
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
If you receive or download a PDF file and find that some of the pages are displayed in the wrong orientation (e.g., sideways or upside down), rotating the PDF file allows you to correct the page orientation for easier reading and viewing. This article will demonstrate how to programmatically rotate PDF pages using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Rotate a Specific Page in PDF in Python
Rotation is based on 90-degree increments. You can rotate a PDF page by 0/90/180/270 degrees. The following are the steps to rotate a PDF page:
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified page using PdfDocument.Pages[pageIndex] property.
- Get the original rotation angle of the page using PdfPageBase.Rotation.value property.
- Increase the original rotation angle by desired degrees.
- Apply the new rotation angle to the page using PdfPageBase.Rotation property
- Save the result document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Get the original rotation angle of the page
rotation = int(page.Rotation.value)
# Rotate the page 180 degrees clockwise based on the original rotation angle
rotation += int(PdfPageRotateAngle.RotateAngle180.value)
page.Rotation = PdfPageRotateAngle(rotation)
# Save the result document
pdf.SaveToFile("RotatePDFPage.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Rotate All Pages in PDF in Python
Spire.PDF for Python also allows you to loop through each page in a PDF file and then rotate them all. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Loop through each page in the document.
- Get the original rotation angle of the page using PdfPageBase.Rotation.value property.
- Increase the original rotation angle by desired degrees.
- Apply the new rotation angle to the page using PdfPageBase.Rotation property.
- Save the result document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("Input.pdf")
# Loop through each page in the document
for i in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Get the original rotation angle of the page
rotation = int(page.Rotation.value)
# Rotate the page 180 degrees clockwise based on the original rotation angle
rotation += int(PdfPageRotateAngle.RotateAngle180.value)
page.Rotation = PdfPageRotateAngle(rotation)
# Save the result document
pdf.SaveToFile("RotatePDF.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Convert PDF to Images in Python (PNG, JPG, BMP, SVG, TIFF)
2023-09-18 01:16:01 Written by Administrator
Converting PDF files to images in Python is a common need for developers and professionals working with digital documents. Whether you want to generate thumbnails, create previews, extract specific content areas, or prepare files for printing, transforming a PDF into image formats gives you flexibility and compatibility across platforms.
This comprehensive guide demonstrates how to convert PDF files into popular image formats—such as PNG, JPG, BMP, SVG, and TIFF—in Python, using practical, easy-to-follow code examples.
Table of Contents
- Why Convert PDF to Image
- Python PDF-to-Image Converter Library
- Simple PDF to PNG, JPG, and BMP Conversion
- Advanced Conversion Options
- Generate Multi-Page TIFF from PDF
- Export PDF as SVG
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Why Convert PDF to Image?
Converting PDF to image formats offers several benefits:
- Cross-platform compatibility: Images are easier to embed in web pages, mobile apps, or presentations.
- Preview and thumbnail generation: Quickly create page snapshots without rendering the full PDF.
- Selective content extraction: Save specific areas of a PDF as images for focused analysis or reuse.
- Simplified sharing: Images can be easily emailed, uploaded, or displayed without special PDF readers.
Python PDF-to-Image Converter Library
Spire.PDF for Python is a powerful and easy-to-use library designed for handling PDF files. It enables developers to convert PDF pages into multiple image formats like PNG, JPG, BMP, SVG, and TIFF with excellent quality and performance.

Installation
You can easily install the library using pip. Simply open your terminal and run the following command:
pip install Spire.PDF
Simple PDF to PNG, JPG, and BMP Conversion
The SaveAsImage method of the PdfDocument class allows you to render each page of a PDF into an image format of your choice.
The code example below demonstrates how to load a PDF file, iterate through its pages, and save each one as a PNG image. You can easily adjust the file format to JPG or BMP by changing the file extension.
from spire.pdf import *
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("template.pdf")
# Loop through pages and save as images
for i in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
# Convert each page to image
with pdf.SaveAsImage(i) as image:
# Save in different formats as needed
image.Save(f"Output/ToImage_{i}.png")
# image.Save(f"Output/ToImage_{i}.jpg")
# image.Save(f"Output/ToImage_{i}.bmp")
# Close the PDF document
pdf.Close()
Advanced Conversion Options
Enable Transparent Image Background
Transparent backgrounds help integrate images seamlessly into designs, avoiding unwanted borders or background colors.
To enable a transparent background during PDF-to-image conversion in Python, use the SetPdfToImageOptions() method with an alpha value of 0. This setting ensures that the background of the output image is fully transparent.
The following example demonstrates how to export each PDF page as a transparent PNG image.
from spire.pdf import *
# Load PDF document from file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("template.pdf")
# Set the transparent value of the image's background to 0
pdf.ConvertOptions.SetPdfToImageOptions(0)
# Loop through all pages and save each as an image
for i in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
# Convert each page to an image
with pdf.SaveAsImage(i) as image:
# Save the image to the output directory
image.Save(f"Output/ToImage_{i}_transparent.png")
# Close the PDF document
pdf.Close()
Note: Transparency is supported in PNG but not in JPG or BMP formats.
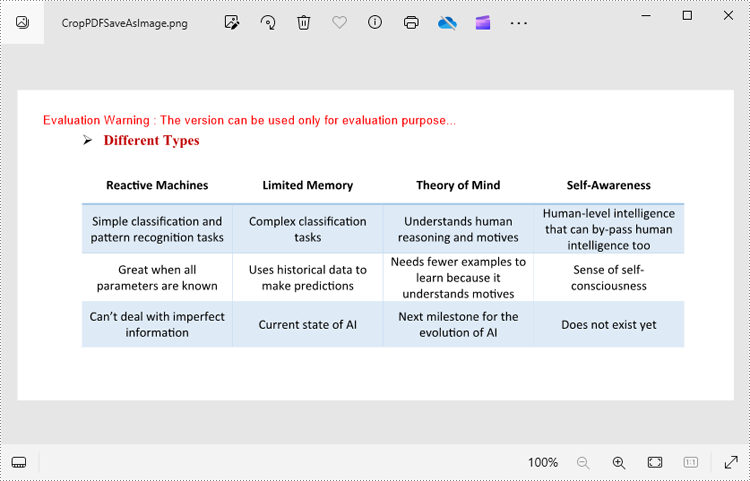
Crop Specific PDF Areas to Image
In some cases, you may only need to export a specific area of a PDF page—such as a chart, table, or block of text. This can be done by adjusting the page’s CropBox before rendering.
The CropBox property defines the visible region of the page used for display and printing. By setting it to a specific RectangleF(x, y, width, height) value, you can isolate and export only the desired portion of the content.
The example below demonstrates how to crop a rectangular area on the first page of a PDF and save that section as a PNG image.
from spire.pdf import *
# Load the PDF document from file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Access the first page of the PDF
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Define the crop area of the page using a rectangle (x, y, width, height)
page.CropBox = RectangleF(0.0, 300.0, 600.0, 260.0)
# Convert the cropped page to an image
with pdf.SaveAsImage(0) as image:
# Save the image to a PNG file
image.Save("Output/CropPDFSaveAsImage.png")
# Close the PDF document
pdf.Close()
Note: You need to adjust the coordinates based on the location of your target content. Coordinates start from the top-left corner of the page.
Generate Multi-Page TIFF from PDF
The TIFF format supports multi-page documents, making it a popular choice for archival and printing purposes. Although Spire.PDF for Python doesn't natively create multi-page TIFFs, you can render individual pages as images and then use the Pillow library to merge them into one .tiff file.
Before proceeding, ensure Pillow is installed by running:
pip install Pillow
The following example illustrates how to:
- Load a PDF
- Convert each page to an image
- Combine all images into a single multi-page TIFF
from spire.pdf import *
from PIL import Image
from io import BytesIO
# Load the PDF document from file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Input.pdf")
# Create an empty list to store PIL Images
images = []
# Iterate through all pages in the document
for i in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
# Convert a specific page to an image stream
with pdf.SaveAsImage(i) as imageData:
# Open the image stream as a PIL image
img = Image.open(BytesIO(imageData.ToArray()))
# Append the PIL image to list
images.append(img)
# Save the PIL Images as a multi-page TIFF file
images[0].save("Output/ToTIFF.tiff", save_all=True, append_images=images[1:])
# Dispose resources
pdf.Dispose()
It’s also possible to convert TIFF files back to PDF. For detailed instructions on it, please refer to the tutorial: Python: Convert PDF to TIFF and TIFF to PDF.
Export PDF as SVG
SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) is an ideal format for content that requires scaling without quality loss, such as charts, vector illustrations, and technical diagrams.
By using the SaveToFile() method with the FileFormat.SVG option, you can export PDF pages as SVG files. This conversion preserves the vector characteristics of the content, making it well-suited for web embedding, responsive design, and further editing in vector graphic tools.
The following example demonstrates how to export an entire PDF document to SVG format.
from spire.pdf import *
# Load the PDF document from file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Example.pdf")
# Save each page of the file to a separate SVG file
pdf.SaveToFile("PdfToSVG/ToSVG.svg", FileFormat.SVG)
# Close the PdfDocument object
pdf.Close()
Note: Each page in the PDF will be saved as a separate SVG file named ToSVG_i.svg, where i is the page number (1-based).
To export specific pages or customize the SVG output size, please refer to our detailed guide: Python: Convert PDF to SVG.
Conclusion
Converting PDF to images in formats like PNG, JPG, BMP, SVG, and TIFF provides flexibility for sharing, displaying, and processing digital documents. With Spire.PDF for Python, you can:
- Export high-quality images from PDFs in various formats
- Crop specific regions for focused content extraction
- Generate multi-page TIFF files for archival purposes
- Create scalable SVG vector graphics for diagrams and charts
By automating PDF to image conversion in Python, you can seamlessly integrate image export into your applications and workflows.
FAQs
Q1: Can I convert a range of pages from a PDF to images?
A1: Yes. You can convert specific pages by specifying their indices in a loop. For example, to export pages 1 to 3:
# Convert only pages 1-3
for i in range(0, 3): # 0-based index
with pdf.SaveAsImage(i) as img:
img.Save(f"page_{i}.png")
Q2: Can I batch convert multiple PDF files to images?
A2: Yes, batch conversion is supported. You can iterate through a list of PDF file paths and convert each one within a loop.
pdf_files = ["a.pdf", "b.pdf", "c.pdf"]
for file in pdf_files:
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile(file)
for i in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
with pdf.SaveAsImage(i) as img:
img.Save(f"{file}_page_{i}.png")
Q3: Is it possible to convert password-protected PDFs to images?
A3: Yes, you can convert secured PDFs to images as long as you provide the correct password when loading the PDF document.
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("protected.pdf", "password")
Q4: Is it possible to extract embedded images from a PDF instead of rendering pages?
A4: Yes. Aside from rendering entire pages, the library also supports extracting images directly from the PDF.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.PDF for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Merging and splitting table cells in PowerPoint are two common functions, mainly used to adjust the layout and structure of the table. Merging cells involves combining adjacent cells into a larger one. It allows users to create title cells that span multiple columns or rows. On the other hand, splitting cells means dividing a cell into several smaller ones, which is useful for creating detailed layouts or accommodating diverse content. In this article, we will show you how to merge and split table cells in PowerPoint programmatically by using Spire.Presentation for .NET.
Install Spire.Presentation for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.Presentation for.NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLLs files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.Presentation
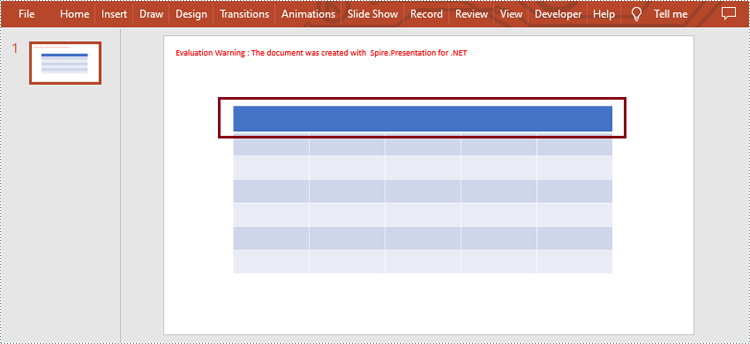
Merge Table Cells in PowerPoint
Spire.Presentation for .NET provides users with ITable[int columnIndex, int rowIndex] property and ITable.MergeCells(Cell startCell, Cell endCell, boolean allowSplitting) method to get and merge the specific cells. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of Presentation class.
- Load a sample file using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the table from the first slide by looping through all shapes.
- Get the specific cells by ITable[int columnIndex, int rowIndex] property and merge them by using ITable.MergeCells(Cell startCell, Cell endCell, boolean allowSplitting) method.
- Save the result file using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Presentation;
namespace MergeCells
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create an object of Presentation class
Presentation presentation = new Presentation();
//Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("sample.pptx");
//Get the table from the first slide by looping through all shapes
ITable table = null;
foreach (IShape shape in presentation.Slides[0].Shapes)
{
if (shape is ITable)
{
table = (ITable)shape;
//Merge the cells from [0,0] to [4,0]
table.MergeCells(table[0, 0], table[4, 0], false);
}
}
//Save the result document
presentation.SaveToFile("MergeCells.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2010);
presentation.Dispose();
}
}
}
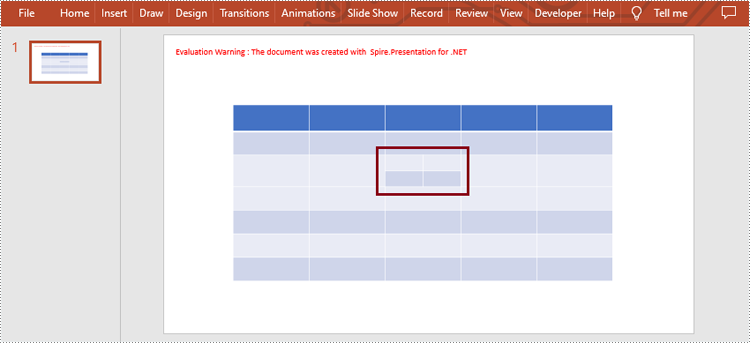
Split Table Cells in PowerPoint
Spire.Presentation for .NET also supports users to get the specific cell and split it into smaller ones by using ITable[int columnIndex, int rowIndex] property and Cell.Split(int RowCount, int ColunmCount) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of Presentation class.
- Load a sample file using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the table from the first slide by looping through all shapes.
- Get the specific cell by ITable[int columnIndex, int rowIndex] property and split it into 2 rows and 2 columns by using Cell.Split(int RowCount, int ColumnCount) method.
- Save the result file using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Presentation;
namespace SplitCells
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create an object of Presentation class
Presentation presentation = new Presentation();
//Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("sample.pptx");
//Get the table from the first slide by looping through all shapes
ITable table = null;
foreach (IShape shape in presentation.Slides[0].Shapes)
{
if (shape is ITable)
{
table = (ITable)shape;
//Split cell [2, 2] into 2 rows and 2 columns
table[2, 2].Split(2, 2);
}
}
//Save the result document
presentation.SaveToFile("SplitCells.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013);
presentation.Dispose();
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
