
Python (355)
In Microsoft Excel, freezing panes is a practical feature that allows you to lock specific rows or columns in place while navigating through a spreadsheet. When you freeze panes, the selected rows or columns remain visible on the screen, even as you scroll through the rest of the worksheet. This feature proves especially useful when dealing with large datasets where headers, titles, or other important reference points must stay visible to provide context.
Unfreezing panes, on the other hand, allows you to release the locked rows or columns. It is beneficial when you no longer need certain sections to remain fixed and want to regain the ability to navigate the entire spreadsheet without any restrictions. In this article, we will demonstrate how to freeze and unfreeze panes in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Freeze Panes in Excel in Python
Rows and columns can be frozen by using the Worksheet.FreezePanes() method. This method takes two parameters - rowIndex (1-based) and columnIndex (1-based). The first parameter represents the index of the row above which all rows will be frozen. The second parameter represents the index of the column to the left of which all columns will be frozen.
The following steps show you how to freeze specific rows and/or columns in Excel using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Freeze specific rows and/or columns in the worksheet using Worksheet.FreezePanes(rowIndex, columnIndex) method.
- Save the result Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * # Specify the paths for the input and output Excel files inputFile = "Sample.xlsx" outputFile = "FreezePanes.xlsx" # Create a Workbook instance workbook = Workbook() # Load an Excel file workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get the first worksheet in the file sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] # Freeze specific rows and/or columns # Freeze the top row sheet.FreezePanes(2, 1) # Or freeze the first column # sheet.FreezePanes(1, 2) # Or freeze the top row and the first column # sheet.FreezePanes(2, 2) # Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013) workbook.Dispose()
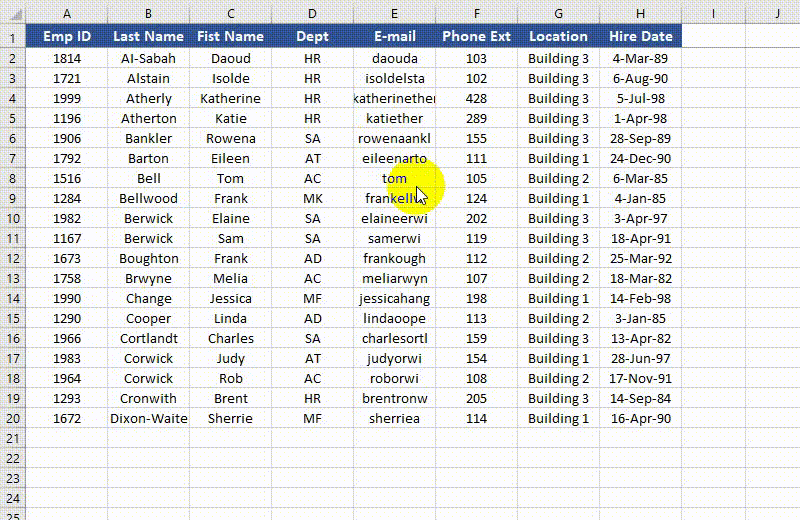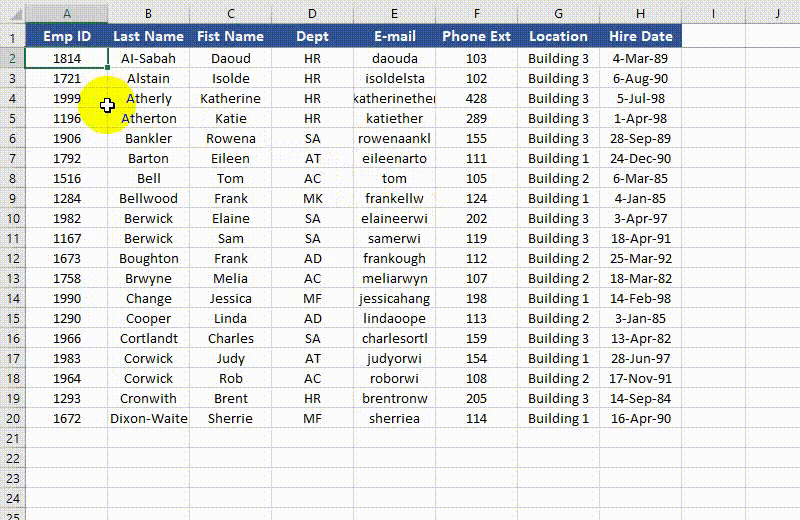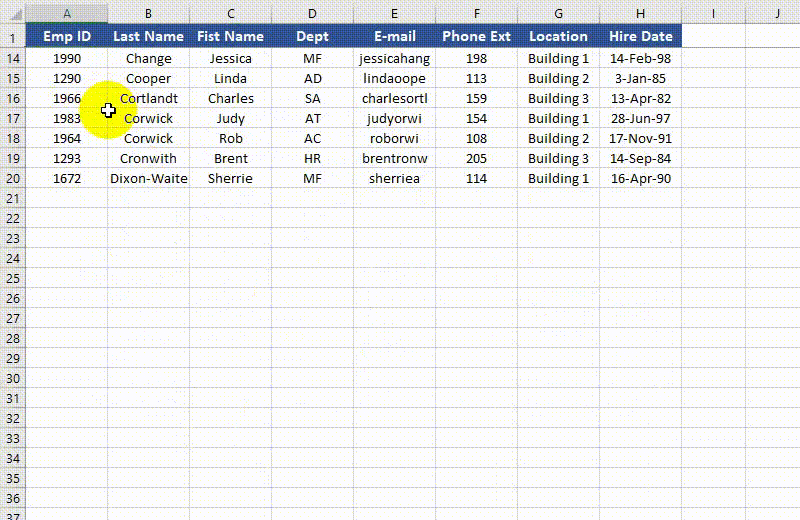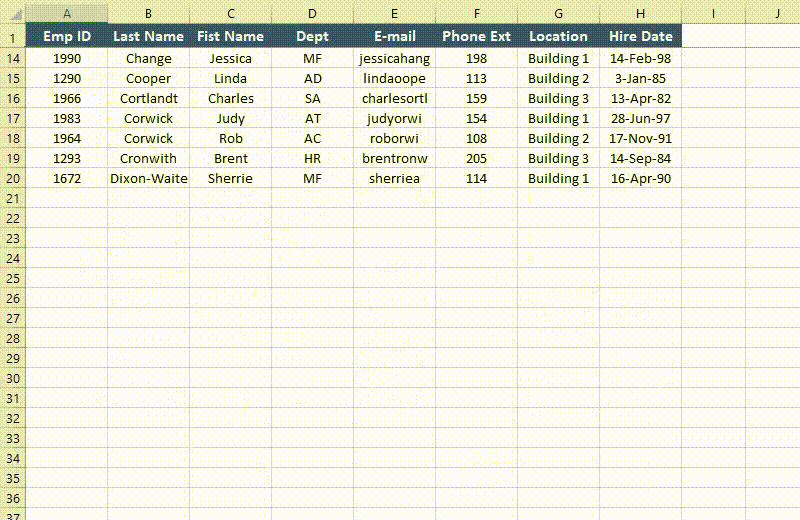
Unfreeze Panes in Excel in Python
To unfreeze rows and columns in Excel, use the Worksheet.RemovePanes() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Unfreeze rows and columns in the worksheet using Worksheet.RemovePanes() method.
- Save the result Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * # Specify the paths for the input and output Excel files inputFile = " FreezePanes.xlsx" outputFile = "UnfreezePanes.xlsx" # Create a Workbook instance workbook = Workbook() # Load an Excel file workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get the first worksheet in the file sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] # Unfreeze rows and/or columns in the worksheet sheet.RemovePanes() # Save the result file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013) workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Efficiently managing Word documents often requires the task of splitting them into smaller sections. However, manually performing this task can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. Fortunately, Spire.Doc for Python provides a convenient and efficient way to programmatically segment Word documents, helping users to extract specific parts of a document, split lengthy documents into smaller chunks, and streamline data extraction. This article demonstrates how to use Spire.Doc for Python to split a Word document into multiple documents in Python.
The splitting of a Word document is typically done by page breaks and section breaks due to the dynamic nature of document content. Therefore, this article focuses on the following two parts:
- Split a Word Document by Page Breaks with Python
- Split a Word Document by Section Breaks with Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Split a Word Document by Page Breaks with Python
Page breaks allow for the forced pagination of a document, thereby achieving a fixed division of content. By using page breaks as divisions, we can split a Word document into smaller content-related documents. The detailed steps for splitting a Word document by page breaks are as follows:
- Create an instance of Document class and load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a new document, add a section to it using Document.AddSection() method.
- Iterate through all body child objects in each section in the original document and check if the child object is a paragraph or a table.
- If the child object is a table, add it to the section in the new document using Section.Body.ChildObjects.Add() method.
- If the child object is a paragraph, add the paragraph object to the section in the new document. Then, iterate through all child objects of the paragraph and check if a child object is a page break.
- If the child object in the paragraph is a page break, get its index using Paragraph.ChildObjects.IndexOf() method and remove it from the paragraph by its index.
- Save the new document using Document.SaveToFile() method and repeat the above process.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
inputFile = "Sample.docx"
outputFolder = "output/SplitDocument/"
# Create an instance of Document
original = Document()
# Load a Word document
original.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Create a new word document and add a section to it
newWord = Document()
section = newWord.AddSection()
original.CloneDefaultStyleTo(newWord)
original.CloneThemesTo(newWord)
original.CloneCompatibilityTo(newWord)
index = 0
# Iterate through all sections of original document
for m in range(original.Sections.Count):
sec = original.Sections.get_Item(m)
# Iterate through all body child objects of each section
for k in range(sec.Body.ChildObjects.Count):
obj = sec.Body.ChildObjects.get_Item(k)
if isinstance(obj, Paragraph):
para = obj if isinstance(obj, Paragraph) else None
sec.CloneSectionPropertiesTo(section)
# Add paragraph object in original section into section of new document
section.Body.ChildObjects.Add(para.Clone())
for j in range(para.ChildObjects.Count):
parobj = para.ChildObjects.get_Item(j)
if isinstance(parobj, Break) and ( parobj if isinstance(parobj, Break) else None).BreakType == BreakType.PageBreak:
# Get the index of page break in paragraph
i = para.ChildObjects.IndexOf(parobj)
# Remove the page break from its paragraph
section.Body.LastParagraph.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(i)
# Save the new document
resultF = outputFolder
resultF += "SplitByPageBreak-{0}.docx".format(index)
newWord.SaveToFile(resultF, FileFormat.Docx)
index += 1
# Create a new document and add a section
newWord = Document()
section = newWord.AddSection()
original.CloneDefaultStyleTo(newWord)
original.CloneThemesTo(newWord)
original.CloneCompatibilityTo(newWord)
sec.CloneSectionPropertiesTo(section)
# Add paragraph object in original section into section of new document
section.Body.ChildObjects.Add(para.Clone())
if section.Paragraphs[0].ChildObjects.Count == 0:
# Remove the first blank paragraph
section.Body.ChildObjects.RemoveAt(0)
else:
# Remove the child objects before the page break
while i >= 0:
section.Paragraphs[0].ChildObjects.RemoveAt(i)
i -= 1
if isinstance(obj, Table):
# Add table object in original section into section of new document
section.Body.ChildObjects.Add(obj.Clone())
# Save the document
result = outputFolder+"SplitByPageBreak-{0}.docx".format(index)
newWord.SaveToFile(result, FileFormat.Docx2013)
newWord.Close()
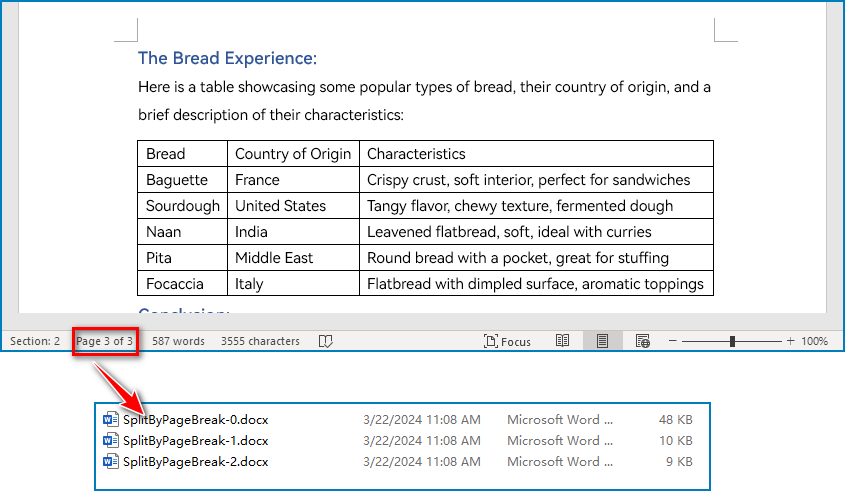
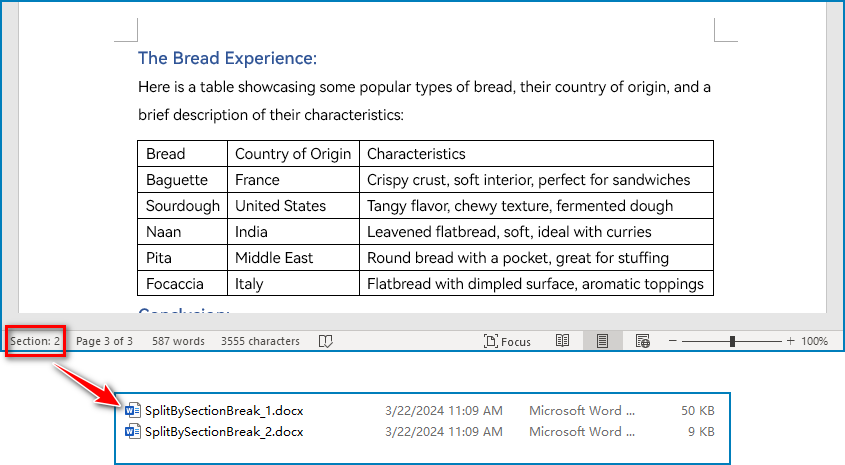
Split a Word Document by Section Breaks with Python
Sections divide a Word document into different logical parts and allow for independent formatting for each section. By splitting a Word document into sections, we can obtain multiple documents with relatively independent content and formatting. The detailed steps for splitting a Word document by section breaks are as follows:
- Create an instance of Document class and load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through each section in the document.
- Get a section using Document.Sections.get_Item() method.
- Create a new Word document and copy the section in the original document to the new document using Document.Sections.Add() method.
- Save the new document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an instance of Document class
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Iterate through all sections
for i in range(document.Sections.Count):
section = document.Sections.get_Item(i)
result = "output/SplitDocument/" + "SplitBySectionBreak_{0}.docx".format(i+1)
# Create a new Word document
newWord = Document()
# Add the section to the new document
newWord.Sections.Add(section.Clone())
#Save the new document
newWord.SaveToFile(result)
newWord.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Excel files often contain sensitive and confidential information, such as financial data, personal information, trade secrets, or proprietary formulas. When sharing these files over the internet or between organizations, there might be a risk of data leaks, theft, or unauthorized modifications. To address this concern, Excel provides a comprehensive set of protection features, such as password-protecting workbooks, restricting editing on worksheets, and locking cells, which enable users to establish multiple layers of security to control data access and maintain the integrity of their Excel files. In this article, you will learn how to protect and unprotect Excel workbooks and worksheets in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Password Protect an Entire Workbook
- Protect a Worksheet with a Specific Protection Type
- Allow Users to Edit Ranges in a Protected Worksheet
- Unprotect a Password Protected Worksheet
- Remove or Reset the Password of an Encrypted Workbook
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Password Protect an Entire Workbook in Python
By encrypting an Excel document with a password, you ensure that the data within the document remains secure and inaccessible to unauthorized individuals. The following are the steps to password-protect a workbook using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Protect the workbook with a password using Workbook.Protect() method.
- Save the workbook to another Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel workbook
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Protect the workbook with a password
workbook.Protect("psd-123")
# Save the workbook to another Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("Encrypted.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
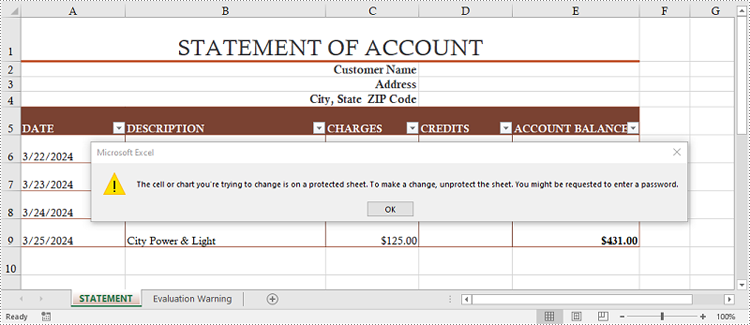
Protect a Worksheet with a Specific Protection Type in Python
If you want to authorize others to view your Excel document while limiting the types of changes they can make to a worksheet, you can protect the worksheet with a specific protection type. The table below lists a variety of pre-defined protection types under the SheetProtectionType enumeration.
| Protection Type | Allow users to |
| Content | Modify or insert content. |
| DeletingColumns | Delete columns. |
| DeletingRows | Delete rows. |
| Filtering | Set filters. |
| FormattingCells | Format cells. |
| FormattingColumns | Format columns. |
| FormattingRows | Format rows. |
| InsertingColumns | Insert columns. |
| InsertingRows | Insert rows. |
| InsertingHyperlinks | Insert hyperlinks . |
| LockedCells | Select locked cells. |
| UnlockedCells | Select unlocked cells. |
| Objects | Modify drawing objects. |
| Scenarios | Modify saved scenarios. |
| Sorting | Sort data. |
| UsingPivotTables | Use pivot table and pivot chart. |
| All | Do any operations listed above on the protected worksheet. |
| none | Do nothing on the protected worksheet. |
The following steps show you how to protect a worksheet with a specific protection type using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Protect the worksheet with a password and a specific protection type using Worksheet.Protect(password:str, options:SheetProtectionType) method.
- Save the workbook to another Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel workbook
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Protect the worksheet with a password and a specific protection type
worksheet.Protect("psd-permission", SheetProtectionType.none)
# Save the workbook to another Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("ProtectWorksheet.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Allow Users to Edit Ranges in a Protected Worksheet in Python
In certain cases, you may want to allow users to edit certain ranges of a worksheet while preserving the integrity of other data. The following steps demonstrate how to accomplish this feature using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Specify editable cell ranges using Worksheet.AddAllowEditRange() method.
- Protect the worksheet with a password and a specific protection type using Worksheet.Protect(password:str, options:SheetProtectionType) method.
- Save the workbook to another Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel workbook
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Add ranges that allow editing
sheet.AddAllowEditRange("Range One", sheet.Range["A5:A6"])
sheet.AddAllowEditRange("Range Two", sheet.Range["A8:B11"])
# Protect the worksheet with a password and a protection type
sheet.Protect("psd-permission", SheetProtectionType.All)
# Save the workbook to another Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("AllowEditRange.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Unprotect a Password Protected Worksheet in Python
To remove the protection of a password-protected worksheet, you need to invoke the Worksheet.Unprotect() method and pass the original password to the method as a parameter. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Remove the password protection using Worksheet.Unprotect(password:str) method.
- Save the workbook to another Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel workbook containing protected worksheet
workbook.LoadFromFile("ProtectWorksheet.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Unprotect the worksheet using the specified password
sheet.Unprotect("psd-permission")
# Save the workbook to another Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("UnprotectWorksheet.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
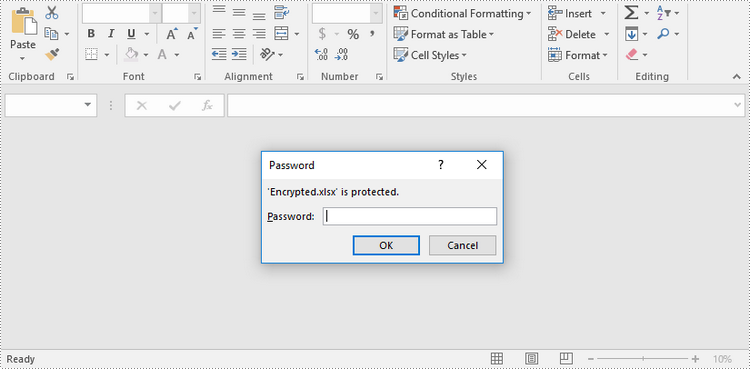
Remove or Reset the Password of an Encrypted Workbook in Python
To remove or reset password of an encrypted workbook, you can use the Workbook.Unprotect() or the Workbook.Protect() method. The following steps show you how to load an encrypted Excel document and delete or change the password of it.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Specify the open password through Workbook.OpenPassword property.
- Load the encrypted Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove the encryption using Workbook.Unprotect() method. Or change the password using Workbook.Protect() method.
- Save the workbook to another Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Specify the open password
workbook.OpenPassword = "psd-123"
# Load an encrypted Excel workbook
workbook.LoadFromFile("Encrypted.xlsx")
# Unprotect the workbook
workbook.UnProtect()
# Reset password
# workbook.Protect("newpassword")
# Save the workbook to another Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("UnprotectWorkbook.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Excel’s AutoFilter feature is a powerful tool that allows you to quickly filter worksheet data based on specific criteria. When applying auto filter to a range of cells, you can display only those rows that meet certain conditions and hide the rest of the data.
However, while filters simplify workflows, knowing how to remove auto filters in Excel is equally critical to maintaining accurate, accessible, and error-free datasets. In this article, you will learn how to add or remove AutoFilters in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python library.
- Installation Guide for Spire.XLS for Python
- How to Use Excel Auto Filters in Python
- How to Remove Auto Filters in Excel
- Conclusion
Installation Guide for Spire.XLS for Python
Spire.XLS for Python is a robust library that enables developers to automate AutoFilter operations in Excel, including adding or removing auto filters.
To install the Python library, open your terminal or command prompt and run the following:
pip install Spire.XLSThe pip tool will search for the latest version of the Spire.XLS library on the Python Package Index (PyPI) and then download and install it along with any necessary dependencies.
How to Use Excel Auto Filters in Python
Add AutoFilter in Excel in Python
Excel AutoFilter can be applied to entire columns or specified cell ranges. The following are the core properties used:
- Worksheet.AutoFilters property: Gets a collection of auto filters in the worksheet, and return an AutoFiltersCollection object.
- AutoFiltersCollection.Range property: Specify the cell range to be filtered.
Code Example:
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
inputFile = "Data.xlsx"
outputFile = "ExcelAutoFilter.xlsx"
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Create an AutoFilter in the sheet and specify the range to be filtered
sheet.AutoFilters.Range = sheet.Range["A1:C1"]
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()Result: Dropdown arrows appear in the header row for filtering.
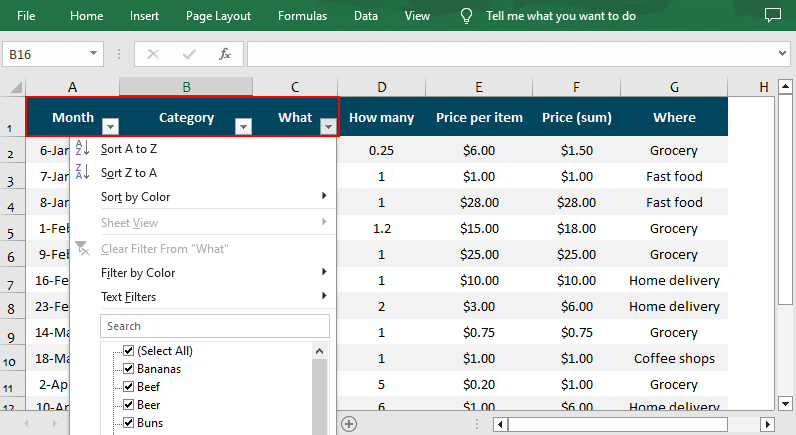
Different Excel Filter Types in Spire.XLS
The AutoFiltersCollection class of the Spire.XLS for Python library offers various methods for you to filter data in Excel in different ways. Check below for the details:
| Filters | Details |
| Filter text data | Use the AddFilter() to filter cells that contain specified text content. |
| Filter dates | Use the AddDateFilter() method to filter dates associated with the specified year/month/date, etc. |
| Filter blank / non-blank cells |
|
| Filter by color |
|
| Custom filter | Use the CustomFilter() method to filter by the custom criteria. |
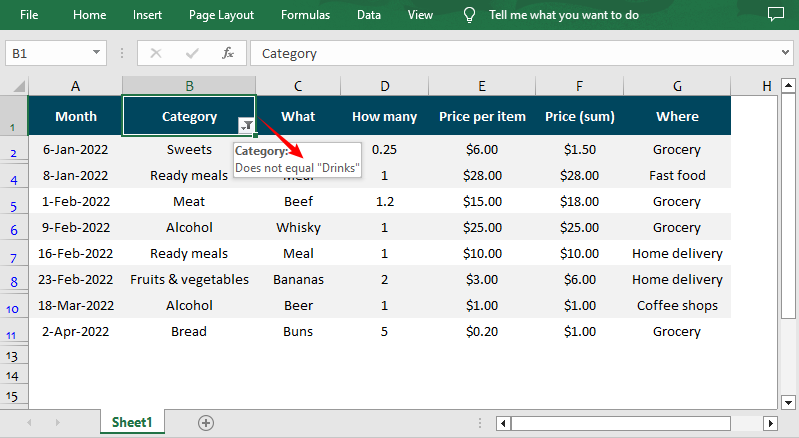
Apply Custom Auto Filter in Excel in Python
After adding one of the above filters, you can use the AutoFiltersCollection.Filter() method to apply the filter within the given range. The following is a code example of applying a custom AutoFilter to filter data that is not equal to the specified text string.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
inputFile = "Data.xlsx"
outputFile = "CustomFilter.xlsx"
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
#Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
#Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Create an auto filter in the sheet and specify the range to be filtered
sheet.AutoFilters.Range = sheet.Range["B1:B12"]
# Get the column to be filtered
filtercolumn = sheet.AutoFilters[0]
# Add a custom filter to filter data that does not contain the string "Drinks"
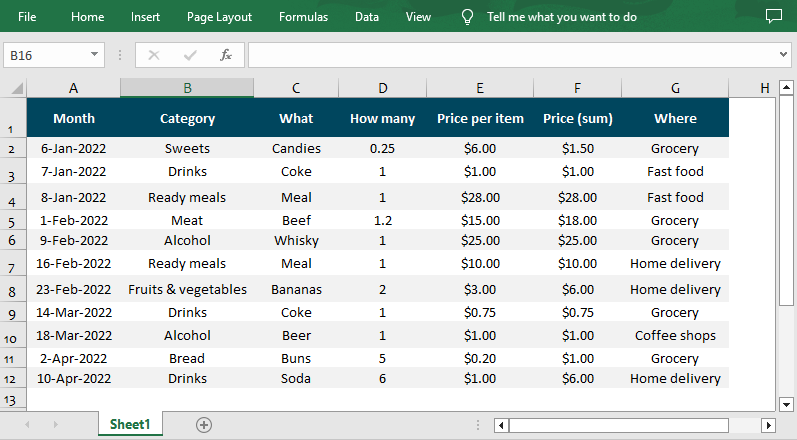
strCrt = String("Drinks")
sheet.AutoFilters.CustomFilter(filtercolumn , FilterOperatorType.NotEqual, strCrt)
# Apply the filter
sheet.AutoFilters.Filter()
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()Result: Only cells that are not equal to the string “Drinks” are visible.
How to Remove Auto Filters in Excel in Python
AutoFilters are great for focusing on specific data, but leaving them active can lead to critical issues. Removing auto filters ensures:
- Full data disclosure: All rows/columns are visible.
- Consistent formatting: Eliminates dropdown arrows for a cleaner look.
- Avoid confusion: Prevents recipients from misinterpreting filtered data as the complete dataset.
Spire.XLS for Python provides the AutoFiltersCollection.Clear() method to remove or delete all AutoFilters from an Excel worksheet. Here’s the complete code example:
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
inputFile = "CustomFilter.xlsx"
outputFile = "RemoveAutoFilter.xlsx"
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Delete AutoFilter from the sheet
sheet.AutoFilters.Clear()
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()Result: All rows are visible, and AutoFilter dropdowns are removed.
Conclusion
With Spire.XLS for Python, adding or removing auto filters in Excel becomes a seamless, automated process. This guide covered installation, basic and custom filters, and code examples to help you streamline data tasks. For more advanced features, explore the Python Excel library’s full documentation.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.XLS for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Protecting valuable and sensitive information from unauthorized access is a crucial task for individuals and organizations alike. When it comes to sharing and storing confidential Word documents, such as financial records, legal documents, or personal records, encrypting the documents provides extra protection for their security and confidentiality. Moreover, using Python, users can easily encrypt large numbers of Word documents. This article shows how to use Spire.Doc for Python to encrypt Word documents in Python programs.
- Encrypt a Word Document with a Password
- Change the Password of a Word Document
- Remove the Encryption from a Word Document
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Encrypt a Word Document with a Password
Using the Document.Encrypt(password: str) method provided by Spire.Doc for Python, developers can set an open password for a Word document, ensuring that only authorized people can open and view the document. The detailed steps for encrypting a Word document with a password are as follows:
- Create an instance of Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Encrypt the document using Document.Encrypt() method.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an instance of Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Encrypt the document
doc.Encrypt("password")
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/EncryptedDocument.docx")
doc.Close()
Change the Encryption from a Word Document
By passing the password as the parameter, developers can load an encrypted document using Document.LoadFromFile(fileName: str, fileFormat: FileFormat, password: str) method. After loading the encrypted document, the Document.Encrypt() method can be used to set a new password. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an instance of Document class.
- Load an encrypted Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Change the password of the document using Document.Encrypt() method.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an instance of Document class
doc = Document()
# Load an encrypted Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("output/EncryptedDocument.docx", FileFormat.Docx, "password")
# Change the password
doc.Encrypt("password1")
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/ChangeDocument.docx")
doc.Close()
Remove the Password from a Word Document
After loading an encrypted Word document, developers can also use Document.RemoveEncryption() method to remove the encryption from the document directly, thus making the document available to all users. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an instance of Document class.
- Load an encrypted Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove the password using Document.RemoveEncryption() method.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an instance of Document class
doc = Document()
# Load an encrypted Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("output/EncryptedDocument.docx", FileFormat.Auto, "password")
# Remove the password
doc.RemoveEncryption()
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/RemovePassword.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
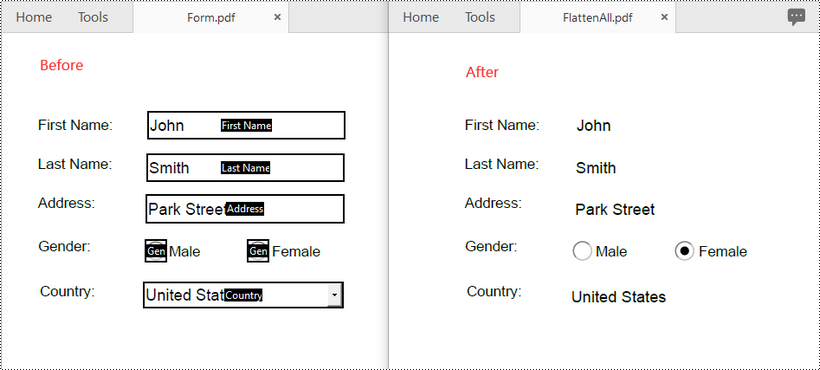
Flattening forms in PDF means transforming the interactive form fields (such as text boxes, checkboxes, and drop-down menus) into static content. Once a form is flattened, it cannot be edited or filled out anymore. When you need to maintain a permanent and unalterable record of a completed form, flattening is essential. This ensures that the data entered into the form fields cannot be modified or tampered with, providing a reliable reference for future use. In this article, we will demonstrate how to flatten forms in PDF in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Flatten All Forms in a PDF in Python
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfDocument.Form.IsFlatten property, which enables you to flatten all forms in a PDF file. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the PdfDocument class.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Flatten all forms in the PDF file by setting the PdfDocument.Form.IsFlatten property to True.
- Save the result file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import * from spire.pdf import * # Specify the input and output PDF file paths input_file = "Form.pdf" output_file = "FlattenAll.pdf" # Create an object of the PdfDocument class doc = PdfDocument() # Load a PDF file doc.LoadFromFile(input_file) # Flatten all forms in the PDF file doc.Form.IsFlatten = True # Save the result file doc.SaveToFile(output_file) doc.Close()
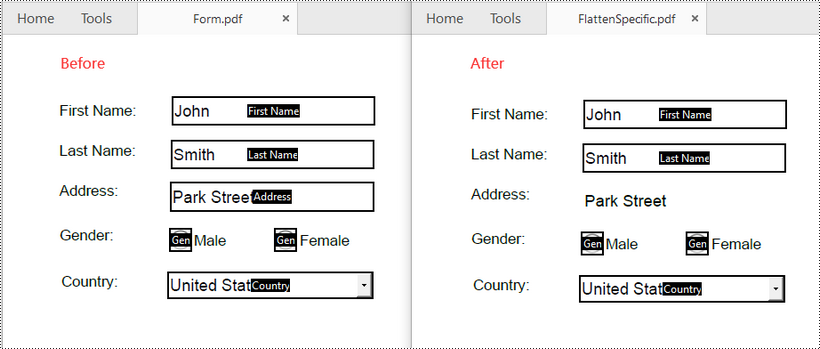
Flatten a Specific Form in a PDF in Python
To flatten a specific form in a PDF file, you can use the PdfField.Flatten property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the PdfDocument class.
- Load a PDF file using the PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the forms of the PDF file using PdfDocument.Form property.
- Get a specific form by its index or name using PdfFormWidget.FieldsWidget.get_Item() method.
- Flatten the form by setting the PdfField.Flatten property to True.
- Save the result file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Specify the input and output PDF file paths
input_file = "Form.pdf"
output_file = "FlattenSpecific.pdf"
# Create an object of the PdfDocument class
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile(input_file)
# Get the forms of the PDF file
loadedForm = doc.Form
# Get a specific form by its index or name
formWidget = PdfFormWidget(loadedForm)
form = formWidget.FieldsWidget.get_Item(2)
# form = formWidget.FieldsWidget.get_Item("Address")
# Flatten the specific form
form.Flatten = True
# Save the result file
doc.SaveToFile(output_file)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Create a Pie Chart or a Doughnut Chart in PowerPoint
2024-03-19 01:13:26 Written by AdministratorPie charts and doughnut charts are two popular types of data visualization tools that are widely used to show the proportional distribution of categories within the whole. Both charts can serve as powerful communication aids, allowing viewers to quickly grasp the significance of each component and how it relates to the overall picture.
While pie charts and doughnut charts share many similarities, they also have unique characteristics that make them suitable for different analytical scenarios. In this article, you will learn how to create a pie chart or a doughnut chart in PowerPoint with Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Create a Pie Chart in PowerPoint with Python
Pie charts are designed to resemble a circle, which is divided into sections or "slices", with each slice representing a portion of the whole.
With Spire.Prensetion for Python, you can add a pie chart to a presentation slide using the ISlide.Shapes.AppendChartInit(type: ChartType, rectangle: RectangleF, init: bool) method and specify the chart type as Pie. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Presentation instance.
- Get the first slide using Prenstion.Slides[] property.
- Add a pie chart at a specified location on the side using ISlide.Shapes.AppendChartInit(type: ChartType, rectangle RectangleF, init bool).
- Set and format the chart title.
- Define some data and append the data to the chart sheet as chart data using IChart.ChartData property.
- Set series labels, category labels, series values and other attributes using the properties of the IChart class.
- Set to show label value and percentage value.
- Save the result file using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation instance
presentation = Presentation()
# Add a pie chart at a specified location on the first slide
rect = RectangleF.FromLTRB (40, 100, 590, 420)
chart = presentation.Slides[0].Shapes.AppendChartInit (ChartType.Pie, rect, False)
# Set and format chart title
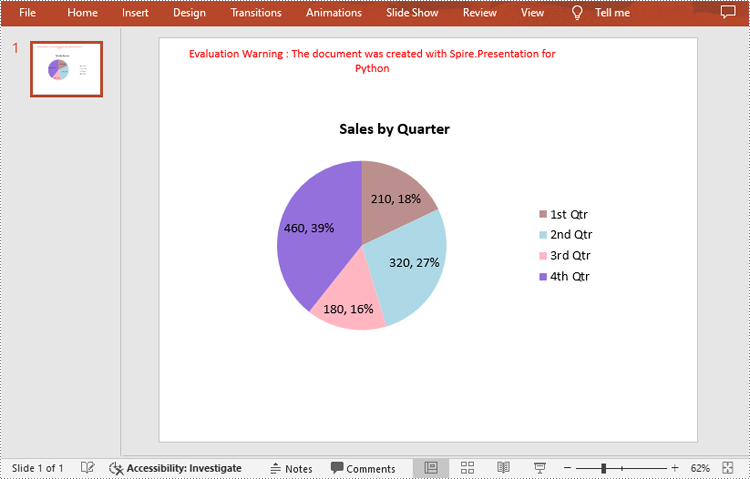
chart.ChartTitle.TextProperties.Text = "Sales by Quarter"
chart.ChartTitle.TextProperties.IsCentered = True
chart.ChartTitle.Height = 30
chart.HasTitle = True
# Define some data
quarters = ["1st Qtr", "2nd Qtr", "3rd Qtr", "4th Qtr"]
sales = [210, 320, 180, 460]
# Append data to ChartData, which represents a data table where the chart data is stored
chart.ChartData[0,0].Text = "Quarters"
chart.ChartData[0,1].Text = "Sales"
i = 0
while i < len(quarters):
chart.ChartData[i + 1,0].Text = quarters[i]
chart.ChartData[i + 1,1].NumberValue = sales[i]
i += 1
# Set series labels and category labels
chart.Series.SeriesLabel = chart.ChartData["B1","B1"]
chart.Categories.CategoryLabels = chart.ChartData["A2","A5"]
# Set values for series
chart.Series[0].Values = chart.ChartData["B2","B5"]
# Add data points to series
for i, unusedItem in enumerate(chart.Series[0].Values):
cdp = ChartDataPoint(chart.Series[0])
cdp.Index = i
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.Add(cdp)
# Fill each data point with a different color
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.get_Item(0).Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.get_Item(0).Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_RosyBrown()
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.get_Item(1).Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.get_Item(1).Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_LightBlue()
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.get_Item(2).Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.get_Item(2).Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_LightPink()
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.get_Item(3).Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.get_Item(3).Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_MediumPurple()
# Set the data labels to display label value and percentage value
chart.Series[0].DataLabels.LabelValueVisible = True
chart.Series[0].DataLabels.PercentValueVisible = True
# Save the result file
presentation.SaveToFile("CreatePieChart.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
presentation.Dispose()
Create a Doughnut Chart in PowerPoint with Python
Doughnut charts are very similar to pie charts, with the primary difference being the presence of a "hole" in the center. This hole can be used to display additional information or to maintain a cleaner look.
To add a donut chart to a presentation slide, you can specify the ChartType parameter of ISlide.Shapes.AppendChartInit() method as Doughnut. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Presentation instance.
- Get the first slide using Prenstion.Slides[] property.
- Add a doughnut chart at a specified location on the side using ISlide.Shapes.AppendChartInit(type: ChartType, rectangle: RectangleF, init: bool).
- Define some data and append the data to the chart sheet as chart data using IChart.ChartData property.
- Set series labels, category labels, series values and other attributes using the properties of the IChart class.
- Set to show label value and percentage value.
- Save the result file using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation instance
presentation = Presentation()
# Add a doughnut chart at a specified location on the first slide
rect = RectangleF.FromLTRB (80, 100, 630, 420)
chart = presentation.Slides[0].Shapes.AppendChartInit(ChartType.Doughnut, rect, False)
# Set and format chart title
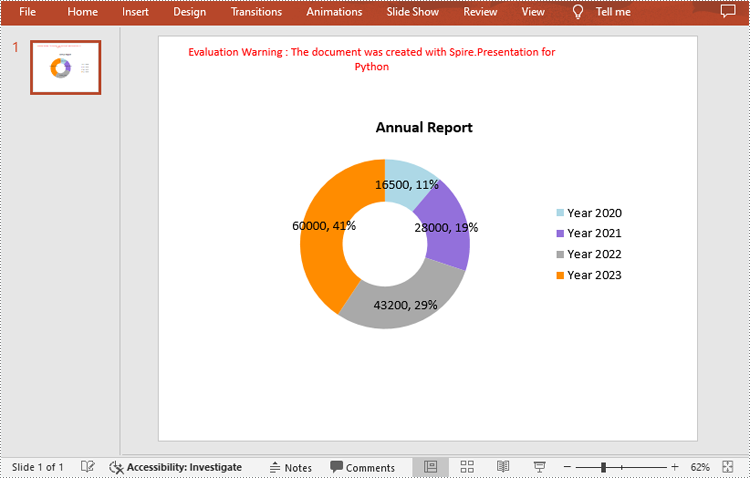
chart.ChartTitle.TextProperties.Text = "Annual Report"
chart.ChartTitle.TextProperties.IsCentered = True
chart.ChartTitle.Height = 30
# Define some data
years = ["Year 2020", "Year 2021", "Year 2022", "Year 2023"]
sales = [16500, 28000, 43200, 60000]
# Append data to ChartData, which represents a data table where the chart data is stored
chart.ChartData[0,0].Text = "Quarters"
chart.ChartData[0,1].Text = "Sales"
i = 0
while i < len(years):
chart.ChartData[i + 1,0].Text = years[i]
chart.ChartData[i + 1,1].NumberValue = sales[i]
i += 1
# Set series labels and category labels
chart.Series.SeriesLabel = chart.ChartData["B1","B1"]
chart.Categories.CategoryLabels = chart.ChartData["A2","A5"]
# Set values for series
chart.Series[0].Values = chart.ChartData["B2","B5"]
# Add data points to series
for i, item in enumerate(chart.Series[0].Values):
cdp = ChartDataPoint(chart.Series[0])
cdp.Index = i
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.Add(cdp)
# Fill each data point with a different color
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.get_Item(0).Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.get_Item(0).Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_LightBlue()
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.get_Item(1).Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.get_Item(1).Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_MediumPurple()
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.get_Item(2).Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.get_Item(2).Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_DarkGray()
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.get_Item(3).Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
chart.Series[0].DataPoints.get_Item(3).Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_DarkOrange()
# Set the data labels to display label value and percentage value
chart.Series[0].DataLabels.LabelValueVisible = True
chart.Series[0].DataLabels.PercentValueVisible = True
# Set the hole size of the doughnut chart
chart.Series[0].DoughnutHoleSize = 50
# Save the result file
presentation.SaveToFile("DoughnutChart.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
presentation.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Typically, the content of a PDF document needs to follow a logical flow, such as a report is usually structured with chapters, sections, and subsections. When the pages within a PDF are not arranged in the correct sequence, the coherence of the document will be affected. By reordering the pages, you can ensure that the information is presented in a clear and understandable manner. In this article, you will learn how to reorder the pages in a PDF file with Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Reorder PDF Pages with Python
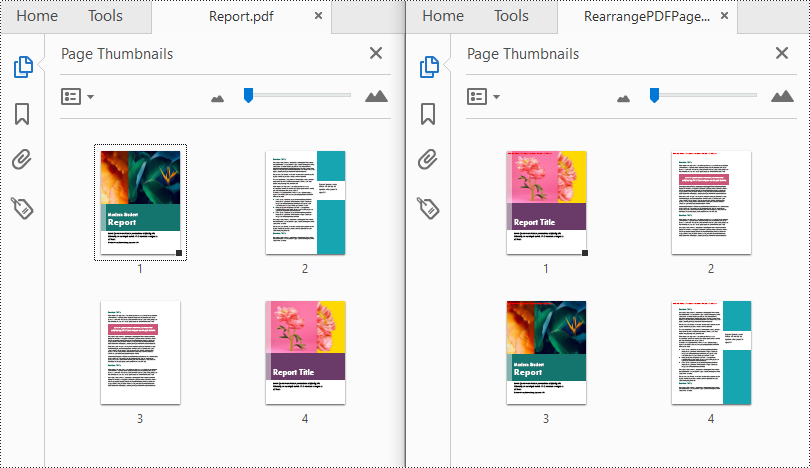
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfDocument.Pages.ReArrange(orderArray: List[int]) method to rearrange the pages in a PDF file. The parameter orderArray is a list of integers which allows you to reorder the PDF pages by specifying the page index in the desired order.
The following are the detailed steps to rearrange the PDF page order with Python:
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a sample PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Rearrange the page order of the PDF file using PdfDocument.Pages.ReArrange(orderArray: List[int]) method.
- Save the result file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import * from spire.pdf import * inputFile = "Report.pdf" outputFile = "RearrangePDFPageOrder.pdf" # Create a PdfDocument instance pdf = PdfDocument() # Load a PDF file pdf.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Reorder pages in the PDF file pdf.Pages.ReArrange([3, 2, 0, 1]) # Save the result file pdf.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.PDF) pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Set the Background Color and Image for Excel Worksheets
2024-03-15 08:01:56 Written by KoohjiFor data analysis and reporting, visual aesthetics play a significant role in presenting information effectively. When working with Excel worksheets, the ability to set background colors and images enhances the overall readability and impact of the data. By leveraging the power of Python, developers can effortlessly manipulate Excel files and customize the appearance of their worksheets. This article demonstrates how to use Spire.XLS for Python to set the background color and image for Excel worksheets with Python programs.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Set the Background Color for an Excel Worksheet
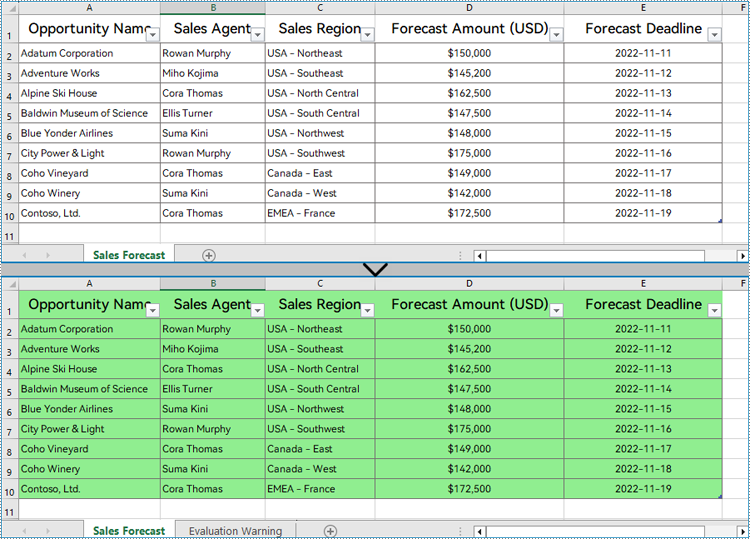
With Spire.XLS for Python, developers can set the background color for a specified cell range through CellRange.Style.Color property. The detailed steps for setting the background color for the used cell range in a worksheet are as follows:
- Create an instance of Workbook class.
- Load an Excel workbook using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Get the used range in the worksheet through Worksheet.AllocatedRange property.
- Set the background color of the used range through CellRange.Style.Color property.
- Save the workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an instance of Workbook class
wb = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
wb.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get a worksheet
sheet = wb.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Get the used range of the worksheet
usedRange = sheet.AllocatedRange
# Set the background color of the used range to a light and soft color
usedRange.Style.Color = Color.FromRgb(144, 238, 144)
# Save the workbook
wb.SaveToFile("output/ExcelBackgroundColor.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
wb.Dispose()
Set the Background Image for an Excel Worksheet
Setting a background image for an Excel worksheet can be accomplished through PageSetup class. Using the Worksheet.PageSetup.BackgroundImage property, developers can set the image background for the entire worksheet. Detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an instance of Workbook class.
- Load an Excel workbook using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Load an image using Stream() method.
- Set the background image of the worksheet through Worksheet.PageSetup.BackgroundImage property.
- Save the workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an instance of Workbook class
wb = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
wb.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get a worksheet
sheet = wb.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Load an image
image = Stream("BackgroundImage.jpg")
# Set the background of the worksheet
sheet.PageSetup.BackgoundImage = image
# Save the workbook
wb.SaveToFile("output/ExcelBackgroundImage.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
wb.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Shapes are a powerful tool in Excel that enables you to transform raw data into visually appealing and informative representations. By inserting and customizing shapes, you can create clear, engaging, and visually impactful spreadsheets that effectively communicate your data and captivate your audience. In this article, we will demonstrate how to insert and remove shapes in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Insert Shapes in Excel in Python
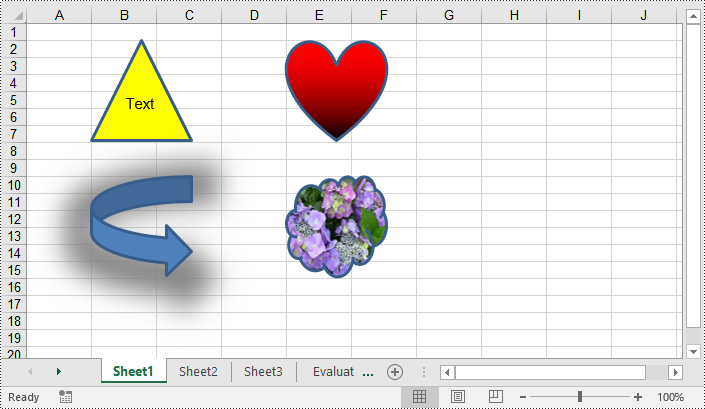
You can add numerous types of shapes, such as lines, rectangles, triangles, and stars, to an Excel worksheet by using the Worksheet.PrstGeomShapes.AddPrstGeomShape() method provided by Spire.XLS for Python. Once added, you can customize the shapes, such as adding text to the shapes, filling the shapes with solid or gradient colors or images, and setting shadow styles for the shapes. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Get the first worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Add a shape to the worksheet using Worksheet.PrstGeomShapes.AddPrstGeomShape() method.
- Add text to the shape using IPrstGeomShape.Text property.
- Fill the shape with a color using IPrstGeomShape.Fill.ForeColor property.
- Set the fill type of the shape as solid using IPrstGeomShape.Fill.FillType property.
- Repeat the above steps to add more shapes to the worksheet.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Add a triangle shape to the worksheet
triangle = sheet.PrstGeomShapes.AddPrstGeomShape(2, 2, 100, 100, PrstGeomShapeType.Triangle)
# Add text to the shape
triangle.Text = "Text"
# Fill the triangle with a solid color
triangle.Fill.ForeColor = Color.get_Yellow()
triangle.Fill.FillType = ShapeFillType.SolidColor
# Add a heart shape to the worksheet
heart = sheet.PrstGeomShapes.AddPrstGeomShape(2, 5, 100, 100, PrstGeomShapeType.Heart)
# Fill the heart with a gradient color
heart.Fill.ForeColor = Color.get_Red()
heart.Fill.FillType = ShapeFillType.Gradient
# Add an arrow shape with the default color to the worksheet
arrow = sheet.PrstGeomShapes.AddPrstGeomShape(10, 2, 100, 100, PrstGeomShapeType.CurvedRightArrow)
# Set shadow style for the arrow
arrow.Shadow.Angle = 90
arrow.Shadow.Distance = 10
arrow.Shadow.Size = 150
arrow.Shadow.Color = Color.get_Gray()
arrow.Shadow.Blur = 30
arrow.Shadow.Transparency = 1
arrow.Shadow.HasCustomStyle = True
# Add a cloud shape to the worksheet
cloud = sheet.PrstGeomShapes.AddPrstGeomShape(10, 5, 100, 100, PrstGeomShapeType.Cloud)
# Fill the cloud with a custom picture
cloud.Fill.CustomPicture(Image.FromFile("Hydrangea.jpg"), "Hydrangea.jpg")
cloud.Fill.FillType = ShapeFillType.Picture
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("InsertShapes.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
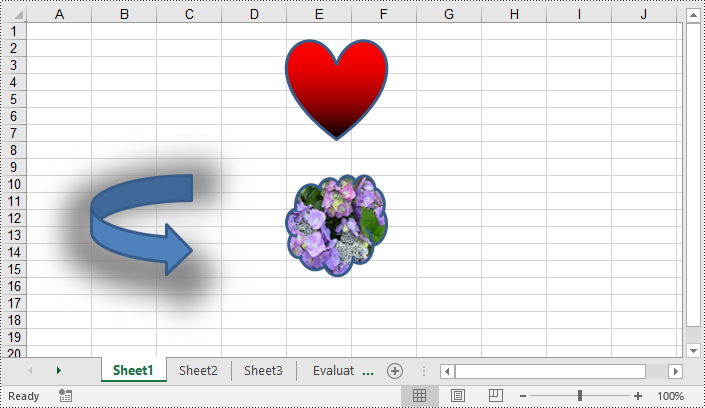
Remove Shapes from Excel in Python
Shapes can improve the visual appearance of your workbook, but they can also increase the file size of it. Removing unnecessary shapes helps reduce the file size, making it more manageable and easier to share or store. Spire.XLS for Python enables you to remove specific shapes from a worksheet effortlessly by using the Worksheet.PrstGeomShapes[index].Remove() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove a specific shape from the Worksheet using Worksheet.PrstGeomShapes[index].Remove() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("InsertShapes.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Remove the first shape from the worksheet
sheet.PrstGeomShapes[0].Remove()
#Save to file.
workbook.SaveToFile("RemoveShapes.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
