If you don't wish to set backgrounds for slides one by one, you can set a background for the slide master, then all slides using the same slide master will be applied with the background automatically. The following steps show how to set a solid background color for a slide master.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific slide master using Presentation.Masters[index] property.
- Access the background of the slide master using IMasterSlide.SlideBackground property.
- Set the type of the slide master's background as a custom type using SlideBackground.Type property.
- Set the fill mode of the slide master's background as a solid fill using SlideBackground.Fill.FillType property.
- Set a color for the slide master's background using SlideBackground.Fill.SolidColor.Color property.
- Save the result presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
ppt = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
ppt.LoadFromFile("Input.pptx")
# Get the first slide master
slideMaster = ppt.Masters[0]
# Access the background of the slide master
background = slideMaster.SlideBackground
# Set the type of the slide master's background as a custom type
background.Type = BackgroundType.Custom
# Set the fill mode of the slide master's background as a solid fill
background.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
# Set a color for the slide master's background
background.Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_PeachPuff()
# Save the result presentation
ppt.SaveToFile("AddBackgroundToSlideMaster.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
ppt.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Comments in Microsoft PowerPoint allow users to add additional information to specific slides or elements of a slide to improve collaboration and communication when sharing presentations. These comments can be related content, suggestions for changes, and so on. This feature is very useful when several people are working on a presentation together. In this article, you will learn how to use Spire.Presentation for Python to add, remove or replace comments on slides in Python programs.
- Add Comments to a Presentation Slide in Python
- Remove Comments from a Presentation Slide in Python
- Replace Comments on a Presentation Slide in Python
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
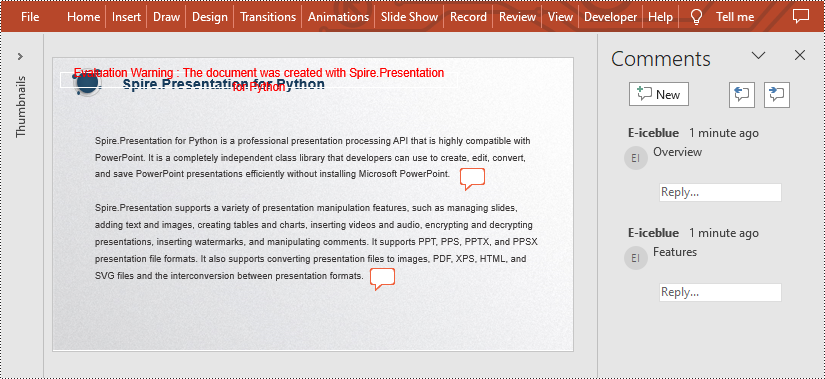
Add Comments to a Presentation Slide in Python
Spire.Presentation for Python provides the Presentation.CommentAuthors.AddAuthor() and Presentation.Slides[].AddComment(author:ICommentAuthor,text:str,position:PointF,dateTime:DateTime) methods to support adding comments to a slide. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a new PowerPoint presentation.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Add the author of the comment by using Presentation.CommentAuthors.AddAuthor() method.
- Then add a comment to the first slide using Presentation.Slides[].AddComment(author:ICommentAuthor,text:str,position:PointF,dateTime:DateTime) method.
- Add another comment using the same method.
- Save the result file using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Sample.pptx"
outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/AddComment.pptx"
# Create a Presentation instance
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a presentation from disk
presentation.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Add the author of the comment
author = presentation.CommentAuthors.AddAuthor("E-iceblue", "comment:")
# Add a comment to the first slide
point = PointF(45.0,12.0)
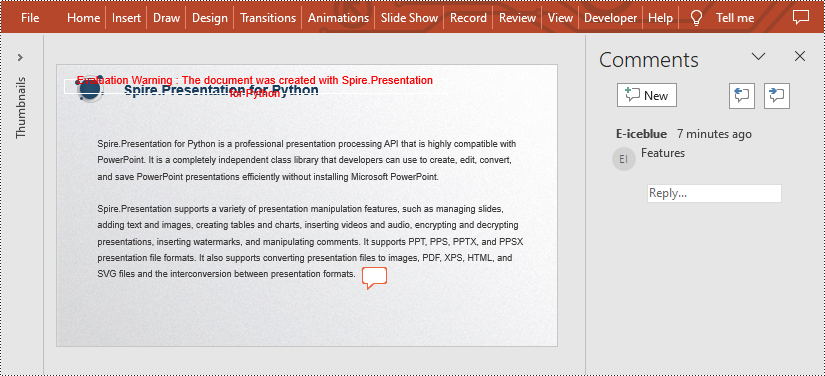
presentation.Slides[0].AddComment(author, "Overview", point, DateTime.get_Now())
# Add another comment to this slide
author = presentation.CommentAuthors.AddAuthor("E-iceblue", "comment:")
point = PointF(35.0,23.0)
presentation.Slides[0].AddComment(author, "Features", point, DateTime.get_Now())
# Save the result file
presentation.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Pptx2010)
presentation.Dispose()
Remove Comments from a Presentation Slide in Python
You can also remove the specific comment from the slides by using Presentation.Slides[].DeleteComment(Comment) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Presentation instance.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove the first comment from the specified slide using Presentation.Slides[].DeleteComment(Comment) method.
- Save the result file using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import * from spire.presentation import * inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/AddComment.pptx" outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/DeleteComment.pptx" # Create a Presentation instance presentation = Presentation() # Load a presentation from disk presentation.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Delete the first comment from the first slide presentation.Slides[0].DeleteComment(presentation.Slides[0].Comments[0]) # Save the result file presentation.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Pptx2010) presentation.Dispose()
Replace Comments on a Presentation Slide in Python
If you want to replace the comment content with new text, please use the Presentation.Slides[].Comments[].Text property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Presentation instance.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
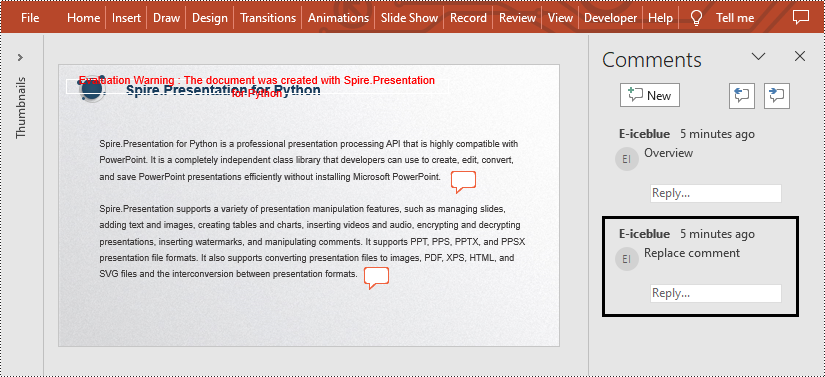
- Replace the content of the second comment with new text by Presentation.Slides[].Comments[].Text property.
- Save the result file using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import * from spire.presentation import * inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/AddComment.pptx" outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/ReplaceComment.pptx" # Create a Presentation instance presentation = Presentation() # Load a presentation from disk presentation.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Replace the content of the second comment with new text presentation.Slides[0].Comments[1].Text = "Replace comment" # Save the result file presentation.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Pptx2010) presentation.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
