
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
The Excel spreadsheet is extensively utilized for organizing, analyzing, and presenting data in a tabular format. The capacity to programmatically interact with Excel files holds great value as it facilitates automation and integration of Excel functionality within software applications. Specifically, knowing how to create new Excel documents, retrieve information from existing ones, and update or modify them as needed through code would be very helpful. This article will demonstrate how to create, read, or update Excel documents in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create an Excel Document in Python
- Read Data from a Worksheet in Python
- Update an Excel Document in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Create an Excel Document in Python
Spire.XLS for Python offers a variety of classes and interfaces that you can use to create and edit Excel documents. Here is a list of important classes, properties and methods involved in this article.
| Member | Description |
| Workbook class | Represents an Excel workbook model. |
| Workbook.Worksheets.Add() method | Adds a worksheet to workbook. |
| Workbook.SaveToFile() method | Saves the workbook to an Excel document. |
| Worksheet class | Represents a worksheet in a workbook. |
| Worksheet.Range property | Gets a specific cell or cell range from worksheet. |
| Worksheet.Range.Text property | Gets or sets the text value of a cell. |
| Worksheet.Rows property | Gets a collection of rows in worksheet. |
| CellRange class | Represents a cell or cell range in worksheet. |
The following are the steps to create an Excel document from scratch using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Add a worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.Add() method.
- Write data to specific cells through Worksheet.Range.Text property.
- Save the workbook to an Excel document using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
wb = Workbook()
# Remove default worksheets
wb.Worksheets.Clear()
# Add a worksheet and name it "Employee"
sheet = wb.Worksheets.Add("Employee")
# Merge the cells between A1 and G1
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Merge()
# Write data to A1 and apply formatting to it
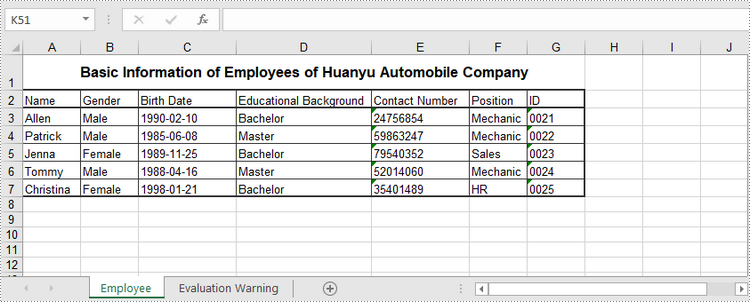
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "Basic Information of Employees of Huanyu Automobile Company"
sheet.Range["A1"].HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1"].VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1"].Style.Font.IsBold = True
sheet.Range["A1"].Style.Font.Size = 13
# Set row height of the first row
sheet.Rows[0].RowHeight = 30
# Write data to specific cells
sheet.Range["A2"].Text = "Name"
sheet.Range["B2"].Text = "Gender"
sheet.Range["C2"].Text = "Birth Date"
sheet.Range["D2"].Text = "Educational Background"
sheet.Range["E2"].Text = "Contact Number"
sheet.Range["F2"].Text = "Position"
sheet.Range["G2"].Text = "ID"
sheet.Range["A3"].Text = "Allen"
sheet.Range["B3"].Text = "Male"
sheet.Range["C3"].Text = "1990-02-10"
sheet.Range["D3"].Text = "Bachelor"
sheet.Range["E3"].Text = "24756854"
sheet.Range["F3"].Text = "Mechanic"
sheet.Range["G3"].Text = "0021"
sheet.Range["A4"].Text = "Patrick"
sheet.Range["B4"].Text = "Male"
sheet.Range["C4"].Text = "1985-06-08"
sheet.Range["D4"].Text = "Master"
sheet.Range["E4"].Text = "59863247"
sheet.Range["F4"].Text = "Mechanic"
sheet.Range["G4"].Text = "0022"
sheet.Range["A5"].Text = "Jenna"
sheet.Range["B5"].Text = "Female"
sheet.Range["C5"].Text = "1989-11-25"
sheet.Range["D5"].Text = "Bachelor"
sheet.Range["E5"].Text = "79540352"
sheet.Range["F5"].Text = "Sales"
sheet.Range["G5"].Text = "0023"
sheet.Range["A6"].Text = "Tommy"
sheet.Range["B6"].Text = "Male"
sheet.Range["C6"].Text = "1988-04-16"
sheet.Range["D6"].Text = "Master"
sheet.Range["E6"].Text = "52014060"
sheet.Range["F6"].Text = "Mechanic"
sheet.Range["G6"].Text = "0024"
sheet.Range["A7"].Text = "Christina"
sheet.Range["B7"].Text = "Female"
sheet.Range["C7"].Text = "1998-01-21"
sheet.Range["D7"].Text = "Bachelor"
sheet.Range["E7"].Text = "35401489"
sheet.Range["F7"].Text = "HR"
sheet.Range["G7"].Text = "0025"
# Set row height of a range
sheet.Range["A2:G7"].RowHeight = 15
# Set column width
sheet.SetColumnWidth(3, 15)
sheet.SetColumnWidth(4, 21)
sheet.SetColumnWidth(5, 15)
# Set border style of a range
sheet.Range["A2:G7"].BorderAround(LineStyleType.Medium)
sheet.Range["A2:G7"].BorderInside(LineStyleType.Thin)
sheet.Range["A2:G2"].BorderAround(LineStyleType.Medium)
sheet.Range["A2:G7"].Borders.KnownColor = ExcelColors.Black
# Save to a .xlsx file
wb.SaveToFile("output/NewSpreadsheet.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
Read Data from a Worksheet in Python
The Worksheet.Range.Value property returns number value or text value of a cell as a string. To get data of a whole worksheet or a cell range, loop through the cells within it. The following are the steps to get data of a worksheet using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get the cell range contain data though Worksheet.AllocatedRange property.
- Iterate through the rows and columns to get cells within the range, and return the value of each cell through CellRange.Value property.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
wb = Workbook()
# Load an existing Excel file
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\NewSpreadsheet.xlsx");
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = wb.Worksheets[0]
# Get the cell range containing data
locatedRange = sheet.AllocatedRange
# Iterate through the rows
for i in range(len(sheet.Rows)):
# Iterate through the columns
for j in range(len(locatedRange.Rows[i].Columns)):
# Get data of a specific cell
print(locatedRange[i + 1, j + 1].Value + " ", end='')
print("")

Update an Excel Document in Python
To change the value of a certain cell, just re-assign a value to it through Worksheet.Range.Value property. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Change the value of a particular cell though Worksheet.Range.Value property.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
wb = Workbook();
# Load an existing Excel file
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\NewSpreadsheet.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = wb.Worksheets[0]
# Change the value of a specific cell
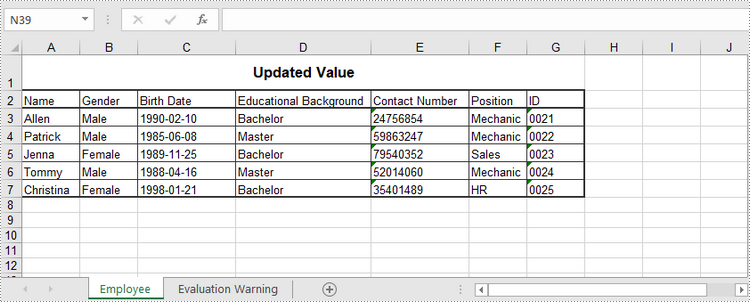
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Updated Value"
# Save to file
wb.SaveToFile("output/Updated.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
The background of a PowerPoint presentation sets the tone and mood of the presentation and can greatly enhance the aesthetic and impact of the slides. There are five types of backgrounds available in PowerPoint presentations, solid color backgrounds, gradient backgrounds, picture backgrounds, texture backgrounds, and patterned backgrounds. They each apply to different usage scenarios. For example, a professional business presentation may benefit from a clean and simple solid color background, while a creative presentation may use inspiring and interesting picture backgrounds to capture the audience's attention. This article is going to show how to set backgrounds for PowerPoint presentations through Java programs using Spire.Presentation for Java.
- Set a Solid Color Background for a PowerPoint Presentation
- Set a Gradient Background for a PowerPoint Presentation
- Set a Picture Background for a PowerPoint Presentation
- Set a Texture Background for a PowerPoint Presentation
- Set a Pattern Background for a PowerPoint Presentation
Install Spire.Presentation for Java
First of all, you're required to add the Spire.Presentation.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.presentation</artifactId>
<version>11.1.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Set a Solid Color Background for a PowerPoint Presentation
Before customizing the background, it is necessary to use the SlideBackground.setType(BackgroundType.CUSTOM) method to allow the customization of the background. Then, the background type can be set to solid color background using the SlideBackground.getFill().setFillType(FillFormatType.SOLID) method, and the color can be set using the FillFormat.getSolidColor().setColor() method.
The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.loadFromFile() method.
- Get the first slide using Presentation.getSlides().get() method.
- Get the background of the slide using ISlide.getSlideBackground() method.
- Set the background type to custom background to enable the customization of the background using SlideBackground.setType(BackgroundType.CUSTOM) method.
- Set the fill type of the background to solid color using SlideBackground.getFill().setFillType(FillFormatType.SOLID) method.
- Customize the background color using FillFormat.getSolidColor().setColor() method.
- Save the presentation using Presentation.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.presentation.FileFormat;
import com.spire.presentation.ISlide;
import com.spire.presentation.Presentation;
import com.spire.presentation.SlideBackground;
import com.spire.presentation.drawing.BackgroundType;
import com.spire.presentation.drawing.FillFormat;
import com.spire.presentation.drawing.FillFormatType;
import org.w3c.dom.css.RGBColor;
import java.awt.*;
public class SolidColor {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//Create an object of Presentation class
Presentation ppt = new Presentation();
//Load a PowerPoint presentation
ppt.loadFromFile("Sample.pptx");
//Get the first slide
ISlide slide = ppt.getSlides().get(0);
//Get the background
SlideBackground background = slide.getSlideBackground();
//Set the background type to custom
background.setType(BackgroundType.CUSTOM);
//Set the background fill type to solid color
background.getFill().setFillType(FillFormatType.SOLID);
//Set the background color
FillFormat fillFormat = background.getFill();
fillFormat.getSolidColor().setColor(new Color(199, 213, 237));
//Save the presentation
ppt.saveToFile("SolidColorBackground.pptx", FileFormat.AUTO);
}
}
Set a Gradient Background for a PowerPoint Presentation
Gradient background can be set by setting the background type to Gradient Background and then setting the gradient type, color, and angle. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.loadFromFile() method.
- Get the first slide using Presentation.getSlides().get() method.
- Get the background of the slide using ISlide.getSlideBackground() method.
- Set the background type to custom background to enable the customization of the background using SlideBackground.setType(BackgroundType.CUSTOM) method.
- Set the fill type of the background to gradient using SlideBackground.getFill().setFillType(FillFormatType.GRADIENT) method.
- Set the gradient type to linear gradient using GradientFillFormat.setGradientShape(GradientShapeType.LINEAR) method.
- Add the gradient stops and set the gradient colors using GradientFillFormat.getGradientStops().append() method.
- Set the angle of the linear gradient using GradientFillFormat.getLinearGradientFill().setAngle() method.
- Save the presentation using Presentation.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.presentation.FileFormat;
import com.spire.presentation.ISlide;
import com.spire.presentation.Presentation;
import com.spire.presentation.SlideBackground;
import com.spire.presentation.drawing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class Gradient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//Create an object of Presentation class
Presentation ppt = new Presentation();
//Load a PowerPoint presentation
ppt.loadFromFile("Sample.pptx");
//Get the first slide
ISlide slide = ppt.getSlides().get(0);
//Get the background
SlideBackground background = slide.getSlideBackground();
//Set the background type to custom
background.setType(BackgroundType.CUSTOM);
//Set the background fill type to gradient color
background.getFill().setFillType(FillFormatType.GRADIENT);
//Set the gradient type to linear
GradientFillFormat gradient = background.getFill().getGradient();
gradient.setGradientShape(GradientShapeType.LINEAR);
//Add gradient stops and set the colors
gradient.getGradientStops().append(0f, new Color(230, 255, 255));
gradient.getGradientStops().append(0.5f, new Color(255, 255, 255));
gradient.getGradientStops().append(1f, new Color(199, 213, 237));
//Set the angle of the linear gradient
gradient.getLinearGradientFill().setAngle(90);
//Save the presentation
ppt.saveToFile("GradientBackground.pptx", FileFormat.AUTO);
}
}
Set a Picture Background for a PowerPoint Presentation
To set the picture background, set the background type to picture, set the picture fill type to stretch fill, and then set the background image. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.loadFromFile() method.
- Load a picture using Presentation.getImages().append() method.
- Get the first slide using Presentation.getSlides().get() method.
- Get the background of the slide using ISlide.getSlideBackground() method.
- Set the background type to custom background to enable the customization of the background using SlideBackground.setType(BackgroundType.CUSTOM) method.
- Set the fill type of the background to picture using SlideBackground.getFill().setFillType(FillFormatType.PICTURE) method.
- Set the picture fill type to stretch fill using PictureFillFormat.setFillType(PictureFillType.STRETCH) method.
- Set the transparency of the background using PictureFillFormat.getPicture().setTransparency() method.
- Set the background image using PictureFillFormat.getPicture().setEmbedImage() method.
- Save the presentation using Presentation.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.presentation.FileFormat;
import com.spire.presentation.ISlide;
import com.spire.presentation.Presentation;
import com.spire.presentation.SlideBackground;
import com.spire.presentation.drawing.*;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.*;
import java.io.File;
public class Picture {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//Create an object of Presentation class
Presentation ppt = new Presentation();
//Load a PowerPoint presentation
ppt.loadFromFile("Sample.pptx");
//Load a picture
IImageData image = ppt.getImages().append(ImageIO.read(new File("background.jpg")));
//Get the first slide
ISlide slide = ppt.getSlides().get(0);
//Get the background
SlideBackground background = slide.getSlideBackground();
//Set the background type to custom
background.setType(BackgroundType.CUSTOM);
//Set the background fill type to picture
background.getFill().setFillType(FillFormatType.PICTURE);
//Set the picture fill type to stretch
PictureFillFormat pictureFillFormat = background.getFill().getPictureFill();
pictureFillFormat.setFillType(PictureFillType.STRETCH);
//Set the transparency of the background
pictureFillFormat.getPicture().setTransparency(50);
//Set the background picture
pictureFillFormat.getPicture().setEmbedImage(image);
//Save the presentation
ppt.saveToFile("PictureBackground.pptx", FileFormat.AUTO);
}
}
Set a Texture Background for a PowerPoint Presentation
Setting a texture background is similar to setting a picture background. The difference is that the image fill type needs to be changed to a tiled fill and the texture alignment needs to be set. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.loadFromFile() method.
- Load the texture using Presentation.getImages().append() method.
- Get the first slide using Presentation.getSlides().get() method.
- Get the background of the slide using ISlide.getSlideBackground() method.
- Set the background type to custom background to enable the customization of the background using SlideBackground.setType(BackgroundType.CUSTOM) method.
- Set the fill type of the background to picture using SlideBackground.getFill().setFillType(FillFormatType.PICTURE) method.
- Set the picture fill type to tile fill using PictureFillFormat.setFillType(PictureFillType.TILE) method.
- Set the transparency of the background using PictureFillFormat.getPicture().setTransparency() method.
- Set the background texture using PictureFillFormat.getPicture().setEmbedImage() method.
- Save the presentation using Presentation.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.presentation.*;
import com.spire.presentation.drawing.*;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.io.File;
public class Texture {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//Create an object of Presentation class
Presentation ppt = new Presentation();
//Load a PowerPoint presentation
ppt.loadFromFile("Sample.pptx");
//Load the texture
IImageData image = ppt.getImages().append(ImageIO.read(new File("texture.png")));
//Get the first slide
ISlide slide = ppt.getSlides().get(0);
//Get the background
SlideBackground background = slide.getSlideBackground();
//Set the background type to custom
background.setType(BackgroundType.CUSTOM);
//Set the background fill type to picture
background.getFill().setFillType(FillFormatType.PICTURE);
//Set the picture fill type to tile
PictureFillFormat pictureFillFormat = background.getFill().getPictureFill();
pictureFillFormat.setFillType(PictureFillType.TILE);
//Set the texture alignment
pictureFillFormat.setAlignment(RectangleAlignment.TOP_LEFT);
//Set the transparency of the background
pictureFillFormat.getPicture().setTransparency(50);
//Set the background texture
pictureFillFormat.getPicture().setEmbedImage(image);
//Save the presentation
ppt.saveToFile("TextureBackground.pptx", FileFormat.AUTO);
}
}
Set a Pattern Background for a PowerPoint Presentation
In adding a pattern background, it is necessary to set the type of pattern as well as the foreground and background colors of the pattern. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.loadFromFile() method.
- Get the first slide using Presentation.getSlides().get() method.
- Get the background of the slide using ISlide.getSlideBackground() method.
- Set the background type to custom background to enable the customization of the background using SlideBackground.setType(BackgroundType.CUSTOM) method.
- Set the fill type of the background to pattern using SlideBackground.getFill().setFillType(FillFormatType.PATTERN) method.
- Set the pattern type using PatternFillFormat.setPatternType() method.
- Set the foreground color of the pattern using PatternFillFormat.getForegroundColor().setColor() method.
- Set the background color of the pattern using PatternFillFormat.getBackgroundColor().setColor() method.
- Save the presentation using Presentation.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.presentation.*;
import com.spire.presentation.drawing.*;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.*;
import java.io.File;
public class Pattern {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//Create an object of Presentation class
Presentation ppt = new Presentation();
//Load a PowerPoint presentation
ppt.loadFromFile("Sample.pptx");
//Get the first slide
ISlide slide = ppt.getSlides().get(0);
//Get the background
SlideBackground background = slide.getSlideBackground();
//Set the background type to custom
background.setType(BackgroundType.CUSTOM);
//Set the background fill type to pattern
background.getFill().setFillType(FillFormatType.PATTERN);
//Set the pattern type
PatternFillFormat patternFillFormat = background.getFill().getPattern();
patternFillFormat.setPatternType(PatternFillType.DOTTED_GRID);
//Set the foreground color of the pattern
patternFillFormat.getForegroundColor().setColor(new Color(230, 255, 255));
//Set the background color of the pattern
patternFillFormat.getBackgroundColor().setColor(new Color(199, 213, 237));
//Save the presentation
ppt.saveToFile("PatternBackground.pptx", FileFormat.AUTO);
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Adding footers to a PDF document is a common practice that enhances the professionalism and readability of the file. Footers provide valuable information such as page numbers, dates, document titles, or copyright notices at the bottom of each page. By including footers, users can easily navigate through lengthy documents, identify specific sections, and maintain consistent branding. In this article, you will learn how to add footers to an existing PDF document in C++ using Spire.PDF for C++.
Install Spire.PDF for C++
There are two ways to integrate Spire.PDF for C++ into your application. One way is to install it through NuGet, and the other way is to download the package from our website and copy the libraries into your program. Installation via NuGet is simpler and more recommended. You can find more details by visiting the following link.
Integrate Spire.PDF for C++ in a C++ Application
Background Knowledge
When using Spire.PDF for C++ to process an existing PDF document, the origin of the coordinate system is located at the top left corner of the page, with the x-axis extending to the right and the y-axis extending downward. Adding a footer to a page means adding content, such as text, images, shapes and automatic fields, to a specified location in the bottom blank area of the page.
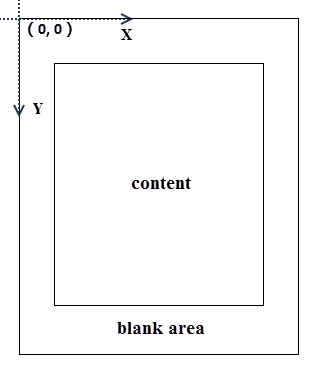
If the blank area is not large enough to accommodate the content you want to add, you can consider increasing the PDF page margins.
Add Footers to an Existing PDF Document in C++
Spire.PDF for C++ offers the PdfCanvas->DrawString() method, PdfCanvas->DrawImage() method, PdfCanvas->DrawLine() method and its similar methods, allowing users to draw text, images and shapes on a PDF page at the specified location. To add dynamic data to the footer, such as page numbers, sections, dates, you need to use the automatic fields. Spire.PDF for C++ provides the PdfPageNumberField class, PdfPageCountField calss, PdfSectionNumberField class etc. to achieve the addition of dynamic information.
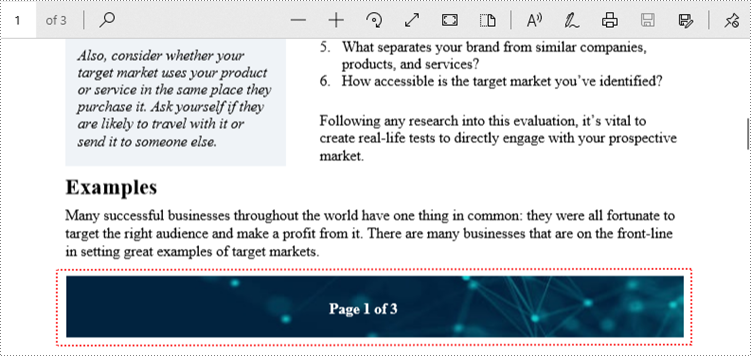
The following are the steps to add a footer consisting of an image and page number to a PDF document using Spire.PDF for C++.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument->LoadFromFile() method.
- Load an image using PdfImage::FromFile() method.
- Draw the image on the bottom blank area of a page using PdfPageBase->GetCanvas()->DrawImage() method.
- Create a PdfPageNumberField object, a PdfPageCountField object, and combine them in a PdfCompositeField object to return the string "Page X of Y".
- Draw page number on the bottom blank area of a page using PdfCompositeField->Draw() method.
- Save the document to another PDF file using PdfDocument->SaveToFile() method.
- C++
#include "Spire.Pdf.o.h"
using namespace Spire::Pdf;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//Create a PdfDocument object
intrusive_ptr<PdfDocument> doc = new PdfDocument();
//Load a PDF file
doc->LoadFromFile(L"C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\TargetMarket.pdf");
//Load an image
intrusive_ptr<PdfImage> footerImage = PdfImage::FromFile(L"C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\bg.jpg");
//Create a true type font
intrusive_ptr<PdfTrueTypeFont> font = new PdfTrueTypeFont(L"Times New Roman", 12.f, PdfFontStyle::Bold, true);
//Create a brush
intrusive_ptr<PdfBrush> brush = PdfBrushes::GetWhite();
//Create a page number field
intrusive_ptr<PdfPageNumberField> pageNumberField = new PdfPageNumberField();
//Create a page count field
intrusive_ptr<PdfPageCountField> pageCountField = new PdfPageCountField();
vector< intrusive_ptr<PdfAutomaticField>> list;
list.push_back(pageNumberField);
list.push_back(pageCountField);
//Create a composite field to combine page count field and page number field in a single string
intrusive_ptr<PdfCompositeField> compositeField = new PdfCompositeField(font, brush, L"Page {0} of {1}", list);
//Get the text size
intrusive_ptr<SizeF> fontSize = font->MeasureString(compositeField->GetText());
//Get the page size
intrusive_ptr<SizeF> pageSize = doc->GetPages()->GetItem(0)->GetSize();
//Set the position of the composite field
compositeField->SetLocation(new PointF((pageSize->GetWidth() - fontSize->GetWidth()) / 2, pageSize->GetHeight() - 45));
//Loop through the pages in the document
for (int i = 0; i < doc->GetPages()->GetCount(); i++)
{
//Get a specific page
intrusive_ptr<PdfPageBase> page = doc->GetPages()->GetItem(i);
//Draw the image on the bottom blank area
page->GetCanvas()->DrawImage(footerImage, 55, pageSize->GetHeight() - 65, pageSize->GetWidth() - 110, 50);
//Draw the composite field on the bottom blank area
compositeField->Draw(page->GetCanvas(),0,0);
}
//Save to file
doc->SaveToFile(L"AddFooter.pdf");
doc->Dispose();
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
