
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
PDF properties refer to the information embedded within the document that provides detailed information about the documents, such as author, creation date, last modification date, etc. Users can check the properties of a PDF document in PDF viewers to quickly grasp the key information of the document. Apart from the built-in properties, PDF documents also offer the feature of customizing properties to help provide additional information about the document. Understanding how to specify and access this document information facilitates the creation of user-friendly documents and the processing of documents in large quantities. In this article, we will explore how to set and retrieve PDF properties through Python programs using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Set PDF Properties with Python
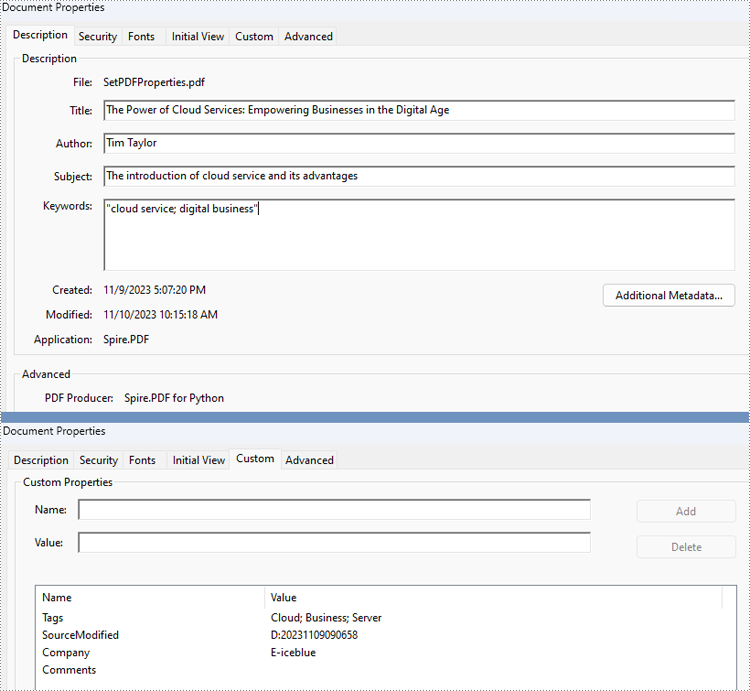
Spire.PDF for Python provides several properties under the PdfDocumentInformation class for setting built-in document properties, such as author, subject, keywords. Besides, it also provides the PdfDocumentInformation.SetCustomProperty() method to set custom properties. The following are the detailed steps to set PDF properties:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the properties of the document through PdfDocument.DocumentInformation property.
- Set the built-in properties through properties under PdfDocumentInformation class.
- Set custom properties using PdfDocumentInformation.SetCustomProperty() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import *
# Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get the properties of the document
properties = pdf.DocumentInformation
# Set built-in properties
properties.Author = "Tim Taylor"
properties.Creator = "Spire.PDF"
properties.Keywords = "cloud service; digital business"
properties.Subject = "The introduction of cloud service and its advantages"
properties.Title = "The Power of Cloud Services: Empowering Businesses in the Digital Age"
properties.Producer = "Spire.PDF for Python"
# Set custom properties
properties.SetCustomProperty("Company", "E-iceblue")
properties.SetCustomProperty("Tags", "Cloud; Business; Server")
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/SetPDFProperties.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Retrieve PDF Properties with Python
Information in built-in PDF properties can be obtained using the properties under the PdfDocumentInformation class, while that in custom PDF properties can be obtained using PdfDocumentInformation.GetCustomProperty() method. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the properties of the document through PdfDocument.DocumentInformation property.
- Retrieve the built-in properties through properties under PdfDocumentInformation class and custom properties using PdfDocumentInformation.GetCustomProperty() method and print them.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import *
# Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("output\SetPDFProperties.pdf")
# Get the properties of the document
properties = pdf.DocumentInformation
# Create a StringBuilder object
information = ""
# Retrieve the built-in properties
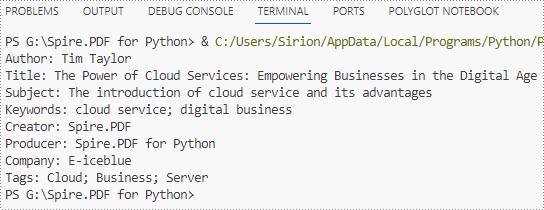
information += "Author: " + properties.Author
information += "\nTitle: " + properties.Title
information += "\nSubject: " + properties.Subject
information += "\nKeywords: " + properties.Keywords
information += "\nCreator: " + properties.Creator
information += "\nProducer: " + properties.Producer
# Retrieve the custom properties
information += "\nCompany: " + properties.GetCustomProperty("Company")
information += "\nTags: " + properties.GetCustomProperty("Tags")
# Print the document properties
print(information)
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
A table is a powerful tool in a Word document that allows you to organize and present information in a structured manner. It consists of rows and columns, forming a grid-like structure. Tables are commonly used for various purposes, such as creating schedules, comparing data, or displaying data in a neat and organized format. In this article, you will learn how to programmatically create tables in a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Create a Simple Table in Word in Python
- Create a Table from an HTML String in Python
- Merge and Split Cells in a Table in Python
- Fill a Table with Data in Word in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Prerequisite Knowledge
Spire.Doc for Python offers the Table class to represent a table in a Word document. You can create table objects either through the constructor or the Section.AddTable() method. After the table object is created, you can use the Table.AddRow() method to dynamically add rows to the table, or specify the number of rows and columns of the table, and then populate it with data in a single pass.
Also, Spire.Doc for Python supports creating tables from an HTML string. This method does not return an object of Table. Therefore, you cannot use the properties or methods under the Table class to deal with the table created from an HTML string. You need to set up the content and style of the table in the HTML string.
Create a Simple Table in Word in Python
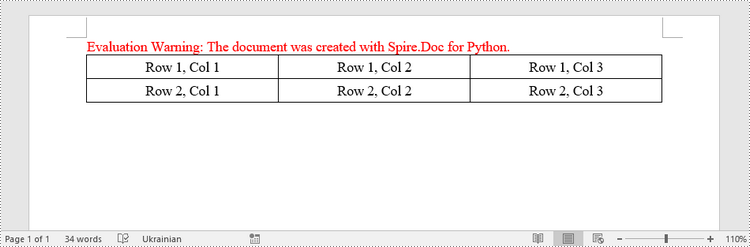
This example demonstrates how to create a simple plain table using the Table class and how to add rows one by one. Here are the main steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section to it using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create a Table object.
- Add a row to it using Table.AddRow() method.
- Get a specific cell of the row through Row.Cells[index] property.
- Add text to the cell using TableCell.AddParagraph().AppendText() method.
- Add the table to the document using Section.AddTable() method.
- Save the document to a .docx file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Create a table
table = Table(doc, True)
# Set the width of table
table.PreferredWidth = PreferredWidth(WidthType.Percentage, int(100))
# Set the border of table
table.TableFormat.Borders.BorderType = BorderStyle.Single
table.TableFormat.Borders.Color = Color.get_Black()
# Add a row
row = table.AddRow(False, 3)
row.Height = 20.0
# Add data to the cells
cell = row.Cells[0]
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
paragraph.AppendText("Row 1, Col 1")
cell = row.Cells[1]
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
paragraph.AppendText("Row 1, Col 2")
cell = row.Cells[2]
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
paragraph.AppendText("Row 1, Col 3")
# Add the second row
row = table.AddRow(False, 3)
row.Height = 20.0
cell = row.Cells[0]
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
paragraph.AppendText("Row 2, Col 1")
cell = row.Cells[1]
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
paragraph.AppendText("Row 2, Col 2")
cell = row.Cells[2]
cell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
paragraph.AppendText("Row 2, Col 3")
# Add the table to the section
section.Tables.Add(table)
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/CreateTable.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
doc.Close()
Create a Table from an HTML String in Python
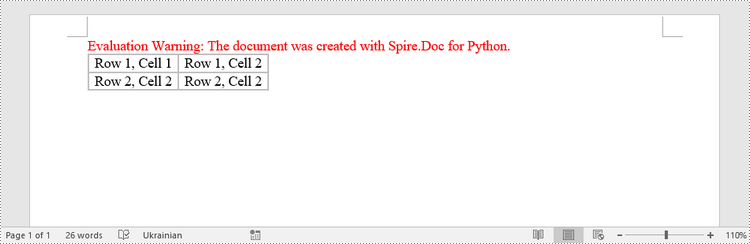
To create a table from an HTML string, use the Paragraph.AppendHTML() method. The following are the steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section to it using Document.AddSection() method.
- Specify the HTML string for generating the table.
- Add a paragraph using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Add the HTML table to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendHTML() method.
- Save the document to a .docx file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Add a section
section = document.AddSection()
# Specify HTML string
HTML = "<table border='2px'>" + "<tr>" + "<td>Row 1, Cell 1</td>" + "<td>Row 1, Cell 2</td>" + \
"</tr>" + "<tr>" + "<td>Row 2, Cell 2</td>" + \
"<td>Row 2, Cell 2</td>" + "</tr>" + "</table>"
# Add a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
# Append HTML string to the paragraph
paragraph.AppendHTML(HTML)
# Save to Word document
document.SaveToFile("output/HtmlTable.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
document.Close()
Merge and Split Cells in a Table in Python
When working with tables, the ability to merge or split cells provides a powerful way to customize and format data. This example shows you how to combine adjacent cells into a single cell and how to divide a single cell into multiple smaller cells using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Add a table using Section.AddTable() method.
- Set the column number and row number of the table using Table.ResetCells() method.
- Horizontally merge cells using Table.ApplyHorizontalMerge() method.
- Vertically merge cells using Table.ApplyVerticalMerge() method.
- Split a cell into multiple smaller cells using TableCell.SplitCell() method.
- Save the document to a .docx file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Add a section
section = document.AddSection()
# Create a table
table = section.AddTable(True)
# Set the row number and column number of table
table.ResetCells(4, 4)
# Set the width of table
table.PreferredWidth = PreferredWidth(WidthType.Percentage, int(100))
# Set row height
for i in range(0, table.Rows.Count):
table.Rows[i].Height = 20.0
# Horizontally merge cells
table.ApplyHorizontalMerge(0, 0, 3)
# Vertically merge cells
table.ApplyVerticalMerge(0, 2, 3)
# Get a cell
cell = table.Rows.get_Item(1).Cells.get_Item(3)
# Split the cell into 3 smaller cells
cell.SplitCell(3, 0)
# Fill specified cells with color
table.Rows[0].Cells[0].CellFormat.BackColor = Color.get_LightBlue()
table.Rows[2].Cells[0].CellFormat.BackColor = Color.get_LightBlue()
table.Rows[1].Cells[3].CellFormat.BackColor = Color.get_LightGray()
table.Rows[1].Cells[4].CellFormat.BackColor = Color.get_LightGray()
table.Rows[1].Cells[5].CellFormat.BackColor = Color.get_LightGray()
# Save to Word document
document.SaveToFile("output/MergeAndSplit.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
document.Close()
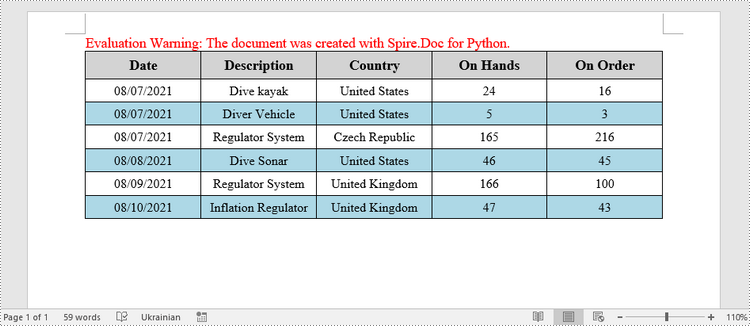
Fill a Table with Data in Word in Python
This example creates a 5x7 table, writes the data from lists into the cells, and applies different formatting to the header row and other rows. The following are the main steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Add a table using Section.AddTable() method.
- Specify the data for filling the table in two lists.
- Reset the row number and column number of the table depending on the height and width of the data using Table.ResetCells() method.
- Write data into the corresponding cells using TableCell.AddParagraph().AppendText() method.
- Apply different colors to different rows through TableCell.CellFormat.BackColor property.
- Save the document to a .docx file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
import math
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Create a table
table = section.AddTable(True)
# Specify table data
header_data = ["Date", "Description", "Country", "On Hands", "On Order"]
row_data = [ ["08/07/2021","Dive kayak","United States","24","16"],
["08/07/2021","Diver Vehicle","United States","5","3"],
["08/07/2021","Regulator System","Czech Republic","165","216"],
["08/08/2021","Dive Sonar","United States","46","45"],
["08/09/2021","Regulator System","United Kingdom","166","100"],
["08/10/2021","Inflation Regulator","United Kingdom","47","43"]]
# Set the row number and column number of table
table.ResetCells(len(row_data) + 1, len(header_data))
# Set the width of table
table.PreferredWidth = PreferredWidth(WidthType.Percentage, int(100))
# Get header row
headerRow = table.Rows[0]
headerRow.IsHeader = True
headerRow.Height = 23
headerRow.RowFormat.BackColor = Color.get_LightGray()
# Fill the header row with data and set the text formatting
i = 0
while i < len(header_data):
headerRow.Cells[i].CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = headerRow.Cells[i].AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
txtRange = paragraph.AppendText(header_data[i])
txtRange.CharacterFormat.Bold = True
txtRange.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 12
i += 1
# Fill the rest rows with data and set the text formatting
r = 0
while r < len(row_data):
dataRow = table.Rows[r + 1]
dataRow.Height = 20
dataRow.HeightType = TableRowHeightType.Exactly
c = 0
while c < len(row_data[r]):
dataRow.Cells[c].CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Middle
paragraph = dataRow.Cells[c].AddParagraph()
paragraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
txtRange = paragraph.AppendText(row_data[r][c])
txtRange.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 11
c += 1
r += 1
# Alternate row color
for j in range(1, table.Rows.Count):
if math.fmod(j, 2) == 0:
row2 = table.Rows[j]
for f in range(row2.Cells.Count):
row2.Cells[f].CellFormat.BackColor = Color.get_LightBlue()
# Set the border of table
table.TableFormat.Borders.BorderType = BorderStyle.Single
table.TableFormat.Borders.LineWidth = 1.0
table.TableFormat.Borders.Color = Color.get_Black()
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/Table.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Images play a crucial role in effectively communicating complex ideas or concepts. When there are low-quality or outdated images in a Word document, it is necessary to replace the images to enhance the overall visual appeal and professionalism of your document. In this article, you will learn how to replace images in a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
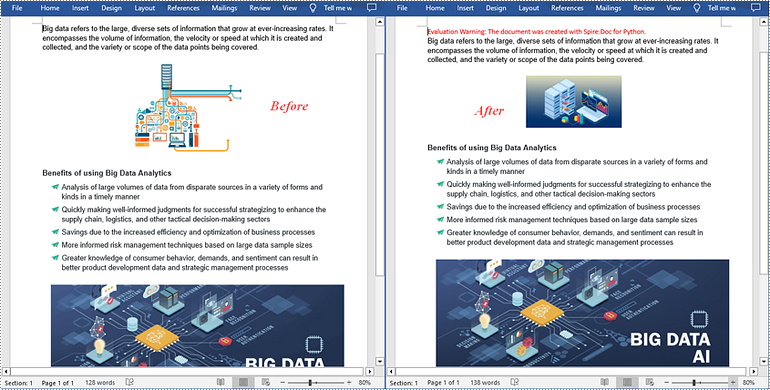
Replace Image with New Image in Word in Python
Spire.Doc for Python supports not only inserting images in Word, but also replacing existing images. The following are the detailed steps to get a specific image in Word and then replace it with a new image.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a list to store the images.
- Iterate through all sections in the document.
- Iterate through all paragraphs in each section.
- Iterate through all child objects in each paragraph.
- Find the images and add them to the list.
- Get a specific image from the list and replace it with another image using DocPicture.LoadImage() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Data.docx")
# Create a list to store the images
pictures = []
# Iterate through all sections in the document
for i in range(doc.Sections.Count):
sec = doc.Sections.get_Item(i)
# Iterate through all paragraphs in each section
for j in range(sec.Paragraphs.Count):
para = sec.Paragraphs.get_Item(j)
# Iterate through all child objects in each paragraph
for k in range(para.ChildObjects.Count):
docObj = para.ChildObjects.get_Item(k)
# Find the images and add them to the list
if docObj.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Picture:
pictures.append(docObj)
# Replace the first picture in the list with a new image
picture = pictures[0] if isinstance(pictures[0], DocPicture) else None
picture.LoadImage("data.jpg")
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("ReplaceImage.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
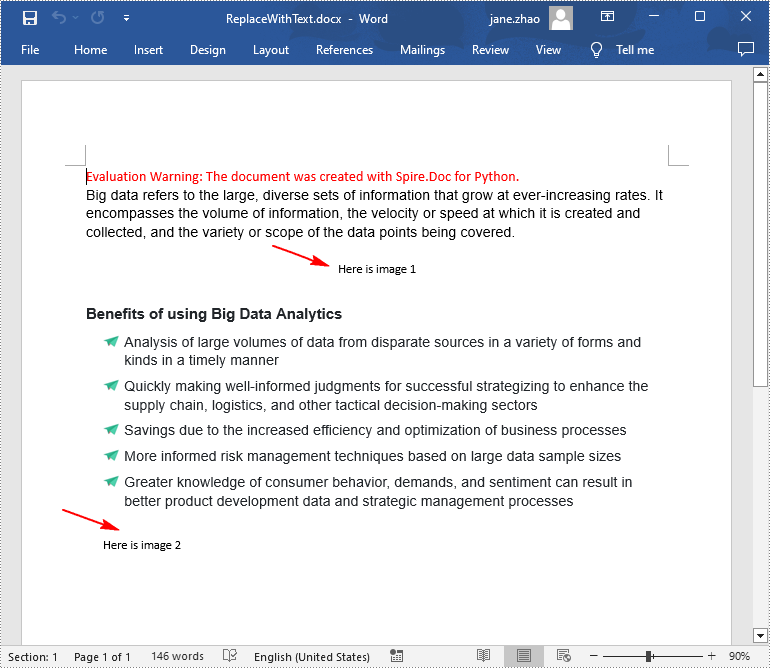
Replace Image with Text in Word in Python
Spire.Doc for Python doesn't provide a direct method to replace image with text, but you can achieve this task by inserting text at the image location and then removing the image from the document.
The following are the steps to replace all images in a Word document with text:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through all sections in the document.
- Iterate through all paragraphs in each section.
- Create a list to store the images.
- Iterate through all child objects in each paragraph.
- Find the images and add them to the list.
- Iterate through the images in the list.
- Get the index of the image in the paragraph using Paragraph.ChildObjects.Indexof() method.
- Initialize an instance of TextRange class and set text for the text range through TextRange.Text property.
- Insert the text range at the image location using Paragraph.ChildObjects.Insert() method.
- Remove the image from the paragraph using Paragraph.ChildObjects.Remove() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Data.docx")
j = 1
# Iterate through all sections in the document
for k in range(doc.Sections.Count):
sec = doc.Sections.get_Item(k)
# Iterate through all sections in the document
for m in range(sec.Paragraphs.Count):
para = sec.Paragraphs.get_Item(m)
# Create a list to store the images
pictures = []
# Find the images and add them to the list
for x in range(para.ChildObjects.Count):
docObj = para.ChildObjects.get_Item(x)
if docObj.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Picture:
pictures.append(docObj)
# Iterate through all images in the list and replace them with text "Here is image {image index}"
for pic in pictures:
index = para.ChildObjects.IndexOf(pic)
textRange = TextRange(doc)
textRange.Text = "Here is image {0}".format(j)
para.ChildObjects.Insert(index, textRange)
para.ChildObjects.Remove(pic)
j += 1
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("ReplaceWithText.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
