
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Dealing with a large number of Word documents can be very challenging. Whether it's editing or reviewing a large number of documents, there's a lot of time wasted on opening and closing documents. What's more, sharing and receiving a large number of separate Word documents can be annoying, as it may require a lot of repeated sending and receiving operations by both the sharer and the receiver. Therefore, in order to enhance efficiency and save time, it is advisable to merge related Word documents into a single file. From this article, you will know how to use Spire.Doc for Python to easily merge Word documents through Python programs.
- Merge Word Documents by Inserting Files with Python
- Merge Word Documents by Cloning Contents with Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Merge Word Documents by Inserting Files with Python
The method Document.insertTextFromFile() is used to insert other Word documents to the current one, and the inserted content will start from a new page. The detailed steps for merging Word documents by inserting are as follows:
- Create an object of Document class and load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Insert the content from another document to it using Document.InsertTextFromFile() method.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of Document class and load a Word document
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample1.docx")
# Insert the content from another Word document to this one
doc.InsertTextFromFile("Sample2.docx", FileFormat.Auto)
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/InsertDocuments.docx")
doc.Close()

Merge Word Documents by Cloning Contents with Python
Merging Word documents can also be achieved by cloning contents from one Word document to another. This method maintains the formatting of the original document, and content cloned from another document continues at the end of the current document without starting a new Page. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create two objects of Document class and load two Word documents using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the last section of the destination document using Document.Sections.get_Item() method.
- Loop through the sections in the document to be cloned and then loop through the child objects of the sections.
- Get a section child object using Section.Body.ChildObjects.get_Item() method.
- Add the child object to the last section of the destination document using Section.Body.ChildObjects.Add() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create two objects of Document class and load two Word documents
doc1 = Document()
doc1.LoadFromFile("Sample1.docx")
doc2 = Document()
doc2.LoadFromFile("Sample2.docx")
# Get the last section of the first document
lastSection = doc1.Sections.get_Item(doc1.Sections.Count - 1)
# Loop through the sections in the second document
for i in range(doc2.Sections.Count):
section = doc2.Sections.get_Item(i)
# Loop through the child objects in the sections
for j in range(section.Body.ChildObjects.Count):
obj = section.Body.ChildObjects.get_Item(j)
# Add the child objects from the second document to the last section of the first document
lastSection.Body.ChildObjects.Add(obj.Clone())
# Save the result document
doc1.SaveToFile("output/MergeByCloning.docx")
doc1.Close()
doc2.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
The ability to set a password for a PDF document or remove the password from an encrypted PDF document is invaluable for securing sensitive information while maintaining the flexibility and convenience of working with PDF files. By setting up passwords for PDF documents, individuals can control access to their files, preventing unauthorized viewing, editing, or copying. Conversely, unprotecting a PDF document can make the document accessible or editable again. In this article, you will learn how to password-protect PDF documents as well as how to remove passwords from encrypt PDF documents using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Protect PDF with Password in Python
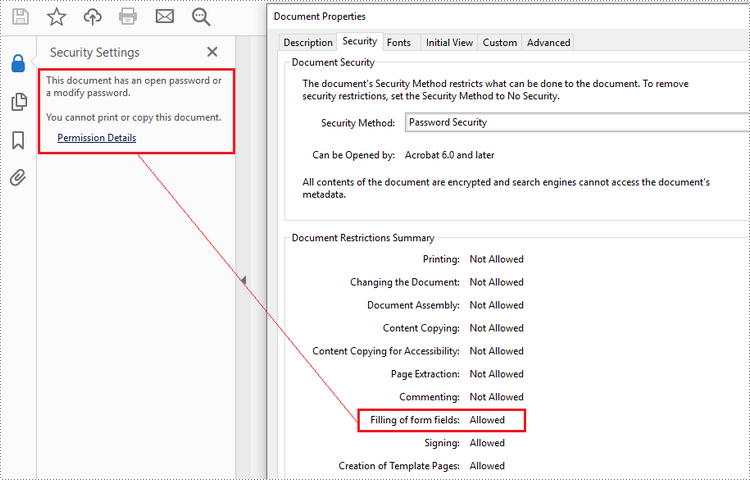
There are two types of passwords that can be used for security purposes: the "open password" and the "permission password". An open password, also known as a user password, is used to restrict unauthorized access to a PDF file. A permission password, also referred to as a master password or owner password, allows you to set various restrictions on what others can do with the PDF file. If a PDF file is secured with both types of passwords, it can be opened with either password.
The PdfDocument.Security.Encrypt(String openPassword, String permissionPassword, PdfPermissionsFlags permissions, PdfEncryptionKeySize keySize) method offered by Spire.PDF for Python allows you to protect PDF files with an open password and/or a permission password. The parameter PdfPermessionsFlags is used to specify the user's permission to operate the document.
Here are the steps to password-protect a PDF with Spire.PDF for Python.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a sample PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Encrypt the PDF file with an open password and permission password using PdfDocument.Security.Encrypt(String openPassword, String permissionPassword, PdfPermissionsFlags permissions, PdfEncryptionKeySize keySize) method.
- Save the result file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a sample PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/input.pdf")
# Encrypt the PDF file with an open password and a permission password
doc.Security.Encrypt("openPsd", "permissionPsd", PdfPermissionsFlags.FillFields, PdfEncryptionKeySize.Key128Bit)
# Save the result file
doc.SaveToFile("output/Encrypted.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
Remove Password from an Encrypted PDF in Python
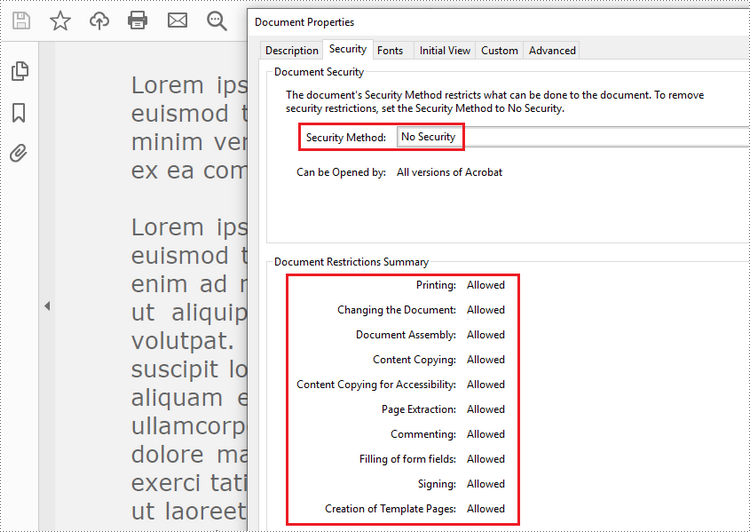
To remove the password from a PDF file, call the PdfDocument.Security.Encrypt() method and leave the open password and permission password empty. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load an encrypted PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile(String fileName, String password) method.
- Decrypt the PDF file by setting the open password and permission password to empty using PdfSecurity.Encrypt(String openPassword, String permissionPassword, PdfPermissionsFlags permissions, PdfEncryptionKeySize keySize, String originalPermissionPassword) method.
- Save the result file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load an encrypted PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Encrypted.pdf", "openPsd")
# Set the open password and permission password as empty
doc.Security.Encrypt(str(), str(), PdfPermissionsFlags.Default, PdfEncryptionKeySize.Key128Bit, "permissionPsd")
# Save the result file
doc.SaveToFile("output/RemovePassword.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
How to Merge Excel Files in Python (.xls & .xlsx) - No Excel Required
2023-11-03 01:27:30 Written by hayes Liu
Merging Excel files is a common task for data analysts and financial teams working with large datasets. While Microsoft Excel supports manual merging, it becomes inefficient and error-prone when dealing with large volumes of files.
In this step-by-step guide, you will learn how to merge multiple Excel files (.xls and .xlsx) using Python and Spire.XLS for Python library. Whether you're combining workbooks, merging worksheets, or automating bulk Excel file processing, this guide will help you save time and streamline your workflow with practical solutions.
Table of Contents
- Why Merge Excel Files with Python?
- Getting Started with Spire.XLS for Python
- How to Merge Multiple Excel Files into One Workbook using Python
- How to Combine Multiple Excel Worksheets into a Single Worksheet using Python
- Conclusion
- FAQs: Merge Excel Files with Python
Why Merge Excel Files with Python?
Using Python to merge Excel files brings several key advantages:
- Automation: Save time and eliminate repetitive manual work by automating the merging process.
- No Excel Dependency: Merge files without installing Microsoft Excel—ideal for headless, server-side, or cloud environments.
- Flexible Merging: Customize merging by selecting specific sheets, ranges, columns, or rows.
- Scalability: Handle hundreds or even thousands of Excel files with consistent performance.
- Error Reduction: Reduce manual errors and ensure data accuracy with automated scripts.
Whether you’re consolidating monthly reports or merging large datasets, Python helps streamline the process efficiently.
Getting Started with Spire.XLS for Python
Spire.XLS for Python is a standalone library that allows developers to create, read, edit, and save Excel files without the need for Microsoft Excel installation.
Key Features Include:
- Supports Multiple Formats: .xls, .xlsx, and more.
- Worksheet Operations: Copy, rename, delete, and merge worksheets seamlessly across workbooks.
- Formula & Formatting Preservation: Retain formulas and formatting during editing or merging.
- Advanced Features: Includes chart creation, conditional formatting, pivot tables, and more.
- File Conversion: Convert Excel files to PDF, HTML, CSV, and more.
Installation
Run the following pip command in your terminal or command prompt to install Spire.XLS from PyPI:
pip install spire.xls
How to Merge Multiple Excel Files into One Workbook using Python
When working with multiple Excel files, consolidating all worksheets into a single workbook can simplify data management and reporting. This approach preserves each original worksheet separately, making it easy to organize and review data from different sources such as department budgets, regional reports, or monthly summaries.
Steps
To merge multiple Excel files into a single workbook using Python, follow these steps:
- Loop through the files.
- Load each Excel file using LoadFromFile().
- For the first file, assign it as the base workbook.
- For subsequent files, copy all worksheets into the base workbook using AddCopy().
- Save the final combined workbook to a new file.
Code Example
import os
from spire.xls import *
# Folder containing Excel files to merge
input_folder = './sample_files'
# Output file name for the merged workbook
output_file = 'merged_workbook.xlsx'
# Initialize merged workbook as None
merged_workbook = None
# Iterate over all files in the input folder
for filename in os.listdir(input_folder):
# Process only Excel files with .xls or .xlsx extensions
if filename.endswith('.xlsx') or filename.endswith('.xls'):
file_path = os.path.join(input_folder, filename)
# Load the current Excel file into a Workbook object
source_workbook = Workbook()
source_workbook.LoadFromFile(file_path)
if merged_workbook is None:
# For the first file, assign it as the base merged workbook
merged_workbook = source_workbook
else:
# For subsequent files, copy each worksheet into the merged workbook
for i in range(source_workbook.Worksheets.Count):
sheet = source_workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(i)
merged_workbook.Worksheets.AddCopy(sheet, WorksheetCopyType.CopyAll)
# Save the combined workbook to the specified output file
merged_workbook.SaveToFile(output_file, ExcelVersion.Version2016)
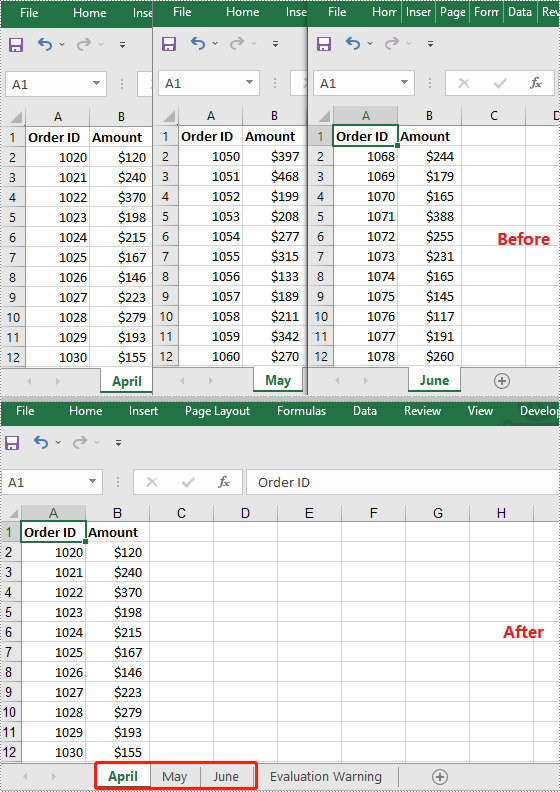
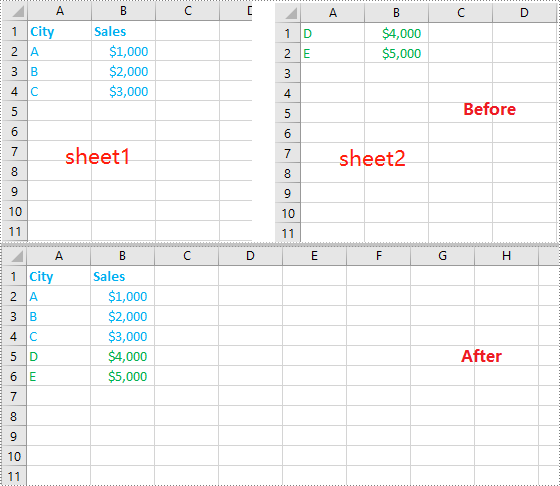
How to Combine Multiple Excel Worksheets into a Single Worksheet using Python
Merging data from multiple Excel worksheets into one worksheet allows you to aggregate information efficiently, especially when working with data such as sales logs, survey responses, or performance reports.
Steps
To combine worksheet data from multiple Excel files into a single worksheet using Python, follow these steps:
- Create a new workbook and select its first worksheet as the destination.
- Loop through the files.
- Load each Excel file using LoadFromFile().
- Get the desired worksheet that you want to merge from the current file.
- Copy the used cell range from the desired worksheet to the destination worksheet, placing data consecutively below the previously copied content.
- Save the combined data into a new Excel file.
Code Example
import os
from spire.xls import *
# Folder containing Excel files to merge
input_folder = './excel_worksheets'
# Output file name for the merged workbook
output_file = 'merged_into_one_sheet.xlsx'
# Create a new workbook to hold merged data
merged_workbook = Workbook()
# Use the first worksheet in the new workbook as the merge target
merged_sheet = merged_workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Initialize the starting row for copying data
current_row = 1
# Loop through all files in the input folder
for filename in os.listdir(input_folder):
# Process only Excel files (.xls or .xlsx)
if filename.endswith('.xlsx') or filename.endswith('.xls'):
file_path = os.path.join(input_folder, filename)
# Load the current Excel file
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile(file_path)
# Get the first worksheet from the current workbook
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the used range from the first worksheet
source_range = sheet.Range
# Set the destination range in the merged worksheet starting at current_row
dest_range = merged_sheet.Range[current_row, 1]
# Copy data from the used range to the destination range
source_range.Copy(dest_range)
# Update current_row to the row after the last copied row to prevent overlap
current_row += sheet.LastRow
# Save the merged workbook to the specified output file in Excel 2016 format
merged_workbook.SaveToFile(output_file, ExcelVersion.Version2016)
Conclusion
When merging multiple Excel files into a single document—whether by appending sheets or combining data row by row—using a Python library like Spire.XLS enables automation and improves accuracy. This approach can help streamline workflows, especially in enterprise scenarios that require handling large datasets without relying on Microsoft Excel.
FAQs: Merge Excel Files with Python
Q1: Can I merge .xls and .xlsx files together?
A1: Yes. Spire.XLS handles both formats without needing conversion.
Q2: Do I need Excel installed on my machine to use Spire.XLS?
A2: No. Spire.XLS is standalone and works without Microsoft Office installed.
Q3: Can I merge only specific sheets from each workbook?
A3: Yes. You can customize your code to merge sheets by name or index. For example:
sheet = source_workbook.Worksheets["Summary"]
Q4: How do I avoid copying header rows multiple times?
A4: Add logic like:
if current_row > 1:
start_row = 2 # Skip header
else:
start_row = 1
Q5: Can I keep track of which file each row came from?
A5: Yes. Add a new column in the merged sheet containing the source file name for each row.
Q6: Is there a file size or row limit when using Spire.XLS?
A6: Spire.XLS follows the same row and column limits as Excel: .xlsx supports up to 1,048,576 rows × 16,384 columns, and .xls supports up to 65,536 rows × 256 columns.
Q7: Can I preserve formulas and formatting while merging?
A7: Yes. When merging Excel files, formatting and formulas are preserved.
