
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
A workbook can consist of one or more worksheets, and each worksheet is independent. When dealing with an existing Excel file or creating a new Excel file from scratch, we can add worksheets as needed to better manage and analyze data. In this article, we will show you how to add worksheets to Excel programmatically by using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Add a Worksheet to an Existing Excel file
- Add a Worksheet to a New Excel file
- Add Multiple Worksheets to a New Excel file
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Add a Worksheet to an Existing Excel file
Spire.XLS for Python allows users to add a new worksheet to an existing Excel file by using Workbook.Worksheets.Add(sheetName) method. The following are detailed steps.
- Create an object of Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Add a new sheet to this file using Workbook.Worksheets.Add(sheetName) method.
- Add desired text to cell A1 by Worksheet.Range[cellName].Text property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
inputFile = "sample.xlsx"
outputFile = "AddWorksheet.xlsx"
#Create an object of Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
#Load an Excel file from disk
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
#Add a new worksheet to this file
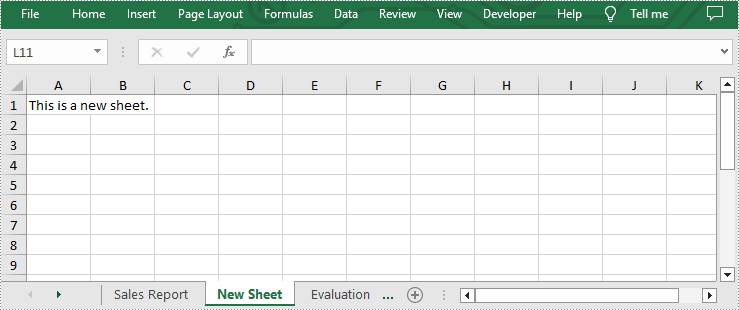
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("New Sheet")
#Add desired text to cell A1
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "This is a new sheet."
#Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Add a Worksheet to a New Excel file
In addition to adding worksheets to existing Excel files, you can also add worksheets to a newly created Excel files with the same method. You just need to clear the default worksheet before adding by calling Workbook.Worksheets.Clear() method. The following are detailed steps.
- Create an object of Workbook class.
- Clear the default worksheets using Workbook.Worksheets.Clear() method.
- Add a new sheet to the new workbook by using Workbook.Worksheets.Add(sheetName) method.
- Add desired text to cell A1 by Worksheet.Range[cellName].Text property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
outputFile = "AddWorksheet.xlsx"
#Create an object of Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
#Clear the default sheets
workbook.Worksheets.Clear()
#Add a new worksheet to the new file
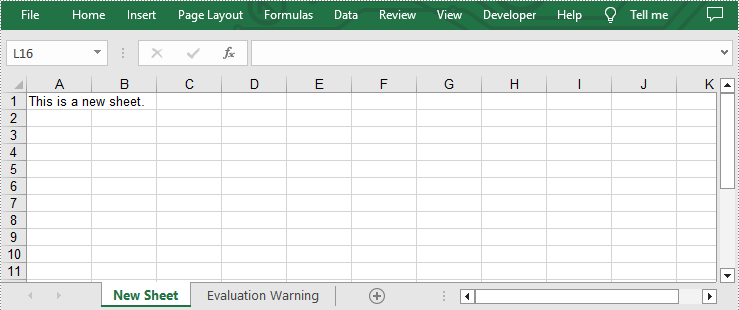
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("New Sheet")
#Add desired text to cell A1
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "This is a new sheet."
#Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Add Multiple Worksheets to a New Excel file
If you want to add multiple worksheets to a newly created Excel file, you can use Workbook.CreateEmptySheets(sheetCount) method to add a specified number of worksheets. The following are detailed steps.
- Create an object of Workbook class.
- Add three sheets to this file by using Workbook.CreateEmptySheets(sheetCount) method.
- Loop through the added worksheets and add text to cell A1 in each worksheet by Worksheet.Range[cellName].Text property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
outputFile = "AddWorksheet.xlsx"
#Create an object of Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
#Add three sheets to this file
sheetCount = 3
workbook.CreateEmptySheets(sheetCount)
#Loop through the added worksheets
for i in range(sheetCount):
#Add text to cell A1 in each worksheet
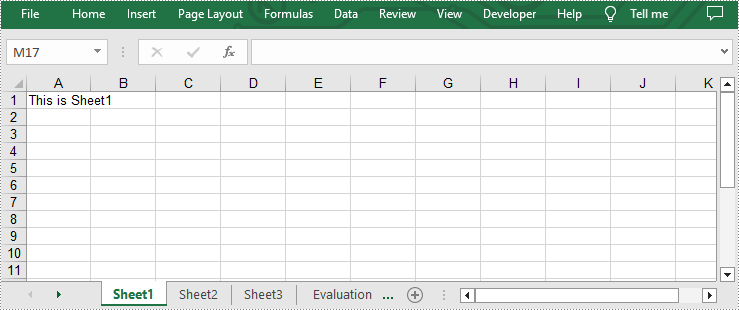
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[i]
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "This is Sheet{}".format(i+1)
#Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Hiding and showing slides are two practical features in PowerPoint that allow you to control the visibility of slides during a slideshow. Hiding slides is useful when you want to skip certain slides or temporarily remove them from the presentation without deleting them. Whereas showing slides is helpful when you want to re-display the hidden slides. In this article, we will demonstrate how to hide and show slides in a PowerPoint presentation in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
- Hide a Specific Slide in PowerPoint in Python
- Show a Hidden Slide in PowerPoint in Python
- Show All Hidden Slides in PowerPoint in Python
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Hide a Specific Slide in PowerPoint in Python
Spire.Presentation for Python provides the ISlide.Hidden property to control the visibility of a slide during a slideshow. If you don’t want a certain slide to be shown, you can hide this slide by setting the ISlide.Hidden property as True. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific slide using Presentation.Slides[index] property.
- Hide the slide by setting the ISlide.Hidden property as True.
- Save the resulting presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
ppt = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
ppt.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Get the second slide and hide it
slide = ppt.Slides[1]
slide.Hidden = True
# Save the resulting presentation to a new .pptx file
ppt.SaveToFile("HideSlide.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
ppt.Dispose()
Show a Hidden Slide in PowerPoint in Python
To show a hidden slide, you can set the ISlide.Hidden property as False. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific slide using Presentation.Slides[index] property.
- Unhide the slide by setting the ISlide.Hidden property as False.
- Save the resulting presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
ppt = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
ppt.LoadFromFile("HideSlide.pptx")
# Get the second slide and unhide it
slide = ppt.Slides[1]
slide.Hidden = False
# Save the resulting presentation to a new .pptx file
ppt.SaveToFile("ShowSlide.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
ppt.Dispose()
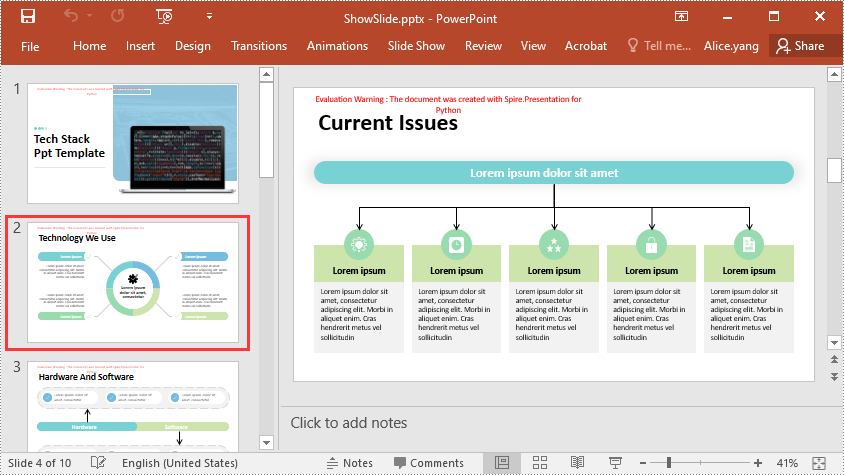
Show All Hidden Slides in PowerPoint in Python
To show all hidden slides in a PowerPoint presentation, you need to loop through all the slides in the presentation, then find the hidden slides and unhide them by setting the ISlide.Hidden property as False. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Loop through the slides in the presentation.
- Check whether the current slide is hidden or not using ISlide.Hidden property. If the result is true, unhide the slide by setting the ISlide.Hidden property as False.
- Save the resulting presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
ppt = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
ppt.LoadFromFile("Sample2.pptx")
# Loop through each slide in the presentation
for i in range(ppt.Slides.Count):
slide = ppt.Slides[i]
# Check if the slide is hidden
if(slide.Hidden):
# Unhide the slide
slide.Hidden = False
# Save the resulting presentation to a new .pptx file
ppt.SaveToFile("ShowAllHidenSlides.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
ppt.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.

Converting Word documents (DOCX or DOC) to HTML format is essential when you want to display formatted content on web pages, import legacy documents into content management systems, or generate web previews for DOCX files. HTML’s universal browser compatibility makes it an ideal format for sharing content online.
This guide shows how to convert Word to HTML in Python using Spire.Doc for Python. It covers both basic and advanced conversion techniques with practical examples, helping you handle diverse conversion needs.
Table of Contents
- Why Convert Word to HTML
- Install Word to HTML Converter in Python
- How to Convert Word to HTML Using Python
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Why Convert Word to HTML?
Here are some typical scenarios where converting Word to HTML is beneficial:
- Web publishing: Display Word content in a browser without requiring users to download the document.
- CMS integration: Import Word-based articles into a web-based content system.
- Content preview: Generate HTML previews for Word attachments or document archives.
- Email rendering: Convert DOCX content into HTML-friendly formats for email templates.
Install Word to HTML Converter in Python
Spire.Doc for Python is a professional library designed for Word document processing and conversion. It provides a reliable way to export Word documents to HTML while preserving accurate formatting and layout. 
Benefits of Using Spire.Doc for Word-to-HTML Conversion
- Accurate formatting: Preserves fonts, colors, styles, tables, and images.
- No Office dependency: Does not require Microsoft Word or Office Interop.
- Supports DOCX and DOC: Compatible with both modern and legacy Word formats.
- Customizable output: Fine-tune HTML export settings, including image embedding and CSS styling.
Installation
Install the library from PyPI using the following command:
pip install spire.doc
Need help with the installation? Check this step-by-step guide: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows.
How to Convert Word to HTML Using Python
This section demonstrates how to convert Word documents to HTML using Spire.Doc for Python. First, you'll see a quick example using default settings for fast export. Then, you'll learn how to customize the HTML output with advanced options.
Quick Conversion with Default Settings
The following code snippet shows how to save a Word document to HTML format using the default export settings. It’s suitable for simple use cases where no customization is needed.
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document instance
document = Document()
# Load a doc or docx document
document.LoadFromFile("Statement.docx")
# Save the document to HTML format
document.SaveToFile("WordToHtml.html", FileFormat.Html)
document.Close()
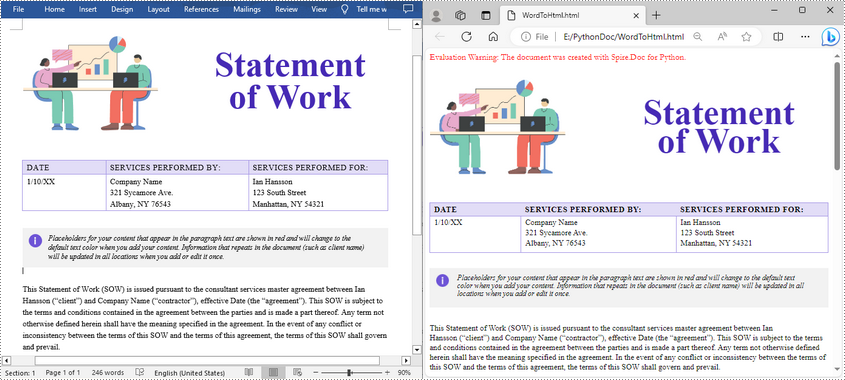
Advanced Conversion Options
You can customize the HTML export to suit your needs by configuring options such as including headers and footers, linking to an external CSS stylesheet, choosing whether to embed images or save them separately, and exporting form fields as plain text. The example below shows how to set these options.
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document instance
document = Document()
# Load a .docx or .doc document
document.LoadFromFile("Statement.docx")
# Control whether to include headers and footers in the exported HTML
document.HtmlExportOptions.HasHeadersFooters = False
# Specify the name of the CSS file to use for styling the exported HTML
document.HtmlExportOptions.CssStyleSheetFileName = "sample.css"
# Set the CSS stylesheet type to external, so the HTML file links to the specified CSS file instead of embedding styles inline
document.HtmlExportOptions.CssStyleSheetType = CssStyleSheetType.External
# Configure image export: do not embed images inside HTML, save them to a separate folder
document.HtmlExportOptions.ImageEmbedded = False
document.HtmlExportOptions.ImagesPath = "Images/"
# Export form fields as plain text instead of interactive form elements
document.HtmlExportOptions.IsTextInputFormFieldAsText = True
# Save the document as an HTML file
document.SaveToFile("ToHtmlExportOption.html", FileFormat.Html)
document.Close()
Conclusion
Spire.Doc for Python delivers high-fidelity Word-to-HTML conversions without requiring Microsoft Word. Whether for quick exports or customized HTML output, it provides a versatile, dependable solution.
Beyond HTML conversion, Spire.Doc supports a wide range of Word automation tasks such as document merging, text replacement, and PDF conversion, empowering developers to build robust document processing pipelines. To explore these capabilities further, check out the full Python Word programming guide and start enhancing your document workflows today.
FAQs
Q1: Can Spire.Doc convert both DOC and DOCX files to HTML?
A1: Yes, it supports exporting both legacy DOC and modern DOCX formats.
Q2: Is Microsoft Word required for conversion?
A2: No, Spire.Doc works independently without needing Microsoft Word or Office Interop.
Q3: Can images be embedded directly in the HTML instead of saved separately?
A3: Yes, you can embed images directly into the HTML output by setting ImageEmbedded to True. This ensures that all images are included within the HTML file itself, without creating separate image files or folders.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
