
Python (355)
Page size refers to the dimensions of a document's page. It determines the width and height of the printable area and plays a crucial role in the overall layout and design of the document. Different types of documents may require specific page sizes, such as standard letter size (8.5 x 11 inches) for business letters or A4 size (210 x 297 mm) for international correspondence. Adjusting the page size ensures that your document is compatible with the intended output or presentation medium. In this article, we will demonstrate how to adjust the page size of a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Adjust the Page Size of a Word Document to a Standard Page Size in Python
- Adjust the Page Size of a Word Document to a Custom Page Size in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Adjust the Page Size of a Word Document to a Standard Page Size in Python
With Spire.Doc for Python, you can easily adjust the page sizes of Word documents to a variety of standard page sizes, such as A3, A4, A5, A6, B4, B5, B6, letter, legal, and tabloid. The following steps explain how to change the page size of a Word document to a standard page size using Spire.Doc for Python:
- Create an instance of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through the sections in the document.
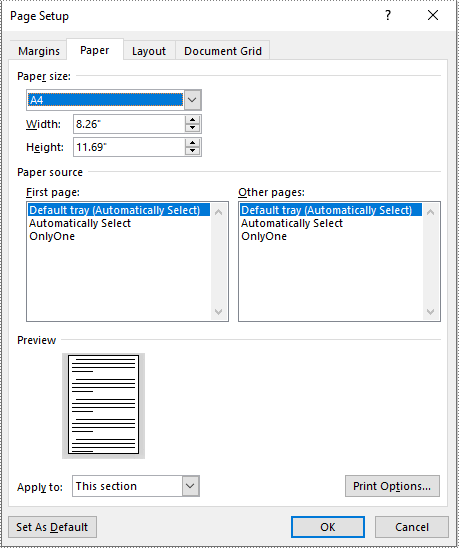
- Set the page size of each section to a standard page size, such as A4, by setting the Section.PageSetup.PageSize property to PageSize.A4().
- Save the result document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an instance of the Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Input.docx")
# Iterate through the sections in the document
for i in range(doc.Sections.Count):
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(i)
# Change the page size of each section to A4
section.PageSetup.PageSize = PageSize.A4()
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("StandardSize.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
doc.Close()
Adjust the Page Size of a Word Document to a Custom Page Size in Python
If you plan to print your document on paper with dimensions that don't match any standard paper size, you can change the page size of your document to a custom page size that matches the exact dimensions of the paper. The following steps explain how to change the page size of a Word document to a custom page size using Spire.Doc for Python:
- Create an instance of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create an instance of the SizeF class with customized dimensions.
- Iterate through the sections in the document.
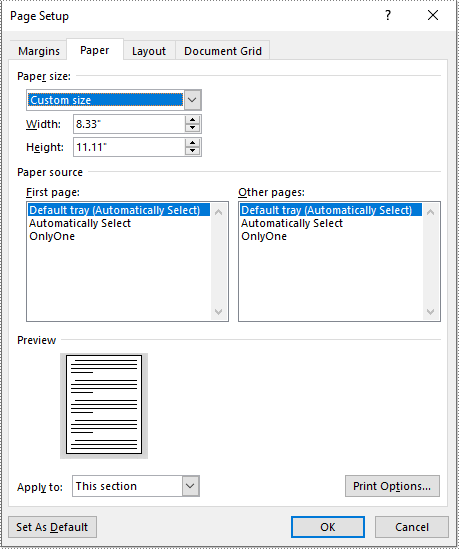
- Set the page size of each section to a custom page size by assigning the SizeF instance to the Section.PageSetup.PageSize property.
- Save the result document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an instance of the Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Input.docx")
# Create an instance of the SizeF class with customized dimensions
customSize = SizeF(600.0, 800.0)
# Iterate through the sections in the document
for i in range(doc.Sections.Count):
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(i)
# Change the page size of each section to the specified dimensions
section.PageSetup.PageSize = customSize
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile("CustomSize.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Converting HTML to PDF in Python is a common need when you want to generate printable reports, preserve web content, or create offline documentation with consistent formatting. In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to convert HTML to PDF in Python— whether you're working with a local HTML file or a HTML string. If you're looking for a simple and reliable way to generate PDF files from HTML in Python, this guide is for you.
Install Spire.Doc to Convert HTML to PDF Easily
To convert HTML to PDF in Python, you’ll need a reliable library that supports HTML parsing and PDF rendering. Spire.Doc for Python is a powerful and easy-to-use HTML to PDF converter library that lets you generate PDF documents from HTML content — without relying on a browser, headless engine, or third-party tools.
Install via pip
You can install the library quickly with pip:
pip install spire.doc
Alternative: Manual Installation
You can also download the Spire.Doc package and perform a custom installation if you need more control over the environment.
Tip: Spire.Doc offers a free version suitable for small projects or evaluation purposes.
Once installed, you're ready to convert HTML to PDF in Python in just a few lines of code.
Convert HTML Files to PDF in Python
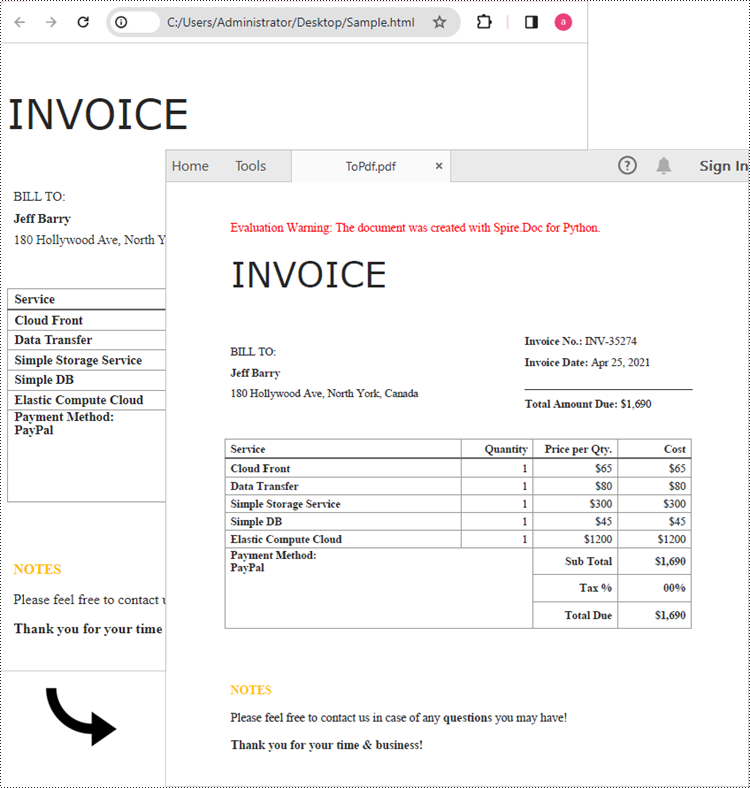
Spire.Doc for Python makes it easy to convert HTML files to PDF. The Document.LoadFromFile() method supports loading various file formats, including .html, .doc, and .docx. After loading an HTML file, you can convert it to PDF by calling Document.SaveToFile() method. Follow the steps below to convert an HTML file to PDF in Python using Spire.Doc.
Steps to convert an HTML file to PDF in Python:
- Create a Document object.
- Load an HTML file using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Convert it to PDF using Document.SaveToFile() method.
The following code shows how to convert an HTML file directly to PDF in Python:
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load an HTML file
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.html", FileFormat.Html, XHTMLValidationType.none)
# Save the HTML file to a pdf file
document.SaveToFile("output/ToPdf.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
document.Close()
Convert an HTML String to PDF in Python
If you want to convert an HTML string to PDF in Python, Spire.Doc for Python provides a straightforward solution. For simple HTML content like paragraphs, text styles, and basic formatting, you can use the Paragraph.AppendHTML() method to insert the HTML into a Word document. Once added, you can save the document as a PDF using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
Here are the steps to convert an HTML string to a PDF file in Python.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method and insert a paragraph using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Specify the HTML string and add it to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendHTML() method.
- Save the document as a PDF file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
Here's the complete Python code that shows how to convert an HTML string to a PDF:
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Add a section to the document
sec = document.AddSection()
# Add a paragraph to the section
paragraph = sec.AddParagraph()
# Specify the HTML string
htmlString = """
<html>
<head>
<title>HTML to Word Example</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
}
h1 {
color: #FF5733;
font-size: 24px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
p {
color: #333333;
font-size: 16px;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
ul {
list-style-type: disc;
margin-left: 20px;
margin-bottom: 15px;
}
li {
font-size: 14px;
margin-bottom: 5px;
}
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
width: 100%;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
th, td {
border: 1px solid #CCCCCC;
padding: 8px;
text-align: left;
}
th {
background-color: #F2F2F2;
font-weight: bold;
}
td {
color: #0000FF;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a Heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
<p>Here's an unordered list:</p>
<ul>
<li>Item 1</li>
<li>Item 2</li>
<li>Item 3</li>
</ul>
<p>And here's a table:</p>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Age</th>
<th>Gender</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>John Smith</td>
<td>35</td>
<td>Male</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Jenny Garcia</td>
<td>27</td>
<td>Female</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
"""
# Append the HTML string to the paragraph
paragraph.AppendHTML(htmlString)
# Save the document as a pdf file
document.SaveToFile("output/HtmlStringToPdf.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
document.Close()
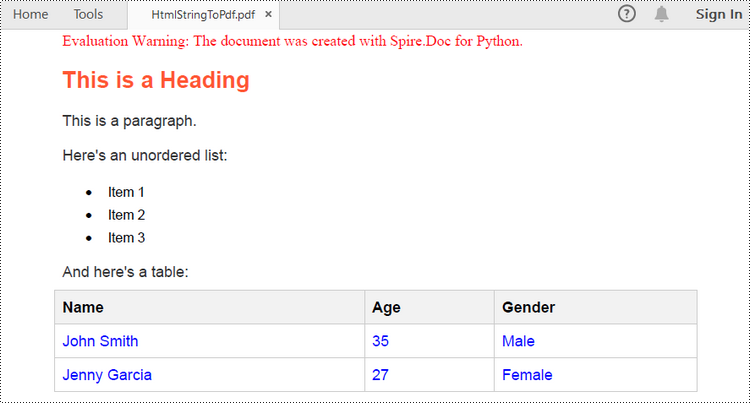
Customize the Conversion from HTML to PDF in Python
While converting HTML to PDF in Python is often straightforward, there are times when you need more control over the output. For example, you may want to set a password to protect the PDF document, or embed fonts to ensure consistent formatting across different devices. In this section, you’ll learn how to customize the HTML to PDF conversion using Spire.Doc for Python.
1. Set a Password to Protect the PDF
To prevent unauthorized viewing or editing, you can encrypt the PDF by specifying a user password and an owner password.
# Create a ToPdfParameterList object
toPdf = ToPdfParameterList()
# Set PDF encryption passwords
userPassword = "viewer"
ownerPassword = "E-iceblue"
toPdf.PdfSecurity.Encrypt(userPassword, ownerPassword, PdfPermissionsFlags.Default, PdfEncryptionKeySize.Key128Bit)
# Save as PDF with password protection
document.SaveToFile("/HtmlToPdfWithPassword.pdf", toPdf)
2. Embed Fonts to Preserve Formatting
To ensure the PDF displays correctly across all devices, you can embed all fonts used in the document.
# Create a ToPdfParameterList object
ppl = ToPdfParameterList()
ppl.IsEmbeddedAllFonts = True
# Save as PDF with embedded fonts
document.SaveToFile("/HtmlToPdfWithEmbeddedFonts.pdf", ppl)
These options give you finer control when you convert HTML to PDF in Python, especially for professional document sharing or long-term storage scenarios.
The Conclusion
Converting HTML to PDF in Python becomes simple and flexible with Spire.Doc for Python. Whether you're handling static HTML files or dynamic HTML strings, or need to secure and customize your PDFs, this library provides everything you need — all in just a few lines of code. Get a free 30-day license and start converting HTML to high-quality PDF documents in Python today!
FAQs
Q1: Can I convert an HTML file to PDF in Python? Yes. Using Spire.Doc for Python, you can convert a local HTML file to PDF with just a few lines of code.
Q2: How do I convert HTML to PDF in Chrome? While Chrome allows manual "Save as PDF", it’s not suitable for batch or automated workflows. If you're working in Python, Spire.Doc provides a better solution for programmatically converting HTML to PDF.
Q3: How do I convert HTML to PDF without losing formatting? To preserve formatting:
- Use embedded or inline CSS (not external files).
- Use absolute URLs for images and resources.
- Embed fonts using Spire.Doc options like IsEmbeddedAllFonts(True).
A page break is a markup that divides the content of a document or spreadsheet into multiple pages for printing or display. This feature can be used to adjust the page layout of a document to ensure that each page contains the appropriate information. By placing page breaks appropriately, you can also ensure that your document is presented in a better format and layout when printed. This article will explain how to insert or remove horizontal/vertical page breaks in Excel on the Python platform by using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Insert Horizontal Page Breaks in Excel Using Python
- Insert Vertical Page Breaks in Excel Using Python
- Remove Horizontal Page Breaks from Excel Using Python
- Remove Vertical Page Breaks from Excel Using Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Insert Horizontal Page Breaks in Excel Using Python
Spire.XLS for Python supports inserting horizontal page breaks to specified cell ranges by calling Worksheet.HPageBreaks.Add(CellRange) method. The following are detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file from disk using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Insert horizontal page breaks to specified cell ranges using Worksheet.HPageBreaks.Add(CellRange) method.
- Set view mode to Preview mode by Worksheet.ViewMode property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Sample.xlsx" outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/InsertHPageBreak.xlsx" #Create a Workbook instance workbook = Workbook() #Load an Excel file from disk workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) #Get the first worksheet of this file sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] #Insert horizontal page breaks to specified cell ranges sheet.HPageBreaks.Add(sheet.Range["A12"]) sheet.HPageBreaks.Add(sheet.Range["A20"]) #Set view mode to Preview mode sheet.ViewMode = ViewMode.Preview #Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013) workbook.Dispose()
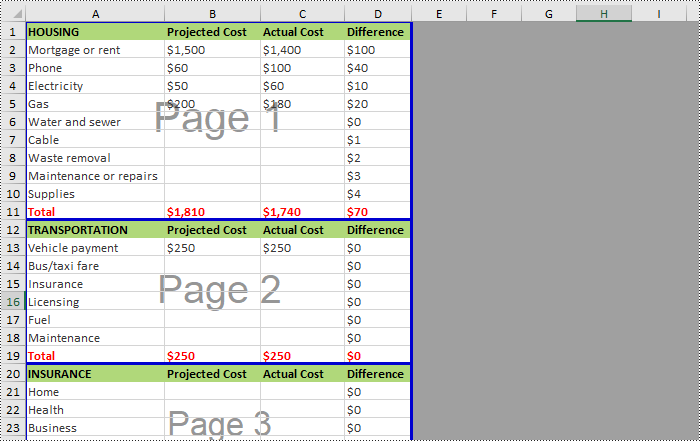
Insert Vertical Page Breaks in Excel Using Python
Spire.XLS for Python also supports inserting vertical page breaks to specified cell ranges by calling Worksheet.VPageBreaks.Add(CellRange) method. The following are detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file from disk using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Insert vertical page breaks to specified cell ranges using Worksheet.VPageBreaks.Add(CellRange) method.
- Set view mode to Preview mode using Worksheet.ViewMode property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Sample.xlsx" outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/InsertVPageBreak.xlsx" #Create a Workbook instance workbook = Workbook() #Load an Excel file from disk workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) #Get the first worksheet of this file sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] #Insert vertical page breaks to specified cell ranges sheet.VPageBreaks.Add(sheet.Range["B1"]) sheet.VPageBreaks.Add(sheet.Range["D3"]) #Set view mode to Preview mode sheet.ViewMode = ViewMode.Preview #Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013) workbook.Dispose()
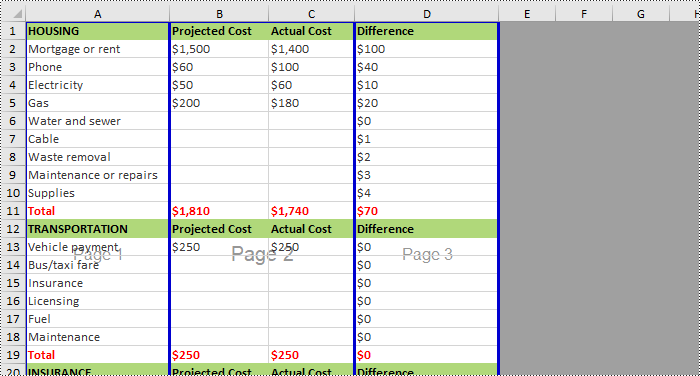
Remove Horizontal Page Breaks from Excel Using Python
If you want to remove horizontal page breaks from Excel, call the Worksheet.HPageBreaks.RemoveAt() or Worksheet.HPageBreaks.Clear() methods. The following are detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file from disk using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Remove all the horizontal page breaks by calling Worksheet.HPageBreaks.Clear() method or remove a specific horizontal page break by calling Worksheet.HPageBreaks.RemoveAt() method.
- Set view mode to Preview mode using Worksheet.ViewMode property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/InsertHPageBreak.xlsx" outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/RemoveHPageBreak.xlsx" #Create a Workbook instance workbook = Workbook() #Load an Excel file from disk workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) #Get the first worksheet from this file sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] #Clear all the horizontal page breaks #sheet.HPageBreaks.Clear() #Remove the first horizontal page break sheet.HPageBreaks.RemoveAt(0) #Set view mode to Preview mode sheet.ViewMode = ViewMode.Preview #Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013) workbook.Dispose()
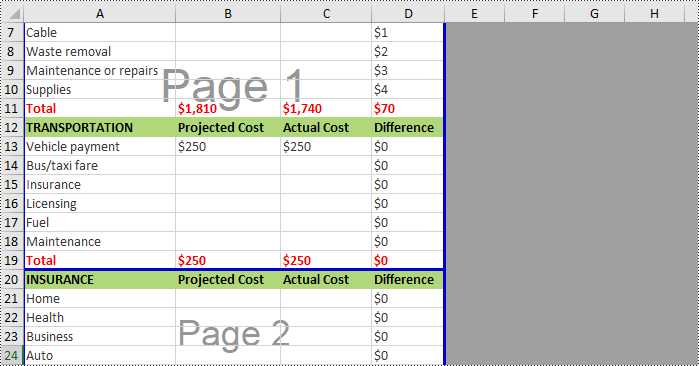
Remove Vertical Page Breaks from Excel Using Python
If you want to remove vertical page breaks from Excel, call the Worksheet.VPageBreaks.RemoveAt() or Worksheet.VPageBreaks.Clear() methods. The following are detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file from disk using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Remove all the vertical page breaks by calling Worksheet.VPageBreaks.Clear() method or remove a specific vertical page break by calling Worksheet.VPageBreaks.RemoveAt() method.
- Set view mode to Preview mode using Worksheet.ViewMode property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/InsertVPageBreak.xlsx" outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/RemoveVPageBreak.xlsx" #Create a Workbook instance workbook = Workbook() #Load an Excel file from disk workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) #Get the first worksheet from this file sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] #Clear all the vertical page breaks #sheet.VPageBreaks.Clear() #Remove the first vertical page break sheet.VPageBreaks.RemoveAt(0) #Set view mode to Preview mode sheet.ViewMode = ViewMode.Preview #Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013) workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
EPUB, short for Electronic Publication, is a widely used standard format for eBooks. It is an open and free format based on web standards, enabling compatibility with various devices and software applications. EPUB files are designed to provide a consistent reading experience across different platforms, including e-readers, tablets, smartphones, and computers. By converting your Word document to EPUB, you can ensure that your content is accessible and enjoyable to a broader audience, regardless of the devices and software they use. In this article, we will demonstrate how to convert Word documents to EPUB format in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Convert Word to EPUB in Python
The Document.SaveToFile(fileName:str, fileFormat:FileFormat) method provided by Spire.Doc for Python supports converting a Word document to EPUB format. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Save the Word document to EPUB format using Document.SaveToFile(fileName:str, fileFormat:FileFormat) method.
- Python
from spire.doc import * from spire.doc.common import * # Specify the input Word document and output EPUB file paths inputFile = "Sample.docx" outputFile = "ToEpub.epub" # Create an object of the Document class doc = Document() # Load a Word document doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Save the Word document to EPUB format doc.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.EPub) # Close the Document object doc.Close()
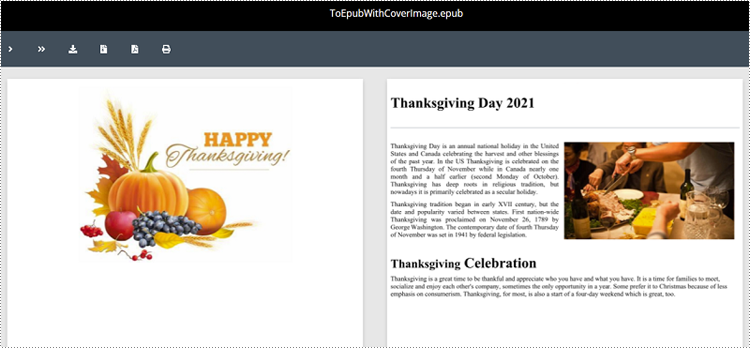
Convert Word to EPUB with a Cover Image in Python
Spire.Doc for Python enables you to convert a Word document to EPUB format and set a cover image for the resulting EPUB file by using the Document.SaveToEpub(fileName:str, coverImage:DocPicture) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create an object of the DocPicture class, and then load an image using DocPicture.LoadImage() method.
- Save the Word document as an EPUB file and set the loaded image as the cover image of the EPUB file using Document.SaveToEpub(fileName:str, coverImage:DocPicture) method.
- Python
from spire.doc import * from spire.doc.common import * # Specify the input Word document and output EPUB file paths inputFile = "Sample.docx" outputFile = "ToEpubWithCoverImage.epub" # Specify the file path for the cover image imgFile = "Cover.png" # Create a Document object doc = Document() # Load the Word document doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Create a DocPicture object picture = DocPicture(doc) # Load the cover image file picture.LoadImage(imgFile) # Save the Word document as an EPUB file and set the cover image doc.SaveToEpub(outputFile, picture) # Close the Document object doc.Close()
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
SVG files are commonly used for web graphics and vector-based illustrations because they can be scaled and adjusted easily. PDF, on the other hand, is a versatile format widely supported across different devices and operating systems. Converting SVG to PDF allows for easy sharing of graphics and illustrations, ensuring that recipients can open and view the files without requiring specialized software or worrying about browser compatibility issues. In this article, we will demonstrate how to convert SVG files to PDF format in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Convert SVG to PDF in Python
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfDocument.LoadFromSvg() method, which allows users to load an SVG file. Once loaded, users can use the PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method to save the SVG file as a PDF file. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the PdfDocument class.
- Load an SVG file using PdfDocument.LoadFromSvg() method.
- Save the SVG file to PDF format using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load an SVG file
doc.LoadFromSvg("Sample.svg")
# Save the SVG file to PDF format
doc.SaveToFile("ConvertSvgToPdf.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
# Close the PdfDocument object
doc.Close()
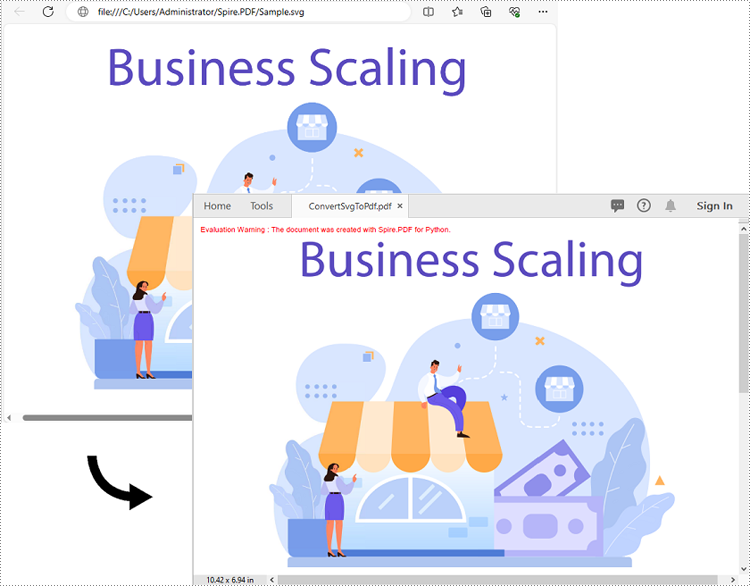
Add SVG to PDF in Python
In addition to converting SVG to PDF directly, Spire.PDF for Python also supports adding SVG files to specific locations in PDF. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the PdfDocument class.
- Load an SVG file using PdfDocument.LoadFromSvg() method.
- Create a template based on the content of the SVG file using PdfDocument. Pages[].CreateTemplate() method.
- Get the width and height of the template.
- Create another object of the PdfDocument class and load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Draw the template with a custom size at a specific location in the PDF file using PdfDocument.Pages[].Canvas.DrawTemplate() method.
- Save the result file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc1 = PdfDocument()
# Load an SVG file
doc1.LoadFromSvg("Sample.svg")
# Create a template based on the content of the SVG
template = doc1.Pages.get_Item(0).CreateTemplate()
# Get the width and height of the template
width = template.Width
height = template.Height
# Create another PdfDocument object
doc2 = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc2.LoadFromFile(""Sample.pdf"")
# Draw the template with a custom size at a specific location on the first page of the loaded PDF file
doc2.Pages.get_Item(0).Canvas.DrawTemplate(template, PointF(10.0, 100.0), SizeF(width*0.8, height*0.8))
# Save the result file
doc2.SaveToFile("AddSvgToPdf.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
# Close the PdfDocument objects
doc2.Close()
doc1.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
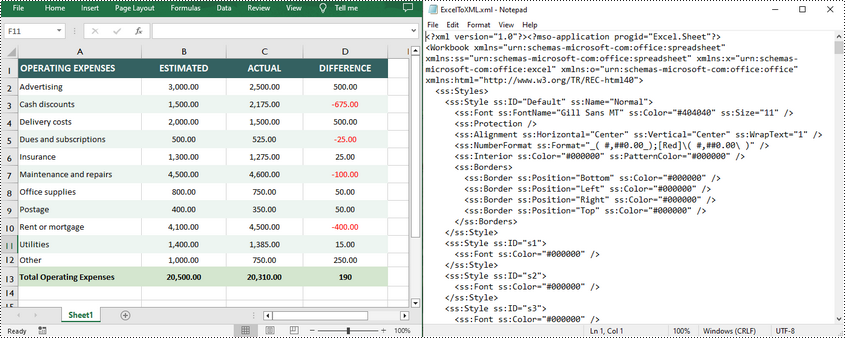
In the context of Excel, Open XML refers to the underlying file format used by Excel to store spreadsheet data, formatting, formulas, and other related information. It provides a powerful and flexible basis for working with Excel files programmatically.
By converting Excel to Open XML, developers gain greater control and automation when working with spreadsheet-related tasks. In turn, you can also generate Excel files from Open XML to take advantage of Excel's built-in capabilities to perform advanced data operations. In this article, you will learn how to convert Excel to Open XML or Open XML to Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Convert Excel to Open XML in Python
Spire.XLS for Python offers the Workbook.SaveAsXml() method to save an Excel file in Open XML format. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Save the Excel file in Open XML format using Workbook.SaveAsXml() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("sample.xlsx")
# Save the Excel file in Open XML file format
workbook.SaveAsXml("ExcelToXML.xml")
workbook.Dispose()
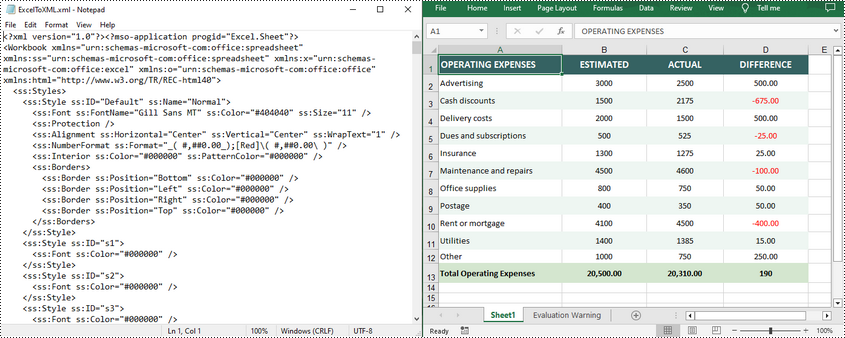
Convert Open XML to Excel in Python
To convert an Open XML file to Excel, you need to load the Open XML file through the Workbook.LoadFromXml() method, and then call the Workbook.SaveToFile() method to save it as an Excel file. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Open XML file using Workbook.LoadFromXml() method.
- Save the Open XML file to Excel using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Open XML file
workbook.LoadFromXml("ExcelToXML.xml")
# Save the Open XML file to Excel XLSX format
workbook.SaveToFile("XMLToExcel.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Comment in Excel is primarily used to add additional instructions or notes to cells. With this feature, users can add relevant content next to a specific cell to explain the data, provide contextual information, or give instructions. It also helps users to better organize and manage the data in the Excel workbook and improve the understanding and readability of the data. Spire.XLS for Python supports adding comments to Excel files. If necessary, you can also use this library to edit the content of the comments or delete unnecessary comments. In this article, we will show you how to edit or remove existing comments in Excel on Python platforms using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
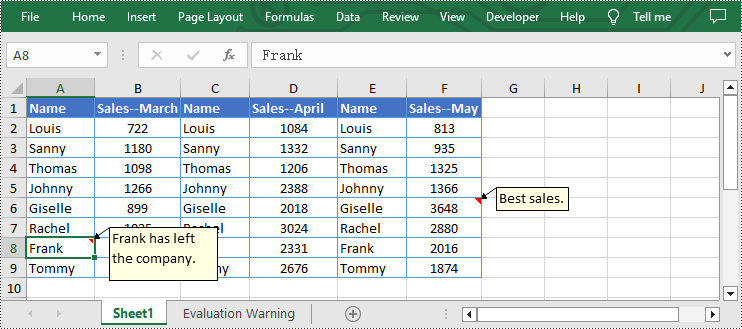
Edit Existing Comments in Excel Using Python
Spire.XLS for Python allows users to edit existing comments in Excel, including setting new text or changing comment box size. The following are detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file from disk using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first worksheet of the Excel file using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Set new text for the existing comments using Worksheet.Range[].Comment.Text property.
- Set the height and width of the existing comment by using Worksheet.Range[].Comment.Height and Worksheet.Range[].Comment.Width properties.
- Automatically adapt to the size of the comment by setting the Worksheet.Range.Comment.AutoSize property to "True".
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
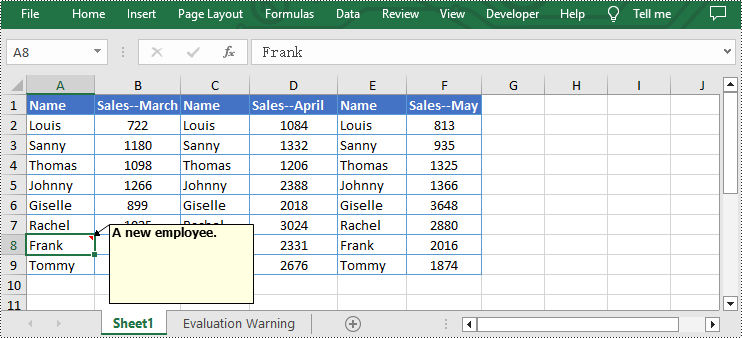
from spire.xls import * from spire.common import * inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Sample.xlsx" outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/EditExcelComment.xlsx" # Create a Workbook instance workbook = Workbook() # Load an Excel file from disk workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get the first worksheet of this file sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] # Set new text for the existing comments sheet.Range["A8"].Comment.Text = "Frank has left the company." sheet.Range["F6"].Comment.Text = "Best sales." # Set the height and width of the comment of A8 sheet.Range["A8"].Comment.Height = 60 sheet.Range["A8"].Comment.Width = 100 # Automatically adapt to the size of the comment of F6 sheet.Range["F6"].Comment.AutoSize = True # Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013) workbook.Dispose()
Remove Existing Comments from Excel Using Python
The Worksheet.Range[].Comment.Remove() method offered by Spire.XLS for Python allows users to remove a specified comment easily. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an Excel file from disk using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first worksheet of the Excel file using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Remove the comment by using Worksheet.Range[].Comment.Remove() method.
- Save the document to another file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.common import * inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Sample.xlsx" outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/RemoveExcelComment.xlsx" # Create a Workbook instance workbook = Workbook() # Load an Excel file from disk workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get the first worksheet of this file sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] # Remove the comment from the sheet sheet.Range["F6"].Comment.Remove() # Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013) workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
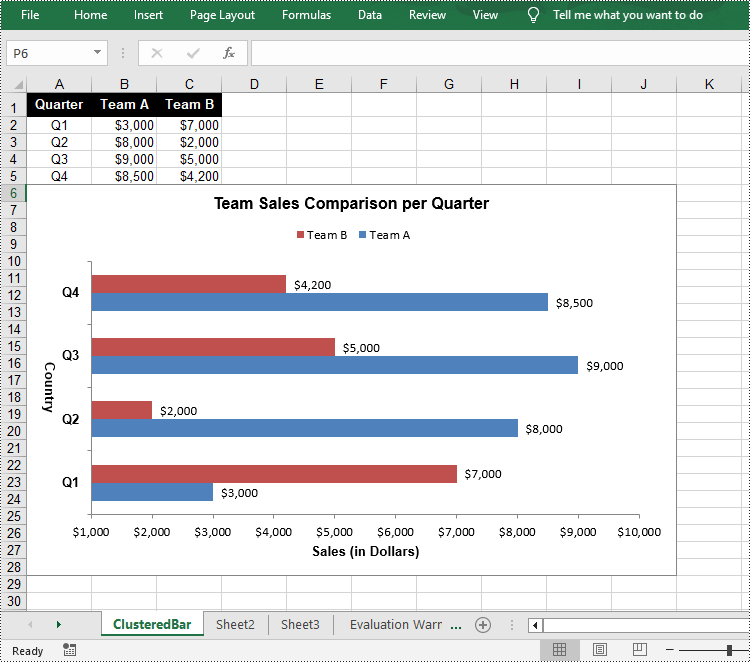
A bar chart is a type of graph that represents categorical data using rectangular bars. It is somewhat like a column chart, but with bars that extend horizontally from the Y-axis. The length of each bar corresponds to the value represented by a particular category or group, and changes, trends, or rankings can be quickly identified by comparing the lengths of the bars. In this article, you will learn how to create a clustered or stacked bar chart in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Create a Clustered Bar Chart in Excel in Python
The Worksheet.Chart.Add(ExcelChartType chartType) method provided by Spire.XLS for Python allows to add a chart to a worksheet. To add a clustered bar chart in Excel, you can set the chart type to BarClustered. The following are the steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Add chart data to specified cells and set the cell styles.
- Add a clustered bar char to the worksheet using Worksheet.Chart.Add(ExcelChartType.BarClustered) method.
- Set data range for the chart using Chart.DataRange property.
- Set position, title, category axis and value axis for the chart.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.common import *
from spire.xls import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first sheet and set its name
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
sheet.Name = "ClusteredBar"
# Add chart data to specified cells
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Quarter"
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "Q1"
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "Q2"
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "Q3"
sheet.Range["A5"].Value = "Q4"
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Team A"
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 3000
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 8000
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 9000
sheet.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 8500
sheet.Range["C1"].Value = "Team B"
sheet.Range["C2"].NumberValue = 7000
sheet.Range["C3"].NumberValue = 2000
sheet.Range["C4"].NumberValue = 5000
sheet.Range["C5"].NumberValue = 4200
# Set cell style
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].RowHeight = 18
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Color = Color.get_Black()
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.IsBold = True
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A2:A5"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["B2:C5"].Style.NumberFormat = "\"$\"#,##0"
# Add a clustered bar chart to the sheet
chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.BarClustered)
# Set data range of the chart
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:C5"]
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = False
# Set position of the chart
chart.LeftColumn = 1
chart.TopRow = 6
chart.RightColumn = 11
chart.BottomRow = 29
# Set and format chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Team Sales Comparison per Quarter"
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 12
# Set and format category axis
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Title = "Country"
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Font.IsBold = True
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.TitleArea.TextRotationAngle = 90
# Set and format value axis
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.Title = "Sales (in Dollars)"
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = False
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinValue = 1000
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = True
# Show data labels for data points
for cs in chart.Series:
cs.Format.Options.IsVaryColor = True
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = True
# Set legend position
chart.Legend.Position = LegendPositionType.Top
#Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("ClusteredBarChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
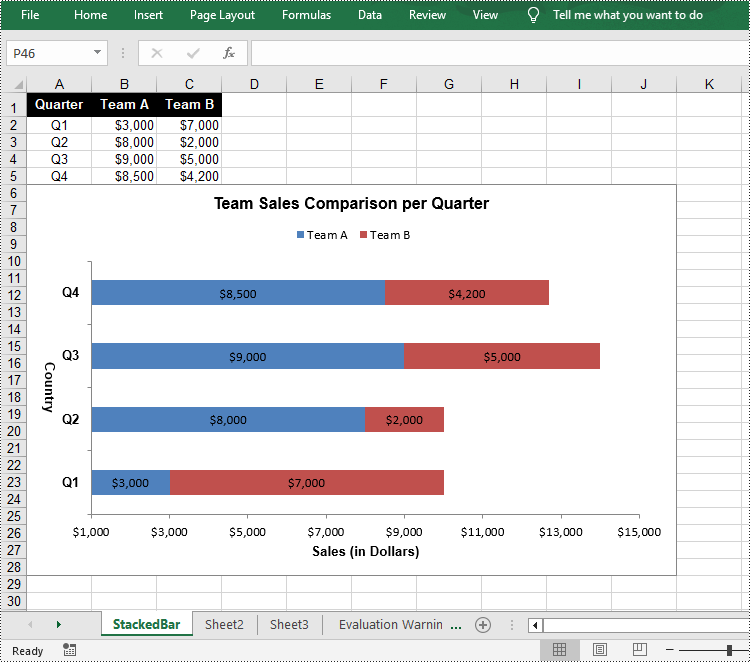
Create a Stacked Bar Chart in Excel in Python
To create a stacked bar chart, you just need to change the Excel chart type to BarStacked. The following are the steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Add chart data to specified cells and set the cell styles.
- Add a clustered bar char to the worksheet using Worksheet.Chart.Add(ExcelChartType.BarStacked) method.
- Set data range for the chart using Chart.DataRange property.
- Set position, title, category axis and value axis for the chart.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.common import *
from spire.xls import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first sheet and set its name
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
sheet.Name = "StackedBar"
# Add chart data to specified cells
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Quarter"
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "Q1"
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "Q2"
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "Q3"
sheet.Range["A5"].Value = "Q4"
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Team A"
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 3000
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 8000
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 9000
sheet.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 8500
sheet.Range["C1"].Value = "Team B"
sheet.Range["C2"].NumberValue = 7000
sheet.Range["C3"].NumberValue = 2000
sheet.Range["C4"].NumberValue = 5000
sheet.Range["C5"].NumberValue = 4200
# Set cell style
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].RowHeight = 18
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Color = Color.get_Black()
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.Font.IsBold = True
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1:C1"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A2:A5"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["B2:C5"].Style.NumberFormat = "\"$\"#,##0"
# Add a clustered bar chart to the sheet
chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.BarStacked)
# Set data range of the chart
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:C5"]
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = False
# Set position of the chart
chart.LeftColumn = 1
chart.TopRow = 6
chart.RightColumn = 11
chart.BottomRow = 29
# Set and format chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Team Sales Comparison per Quarter"
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 12
# Set and format category axis
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Title = "Country"
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Font.IsBold = True
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.TitleArea.TextRotationAngle = 90
# Set and format value axis
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.Title = "Sales (in Dollars)"
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = False
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinValue = 1000
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = True
# Show data labels for data points
for cs in chart.Series:
cs.Format.Options.IsVaryColor = True
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = True
# Set legend position
chart.Legend.Position = LegendPositionType.Top
#Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("StackedBarChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
RTF (Rich Text Format) is a versatile file format that can be opened and viewed by various word processing software. It supports a wide range of text formatting options, such as font style, size, color, tables, images, and more. When working with RTF files, you may sometimes need to convert them to PDF files for better sharing and printing, or to HTML format for publishing on the web. In this article, you will learn how to convert RTF to PDF or HTML with Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Convert RTF to PDF in Python
To convert an RTF file to PDF, simply load a file with .rtf extension and then save it as a PDF file using Document.SaveToFile(fileName, FileFormat.PDF) method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Load an RTF file using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Save the RTF file as a PDF file using Document.SaveToFile(fileName, FileFormat.PDF) method.
- Python
from spire.doc import * from spire.doc.common import * inputFile = "input.rtf" outputFile = "RtfToPDF.pdf" # Create a Document object doc = Document() # Load an RTF file from disk doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Save the RTF file as a PDF file doc.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.PDF) doc.Close()
Convert RTF to HTML in Python
Spire.Doc for Python also allows you to use the Document.SaveToFile(fileName, FileFormat.Html) method to convert the loaded RTF file to HTML format. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Load an RTF file using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Save the RTF file in HTML format using Document.SaveToFile(fileName, FileFormat.Html) method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
inputFile = "input.rtf"
outputFile = "RtfToHtml.html"
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load an RTF file from disk
doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Save the RTF file in HTML format
doc.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Html)
doc.Close()
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
PDF/A is a specialized format designed specifically for long-term archiving and preservation of electronic documents. It guarantees that the content, structure, and visual appearance of the documents remain unchanged over time. By converting PDF files to PDF/A format, you ensure the long-term accessibility of the documents, regardless of software, operating systems, or future technological advancements. Conversely, converting PDF/A files to standard PDF format makes it easier to edit, share, and collaborate on the documents, ensuring better compatibility across different applications, devices, and platforms. In this article, we will explain how to convert PDF to PDF/A and vice versa in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Convert PDF to PDF/A in Python
The PdfStandardsConverter class provided by Spire.PDF for Python supports converting PDF to various PDF/A formats, including PDF/A-1a, 2a, 3a, 1b, 2b and 3b. Moreover, it also supports converting PDF to PDF/X-1a:2001. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Specify the input file path and output folder.
- Create a PdfStandardsConverter object and pass the input file path to the constructor of the class as a parameter.
- Convert the input file to a Pdf/A-1a conformance file using PdfStandardsConverter.ToPdfA1A() method.
- Convert the input file to a Pdf/A-1b file using PdfStandardsConverter.ToPdfA1B() method.
- Convert the input file to a Pdf/A-2a file using PdfStandardsConverter.ToPdfA2A() method.
- Convert the input file to a Pdf/A-2b file using PdfStandardsConverter.ToPdfA2B() method.
- Convert the input file to a Pdf/A-3a file using PdfStandardsConverter.ToPdfA3A() method.
- Convert the input file to a Pdf/A-3b file using PdfStandardsConverter.ToPdfA3B() method.
- Convert the input file to a PDF/X-1a:2001 file using PdfStandardsConverter.ToPdfX1A2001() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import * from spire.pdf import * # Specify the input file path and output folder inputFile = "Sample.pdf" outputFolder = "Output/" # Create an object of the PdfStandardsConverter class converter = PdfStandardsConverter(inputFile) # Convert the input file to PdfA1A converter.ToPdfA1A(outputFolder + "ToPdfA1A.pdf") # Convert the input file to PdfA1B converter.ToPdfA1B(outputFolder + "ToPdfA1B.pdf") # Convert the input file to PdfA2A converter.ToPdfA2A(outputFolder + "ToPdfA2A.pdf") # Convert the input file to PdfA2B converter.ToPdfA2B(outputFolder + "ToPdfA2B.pdf") # Convert the input file to PdfA3A converter.ToPdfA3A(outputFolder + "ToPdfA3A.pdf") # Convert the input file to PdfA3B converter.ToPdfA3B(outputFolder + "ToPdfA3B.pdf") # Convert the input file to PDF/X-1a:2001 converter.ToPdfX1A2001(outputFolder + "ToPdfX1a.pdf")
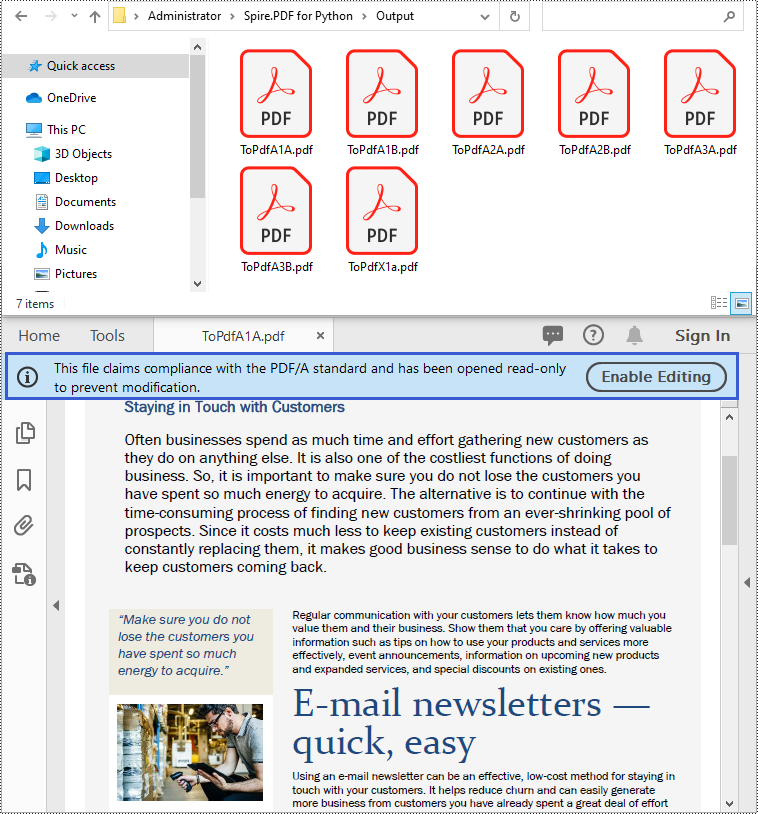
Convert PDF/A to PDF in Python
To convert a PDF/A file back to a standard PDF format, you need to create a new standard PDF file, and then draw the page content of the PDF/A file to the newly created PDF file. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF/A file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a PdfNewDocument object and set its compression level as none.
- Loop through the pages in the original PDF/A file.
- Add pages to the newly created PDF using PdfDocumentBase.Pages.Add() method.
- Draw the page content of the original PDF/A file to the corresponding pages of the newly created PDF using PdfPageBase.CreateTemplate.Draw() method.
- Create a Stream object and then save the new PDF to the stream using PdfNewDocument.Save() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Specify the input and output file paths
inputFile = "Output/ToPdfA1A.pdf"
outputFile = "PdfAToPdf.pdf"
# Create an object of the PdfDocument class
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Create a new standard PDF file
newDoc = PdfNewDocument()
newDoc.CompressionLevel = PdfCompressionLevel.none
# Add pages to the newly created PDF and draw the page content of the loaded PDF onto the corresponding pages of the newly created PDF
for i in range(doc.Pages.Count):
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(i)
size = page.Size
p = newDoc.Pages.Add(size, PdfMargins(0.0))
page.CreateTemplate().Draw(p, 0.0, 0.0)
# Save the new PDF to a PDF file
fileStream = Stream(outputFile)
newDoc.Save(fileStream)
fileStream.Close()
newDoc.Close(True)
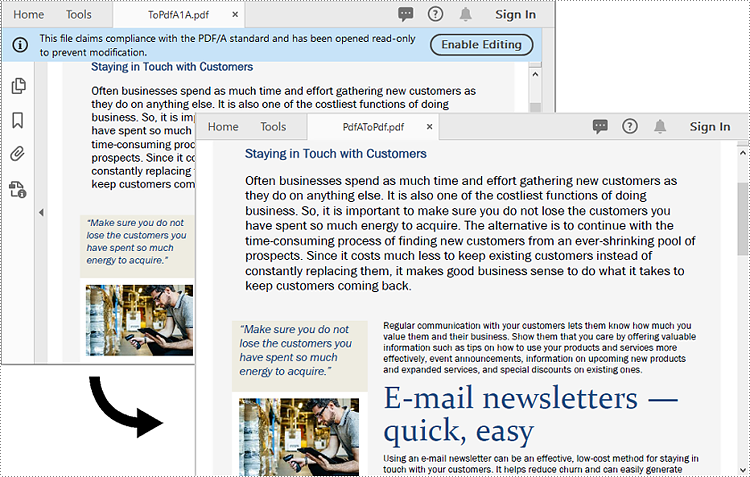
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
