
Python (355)
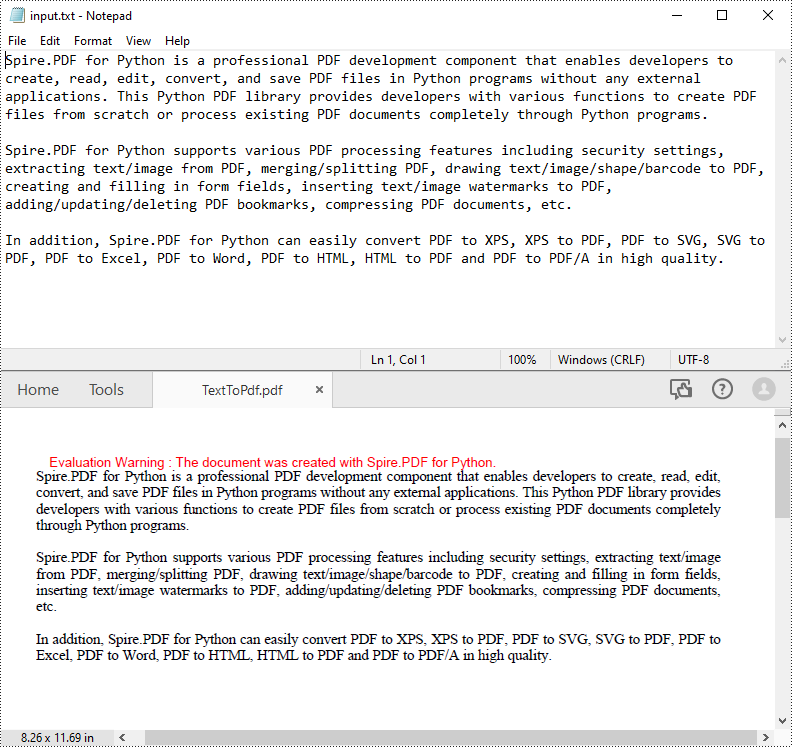
PDF is an ideal file format for sharing and archiving. If you are working with text files, you may find it beneficial to convert them to PDF files for enhanced portability, security and format preservation. In this article, you will learn how to convert TXT files to PDF in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Convert TXT to PDF with Python
Spire.PDF for Python allows to convert text files to PDF by reading the text content from the input TXT file, and then drawing it onto the pages of a PDF document. Some of the core classes and methods used are listed below:
- PdfDocument class: Represents a PDF document model.
- PdfTextWidget class: Represents the text area with the ability to span several pages.
- File.ReadAllText() method: Reads the text in the text file into a string object.
- PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method: Adds a page to a PDF document.
- PdfTextWidget.Draw() method: Draws the text widget at a specified location on the page.
The following are the detailed steps to convert TXT to PDF in Python:
- Read text from the TXT file using File.ReadAllText() method.
- Create a PdfDocument instance and add a page to the PDF file.
- Create a PDF font and brush objects.
- Set the text format and layout.
- Create a PdfTextWidget object to hold the text content.
- Draw the text widget at a specified location on the PDF page using PdfTextWidget.Draw() method.
- Save the PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
def ReadFromTxt(fname: str) -> str:
with open(fname, 'r') as f:
text = f.read()
return text
inputFile = "input.txt"
outputFile = "TextToPdf.pdf"
# Get text from the txt file
text = ReadFromTxt(inputFile)
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a page
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
# Create a PDF font and PDF brush
font = PdfFont(PdfFontFamily.TimesRoman, 11.0)
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Black()
# Set the text alignment and line spacing
strformat = PdfStringFormat()
strformat.LineSpacing = 10.0
strformat.Alignment = PdfTextAlignment.Justify
# Set the text layout
textLayout = PdfTextLayout()
textLayout.Break = PdfLayoutBreakType.FitPage
textLayout.Layout = PdfLayoutType.Paginate
# Create a PdfTextWidget instance to hold the text content
textWidget = PdfTextWidget(text, font, brush)
# Set the text format
textWidget.StringFormat = strformat
# Draw the text at the specified location on the page
bounds = RectangleF(PointF(0.0, 20.0), page.Canvas.ClientSize)
textWidget.Draw(page, bounds, textLayout)
# Save the result file
pdf.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.PDF)
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
If you have additional pieces of information to include in your spreadsheet, inserting rows or columns can provide room for these new fields. In addition,
adding blank rows or columns between data sets can also help to effectively separate different categories of information, making them easier to read and analyze. This article will demonstrate how to insert rows and columns in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
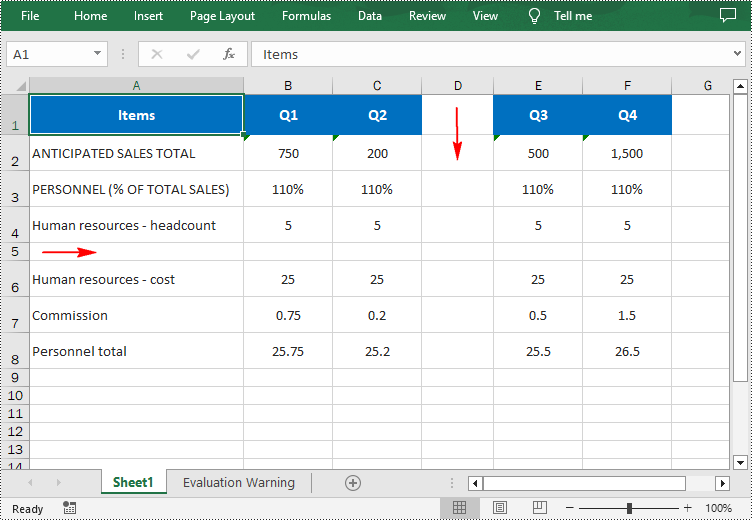
Insert a Row and a Column in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python provides the Worksheet.InsertRow(rowIndex: int) and Worksheet.InsertColumn(columnIndex: int) methods for inserting a blank row and a blank column in an Excel worksheet. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Insert a row into the worksheet using Worksheet.InsertRow(rowIndex: int) method.
- Insert a column into the worksheet using Worksheet.InsertColumn(columnIndex: int) method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "input.xlsx" outputFile = "InsertRowAndColumn.xlsx" # Create a Workbook instance workbook = Workbook() # Load an Excel document workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get a specified worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] # Insert a blank row as the 5th row in the worksheet worksheet.InsertRow(5) # Insert a blank column as the 4th column in the worksheet worksheet.InsertColumn(4) # Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2016) workbook.Dispose()
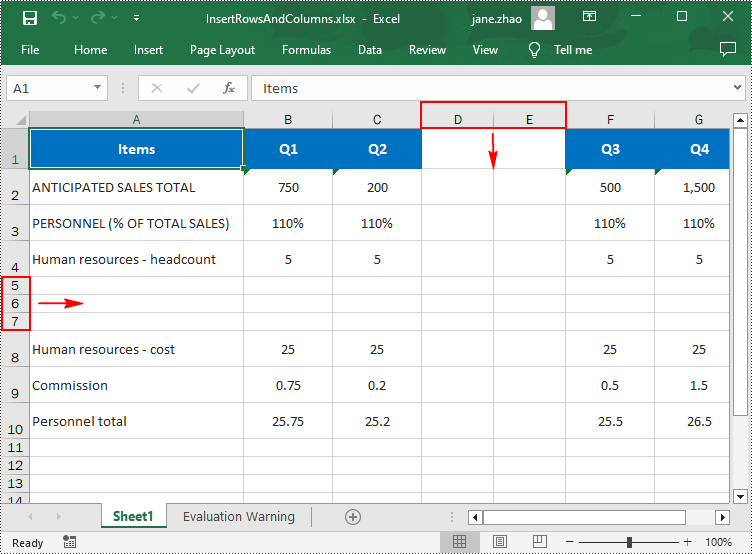
Insert Multiple Rows and Columns in Excel in Python
To insert multiple rows and columns into a worksheet, you can use the Worksheet.InsertRow(rowIndex: int, rowCount: int) and Worksheet.InsertColumn(columnIndex: int, columnCount: int) methods. The following are detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Insert multiple rows into the worksheet using Worksheet.InsertRow(rowIndex: int, rowCount: int) method.
- Insert multiple columns into the worksheet using Worksheet.InsertColumn(columnIndex: int, columnCount: int) method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "input.xlsx" outputFile = "InsertRowsAndColumns.xlsx" # Create a Workbook instance workbook = Workbook() # Load an Excel document workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get a specified worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] # Insert three blank rows into the worksheet worksheet.InsertRow(5, 3) #Insert two blank columns into the worksheet worksheet.InsertColumn(4, 2) # Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2016) workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Incorporating audio and videos in slides has become a common practice for creating interactive and dynamic PowerPoint presentations, which helps the presenter in sharing information, engaging the audience, and delivering impactful messages. However, as content requirements change, there arises a need to replace or update these multimedia elements. This article will show how to use Spire.Presentation for Python to replace audio and videos in PowerPoint presentations for content updating needs such as updating outdated videos, enhancing audio quality, or simply swapping in new content.
- Replace a Video in a PowerPoint Presentation with Python
- Replace an Audio in a PowerPoint Presentation with Python
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
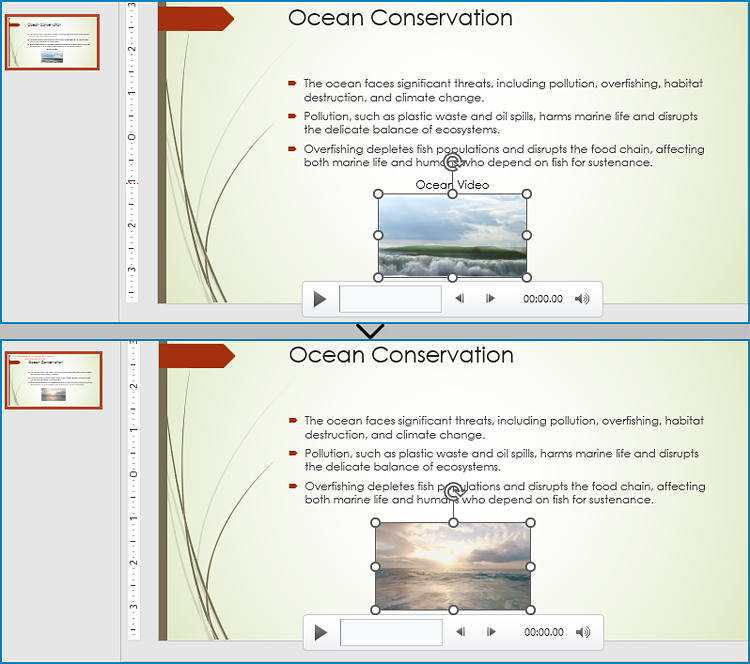
Replace a Video in a PowerPoint Presentation with Python
With Spire.Presentation for Python, developers can find the video shapes in slides and replace the video data through IVideo.EmbeddedVideoData property. It is important to note that, after replacing the video, the preview of the video should also be updated with the IVideo.PictureFill.Picture property. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Presentation class and load a PowerPoint presentation file using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the collection of the videos embedded in the presentation through Presentation.Videos property.
- Get the slide that contains the video to be replaced through Presentation.Slides[] property.
- Iterate through the shapes in the slide and determine if a shape is an instance of IVideo class. If it is, append the new video to the video collection using VideoCollection.AppendByStream() method and replace the original video with the new video through IVideo.EmbeddedVideoData property.
- Embed a new image to the presentation using Presentation.Images.AppendStream() method and set it as the preview of the video through IVideo.PictureFill.Picture.EmbedImage property. You can also set an online image as the preview through IVideo.PictureFill.Picture.Url property.
- Save the presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
from spire.presentation.common import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
pres = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
pres.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Get the second slide
slide = pres.Slides[1]
# Get the videos in the presentation
videos = pres.Videos
# Iterate through the shapes on the slide
for shape in slide.Shapes:
# Check if the shape is a video
if isinstance(shape, IVideo):
video = shape if isinstance(shape, IVideo) else None
# Append a new video to the video collection
videoData = videos.AppendByStream(Stream("Ocean2.mp4"))
# Replace the video in the shape with the new video
video.EmbeddedVideoData = videoData
# Embed a picture in the presentation
imageData = pres.Images.AppendStream(Stream("Ocean2.png"))
# Set the new picture as the preview of the video
video.PictureFill.Picture.EmbedImage = imageData
# Save the presentation
pres.SaveToFile("output/ReplaceVideo.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
pres.Dispose()
Replace an Audio in a PowerPoint Presentation with Python
Similarly, developers can also use Spire.Presentation for Python to find specific audio in a presentation slide and replace the audio data. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Presentation class and load a PowerPoint presentation file using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the collection of the audio embedded in the presentation through Presentation.WavAudios property.
- Get the slide that contains audio to be replaced through Presentation.Slides[] property.
- Iterate through each shape in the slide and check if a shape is an instance of IAudio class. If it is, append the new audio to the audio collection using WavAudioCollection.Append() method and replace the original audio with the new audio through IAudio.Data property.
- Save the presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
from spire.presentation.common import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
pres = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation file
pres.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Get the audio collection from the presentation
audios = pres.WavAudios
# Get the slide that contains the audio
slide = pres.Slides[0]
# Iterate through each shape in the slide
for shape in slide.Shapes:
# Check if the shape is an audio shape
if isinstance(shape, IAudio):
audio = shape if isinstance(shape, IAudio) else None
# Load an audio file
stream = Stream("Wave.wav")
# Replace the audio in the shape
audioData = audios.Append(stream)
audio.Data = audioData
# Save the presentation
pres.SaveToFile("output/ReplaceAudio.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
pres.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Directly extracting text has emerged as a crucial method for obtaining textual information from information-dense PowerPoint presentations. By utilizing Python programs, users can conveniently and quickly access the content within slides, enabling efficient collection of information and further data processing. This article shows how to use Spire.Presentation for Python to extract text from PowerPoint presentations, including text in slides, speaker notes, and comments.
- Extract Text from Presentation Slides with Python
- Extract Text from Speaker Notes with Python
- Extract Text from Presentation Comments with Python
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Extract Text from Presentation Slides with Python
The text within PowerPoint presentation slides is placed within shapes. Therefore, developers can extract the text from the presentation by accessing all the shapes within each slide and extracting the text contained within them. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Presentation class and load PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through the slides in the presentation and then iterate through the shapes in each slide.
- Check if a shape is an IAutoShape instance. If it is, get the paragraphs in the shape through IAutoShape.TextFrame.Paragraphs property and then get the text in the paragraphs through Paragraph.Text property.
- Write the slide text to a text file.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
from spire.presentation.common import *
# Create an object of Presentation class
pres = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
pres.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
text = []
# Loop through each slide
for slide in pres.Slides:
# Loop through each shape
for shape in slide.Shapes:
# Check if the shape is an IAutoShape instance
if isinstance(shape, IAutoShape):
# Extract the text from the shape
for paragraph in (shape if isinstance(shape, IAutoShape) else None).TextFrame.Paragraphs:
text.append(paragraph.Text)
# Write the text to a text file
f = open("output/SlideText.txt","w", encoding = 'utf-8')
for s in text:
f.write(s + "\n")
f.close()
pres.Dispose()
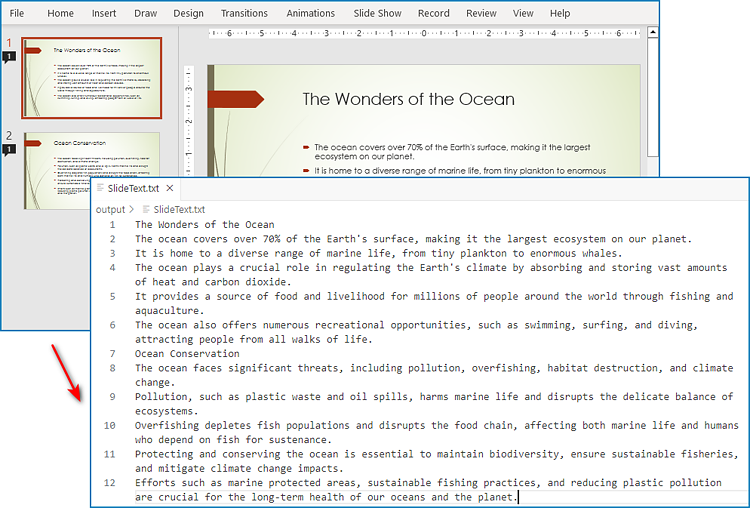
Extract Text from Speaker Notes with Python
Speaker notes are additional information that provides guidance to the presenter and are not visible to the audience. The text in speaker notes of each slide is stored in the notes slide and developers can extract the text through NotesSlide.NotesTextFrame.Text property. The detailed steps for extracting text in speaker notes are as follows:
- Create an object of Presentation class and load PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through each slide.
- Get the note slide through ISlide.NotesSlide property and retrieve the text through NotesSlide.NotesTextFrame.Text property.
- Write the speaker note text to a text file.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
from spire.presentation.common import *
# Create an object of Presentation class
pres = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
pres.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
list = []
# Iterate through each slide
for slide in pres.Slides:
# Get the notes slide
notesSlide = slide.NotesSlide
# Get the notes
notes = notesSlide.NotesTextFrame.Text
list.append(notes)
# Write the notes to a text file
f = open("output/SpeakerNoteText.txt", "w", encoding="utf-8")
for note in list:
f.write(note)
f.write("\n")
f.close()
pres.Dispose()

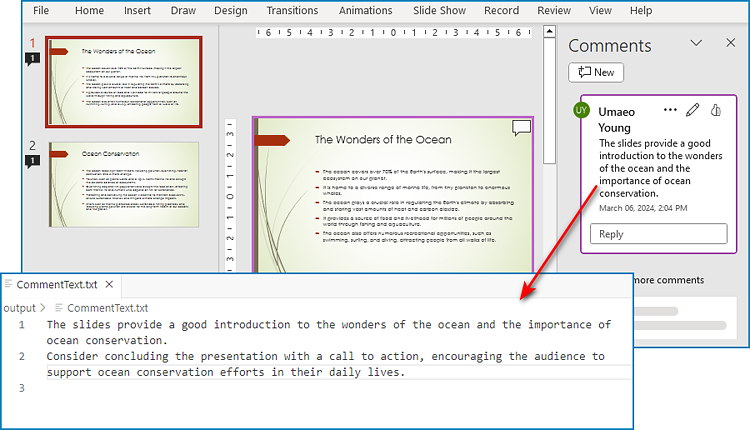
Extract Text from Presentation Comments with Python
With Spire.Presentation for Python, developers can also extract the text from comments in PowerPoint presentations by getting comments from slides with ISlide.Comments property and retrieving text from comments with Comment.Text property. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of Presentation class and load PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through each slide and get the comment from each slide through ISlide.Comments property.
- Iterate through each comment and retrieve the text from each comment through Comment.Text property.
- Write the comment text to a text file.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
from spire.presentation.common import *
# Create an object of Presentation class
pres = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
pres.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
list = []
# Iterate through all slides
for slide in pres.Slides:
# Get all comments from the slide
comments = slide.Comments
# Iterate through the comments
for comment in comments:
# Get the comment text
commentText = comment.Text
list.append(commentText)
# Write the comments to a text file
f = open("output/CommentText.txt", "w", encoding="utf-8")
for i in range(len(list)):
f.write(list[i] + "\n")
f.close()
pres.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Moving and deleting worksheets in Excel are essential operations that allow you to organize and manage your workbook efficiently. Moving worksheets enables you to adjust the order of worksheets to match your specific needs or bring related information together. While deleting worksheets helps you eliminate unwanted or redundant sheets, creating a cleaner and more organized workspace. In this article, we will demonstrate how to move and delete worksheets in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
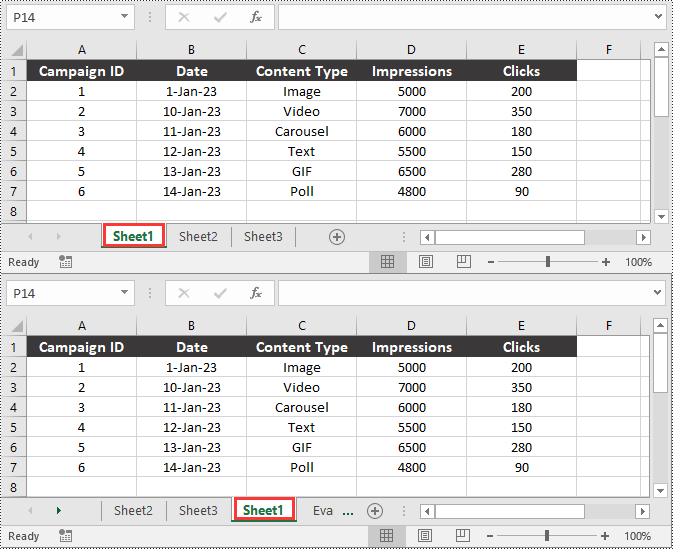
Move a Worksheet in Excel in Python
You can easily move a worksheet in an Excel file to another position by using the Worksheet.MoveWorksheet() method provided by Spire.XLS for Python. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet in the file using the Workbook.Worksheet[] property.
- Move the worksheet to another position in the file using the Worksheet.MoveWorksheet() method.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load a sample Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet in the file by its index
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Or get a specific worksheet in the file by its name
# sheet = workbook.Worksheets["Sheet1"]
# Move the worksheet to the 3rd position in the file
sheet.MoveWorksheet(2)
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("MoveWorksheet.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
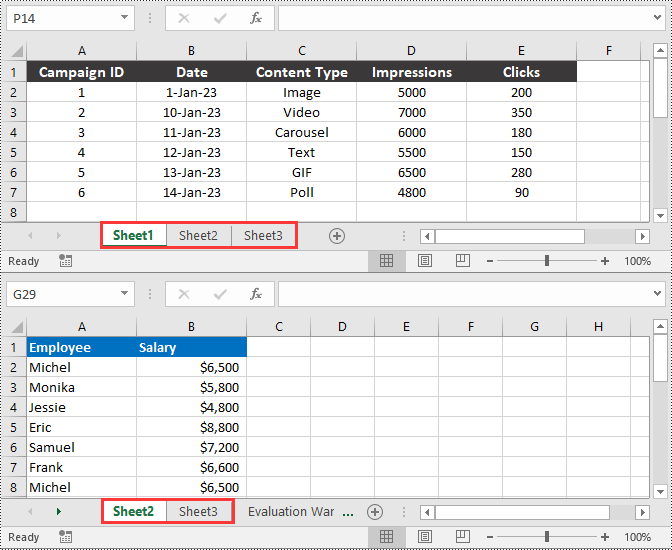
Delete a Worksheet in Excel in Python
You can delete a specific worksheet from an Excel file by using the Workbook.Worksheets.RemoveAt() or Workbook.Worksheets.Remove() method provided by Spire.XLS for Python. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove a specific worksheet from the file using the Workbook.Worksheets.RemoveAt() or Workbook.Worksheets.Remove() method.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load a sample Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Remove a specific worksheet in the file by its index
workbook.Worksheets.RemoveAt(0)
# Or get a specific worksheet in the file by its name and then remove it
# worksheet = workbook.Worksheets["Sheet1"]
# workbook.Worksheets.Remove(worksheet)
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("DeleteWorksheet.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Comparing two Word documents for differences is a crucial task when reviewing changes, ensuring accuracy, and collaborating on content. This process allows you to identify additions, deletions, and modifications made between different document iterations. By comparing versions, you can efficiently track alterations, verify updates, and maintain document integrity. In this article, you will learn how to compare two versions of a Word document in Python using the Spire.Doc for Python library.
- Compare Two Versions of a Word Document in Python
- Compare Two Versions of a Word Document While Ignoring Formatting in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Compare Two Versions of a Word Document in Python
MS Word also offers a "Compare" feature that allows you to directly compare two versions of a document. This feature generates a new document that highlights the differences between the two versions.
To achieve similar results using Spire.Doc for Python, load the original and revised versions into two separate Document objects. Then, use the Compare() method to compare the revised version against the original. Finally, save the comparative document, which highlights the alterations, using the SaveToFile() method.
The steps to compare two version of a Word document using Python are as follows.
- Load the first document (original version) while initializing the Document object.
- Load the second document (revised version) while initializing the Document object.
- Call Compare() method of the first Document object to compare the revised version against the original version.
- Save the comparison results in a new Word document.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Load the first document while initializing the Document object
firstDoc = Document("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Original.docx")
# Load the second document while initializing the Document object
secondDoc = Document("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Revised.docx")
# Compare two documents
firstDoc.Compare(secondDoc, "E-ICEBLUE")
# Save the comparison results in a new document
firstDoc.SaveToFile("Output/Differences.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
# Dispose resources
firstDoc.Dispose()
secondDoc.Dispose()

Compare Two Versions of a Word Document While Ignoring Formatting in Python
Comparing two versions of a Word document while ignoring formatting can be useful when you want to focus solely on the textual changes and disregard any formatting modifications.
To customize the comparison options in Spire.Doc for Python, use the CompareOptions class. If you want to exclude formatting from the comparison process, you can set the IgnoreFormatting property of the CompareOptions object to True. When you call the Compare() method, simply pass the CompareOptions object as an argument to achieve the desired comparison behavior.
The following are the steps to compare two versions of a Word document while ignoring formatting using Python.
- Load the first document (original version) while initializing the Document object.
- Load the second document (revised version) while initializing the Document object.
- Create a CompareOptions object and set its IgnoreFormatting property to True.
- Call Compare() method of the first Document object, passing the CompareOptions object as a parameter, to compare the revision against the original while ignoring formatting.
- Save the comparison results in a new Word document.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Load the first document while initializing the Document object
firstDoc = Document("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Original.docx")
# Load the second document while initializing the Document object
secondDoc = Document("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Revised.docx")
# Set compare option to ignore formatting changes
compareOptions = CompareOptions()
compareOptions.IgnoreFormatting = True
# Compare the two Word documents with options
firstDoc.Compare(secondDoc, "E-ICEBLUE", compareOptions)
# Save the comparison results in a new document
firstDoc.SaveToFile("Output/DifferencesWithoutFormattingChanges.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
# Dispose resources
firstDoc.Dispose()
secondDoc.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Cell borders play a crucial role in enhancing the visual clarity and organization of data in Excel spreadsheets. Adding borders to cells can help draw attention to specific data points, highlight headers, or create clear boundaries between different sections of your worksheet. On the other hand, removing borders can provide a sleek and seamless appearance, especially when you want to eliminate distractions and focus solely on the data itself.
In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the process of adding or removing cell borders in Excel by using the Spire.XLS for Python library.
- Add Borders to a Selected Cell or Cell Range in a Worksheet
- Add Borders to the Cell Range Containing Data in a Worksheet
- Add Left, Top, Right, Bottom, Diagonal Borders to a Cell
- Remove Borders of a Cell or Cell Range in a Worksheet
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
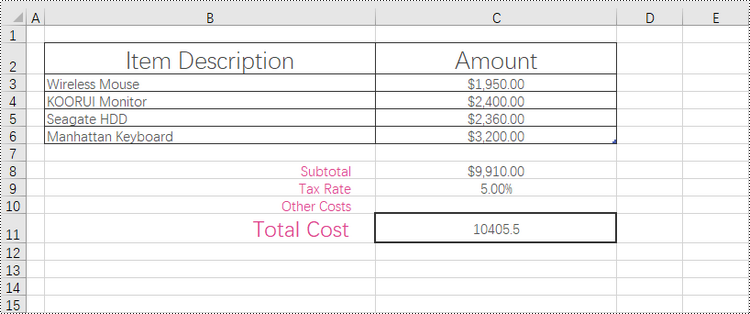
Add Borders to a Selected Cell or Cell Range in a Worksheet in Python
Borders can be applied to individual cells, groups of cells, or even entire ranges to create clear boundaries and make data stand out. By adding borders, you can effectively organize and structure your data, making it easier to analyze and understand.
With Spire.XLS for Python, accessing specific cells or cell ranges is made easy through the Worksheet.Range[name: str] property. Once you have obtained the desired cell or cell range, you can apply an outside border using the CellRange.BorderAround() method. Additionally, you can apply inside borders to a cell range using the CellRange.BorderInside() method.
To apply borders to a cell or cell range, follow the steps below.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document from the specified path.
- Get a specific worksheet from the workbook.
- Get a cell or cell range using Worksheet.Range[name: str] property.
- Apply outside borders to the cell or cell range using CellRange.BorderAround() method.
- Apply inside borders to the cell range using CellRange.BorderInside() method.
- Save the workbook to a new Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get a specific cell
cell = worksheet.Range["C11"]
# Apply borders to the cell
cell.BorderAround(LineStyleType.Medium, Color.get_Black())
# Get a cell range
cellRange = worksheet.Range["B2:C6"]
# Apply outside borders to the cell range
cellRange.BorderAround(LineStyleType.Thin, Color.get_Black())
# Apply inside borders to the cell range
cellRange.BorderInside(LineStyleType.Thin, Color.get_Black())
# Save the document
workbook.SaveToFile("Output/AddBordersToCellRange.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
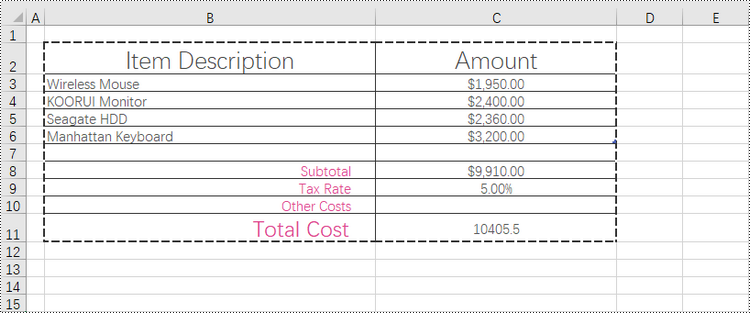
Add Borders to the Cell Range Containing Data in a Worksheet in Python
The range that contains data in a worksheet is commonly referred to as the "allocated range" or "used range". It represents the rectangular area that encompasses all the cells with data, including text, numbers, formulas, and other types of content.
To retrieve the cell range having data, use the Worksheet.AllocatedRange property. Then, you can easily apply borders to this range using the BorderAround() and BorderInside() methods.
The steps to add borders to the cell range containing data are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document from the specified path.
- Get a specific worksheet from the workbook.
- Get the cell range that contains data using Worksheet.AllocatedRange property.
- Apply outside borders to the cell or cell range using CellRange.BorderAround() method.
- Apply inside borders to the cell range using CellRange.BorderInside() method.
- Save the workbook to a new Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the cell range that contains data
locatedRange = worksheet.AllocatedRange
# Apply outside borders to the cell range
locatedRange .BorderAround(LineStyleType.MediumDashed, Color.get_Black())
# Apply inside borders to the cell range
locatedRange .BorderInside(LineStyleType.Thin, Color.get_Black())
# Save the document
workbook.SaveToFile("Output/AddBordersToLocatedRange.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
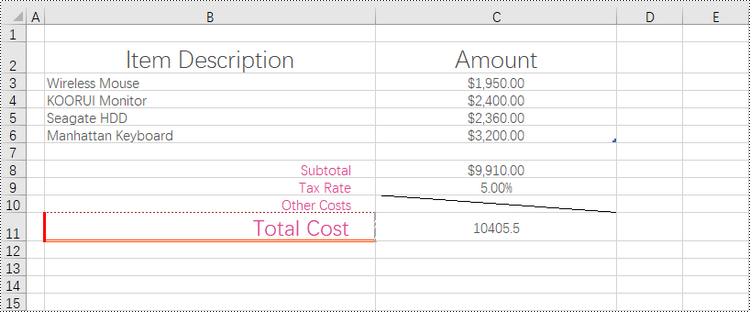
Add Left, Top, Right, Bottom, Diagonal Borders to a Cell in Python
In addition to applying outside and inside borders, you have the option to add left, top, right, bottom, and diagonal borders to individual cells or cell ranges. This feature allows you to go beyond basic border customization and provides additional flexibility to highlight important information, separate sections within your worksheet, or provide a visual structure to your data.
Spire.XLS provides convenient access to specific borders, including the left, right, top, bottom, and diagonal borders, through properties such as CellRange.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeLeft]. Once you have obtained the desired border, you have the flexibility to customize its appearance by utilizing the IBorder.LineStyle property and the IBorder.Color property.
To add left, top, right, bottom, diagonal borders to a cell, follow the following steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document from the specified path.
- Get a specific worksheet from the workbook.
- Get a specific cell using Worksheet.Range property.
- Get the left, top, right, bottom and diagonal borders of the cell using the properties such as CellRange.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeLeft].
- Set the line style of the border using IBorder.LineStyle property
- Set the color of the border using IBorder.Color property.
- Save the workbook to a new Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get a cell
cell = worksheet.Range["B11"]
# Get the left, top, right, bottom border of the cell
leftBorder = cell.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeLeft]
topBorder = cell.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeTop]
rightBorder = cell.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeRight]
bottomBorder = cell.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom]
# Set the border type respectively
leftBorder.LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thick
topBorder.LineStyle = LineStyleType.Dotted
rightBorder.LineStyle = LineStyleType.SlantedDashDot
bottomBorder.LineStyle = LineStyleType.Double
# Set the border color respectively
leftBorder.Color = Color.get_Red()
topBorder.Color = Color.get_Brown()
rightBorder.Color = Color.get_DarkGray()
bottomBorder.Color = Color.get_OrangeRed()
# Get a specific cell
cell = worksheet.Range["C10"]
# Get the diagonal border of the cell
diagonalBorder = cell.Borders[BordersLineType.DiagonalDown]
# Set the border style
diagonalBorder.LineStyle = LineStyleType.Thin
# Save the document
workbook.SaveToFile("Output/BorderOfEdge.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
Remove Borders of a Cell or Cell Range in a Worksheet in Python
Borders can be removed from individual cells, groups of cells, or even entire ranges, allowing you to reduce visual noise and clutter, making your data easier to interpret and analyze. Additionally, you can choose to remove borders from specific sides of a cell, such as the left, top, right, or bottom, which can alter the visual appearance and enhance the overall presentation.
To eliminate borders surrounding or within a cell or cell range, you can easily achieve this by setting the CellRange.Borders.LineStyle property to LineStyleType.none. Similarly, if you want to remove a border on a specific side, such as the left side, you can accomplish this by setting the CellRange.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeLeft].LineStyle property to LineStyleType.none.
The steps to remove borders of a cell or cell range as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document from the specified path.
- Get a specific worksheet from the workbook.
- Get a specific cell or cell range using Worksheet.Range property.
- Remove all borders of the cell or cell range by setting CellRange.Borders.LineStyle property to LineStyleType.none.
- Save the workbook to a new Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\BorderExample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get a cell
cell = worksheet.Range["C11"]
# Remove borders by setting line style to none
cell.Borders.LineStyle = LineStyleType.none
# Remove border on a specific side
# cell.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeLeft].LineStyle = LineStyleType.none
# Get a cell range
cellRange = worksheet.Range["B2:C6"]
# Remove borders by setting line style to none
cellRange.Borders.LineStyle = LineStyleType.none
# Save the document
workbook.SaveToFile("Output/RemoveBorders.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Gridlines in Microsoft Excel provide a visual aid that helps users navigate through data and maintain a structured layout. By default, Excel displays gridlines in a light color to separate cells, making it easier to distinguish and locate specific data. However, there are instances when you may want to hide or even modify the appearance of gridlines to suit your specific needs. In this article, we will explore how to hide, show, and change gridlines in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Hide or Show Gridlines in Excel in Python
The Worksheet.GridLinesVisible property provided by Spire.XLS for Python is used to control the visibility of gridlines in an Excel worksheet. If you want to hide the gridlines in the worksheet, set this property to False. Conversely, if you wish to make the hidden gridlines visible again, set this property to True. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Hide or show the gridlines in the worksheet by setting the Worksheet.GridLinesVisible property as False or True.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Input.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Hide the gridlines in the worksheet
sheet.GridLinesVisible = False
# Show the hidden gridlines in the worksheet
# sheet.GridLinesVisible = True
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("HideGridlines.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
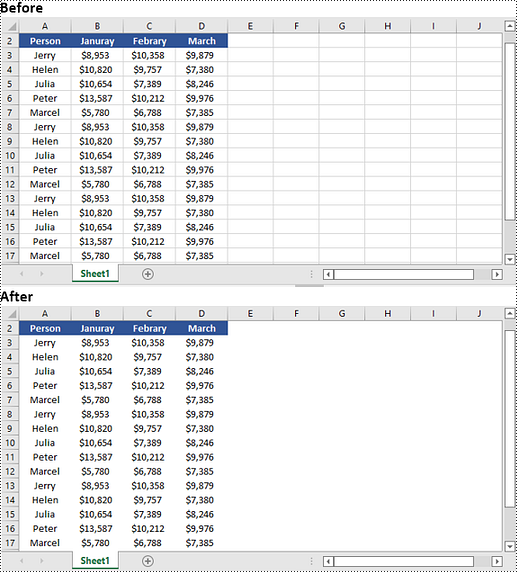
Change Gridlines in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python provides the Worksheet.GridLineColor property, which allows you to customize the color of gridlines in an Excel worksheet. By using this property, you can change the default color of gridlines to your desired choice. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Change the color of the gridlines in the worksheet using the Worksheet.GridLineColor property.
- Save the result file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Input.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Change the color of the gridlines in the worksheet
sheet.GridLineColor = ExcelColors.Red
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("ChangeGridlineColor.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
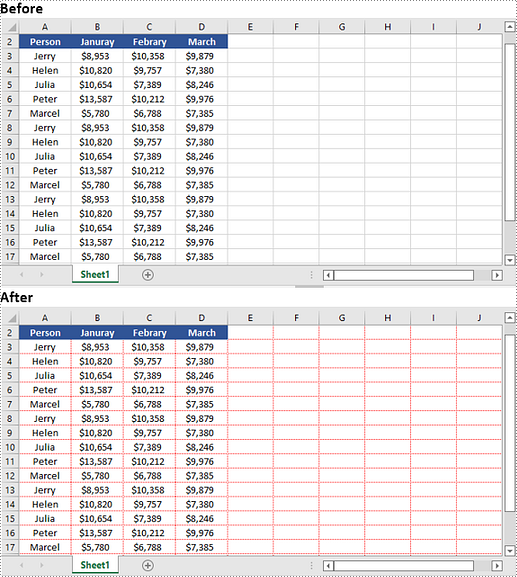
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
In PowerPoint, properly sized slides help make the document look professional. When giving presentations in different scenarios, adjusting slide sizes to match the aspect ratio of the projector or screen ensures an optimal viewing experience for all audience members, thus increasing engagement. In this article, you will learn how to change the slide size of a PowerPoint presentation in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
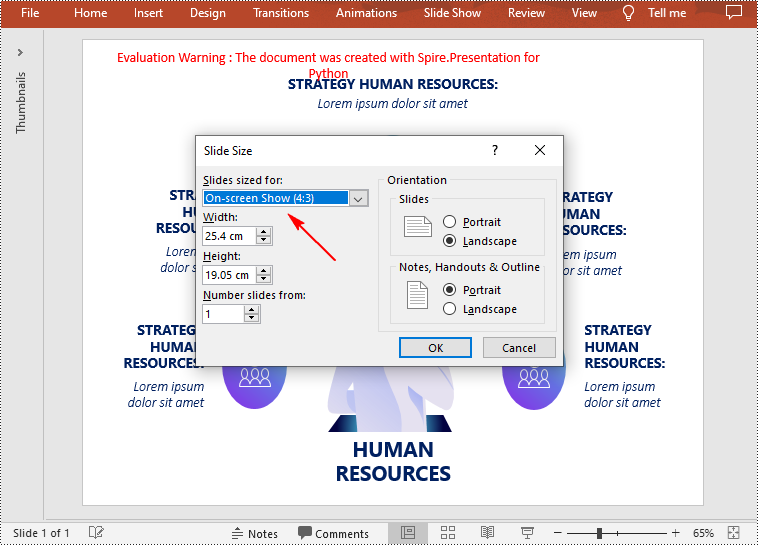
Change the Slide Size to a Preset Size in Python
Spire.Presentation for Python provides the Presentation.SlideSize.Type property to set or change the slide size to a preset size. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Presentation instance.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Change the slide size of the presentation using Presentation.SlideSize.Type property.
- Save the result document using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation instance
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint document
presentation.LoadFromFile("sample.pptx")
# Set or change the slide size
presentation.SlideSize.Type = SlideSizeType.Screen4x3
# Save the result document
presentation.SaveToFile("ChangeSlideSize.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
presentation.Dispose()
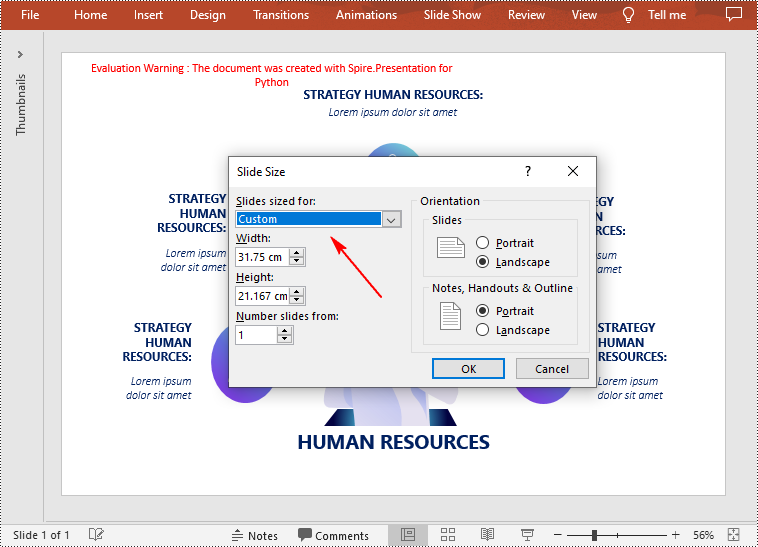
Change the Slide Size to a Custom Size in Python
Customizing the size of slides requires changing the slide size type to Custom first, and then you can set a desired size through the Presentation.SlideSize.Size property. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Presentation instance.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Change the slide size type to custom using Presentation.SlideSize.Type property.
- Customize the slide size using Presentation.SlideSize.Size property.
- Save the result document using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation instance
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint document
presentation.LoadFromFile("sample.pptx")
# Change the slide size type to custom
presentation.SlideSize.Type = SlideSizeType.Custom
# Set the slide size
presentation.SlideSize.Size = SizeF(900.0,600.0)
# Save the result document
presentation.SaveToFile("CustomSlideSize.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
presentation.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
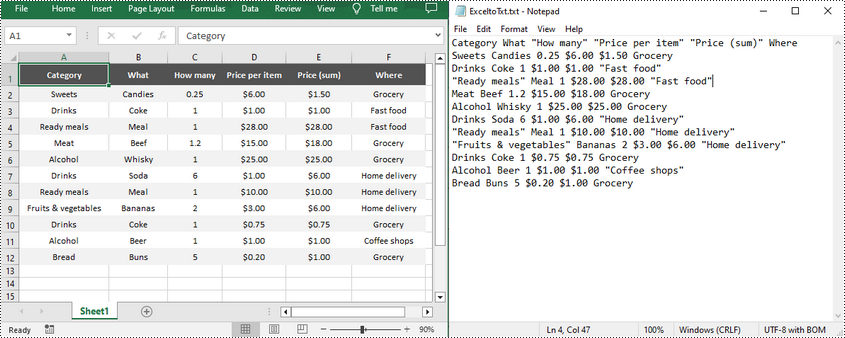
Text files have a distinct advantage over Excel spreadsheets in terms of simplicity as they don't contain complex formatting, macros or formulas. This streamlined nature not only enhances portability, but also reduces the possibility of file corruption. Consequently, converting Excel files to text files can greatly facilitates data parsing and ensures compatibility with various applications. In this article, you will learn how to convert Excel to TXT text file in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Convert Excel to TXT in Python
Spire.XLS for Python offers the Worksheet.SaveToFile(fileName: str, separator: str, encoding: Encoding) method to convert a specified worksheet to a TXT text file. The three parameters represent:
- fileName: Specifies the path and the name of the output text file.
- separator: Specifies the separator for the output text file. Common separators include commas (,), tabs, semicolons (;), etc.
- encoding: Specifies the encoding format of the file, e.g. UTF-8, Unicode, ASCII, etc. You need to use the correct encoding format to ensure that the text is represented and interpreted correctly.
The following are the detailed steps to convert Excel to text files in Python.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet by its index using Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Convert the Excel worksheet to a TXT file using Worksheet.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
import os import sys curPath = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)) rootPath = os.path.split(curPath)[0] sys.path.append(rootPath) from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "Inventories.xlsx" outputFile = "ExceltoTxt.txt" # Create a Workbook instance workbook = Workbook() # Load an Excel document from disk workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get the first worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] # Save the worksheet as a txt file sheet.SaveToFile(outputFile, " ", Encoding.get_UTF8()) workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
