
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
To get the number of pages in a PDF file, you can open the file in a PDF viewer such as Adobe, which has a built-in page count feature. However, when there is a batch of PDF files, opening each file to check how many pages it contains is a time-consuming task. In this article, you will learn how to quicky count the number of pages in a PDF file through programming using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Count the Number of Pages in a PDF File in Python
Spire.PDF for Python offers the PdfDocument.Pages.Count property to quickly count the number of pages in a PDF file without opening it. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a sample PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Count the number of pages in the PDF document using PdfDocument.Pages.Count property.
- Write the result to a TXT file or print it out directly.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
def AppendText(fname: str, text: str):
fp = open(fname, "w")
fp.write(text + "\n")
fp.close()
# Specify the input and output files
inputFile = "contract.pdf"
outputFile = "GetNumberOfPages.txt"
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document from disk
pdf.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Count the number of pages in the document
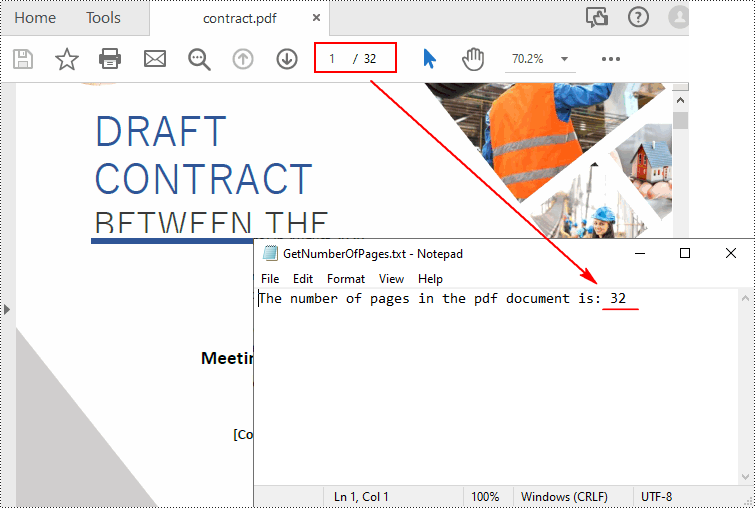
count = pdf.Pages.Count
# Print the result
print("Total Pages:", count)
# Write the result to a TXT file
AppendText(
outputFile, "The number of pages in the pdf document is: " + str(count))
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Hyperlinks in PDF are interactive elements that, when clicked, can jump to a specific location in the document, to an external website, or to other resources. By inserting hyperlinks in a PDF document, you can provide supplementary information and enhance the overall integrity of the document. This article will demonstrate how to add hyperlinks to PDF files in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Add Hyperlinks to a PDF Document in Python
With Spire.PDF for Python, you can add web links, email links and file links to a PDF document. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a pdf document and add a page to it.
- Specify a URL address and draw it directly on the page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Create a PdfTextWebLink object.
- Set the link's display text, URL address, and the font and brush used to draw it using properties of PdfTextWebLink class.
- Draw the link on the page using PdfTextWebLink.DrawTextWebLink() method.
- Create a PdfFileLinkAnnotation object and with a specified file.
- Add the file link to the page annotations using PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.Add(PdfFileLinkAnnotation) method.
- Draw hypertext of the file link using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Save the result file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a page
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
# Initialize x, y coordinates
y = 30.0
x = 10.0
# Create true type fonts
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 14.0,PdfFontStyle.Regular,True)
font1 = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 14.0, PdfFontStyle.Underline,True)
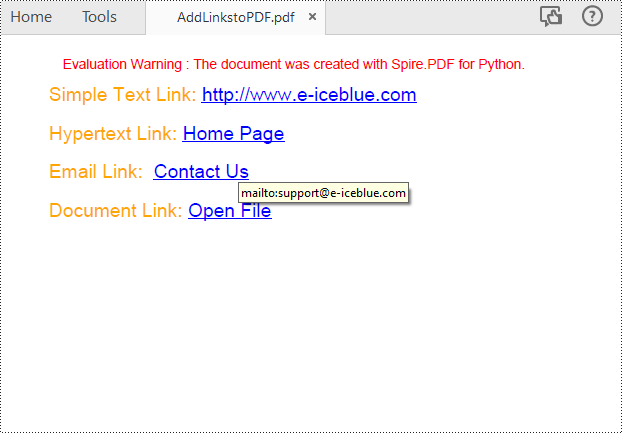
# Add a simply link
label = "Simple Text Link: "
format = PdfStringFormat()
format.MeasureTrailingSpaces = True
page.Canvas.DrawString(label, font, PdfBrushes.get_Orange(), 0.0, y, format)
x = font.MeasureString(label, format).Width
url = "http://www.e-iceblue.com"
page.Canvas.DrawString(url, font1, PdfBrushes.get_Blue(), x, y)
y = y + 28
# Add a hypertext link
label = "Hypertext Link: "
page.Canvas.DrawString(label, font, PdfBrushes.get_Orange(), 0.0, y, format)
x = font.MeasureString(label, format).Width
webLink = PdfTextWebLink()
webLink.Text = "Home Page"
webLink.Url = url
webLink.Font = font1
webLink.Brush = PdfBrushes.get_Blue()
webLink.DrawTextWebLink(page.Canvas, PointF(x, y))
y = y + 28
# Add an Email link
label = "Email Link: "
page.Canvas.DrawString(label, font, PdfBrushes.get_Orange(), 0.0, y, format)
x = font.MeasureString(label, format).Width
link = PdfTextWebLink()
link.Text = "Contact Us"
link.Url = "mailto:support@e-iceblue.com"
link.Font = font1
link.Brush = PdfBrushes.get_Blue()
link.DrawTextWebLink(page.Canvas, PointF(x, y))
y = y + 28
# Add a file link
label = "Document Link: "
page.Canvas.DrawString(label, font, PdfBrushes.get_Orange(), 0.0, y, format)
x = font.MeasureString(label, format).Width
text = "Open File"
location = PointF(x, y)
size = font1.MeasureString(text)
linkBounds = RectangleF(location, size)
fileLink = PdfFileLinkAnnotation(linkBounds,"C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Report.xlsx")
fileLink.Border = PdfAnnotationBorder(0.0)
page.AnnotationsWidget.Add(fileLink)
page.Canvas.DrawString(text, font1, PdfBrushes.get_Blue(), x, y)
#Save the result pdf file
pdf.SaveToFile("AddLinkstoPDF.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Insert Hyperlinks into Existing Text in PDF in Python
Adding a hyperlink to existing text in a PDF document requires locating the text first. Once the location has been obtained, an object of PdfUriAnnotation class with the link can be created and added to the position. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first page using PdfDocument.Pages property.
- Find all occurrences of the specified text on the page using PdfPageBase.FindText() method.
- Loop through all occurrences of the found text and create a PdfUriAnnotation instance based on the text bounds of each occurrence.
- Set the hyperlink URL, border, and border color using properties under PdfUriAnnotation class.
- Insert the hyperlink to the page annotations using PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.Add(PdfUriAnnotation) method.
- Save the PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
pdf.LoadFromFile("input.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Find all occurrences of the specified text on the page
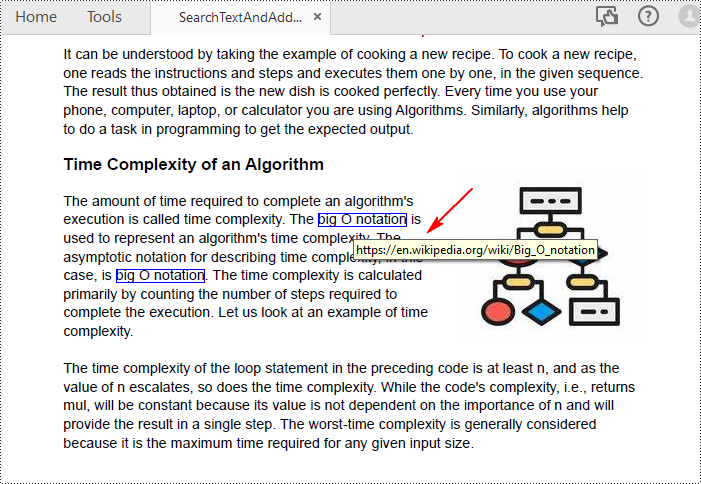
collection = page.FindText("big O notation", TextFindParameter.IgnoreCase)
# Loop through all occurrences of the specified text
for find in collection.Finds:
# Create a hyperlink annotation
uri = PdfUriAnnotation(find.Bounds)
# Set the URL of the hyperlink
uri.Uri = "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Big_O_notation"
# Set the border of the hyperlink annotation
uri.Border = PdfAnnotationBorder(1.0)
# Set the color of the border
uri.Color = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Blue())
# Add the hyperlink annotation to the page
page.AnnotationsWidget.Add(uri)
#Save the result file
pdf.SaveToFile("SearchTextAndAddHyperlink.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Excel provides various options to compress, resize, or move images, allowing users to effectively manage and optimize their spreadsheets. By utilizing these features, you can significantly reduce file size, adjust image dimensions to fit within cells, and effortlessly reposition images to enhance the visual appeal of your Excel documents. This article introduces how to programmatically compress, resize or move images in an Excel document in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Compress Images in an Excel Document in Python
- Resize an Image in an Excel Worksheet in Python
- Move an Image within the Same Worksheet in Python
- Move an Image from a Worksheet to Another in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Compress Images in an Excel Document in Python
To compress the quality of an image, Spire.XLS for Python offers the ExcelPicture.Compress() method. The following are the steps to compress images in an Excel document using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through the worksheets in the document, and get the images from a specific sheet through Worksheet.Pictures property.
- Get a specific image from the image collection and compress it using ExcelPicture.Compress() method.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
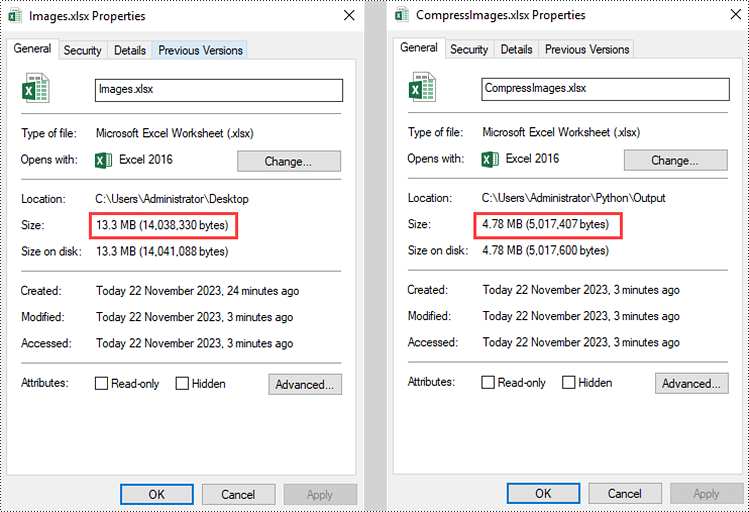
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Images.xlsx")
# Loop through the worksheets in the document
for sheet in workbook.Worksheets:
# Loop through the images in the worksheet
for picture in sheet.Pictures:
# Compress a specific image
picture.Compress(50)
# Save the file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/CompressImages.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Resize an Image in an Excel Worksheet in Python
The width and height of an image can be set or get through the ExcelPicture.Width property and the ExcelPicture.Height property. To resize an image in Excel, follow the steps below.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet though Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific image from the worksheet through Worksheet.Pictures[index] property.
- Reset the size of the image through ExcelPicture.Width property and ExcelPicture.Height property.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Image.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get a specific picture from the worksheet
picture = sheet.Pictures[0]
# Resize the picture
picture.Width = (int)(picture.Width / 2)
picture.Height = (int)(picture.Height / 2)
# Save to file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/ResizeImage.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()

Move an Image within the Same Worksheet in Python
The start position of an image can be set or get through the ExcelPicture.TopRow property and the ExcelPicture.LetColumn property. To move an image within the same worksheet, follow the steps below.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet though Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific image from the worksheet through Worksheet.Pictures[index] property.
- Reset the position of the image in the worksheet through ExcelPicture.TopRow property and ExcelPicture.LeftColumn property.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Image.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get a specific picture from the worksheet
picture = sheet.Pictures[0]
# Reset the position of the picture
picture.TopRow = 5
picture.LeftColumn = 6
# Save to file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/MoveImage.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()

Move an Image from a Worksheet to Another in Python
Besides moving images in the same worksheet, you can also move images in different worksheets of the workbook. First, you need to get the desired image from a worksheet and add it to a different worksheet using the Worksheet.Pictures.Add() method, and then delete the original image using the ExcelPicture.Remove() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet though Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific image from the worksheet through Worksheet.Pictures[index] property.
- Get another worksheet though Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Add the image to the target worksheet using Worksheet.Pictures.Add() method.
- Remove the image from the source worksheet using ExcelPicture.Remove() method.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Image.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the first picture from the worksheet
picture = sheet.Pictures[0]
# Get the second worksheet
sheet_two = workbook.Worksheets[1]
# Add the picture to the second worksheet
sheet_two.Pictures.Add(1, 1, picture.Picture)
# Remove the picture in the first worksheet
picture.Remove()
# Save to file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/MoveImage.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
