
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Spire.XLS for C++ is an Excel library built for developers to manipulate Excel documents (XLS, XLSX, XLSB and XLSM) in any type of C++ applications. This article demonstrates how to integrate Spire.XLS for C++ into your C++ application in two different ways.
Install Spire.XLS for C++ via NuGet
Step 1
Create a C++ project in Visual Studio 2022.
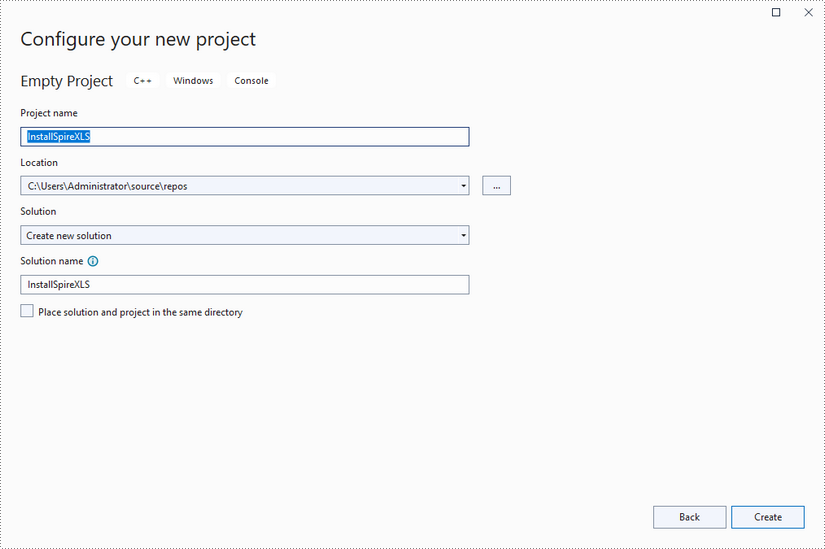
Step 2
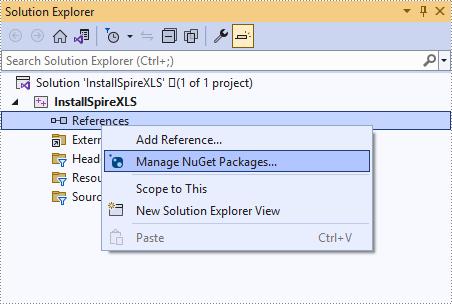
Right-click 'References' in the Solution Explorer and choose 'Manage NuGet Package' in the popup menu.
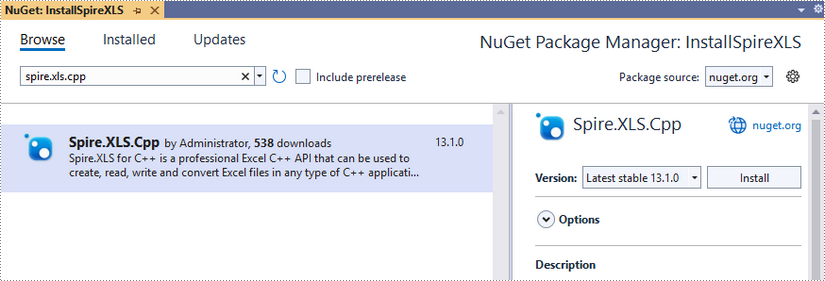
Click 'Browse', search for 'spire.xls.cpp', and install it in your project.
Step 3
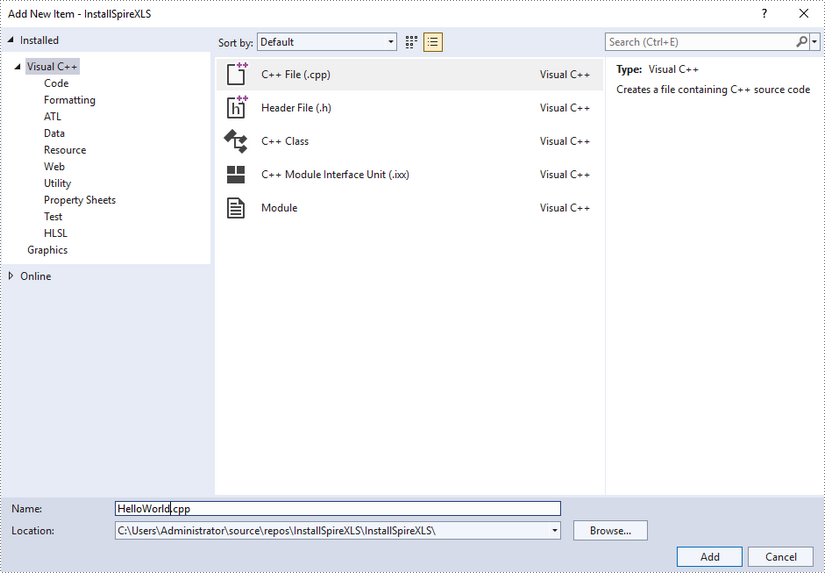
Right-click 'Source Files' in the Solution Explorer, choose 'Add' and then 'New Item'.
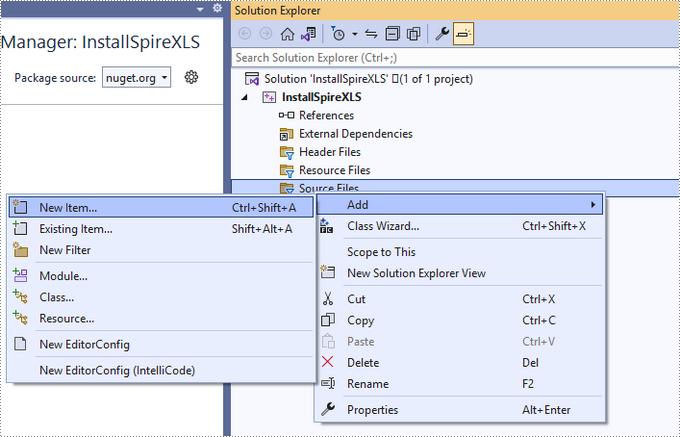
Create a .cpp file.
Step 4
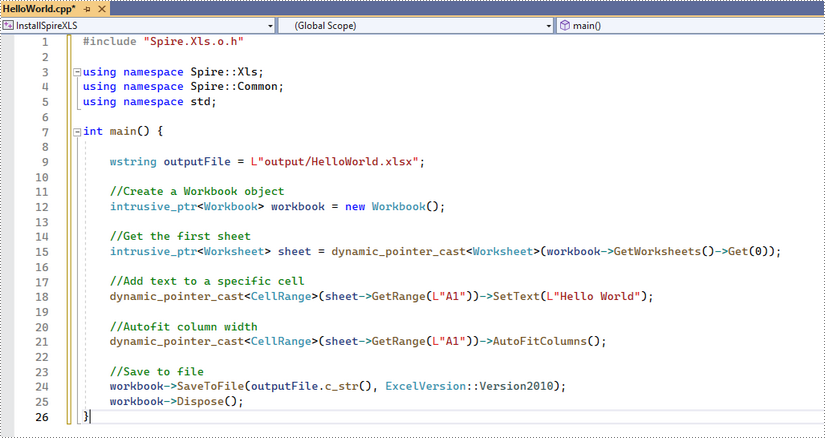
Click the .cpp file you just created to write code. Before starting, you need to include the header file “Spire.Xls.o.h” by adding the following line of code to your program.
- C++
#include "Spire.Xls.o.h"
The code example below shows you how to create a simple Excel file using Spire.XLS for C++.
Install Spire.XLS for C++ by Manually Importing Libraries
Step 1
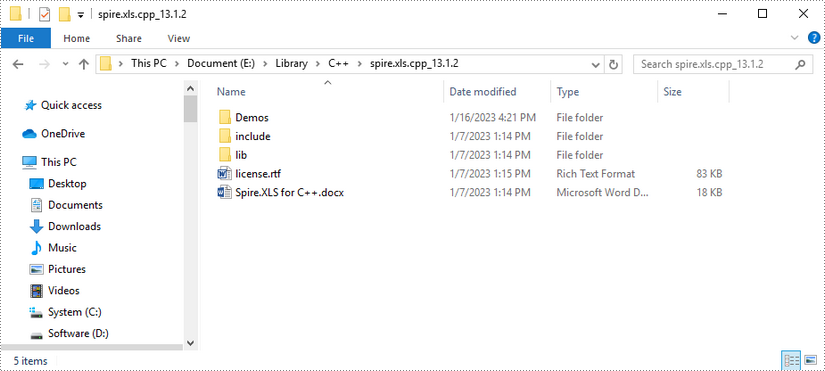
Download Spire.XLS for C++ package and unzip it somewhere on your disc to get the following files.
Step 2
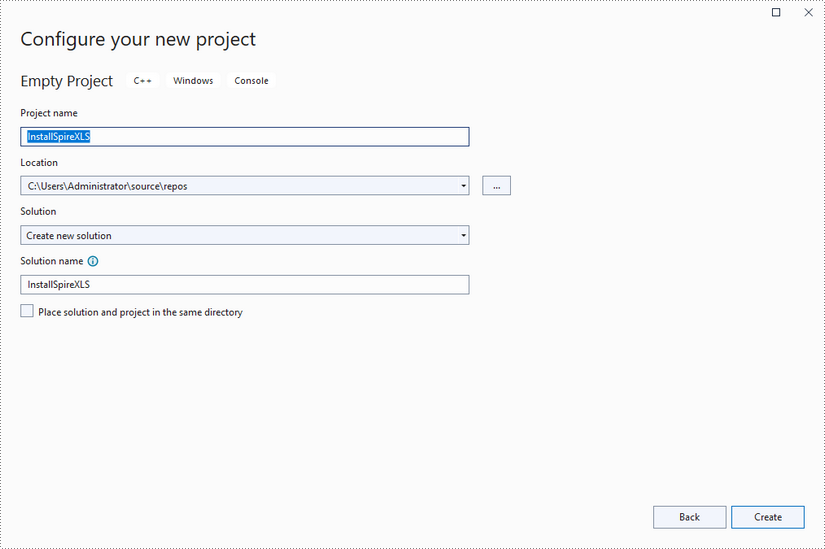
Create a C++ project in Visual Studio 2022.
Step 3
Copy the 'include' folder and the 'lib' folder from the product package to your project, and save them under the same folder where the .sln file exists.
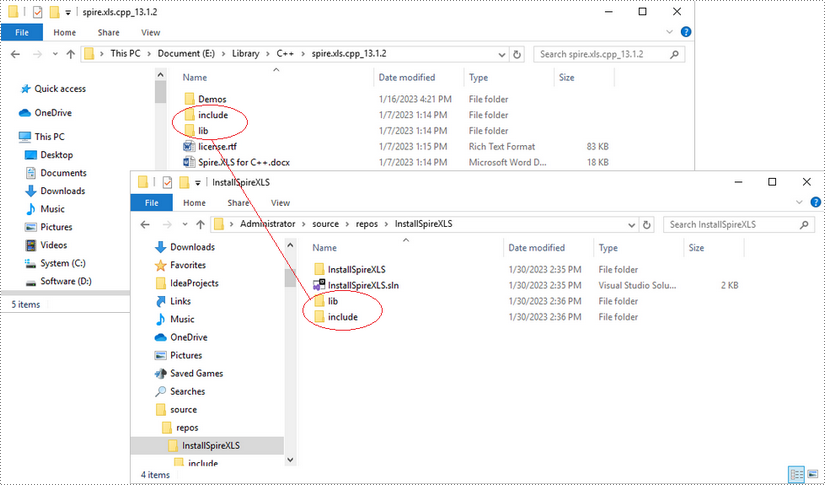
Step 4
Right-click the project name and select 'Properties'.
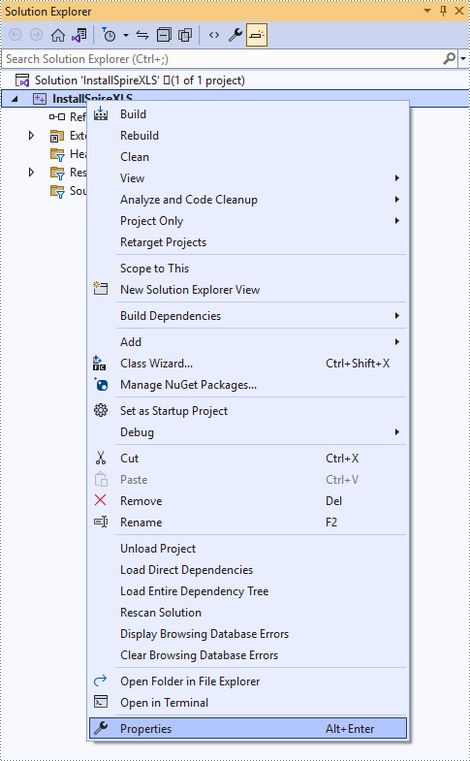
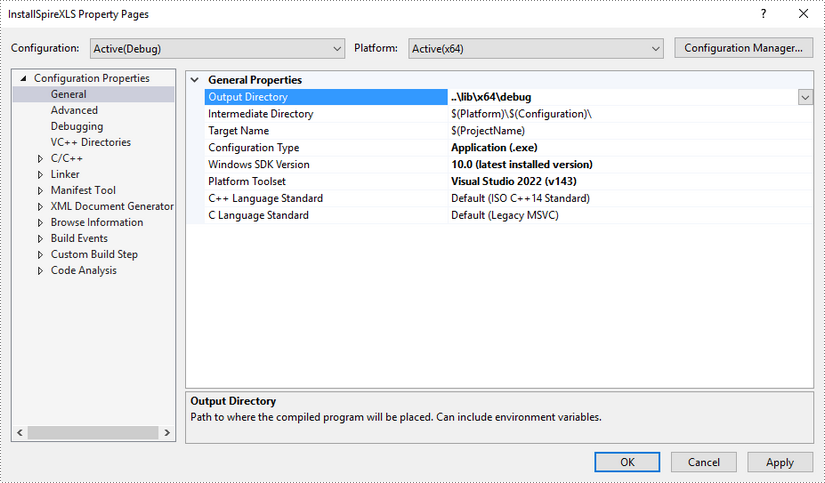
Configure output directory. Depending on the build mode (Debug or Release) you choose, you can set the output directory to '..\lib\x64\debug' or '..\lib\x64\release'.
Click 'C/C++', select 'Command Line', and then input '/bigobj' in the 'Additional Options' field.
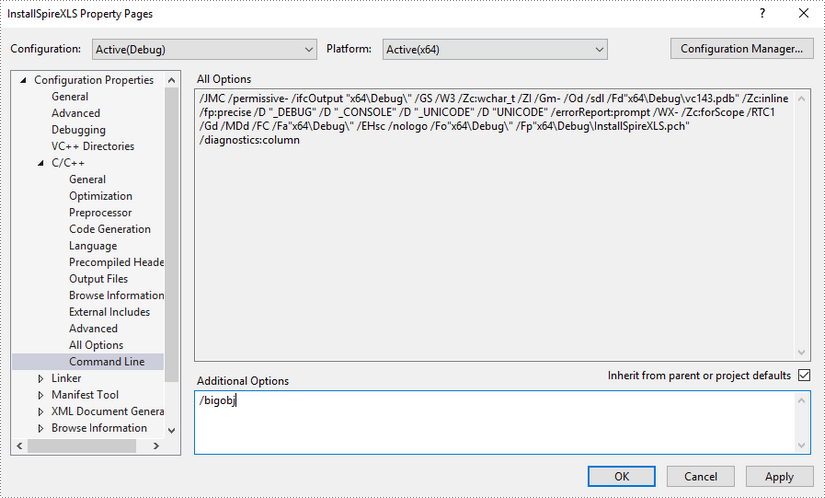
Step 5
Right-click 'Source Files' in the Solution Explorer, choose 'Add' and then 'New Item'.
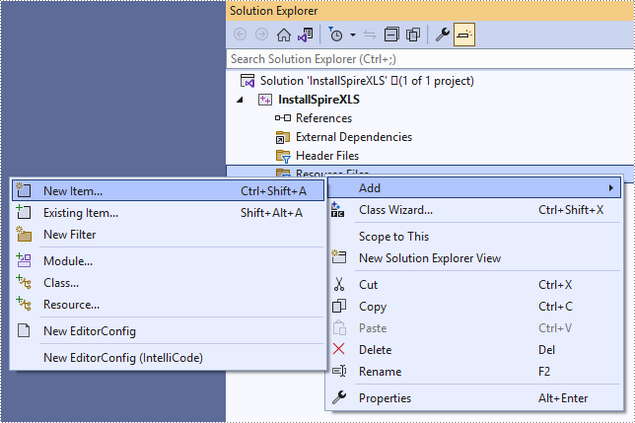
Create a .cpp file.
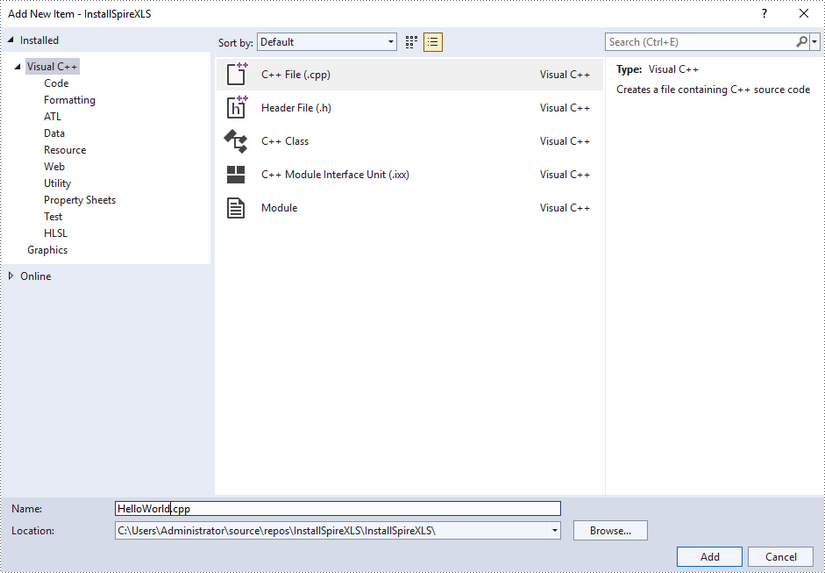
Step 6
Click the .cpp file you just created to write code. Before starting, you need to include the following two lines of code to your program.
- C++
#include "../include/Spire.Xls.o.h" #pragma comment(lib,"../lib/x64/debug/Spire.Xls.Cpp.lib")
The code example below shows you how to create a simple Excel file using Spire.XLS for C++.
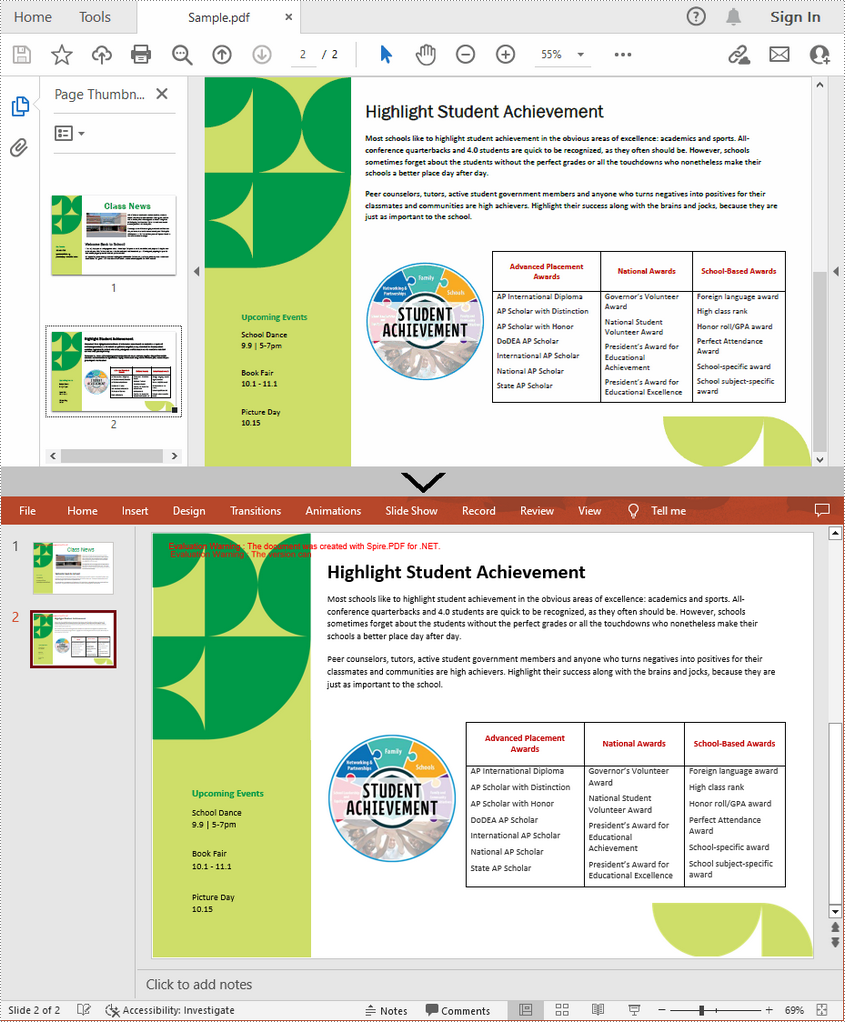
PDF files are great for presenting on different types of devices and sharing across platforms, but it has to admit that editing PDF is a bit challenging. When you receive a PDF file and need to prepare a presentation based on the content inside, it is recommended to convert the PDF file to a PowerPoint document to have a better presentation effect and also to ensure the content can be further edited. This article will demonstrate how to programmatically convert PDF to PowerPoint presentation using Spire.PDF for .NET.
Install Spire.PDF for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.PDF for.NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLLs files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.PDF
Convert PDF to PowerPoint Presentation in C# and VB.NET
From Version 8.11.10, Spire.PDF for .NET supports converting PDF to PPTX using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method. With this method, each page of your PDF file will be converted to a single slide in PowerPoint. Below are the steps to convert a PDF file to an editable PowerPoint document.
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a sample PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Save the document as a PowerPoint document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile(string filename, FileFormat.PPTX) method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Pdf;
namespace PDFtoPowerPoint
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a PdfDocument instance
PdfDocument pdf = new PdfDocument();
//Load a sample PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile(@"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Sample.pdf");
//Convert the PDF to PPTX document
pdf.SaveToFile("ConvertPDFtoPowerPoint.pptx", FileFormat.PPTX);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
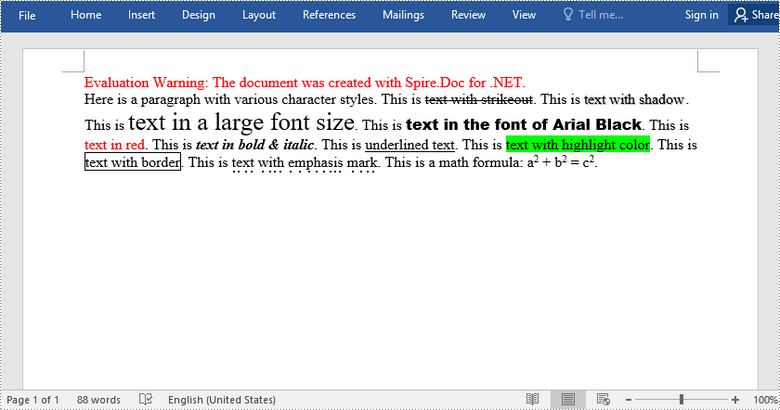
Character formatting is used to change the appearance of individual words or phrases. Formatted text can direct the reader's attention to select sections of a document and highlight key information. There are quite a lot of forms of characters formatting that you can use in Word. In this article, you will learn how to apply various types of formatting to characters in Word in C# and VB.NET using Spire.Doc for .NET.
- Font Name
- Font Size
- Font Color
- Highlight Color
- Bold
- Italic
- Underline
- Strikethrough
- Border
- Shadow Effect
- Emphasis Mark
- Subscript and Superscript
Install Spire.Doc for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.Doc for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.Doc
Apply Formatting to Characters in Word in C# and VB.NET
In order to apply formatting to a piece of text, you need to get the text in a TextRange and then format the characters within the TextRange through the CharacterFormat property. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section to the document using Document.AddSection() method.
- Add a paragraph to the section using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Append text to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendText() method and return a TextRange object.
- Apply formatting such as font name, font size, border and highlight color to the characters within the text range through TextRange.CharacterFormat property.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
using Spire.Doc.Fields;
using System.Drawing;
namespace ApplyFormattingToCharacters
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Document object
Document document = new Document();
//Add a section
Section sec = document.AddSection();
//Add a paragraph
Paragraph paragraph = sec.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("Here is a paragraph with various character styles. This is ");
//Append text to the paragraph and return a TextRange object
TextRange tr = paragraph.AppendText("text with strikeout");
//Set the character format to strikeout via TextRange object
tr.CharacterFormat.IsStrikeout = true;
//Apply shadow effect to text
paragraph.AppendText(". This is ");
tr = paragraph.AppendText("text with shadow");
tr.CharacterFormat.IsShadow = true;
//Set font size
paragraph.AppendText(". This is ");
tr = paragraph.AppendText("text in a large font size");
tr.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 20;
//Set font name
paragraph.AppendText(". This is ");
tr = paragraph.AppendText("text in the font of Arial Black");
tr.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial Black";
//Set font color
paragraph.AppendText(". This is ");
tr = paragraph.AppendText("text in red");
tr.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.Red;
//Apply bold & italic to text
paragraph.AppendText(". This is ");
tr = paragraph.AppendText("text in bold & italic");
tr.CharacterFormat.Bold = true;
tr.CharacterFormat.Italic = true;
//Apply underline to text
paragraph.AppendText(". This is ");
tr = paragraph.AppendText("underlined text");
tr.CharacterFormat.UnderlineStyle = UnderlineStyle.Single;
//Apply background color to text
paragraph.AppendText(". This is ");
tr = paragraph.AppendText("text with highlight color");
tr.CharacterFormat.HighlightColor = Color.Green;
//Apply border to text
paragraph.AppendText(". This is ");
tr = paragraph.AppendText("text with border");
tr.CharacterFormat.Border.BorderType = Spire.Doc.Documents.BorderStyle.Single;
tr.CharacterFormat.Border.Color = Color.Black;
//Apply emphasis mark to text
paragraph.AppendText(". This is ");
tr = paragraph.AppendText("text with emphasis mark");
tr.CharacterFormat.EmphasisMark = Emphasis.DotBelow;
//Apply superscript to text
paragraph.AppendText(". This is a math formula: a");
tr = paragraph.AppendText("2");
tr.CharacterFormat.SubSuperScript = SubSuperScript.SuperScript;
paragraph.AppendText(" + b");
tr = paragraph.AppendText("2");
tr.CharacterFormat.SubSuperScript = SubSuperScript.SuperScript;
paragraph.AppendText(" = c");
tr = paragraph.AppendText("2");
tr.CharacterFormat.SubSuperScript = SubSuperScript.SuperScript;
paragraph.AppendText(".");
//Save to file
document.SaveToFile("SetCharacterFormat.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
