
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Excel spreadsheets are scalable grid-based files that are used to organize data and perform calculations. People all across the world use spreadsheets to create tables for personal and business usage. To write a large amount of data into an Excel spreadsheet, it is recommended to use the programming method, which saves time and is less error-prone. In this article, you will learn how to write data into Excel in C# and VB.NET using Spire.XLS for .NET.
- Write Text or Number Values to Specific Cells
- Write Arrays to a Worksheet
- Write a DataTable to a Worksheet
Install Spire.XLS for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.XLS for .NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.XLS
Write Text or Number Values to Specific Cells
A certain cell in a worksheet can be accessed by Worksheet.Range[int row, int column] property. Then, you can add a text value or a number value to the cell through the XlsRange.Value or XlsRange.Value2 property. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get the first worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Get a specific cell through Workhseet.Range[] property.
- Add a text value or a number value to the cell through XlsRange.Value or XlsRange.Value2 property.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
namespace WriteDataToCells
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Write data to specific cells
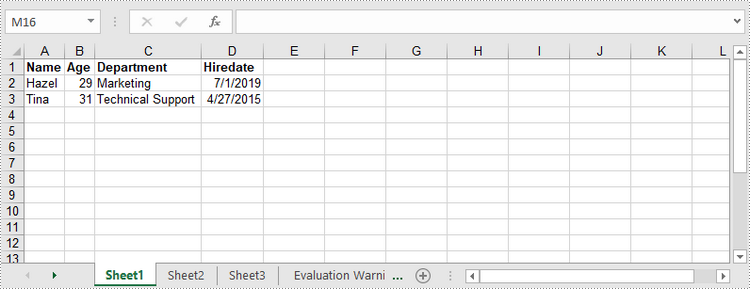
worksheet.Range[1, 1].Value = "Name";
worksheet.Range[1, 2].Value = "Age";
worksheet.Range[1, 3].Value = "Department";
worksheet.Range[1, 4].Value = "Hiredate";
worksheet.Range[1, 2].Value = "Hazel";
worksheet.Range[2, 2].Value2 = 29;
worksheet.Range[2, 3].Value = "Marketing";
worksheet.Range[2, 4].Value = "2019-07-01";
worksheet.Range[3, 1].Value = "Tina";
worksheet.Range[3, 2].Value2 = 31;
worksheet.Range[3, 3].Value = "Technical Support";
worksheet.Range[3, 4].Value = "2015-04-27";
//Auto fit column widths
worksheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns();
//Apply a style to the first row
CellStyle style = workbook.Styles.Add("newStyle");
style.Font.IsBold = true;
worksheet.Range[1, 1, 1, 4].Style = style;
//Save to an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("WriteToCells.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
}
Write Arrays to a Worksheet
Spire.XLS for .NET provides the Worksheet.InsertArrary() method, allowing programmers to write one-dimensional arrays or two-dimensional arrays into the specified cell range of a worksheet. The steps to write arrays to a worksheet are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get the first worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Create a one-dimensional array and a two-dimensional array.
- Insert the arrays to worksheet using Worksheet.InsertArray() method.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Xls;
namespace WriteArraysToWorksheet
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Create a one-dimensional array
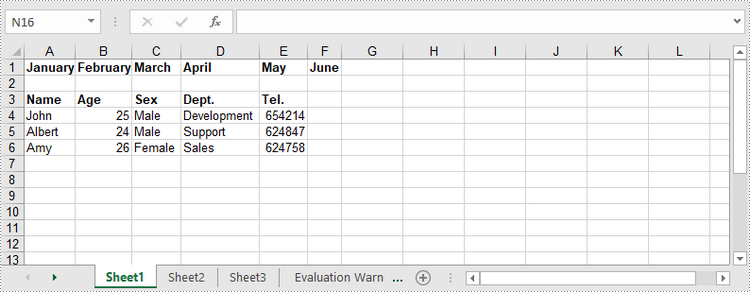
string[] oneDimensionalArray = new string[] { "January", "February", "March", "April", "May", "June" };
//Write the array to the first row of the worksheet
worksheet.InsertArray(oneDimensionalArray, 1, 1, false);
//Create a two-dimensional array
string[,] twoDimensionalArray = new string[,]{
{"Name", "Age", "Sex", "Dept.", "Tel."},
{"John", "25", "Male", "Development","654214"},
{"Albert", "24", "Male", "Support","624847"},
{"Amy", "26", "Female", "Sales","624758"}
};
//Write the array to the worksheet starting from the cell A3
worksheet.InsertArray(twoDimensionalArray, 3, 1);
//Auto fit column width in the located range
worksheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns();
//Apply a style to the first and the third row
CellStyle style = workbook.Styles.Add("newStyle");
style.Font.IsBold = true;
worksheet.Range[1, 1, 1, 6].Style = style;
worksheet.Range[3, 1, 3, 6].Style = style;
//Save to an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("InsertArrays.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
}
Write a DataTable to a Worksheet
To import data from a DataTable to a worksheet, use the Worksheet.InsertDataTable() method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get the first worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Create a DataTable with random data.
- Write the DataTable to the worksheet at the specified location using Worksheet.InsertDataTable() method.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using System;
using System.Data;
using Spire.Xls;
namespace WriteDataTableToWorksheet
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Create a DataTable object
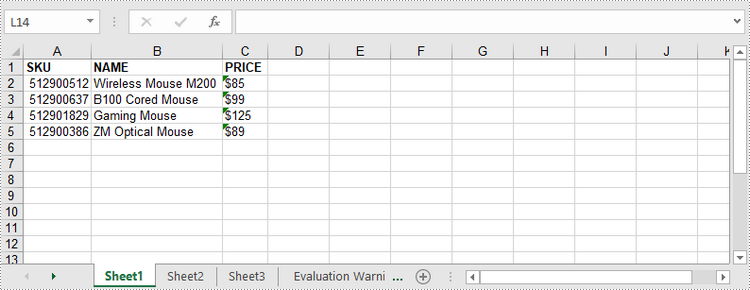
DataTable dataTable = new DataTable();
dataTable.Columns.Add("SKU", typeof(Int32));
dataTable.Columns.Add("NAME", typeof(String));
dataTable.Columns.Add("PRICE", typeof(String));
//Create rows and add data
DataRow dr = dataTable.NewRow();
dr[0] = 512900512;
dr[1] = "Wireless Mouse M200";
dr[2] = "$85";
dataTable.Rows.Add(dr);
dr = dataTable.NewRow();
dr[0] = 512900637;
dr[1] = "B100 Cored Mouse";
dr[2] = "$99";
dataTable.Rows.Add(dr);
dr = dataTable.NewRow();
dr[0] = 512901829;
dr[1] = "Gaming Mouse";
dr[2] = "$125";
dataTable.Rows.Add(dr);
dr = dataTable.NewRow();
dr[0] = 512900386;
dr[1] = "ZM Optical Mouse";
dr[2] = "$89";
dataTable.Rows.Add(dr);
//Write datatable to the worksheet
worksheet.InsertDataTable(dataTable, true, 1, 1, true);
//Auto fit column width in the located range
worksheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns();
//Apply a style to the first and the third row
CellStyle style = workbook.Styles.Add("newStyle");
style.Font.IsBold = true;
worksheet.Range[1, 1, 1, 3].Style = style;
//Save to an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("InsertDataTable.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.

Looking to automate Excel data entry in Java? Manually inputting data into Excel worksheets is time-consuming and error-prone, especially when dealing with large datasets. The good news is that with the right Java Excel library, you can streamline this process. This comprehensive guide explores three efficient methods to write data to Excel in Java using the powerful Spire.XLS for Java library, covering basic cell-by-cell entries, bulk array inserts, and DataTable exports.
- Prerequisites: Setup & Installation
- 3 Ways to Write Data to Excel using Java
- Performance Tips for Large Datasets
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Final Thoughts
Prerequisites: Setup & Installation
Before you start, you’ll need to add Spire.XLS for Java to your project. Here’s how to do it quickly:
Option 1: Download the JAR File
- Visit the Spire.XLS for Java download page.
- Download the latest JAR file.
- Add the JAR to your project’s build path.
Option 2: Use Maven
If you’re using Maven, add the following repository and dependency to your pom.xml file. This automatically downloads and integrates the library:
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.7.7</version>
</dependency>
3 Ways to Write Data to Excel using Java
Spire.XLS for Java offers flexible methods to write data, tailored to different scenarios. Let’s explore each with complete code samples, explanations, and use cases.
1. Write Text or Numbers to Excel Cells
Need to populate individual cells with text or numbers? Spire.XLS lets you directly target a specific cell using row/column indices (e.g., (2,1) for row 2, column 1) or Excel-style references (e.g., "A1", "B3"):
How It Works:
- Use the Worksheet.get(int row, int column) or Worksheet.get(String name) method to access a specific Excel cell.
- Use the setValue() method to write a text value to the cell.
- Use the setNumberValue() method to write a numeric value to the cell.
**Java code to write data to Excel: **
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class WriteToCells {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Write data to specific cells
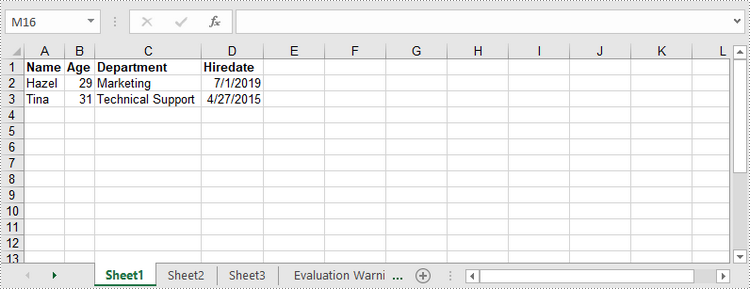
worksheet.get("A1").setValue("Name");
worksheet.get("B1").setValue("Age");
worksheet.get("C1").setValue("Department");
worksheet.get("D1").setValue("Hiredate");
worksheet.get(2,1).setValue("Hazel");
worksheet.get(2,2).setNumberValue(29);
worksheet.get(2,3).setValue("Marketing");
worksheet.get(2,4).setValue("2019-07-01");
worksheet.get(3,1).setValue("Tina");
worksheet.get(3,2).setNumberValue(31);
worksheet.get(3,3).setValue("Technical Support");
worksheet.get(3,4).setValue("2015-04-27");
// Autofit column widths
worksheet.getAllocatedRange().autoFitColumns();
// Apply a style to the first row
CellStyle style = workbook.getStyles().addStyle("newStyle");
style.getFont().isBold(true);
worksheet.getRange().get(1,1,1,4).setStyle(style);
// Save to an Excel file
workbook.saveToFile("output/WriteToCells.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
When to use this: Small datasets where you need precise control over cell placement (e.g., adding a title, single-row entries).
2. Write Arrays to Excel Worksheets
For bulk data, writing arrays (1D or 2D) is far more efficient than updating cells one by one. Spire.XLS for Java allows inserting arrays into a contiguous cell range.
insertArray() Method Explained:
The insertArray() method handles 1D arrays (single rows) and 2D arrays (multiple rows/columns) effortlessly. Its parameters are:
- Object[] array/ Object[][] array: The 1D or 2D array containing data to insert.
- int firstRow: The starting row index (1-based).
- int firstColumn: The starting column index (1-based).
- boolean isVertical: A boolean indicating the insertion direction:
- false: Insert horizontally (left to right).
- true: Insert vertically (top to bottom).
**Java code to insert arrays into Excel: **
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class WriteArrayToWorksheet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Create a one-dimensional array
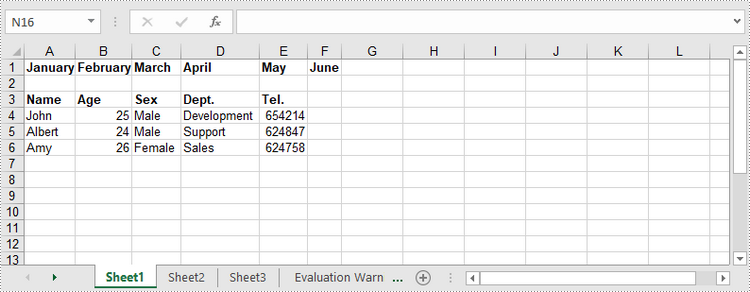
Object[] oneDimensionalArray = {"January", "February", "March", "April","May", "June"};
// Write the array to the first row of the worksheet
worksheet.insertArray(oneDimensionalArray, 1, 1, false);
// Create a two-dimensional array
Object[][] twoDimensionalArray = {
{"Name", "Age", "Sex", "Dept.", "Tel."},
{"John", "25", "Male", "Development","654214"},
{"Albert", "24", "Male", "Support","624847"},
{"Amy", "26", "Female", "Sales","624758"}
};
// Write the array to the worksheet starting from the cell A3
worksheet.insertArray(twoDimensionalArray, 3, 1);
// Autofit column width in the located range
worksheet.getAllocatedRange().autoFitColumns();
// Apply a style to the first and the third row
CellStyle style = workbook.getStyles().addStyle("newStyle");
style.getFont().isBold(true);
worksheet.getRange().get(1,1,1,6).setStyle(style);
worksheet.getRange().get(3,1,3,6).setStyle(style);
// Save to an Excel file
workbook.saveToFile("WriteArrays.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
When to use this: Sequential data (e.g., inventory logs, user lists) that needs bulk insertion.
3. Write DataTable to Excel
If your data is stored in a DataTable (e.g., from a database), Spire.XLS lets you directly export it to Excel with insertDataTable(), preserving structure and column headers.
insertDataTable() Method Explained:
The insertDataTable() method is a sophisticated bulk-insert operation designed specifically for transferring structured data collections into Excel. Its parameters are:
- DataTable dataTable: The DataTable object containing the data to insert.
- boolean columnHeaders: A boolean indicating whether to include column names from the DataTable as headers in Excel.
- true: Inserts column names as the first row.
- false: Skips column names; data starts from the first row.
- int firstRow: The starting row index (1-based).
- int firstColumn: The starting column index (1-based).
- boolean transTypes: A boolean indicating whether to preserve data types.
Java code to export DataTable to Excel:
import com.spire.xls.*;
import com.spire.xls.data.table.DataRow;
import com.spire.xls.data.table.DataTable;
public class WriteDataTableToWorksheet {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Create a Workbook instance
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
// Create a DataTable object
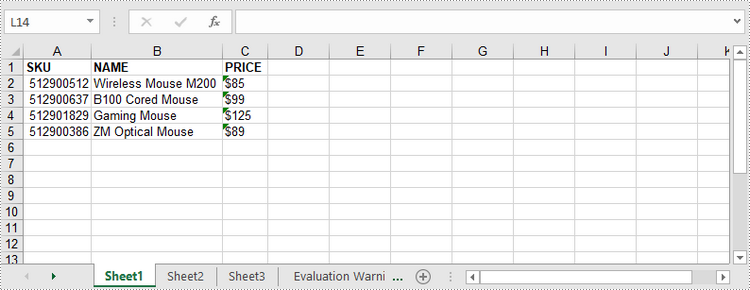
DataTable dataTable = new DataTable();
dataTable.getColumns().add("SKU", Integer.class);
dataTable.getColumns().add("NAME", String.class);
dataTable.getColumns().add("PRICE", String.class);
// Create rows and add data
DataRow dr = dataTable.newRow();
dr.setInt(0, 512900512);
dr.setString(1,"Wireless Mouse M200");
dr.setString(2,"$85");
dataTable.getRows().add(dr);
dr = dataTable.newRow();
dr.setInt(0,512900637);
dr.setString(1,"B100 Cored Mouse ");
dr.setString(2,"$99");
dataTable.getRows().add(dr);
dr = dataTable.newRow();
dr.setInt(0,512901829);
dr.setString(1,"Gaming Mouse");
dr.setString(2,"$125");
dataTable.getRows().add(dr);
dr = dataTable.newRow();
dr.setInt(0,512900386);
dr.setString(1,"ZM Optical Mouse");
dr.setString(2,"$89");
dataTable.getRows().add(dr);
// Write datatable to the worksheet
worksheet.insertDataTable(dataTable,true,1,1,true);
// Autofit column width in the located range
worksheet.getAllocatedRange().autoFitColumns();
// Apply a style to the first row
CellStyle style = workbook.getStyles().addStyle("newStyle");
style.getFont().isBold(true);
worksheet.getRange().get(1,1,1,3).setStyle(style);
// Save to an Excel file
workbook.saveToFile("output/WriteDataTable.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
When to use this: Database exports, CRM data, or any structured data stored in a DataTable (e.g., SQL query results, CSV imports).
Performance Tips for Large Datasets
- Use bulk operations (insertArray()/insertDataTable()) instead of writing cells one by one.
- Disable auto-fit columns or styling during data insertion, then apply them once after all data is written.
- For datasets with 100,000+ rows, consider streaming mode to reduce memory usage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What Excel formats does Spire.XLS support for writing data?
A: Spire.XLS for Java supports all major Excel formats, including:
- Legacy formats: XLS (Excel 97-2003)
- Modern formats: XLSX, XLSM (macro-enabled), XLSB, and more.
You can specify the output format when saving Excel with the saveToFile() method.
Q2: How do I format cells (colors, fonts, borders) when writing data?
A: Spire.XLS offers robust styling options. Check these guides:
- Set Background Color for Excel Cells in Java
- Apply Different Fonts to Excel Cells in Java
- Add Cell Borders in Excel in Java
Q3: How do I avoid the "Evaluation Warning" in output files?
A: To remove the evaluation sheets, get a 30-day free trial license here and then apply the license key in your code before creating the Workbook object:
com.spire.xls.license.LicenseProvider.setLicenseKey("Key");
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
Final Thoughts
Mastering Excel export functionality is crucial for Java developers in data-driven applications. The Spire.XLS for Java library provides three efficient approaches to write data to Excel in Java:
- Precision control with cell-by-cell writing
- High-performance bulk inserts using arrays
- Database-style exporting with DataTables
Each method serves distinct use cases - from simple reports to complex enterprise data exports. By following the examples in the article, developers can easily create and write to Excel files in Java applications.
The Excel print options (also known as sheet options) allow you to control the print options when printing Excel documents. Spire.XLS for Java offers the PageSetup class to set the print options, such as print area, print titles and print order. This article will demonstrate how to set different printing settings using Spire.XLS for Java from the following aspects:
- Set the print area in Excel
- Print titles in Excel
- Print gridlines in Excel
- Print comments in Excel
- Print Excel in black and white mode
- Set print quality
- Set the print order of worksheet pages
Install Spire.XLS for Java
First, you're required to add the Spire.Xls.jar file as a dependency in your Java program. The JAR file can be downloaded from this link. If you use Maven, you can easily import the JAR file in your application by adding the following code to your project's pom.xml file.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>com.e-iceblue</id>
<name>e-iceblue</name>
<url>https://repo.e-iceblue.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>e-iceblue</groupId>
<artifactId>spire.xls</artifactId>
<version>15.12.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Setting Excel Print Options via Page Setup
The detailed steps of controlling the Excel printing settings are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load a sample Excel document using Workbook.loadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.getWorksheets().get() method.
- Get the PageSetup object of the first worksheet.
- Select a specific print area of a worksheet using PageSetup.setPrintArea() method.
- Set the rows to repeat at top when printing using PageSetup.setPrintTitleRows() method.
- Set printing with gridlines using PageSetup.isPrintGridlines(true) method.
- Set printing with comments using PageSetup.setPrintComments() method.
- Print worksheet in black & white mode using PageSetup.setBlackAndWhite(true) method.
- Set the printing quality using PageSetup.setPrintQuality() method.
- Set the printing order using PageSetup.setOrder() method.
- Save the document to another file using Workbook.saveToFile() method.
- Java
import com.spire.xls.*;
public class pageSetupForPrinting {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//Create a workbook
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
//Load the Excel document from disk
workbook.loadFromFile("Sample.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Get the PageSetup object of the first worksheet
PageSetup pageSetup = worksheet.getPageSetup();
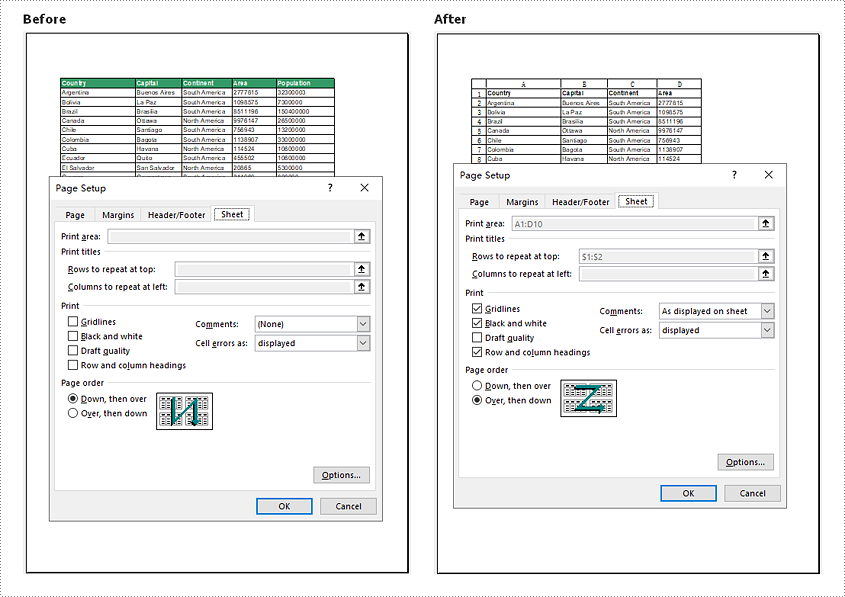
//Specifying the print area
pageSetup.setPrintArea("A1:D10");
//Define row numbers 1 as title rows
pageSetup.setPrintTitleRows("$1:$2");
//Allow to print with row/column headings
pageSetup.isPrintHeadings(true);
//Allow to print with gridlines
pageSetup.isPrintGridlines(true);
//Allow to print comments as displayed on worksheet
pageSetup.setPrintComments(PrintCommentType.InPlace);
//Set printing quality
pageSetup.setPrintQuality(150);
//Allow to print worksheet in black & white mode
pageSetup.setBlackAndWhite(true);
//Set the printing order
pageSetup.setOrder(OrderType.OverThenDown);
//Save the document to file
workbook.saveToFile("PagePrintOptions.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016);
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
