
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
How to Convert PDF to Excel with Formatting in Python (Step-by-Step Guide)
2023-09-07 01:11:29 Written by Koohji
Converting PDF files to Excel spreadsheets in Python is an effective way to extract structured data for analysis, reporting, and automation. While PDFs are excellent for preserving layout across platforms, their static format often makes data extraction challenging.
Excel, on the other hand, provides robust features for sorting, filtering, calculating, and visualizing data. By using Python along with the Spire.PDF for Python library, you can automate the entire PDF to Excel conversion process — from basic one-page documents to complex, multi-page PDFs.
Whether you're automating data extraction from PDFs or integrating PDF content into Excel workflows, this tutorial will walk you through both quick-start and advanced methods for reliable Python PDF to Excel conversion.
Table of Contents
- Why Convert PDF to Excel Programmatically in Python
- Setting Up Your Development Environment
- Quick Start: Convert PDF to Excel in Python
- Advanced PDF to Excel Conversion with Layout Control and Formatting Options
- Conclusion
Why Convert PDF to Excel Programmatically in Python
PDFs are ideal for sharing documents with consistent formatting, but their fixed structure makes them difficult to analyze or reuse, especially if they contain tables.
Converting PDF to Excel allows you to:
- Extract tabular data for analysis or visualization
- Automate monthly or recurring report extraction
- Enable downstream processing in Excel
- Save hours of manual copy-pasting
Using Python for this task adds automation, flexibility, and scalability — ideal for integration into data pipelines or backend services.
Setting Up Your Development Environment
Before you start converting PDF files to Excel using Python, it’s essential to set up your development environment properly. This ensures you have all the necessary tools and libraries installed to follow the tutorial smoothly.
Install Python
If you haven’t already installed Python on your system, download and install the latest version from the official website.
Make sure to add Python to your system PATH during installation to run Python commands from the terminal or command prompt easily.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
Spire.PDF for Python is the core library used in this tutorial to load, manipulate, and convert PDF documents.
To install it, open your terminal and run:
pip install Spire.PDF
This command downloads and installs Spire.PDF along with any required dependencies.
If you encounter any issues or need detailed installation help, please refer to our step-by-step guide: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Quick Start: Convert PDF to Excel in Python
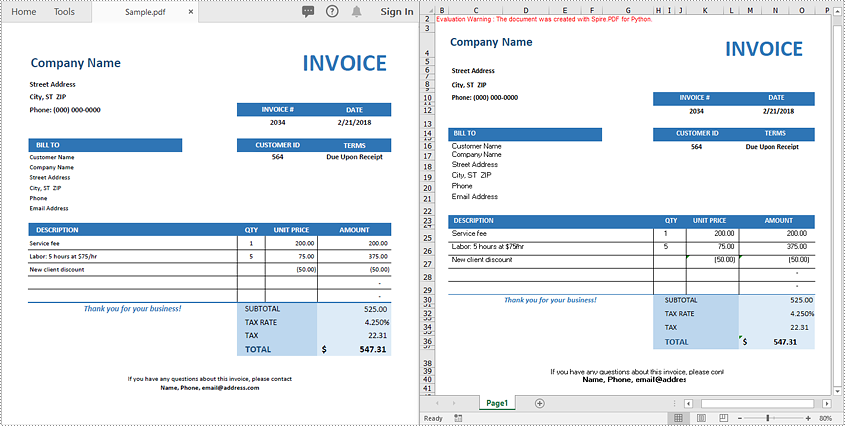
If your PDF has a clean and simple layout without complex formatting or multiple page structures, you can convert it directly to Excel with just 3 lines of code using Spire.PDF for Python.
Steps to Quickly Export PDF to Excel
Follow these straightforward steps to export your PDF file to an Excel spreadsheet in Python:
- Import the required classes.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load your PDF file with the LoadFromFile method.
- Export the PDF to Excel (.xlsx) format using the SaveToFile method and specify FileFormat.XLSX as the output format.
Code Example
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load your PDF file
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Convert and save the PDF to Excel
pdf.SaveToFile("output.xlsx", FileFormat.XLSX)
# Close the document
pdf.Close()
Advanced PDF to Excel Conversion with Layout Control and Formatting Options
For more complex PDF documents—such as those containing multiple pages, rotated text, table cells with multiple lines of text, or overlapping content - you can use the XlsxLineLayoutOptions class to gain precise control over the conversion process.
This allows you to preserve the original structure and formatting of your PDF more accurately when exporting to Excel.
Layout Options You Can Configure
The XlsxLineLayoutOptions class in Spire.PDF provides several properties that give you granular control over how PDF content is exported to Excel. Below is a breakdown of each option and its behavior:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| convertToMultipleSheet | Determines whether to convert each PDF page into a separate worksheet. The default value is true. |
| rotatedText | Specifies whether to preserve the original rotation of angled text. The default value is true. |
| splitCell | Determines whether to split a PDF table cell with multiple lines of text into separate rows in the Excel output. The default value is true. |
| wrapText | Determines whether to enable word wrap inside Excel cells. The default value is true. |
| overlapText | Specifies whether text overlapping in the original PDF should be preserved in the Excel output. The default value is false. |
Code Example
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load your PDF file
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Define layout options
# Parameters: convertToMultipleSheet, rotatedText, splitCell, wrapText, overlapText
layout_options = XlsxLineLayoutOptions(True, True, False, True, False)
# Apply layout options
pdf.ConvertOptions.SetPdfToXlsxOptions(layout_options)
# Convert and save the PDF to Excel
pdf.SaveToFile("advanced_output.xlsx", FileFormat.XLSX)
# Close the document
pdf.Close()
Conclusion
Converting PDF files to Excel in Python is an efficient way to automate data extraction and processing tasks. Whether you need a quick conversion or fine-grained layout control, Spire.PDF for Python offers flexible options that scale from simple to complex scenarios.
Ready to automate your PDF to Excel conversions?
Get a free trial license for Spire.PDF for Python and explore the full Spire.PDF Documentation to get started today!
FAQs
Q1: Can I convert each PDF page into a separate Excel worksheet?
A1: Yes. Use the convertToMultipleSheet=True option in the XlsxLineLayoutOptions class to export each page to its own sheet.
Q2. What Excel format does Spire.PDF export to?
A2: Spire.PDF converts PDFs to .xlsx, the modern Excel format supported by Excel 2007 and later.
Q3: Can I convert a PDF to Excel in Python without losing formatting?
A3: Yes. Using Spire.PDF for Python, you can retain the original formatting, including merged cells, cell background colors, and other format settings when saving PDFs to Excel.
Q4: Can I extract only a specific table from a PDF to Excel instead of converting the whole document?
A4: Yes, Spire.PDF for Python supports extracting specific tables from PDF files. You can then write the extracted table data to Excel using our Excel processing library - Spire.XLS for Python.
Merging PDF files is a common task in many applications, from combining report sections to creating comprehensive document collections. For developers, using Python to merge PDF files programmatically can significantly streamline the process and help build automated workflows.
This article explores how to merge PDFs in Python using Spire.PDF for Python - a robust library designed for efficient PDF manipulation.
Table of Contents:
- 5 Reasons Why You Should Use Python to Combine PDFs
- Step-by-Step: Merge PDF Files in Python
- Advanced: Merge Selected Pages from PDFs in Python
- Batch Processing: Merge Multiple PDF Files in a Folder
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
5 Reasons Why You Should Use Python to Combine PDFs
While GUI tools like Adobe Acrobat offer PDF merging capabilities, Python provides distinct advantages for developers and enterprises. Python’s PDF merging feature shines when you need to:
- Process documents in bulk
- Schedule scripts to run automatically (e.g., daily report merging).
- Integrate with data workflows
- Implement business-specific logic
- Deploy in server/cloud environments
Step-by-Step: Merge PDF Files in Python
Step 1: Install Spire.PDF for Python
Before you can start combining PDFs with Spire.PDF for Python, you need to install the library. You can do this using pip, the Python package manager. Open your terminal and run the following command:
pip install Spire.PDF
Step 2: Merge Multiple PDF Files into One
Now, let's dive into the Python code for merging multiple PDF files into a single PDF.
1. Import the Required Classes
First, import the necessary classes from the Spire.PDF library:
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
2. Define Paths of PDFs to Merge
Define three PDF file paths and stored them in a list. You can modify these paths or adjust the number of files according to your needs.
inputFile1 = "Sample1.pdf"
inputFile2 = "Sample2.pdf"
inputFile3 = "Sample3.pdf"
files = [inputFile1, inputFile2, inputFile3]
3. Merge PDF Files
The MergeFiles() method combines all PDFs in the list into a new PDF document object.
pdf = PdfDocument.MergeFiles(files)
4. Save the Merged PDF Finally, save the combined PDF to a specified output path.
pdf.Save("output/MergePDF.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
Full Python Code to Combine PDFs:
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a list of the PDF file paths
inputFile1 = "Sample1.pdf"
inputFile2 = "Sample2.pdf"
inputFile3 = "Sample3.pdf"
files = [inputFile1, inputFile2, inputFile3]
# Merge the PDF documents
pdf = PdfDocument.MergeFiles(files)
# Save the result document
pdf.Save("output/MergePDF.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
pdf.Close()
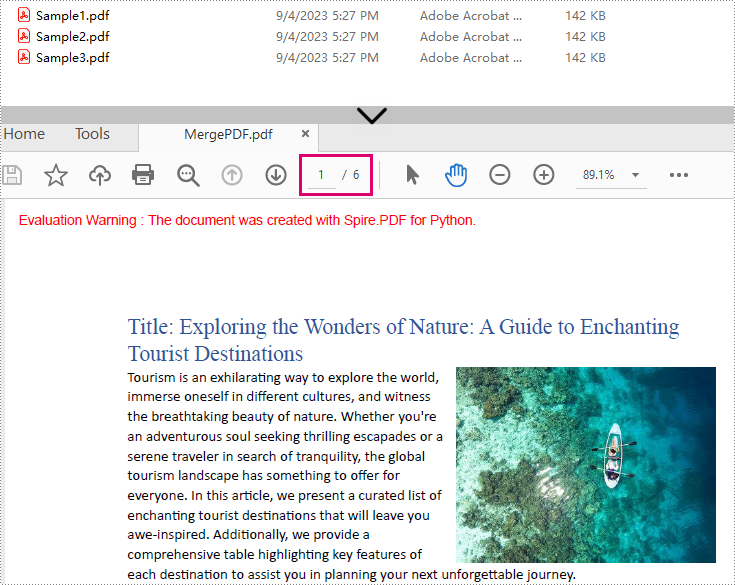
Result: Combine three PDF files (total of 6 pages) into one PDF file.
Advanced: Merge Selected Pages from PDFs in Python
In some cases, you may only want to merge specific pages of multiple PDFs. Spire.PDF for Python makes this easy by allowing you to select pages from different PDF documents and insert them into a new PDF file.
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import *
# Create a list of the PDF file paths
file1 = "Sample1.pdf"
file2 = "Sample2.pdf"
file3 = "Sample3.pdf"
files = [file1, file2, file3]
# Load each PDF file as an PdfDocument object and add them to a list
pdfs = []
for file in files:
pdfs.append(PdfDocument(file))
# Create an object of PdfDocument class
newPdf = PdfDocument()
# Insert the selected pages from the loaded PDF documents into the new document
newPdf.InsertPage(pdfs[0], 0)
newPdf.InsertPage(pdfs[1], 1)
newPdf.InsertPageRange(pdfs[2], 0, 1)
# Save the new PDF document
newPdf.SaveToFile("output/SelectedPages.pdf")
Explanation:
- PdfDocument(): Initializes a new PDF document object.
- InsertPage(): Insert a specified page to the new PDF (Page index starts at 0).
- InsertPageRange(): Inserts a range of pages to the new PDF.
- SaveToFile(): Save the combined PDF to the specified output path.
Result: Combine selected pages from three separate PDF files into a new PDF.
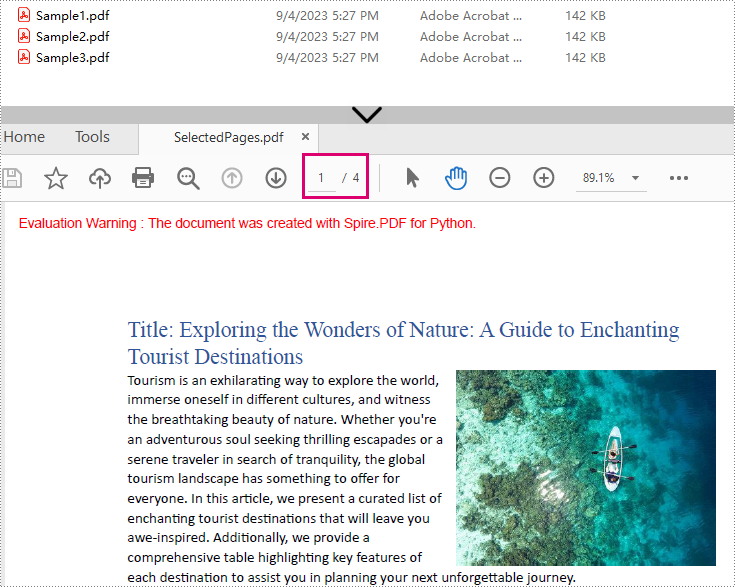
Batch Processing: Merge Multiple PDF Files in a Folder
The Python script loops through each source PDF in a specified folder, then appends all pages from the source PDFs to a new PDF file.
import os
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Specify the directory where the source PDFs are stored
folder = "pdf_folder/"
# Create a new PDF to hold the combined content.
merged_pdf = PdfDocument()
# Loop through each source PDF
for file in os.listdir(folder):
if file.endswith(".pdf"):
pdf = PdfDocument(os.path.join(folder, file))
# Appends all pages from each source PDF to the new PDF
merged_pdf.AppendPage(pdf)
pdf.Close() # Close source PDF
# Save the merged PDF after processing all files
merged_pdf.SaveToFile("BatchCombinePDFs.pdf")
merged_pdf.Close() # Release resources
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Is Spire.PDF for Python free?
A: Spire.PDF for Python offers a 30-day free trial with full features. There’s also a free version available but with page limits.
Q2: Can I merge scanned/image-based PDFs?
A: Yes, Spire.PDF handles image-only PDFs. However, OCR/text extraction requires the Spire.OCR for Python library.
Q3: How to add page numbers to the merged PDF?
A: Refer to this comprehensive guide: Add Page Numbers to PDF in Python
Q4: How to reduce the size of the merged PDF?
A: You can compress the high-resolution images and fonts contained in the merged PDF file. A related tutorial: Compress PDF Documents in Python.
Conclusion
Merging PDFs with Python doesn't have to be a complex task. With Spire.PDF for Python, you can efficiently combine multiple PDF files into a single document with just a few lines of code. Whether you need to merge entire documents, specific pages, or a batch merge, this guide outlines step-by-step instructions to help you automate the PDF merging process.
Explore Spire.PDF's online documentation for more PDF prcessing features with Python.
Creating, reading, and updating Word documents is a common need for many developers working with the Python programming language. Whether it's generating reports, manipulating existing documents, or automating document creation processes, having the ability to work with Word documents programmatically can greatly enhance productivity and efficiency. In this article, you will learn how to create, read, or update Word documents in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Create a Word Document from Scratch in Python
- Read Text of a Word Document in Python
- Update a Word Document in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Create a Word Document from Scratch in Python
Spire.Doc for Python offers the Document class to represent a Word document model. A document must contain at least one section (represented by the Section class) and each section is a container for various elements such as paragraphs, tables, charts, and images. This example shows you how to create a simple Word document containing several paragraphs using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Set the page margins through Section.PageSetUp.Margins property.
- Add several paragraphs to the section using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Add text to the paragraphs using Paragraph.AppendText() method.
- Create a ParagraphStyle object, and apply it to a specific paragraph using Paragraph.ApplyStyle() method.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Set the page margins
section.PageSetup.Margins.All = 40
# Add a title
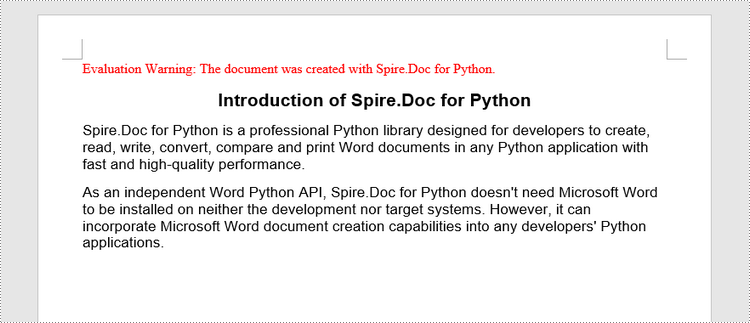
titleParagraph = section.AddParagraph()
titleParagraph.AppendText("Introduction of Spire.Doc for Python")
# Add two paragraphs
bodyParagraph_1 = section.AddParagraph()
bodyParagraph_1.AppendText("Spire.Doc for Python is a professional Python library designed for developers to " +
"create, read, write, convert, compare and print Word documents in any Python application " +
"with fast and high-quality performance.")
bodyParagraph_2 = section.AddParagraph()
bodyParagraph_2.AppendText("As an independent Word Python API, Spire.Doc for Python doesn't need Microsoft Word to " +
"be installed on neither the development nor target systems. However, it can incorporate Microsoft Word " +
"document creation capabilities into any developers' Python applications.")
# Apply heading1 to the title
titleParagraph.ApplyStyle(BuiltinStyle.Heading1)
# Create a style for the paragraphs
style2 = ParagraphStyle(doc)
style2.Name = "paraStyle"
style2.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
style2.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 13
doc.Styles.Add(style2)
bodyParagraph_1.ApplyStyle("paraStyle")
bodyParagraph_2.ApplyStyle("paraStyle")
# Set the horizontal alignment of the paragraphs
titleParagraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center
bodyParagraph_1.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Left
bodyParagraph_2.Format.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Left
# Set the after spacing
titleParagraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 10
bodyParagraph_1.Format.AfterSpacing = 10
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/WordDocument.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019)
Read Text of a Word Document in Python
To get the text of an entire Word document, you could simply use Document.GetText() method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get text from the entire document using Document.GetText() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\WordDocument.docx")
# Get text from the entire document
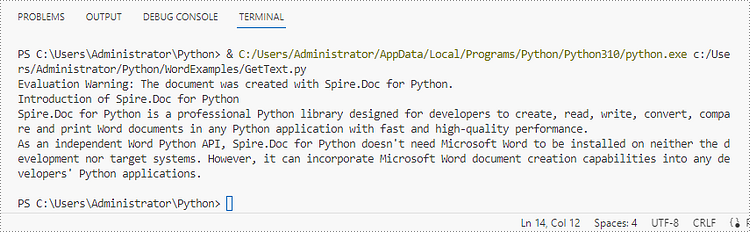
text = doc.GetText()
# Print text
print(text)
Update a Word Document in Python
To access a specific paragraph, you can use the Section.Paragraphs[index] property. If you want to modify the text of the paragraph, you can reassign text to the paragraph through the Paragraph.Text property. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific section through Document.Sections[index] property.
- Get a specific paragraph through Section.Paragraphs[index] property.
- Change the text of the paragraph through Paragraph.Text property.
- Save the document to another Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\WordDocument.docx")
# Get a specific section
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get a specific paragraph
paragraph = section.Paragraphs.get_Item(1)
# Change the text of the paragraph
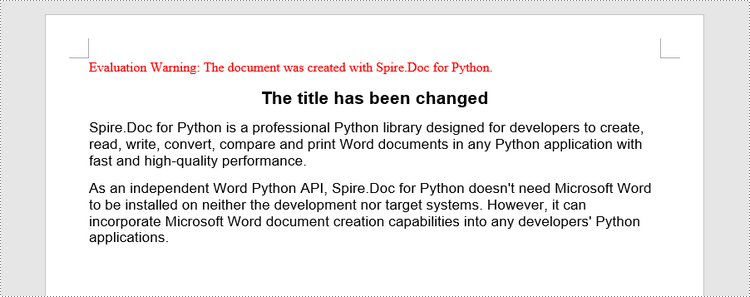
paragraph.Text = "The title has been changed"
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/Updated.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
