
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Comment in Excel is primarily used to add additional instructions or notes to cells. With this feature, users can add relevant content next to a specific cell to explain the data, provide contextual information, or give instructions. It also helps users to better organize and manage the data in the Excel workbook and improve the understanding and readability of the data. Spire.XLS for Python supports adding comments to Excel files. If necessary, you can also use this library to edit the content of the comments or delete unnecessary comments. In this article, we will show you how to edit or remove existing comments in Excel on Python platforms using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Edit Existing Comments in Excel Using Python
Spire.XLS for Python allows users to edit existing comments in Excel, including setting new text or changing comment box size. The following are detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file from disk using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first worksheet of the Excel file using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
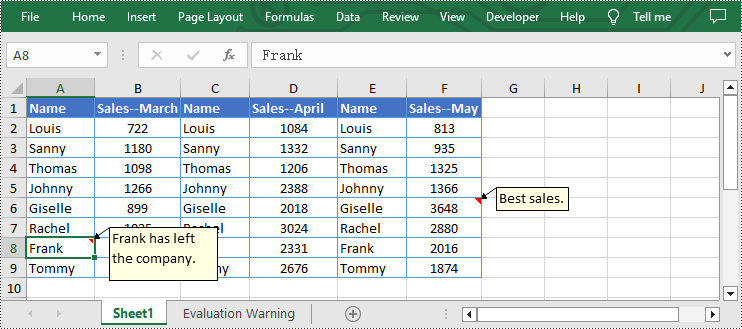
- Set new text for the existing comments using Worksheet.Range[].Comment.Text property.
- Set the height and width of the existing comment by using Worksheet.Range[].Comment.Height and Worksheet.Range[].Comment.Width properties.
- Automatically adapt to the size of the comment by setting the Worksheet.Range.Comment.AutoSize property to "True".
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.common import * inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Sample.xlsx" outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/EditExcelComment.xlsx" # Create a Workbook instance workbook = Workbook() # Load an Excel file from disk workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get the first worksheet of this file sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] # Set new text for the existing comments sheet.Range["A8"].Comment.Text = "Frank has left the company." sheet.Range["F6"].Comment.Text = "Best sales." # Set the height and width of the comment of A8 sheet.Range["A8"].Comment.Height = 60 sheet.Range["A8"].Comment.Width = 100 # Automatically adapt to the size of the comment of F6 sheet.Range["F6"].Comment.AutoSize = True # Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013) workbook.Dispose()
Remove Existing Comments from Excel Using Python
The Worksheet.Range[].Comment.Remove() method offered by Spire.XLS for Python allows users to remove a specified comment easily. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file from disk using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first worksheet of the Excel file using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
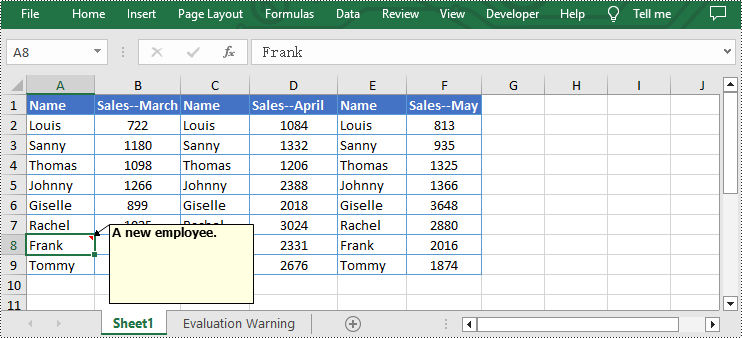
- Remove the comment by using Worksheet.Range[].Comment.Remove() method.
- Save the document to another file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.common import * inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Sample.xlsx" outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/RemoveExcelComment.xlsx" # Create a Workbook instance workbook = Workbook() # Load an Excel file from disk workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get the first worksheet of this file sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] # Remove the comment from the sheet sheet.Range["F6"].Comment.Remove() # Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013) workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
A bar chart is a type of graph that represents categorical data using rectangular bars. It is somewhat like a column chart, but with bars that extend horizontally from the Y-axis. The length of each bar corresponds to the value represented by a particular category or group, and changes, trends, or rankings can be quickly identified by comparing the lengths of the bars. In this article, you will learn how to create a clustered or stacked bar chart in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Create a Clustered Bar Chart in Excel in Python
The Worksheet.Chart.Add(ExcelChartType chartType) method provided by Spire.XLS for Python allows to add a chart to a worksheet. To add a clustered bar chart in Excel, you can set the chart type to BarClustered. The following are the steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Add chart data to specified cells and set the cell styles.
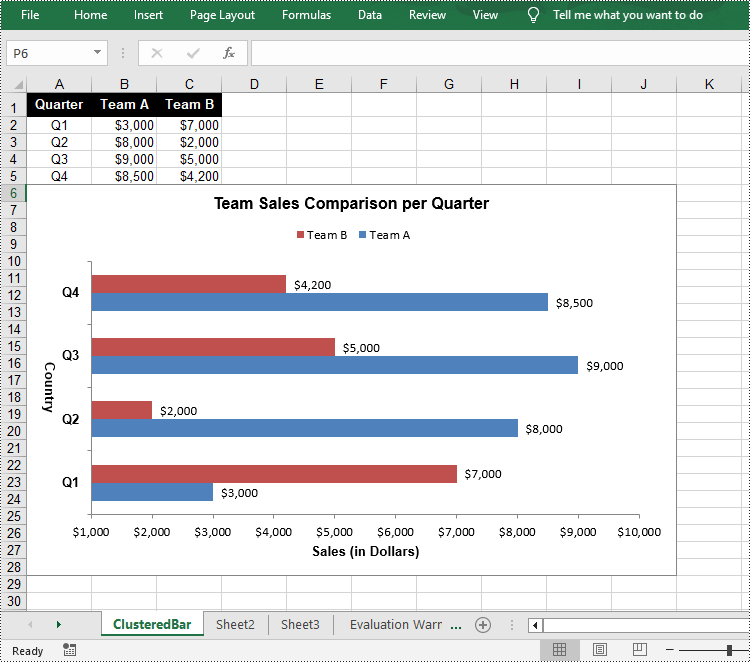
- Add a clustered bar char to the worksheet using Worksheet.Chart.Add(ExcelChartType.BarClustered) method.
- Set data range for the chart using Chart.DataRange property.
- Set position, title, category axis and value axis for the chart.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.common import *
from spire.xls import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first sheet and set its name
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
sheet.Name = "ClusteredBar"
# Add chart data to specified cells
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Quarter"
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "Q1"
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "Q2"
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "Q3"
sheet.Range["A5"].Value = "Q4"
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Team A"
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 3000
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 8000
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 9000
sheet.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 8500
sheet.Range["C1"].Value = "Team B"
sheet.Range["C2"].NumberValue = 7000
sheet.Range["C3"].NumberValue = 2000
sheet.Range["C4"].NumberValue = 5000
sheet.Range["C5"].NumberValue = 4200
# Set cell style
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].RowHeight = 18
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Color = Color.get_Black()
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.IsBold = True
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A2:A5"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["B2:C5"].Style.NumberFormat = "\"$\"#,##0"
# Add a clustered bar chart to the sheet
chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.BarClustered)
# Set data range of the chart
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:C5"]
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = False
# Set position of the chart
chart.LeftColumn = 1
chart.TopRow = 6
chart.RightColumn = 11
chart.BottomRow = 29
# Set and format chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Team Sales Comparison per Quarter"
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 12
# Set and format category axis
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Title = "Country"
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Font.IsBold = True
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.TitleArea.TextRotationAngle = 90
# Set and format value axis
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.Title = "Sales (in Dollars)"
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = False
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinValue = 1000
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = True
# Show data labels for data points
for cs in chart.Series:
cs.Format.Options.IsVaryColor = True
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = True
# Set legend position
chart.Legend.Position = LegendPositionType.Top
#Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("ClusteredBarChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Create a Stacked Bar Chart in Excel in Python
To create a stacked bar chart, you just need to change the Excel chart type to BarStacked. The following are the steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Add chart data to specified cells and set the cell styles.
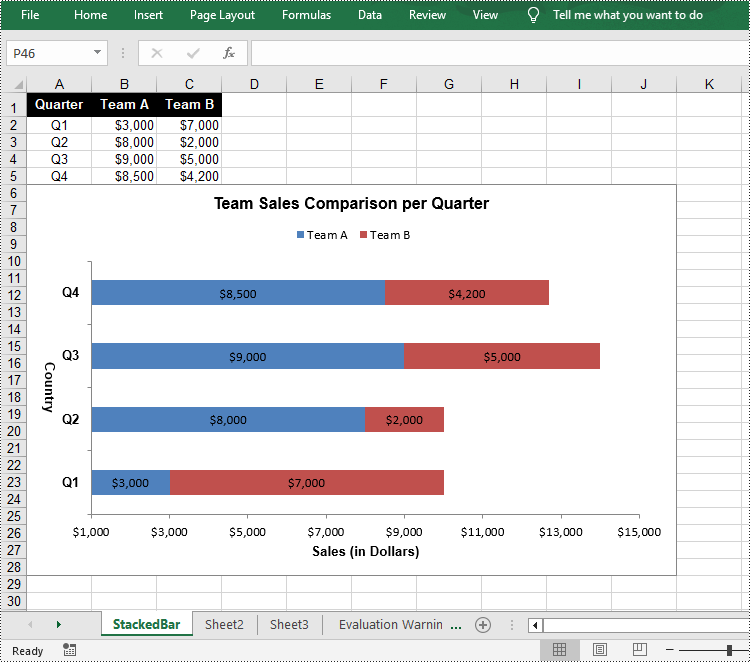
- Add a clustered bar char to the worksheet using Worksheet.Chart.Add(ExcelChartType.BarStacked) method.
- Set data range for the chart using Chart.DataRange property.
- Set position, title, category axis and value axis for the chart.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.common import *
from spire.xls import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first sheet and set its name
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
sheet.Name = "StackedBar"
# Add chart data to specified cells
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Quarter"
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "Q1"
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "Q2"
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "Q3"
sheet.Range["A5"].Value = "Q4"
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Team A"
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 3000
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 8000
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 9000
sheet.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 8500
sheet.Range["C1"].Value = "Team B"
sheet.Range["C2"].NumberValue = 7000
sheet.Range["C3"].NumberValue = 2000
sheet.Range["C4"].NumberValue = 5000
sheet.Range["C5"].NumberValue = 4200
# Set cell style
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].RowHeight = 18
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Color = Color.get_Black()
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.IsBold = True
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A2:A5"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["B2:C5"].Style.NumberFormat = "\"$\"#,##0"
# Add a clustered bar chart to the sheet
chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.BarStacked)
# Set data range of the chart
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:C5"]
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = False
# Set position of the chart
chart.LeftColumn = 1
chart.TopRow = 6
chart.RightColumn = 11
chart.BottomRow = 29
# Set and format chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Team Sales Comparison per Quarter"
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 12
# Set and format category axis
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Title = "Country"
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Font.IsBold = True
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.TitleArea.TextRotationAngle = 90
# Set and format value axis
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.Title = "Sales (in Dollars)"
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = False
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinValue = 1000
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = True
# Show data labels for data points
for cs in chart.Series:
cs.Format.Options.IsVaryColor = True
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = True
# Set legend position
chart.Legend.Position = LegendPositionType.Top
#Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("StackedBarChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
RTF (Rich Text Format) is a versatile file format that can be opened and viewed by various word processing software. It supports a wide range of text formatting options, such as font style, size, color, tables, images, and more. When working with RTF files, you may sometimes need to convert them to PDF files for better sharing and printing, or to HTML format for publishing on the web. In this article, you will learn how to convert RTF to PDF or HTML with Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
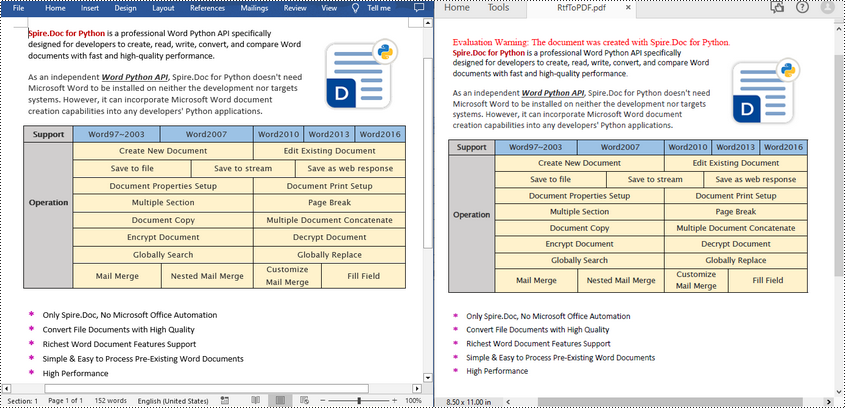
Convert RTF to PDF in Python
To convert an RTF file to PDF, simply load a file with .rtf extension and then save it as a PDF file using Document.SaveToFile(fileName, FileFormat.PDF) method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Load an RTF file using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Save the RTF file as a PDF file using Document.SaveToFile(fileName, FileFormat.PDF) method.
- Python
from spire.doc import * from spire.doc.common import * inputFile = "input.rtf" outputFile = "RtfToPDF.pdf" # Create a Document object doc = Document() # Load an RTF file from disk doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Save the RTF file as a PDF file doc.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.PDF) doc.Close()
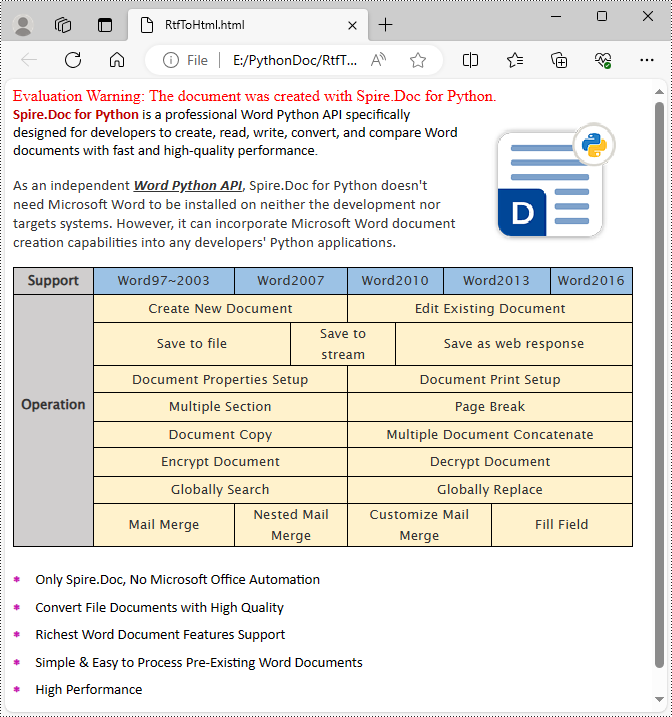
Convert RTF to HTML in Python
Spire.Doc for Python also allows you to use the Document.SaveToFile(fileName, FileFormat.Html) method to convert the loaded RTF file to HTML format. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Load an RTF file using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Save the RTF file in HTML format using Document.SaveToFile(fileName, FileFormat.Html) method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
inputFile = "input.rtf"
outputFile = "RtfToHtml.html"
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load an RTF file from disk
doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Save the RTF file in HTML format
doc.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Html)
doc.Close()
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
