
Python (355)
In PowerPoint, sections are a powerful tool for organizing and managing slides. By dividing slides into different sections, you can better organize content, navigate through your presentation, and present information in a more structured manner. This article will demonstrate how to add and remove sections in a PowerPoint presentation using Spire.Presentation for Python.
- Add a Section at the End of a PowerPoint
- Insert a Section Before a Specified Section
- Add a Section Before a Specified Slide in PowerPoint
- Remove a Section from a PowerPoint
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Add a Section at the End of a PowerPoint in Python
Spire.Presentation for Python provides the Presentation.SectionList.Append(section_name) method to add a section at the end of a presentation. Here are the specific steps to perform this operation:
- Create a Presentation class instance.
- Load a PowerPoint document using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Add a section at the end using the Presentation.SectionList.Append() method.
- Save the document using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a new presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a sample PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("sample.pptx")
# Append a new section
presentation.SectionList.Append("New Section")
# Save the presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("AddSection.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
# Dispose of the presentation object
presentation.Dispose()
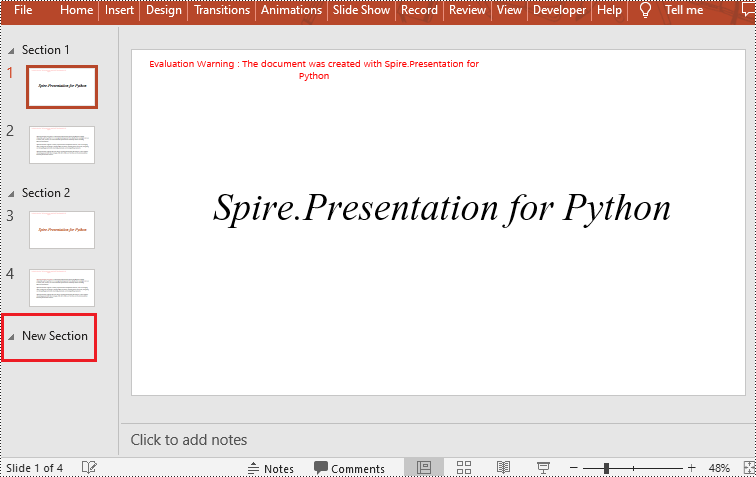
Insert a Section Before a Specified Section in Python
You can also use the Presentation.SectionList.Insert(index, section_name) method to insert a new section before a specific section. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Presentation class instance.
- Load a PowerPoint document using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Insert a new section before a specific section using the Presentation.SectionList.Insert() method, where index is the position of the specific section.
- Save the document using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a new presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a sample PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("sample.pptx")
# Insert a new section before the second section
presentation.SectionList.Insert(1," New Section")
# Save the presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("AddSection.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
# Dispose of the presentation object
presentation.Dispose()
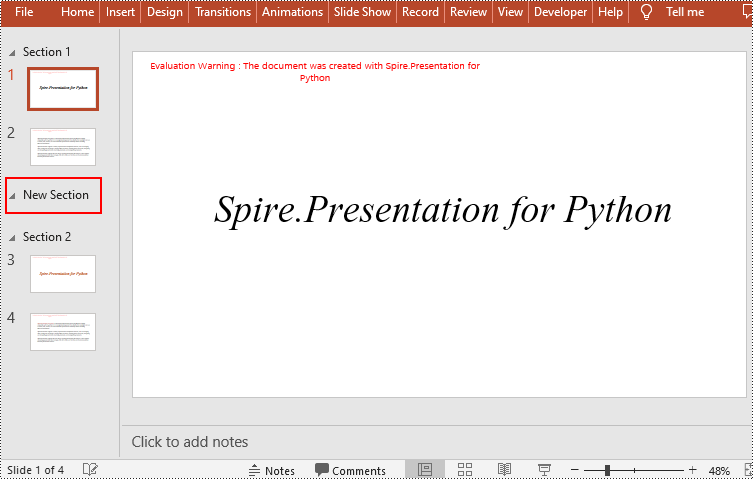
Add a Section Before a Specified Slide in Python
You can also use the Presentation.SectionList.Add(section_name, slide) method to insert a new section before a specific slide. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Presentation class instance.
- Load a PowerPoint document using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Insert a new section before a specific slide using the Presentation.SectionList.Add() method
- Save the document using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a new presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a sample PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("sample.pptx")
# Get the second slide
slide=presentation.Slides[1]
# Add a new section before the second slide
presentation.SectionList.Add("New Section",slide)
# Save the presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("AddSection.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
# Dispose of the presentation object
presentation.Dispose()
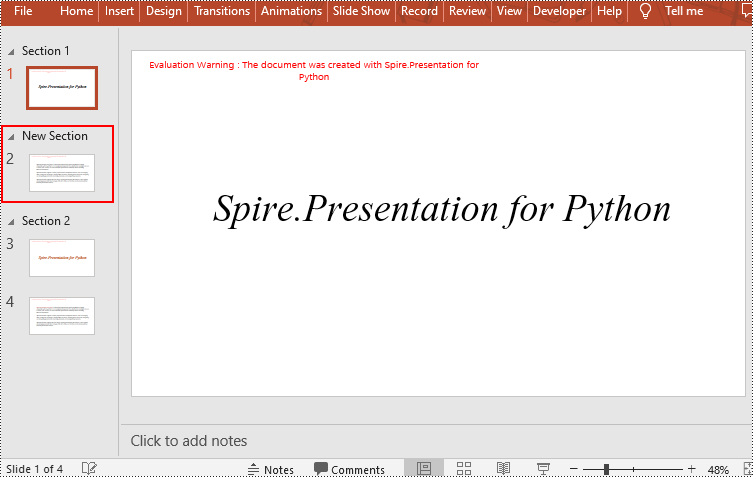
Remove a Section from a PowerPoint in Python
If you don't need a specific section, you can simply remove it using the Presentation.SectionList.RemoveAt(index_to_remove) method. Please note that removing a section does not delete the slides within that section. Here are the steps to delete a specific section while preserving its slides:
- Create a Presentation class instance.
- Load a PowerPoint document using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove a specific section using the Presentation.SectionList.RemoveAt(index_to_remove) method, which takes an integer index as a parameter. You can also remove all sections using the Presentation.Slides.RemoveAll() method.
- Save the document using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a new presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a sample PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("sample.pptx")
# Remove the second section
presentation.SectionList.RemoveAt(1)
# # Remove all sections
# presentation.SectionList.RemoveAll()
# Save the presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("RemoveSection.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
# Dispose of the presentation object
presentation.Dispose()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Add Tables to Excel Documents or Delete Tables from Excel Documents
2024-01-18 01:07:41 Written by KoohjiTables in Excel are powerful tools for organizing, storing, analyzing, and visualizing data. They are widely used in various industries and fields, including finance, business, science, education, and more. The table functionality in Excel makes data processing easier and provides users with flexibility and efficiency to make decisions and solve problems. This article will explain how to use Spire.XLS for Python to add or delete tables in Excel documents using Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Add Tables to an Excel Document in Python
Spire.XLS for Python creates table objects for the specified data source using the Worksheet.ListObjects.Create(tableName, range) method. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Use the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method to load an Excel document.
- Use the Workbook.Worksheets[] property to retrieve the desired worksheet.
- Create a table object using the Worksheet.ListObjects.Create() method.
- Set the table style using the Worksheet.ListObjects[].BuiltInTableStyle property.
- Use the Workbook.SaveToFile() method to save the resulting file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an .xlsx document
workbook.LoadFromFile("Data/sample1.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Create a table named "table" in the worksheet, with range [1,1,13,5]
sheet.ListObjects.Create("table", sheet.Range[1,1,13,5])
# Set the built-in table style of the first table to TableStyleLight9
sheet.ListObjects[0].BuiltInTableStyle = TableBuiltInStyles.TableStyleLight9
# Save the workbook to a file
workbook.SaveToFile("AddTable.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Release resources and clean up the workbook object
workbook.Dispose()
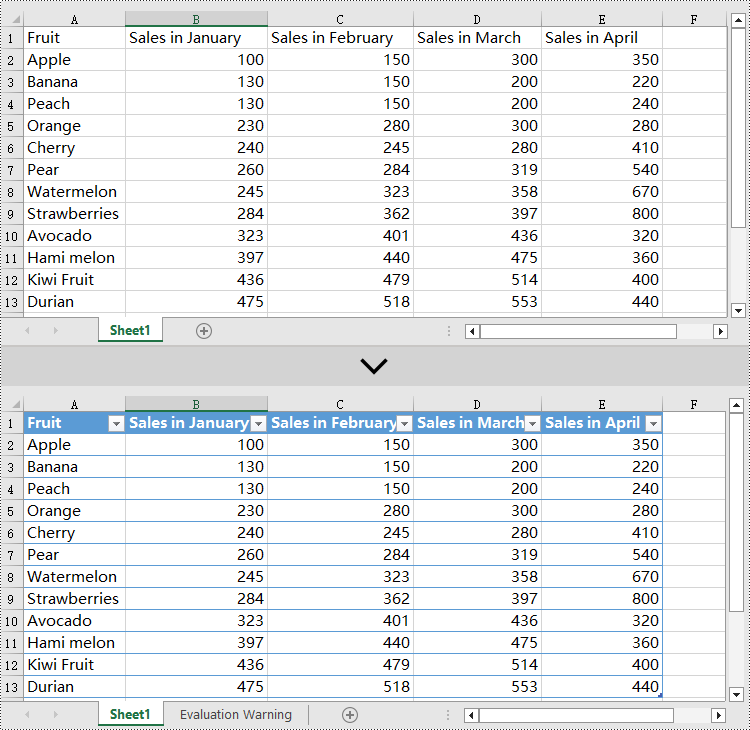
Delete Tables from an Excel Document in Python
Excel table objects are located in the Worksheet.ListObjects collection. To delete a table object, you need to iterate through the collection, find the table object based on its name, and remove it from the collection. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Use the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method to load an Excel document.
- Use the Workbook.Worksheets[] property to retrieve the desired worksheet.
- Iterate through the Worksheet.ListObjects collection in the worksheet to obtain the name of each ListObject object for finding the table object to delete.
- Use the Worksheet.ListObjects.RemoveAt() method to remove the table object.
- Use the Workbook.SaveToFile() method to save the resulting file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an .xlsx document
workbook.LoadFromFile("Data/Sample2.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Iterate through all the tables in the worksheet
for i in range(len(sheet.ListObjects)):
# Check if the table's name is "FruitTable"
if sheet.ListObjects[i].Name == "FruitTable":
# If a matching table is found, remove it
sheet.ListObjects.RemoveAt(i)
# Save the workbook to a file
workbook.SaveToFile("DeleteTable.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Release resources and clean up the workbook object
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
By incorporating supplemental resources directly into the PDF, it consolidates all relevant information in a single file, making it easier to organize, share, and archive. This feature enables users to seamlessly share supporting documents, images, or multimedia elements, eliminating the need for separate file transfers or external links. It streamlines communication, improves efficiency, and ensures that recipients have convenient access to all the necessary resources within the PDF itself. In this article, you will learn how to attach files to a PDF document in Python with the help of Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Background Knowledge
There are generally two types of attachments in PDF, namely document level attachment and annotation attachment. Both are supported by Spire.PDF for Python. The table below lists the differences between them.
| Attachment type | Represented by | Definition |
| Document level attachment | PdfAttachment class | A file attached to a PDF at the document level won't appear on a page, but can be viewed in the "Attachments" panel of a PDF reader. |
| Annotation attachment | PdfAnnotationAttachment class | A file attached as an annotation can be found on a page or in the "Attachment" panel. An Annotation attachment is shown as a paper clip icon on the page; reviewers can double-click the icon to open the file. |
Attach Files to a PDF Document in Python
To attach files to PDFs at the document level, you first need to create a PdfAttachment object based on an external file, and then you can add it to a PDF document using the PdfDocument.Attachments.Add() method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a PdfAttachment object based on an external file.
- Add the attachment to the document using PdfDocument.Attachments.Add() method.
- Save the document to a different PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a sample PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.pdf")
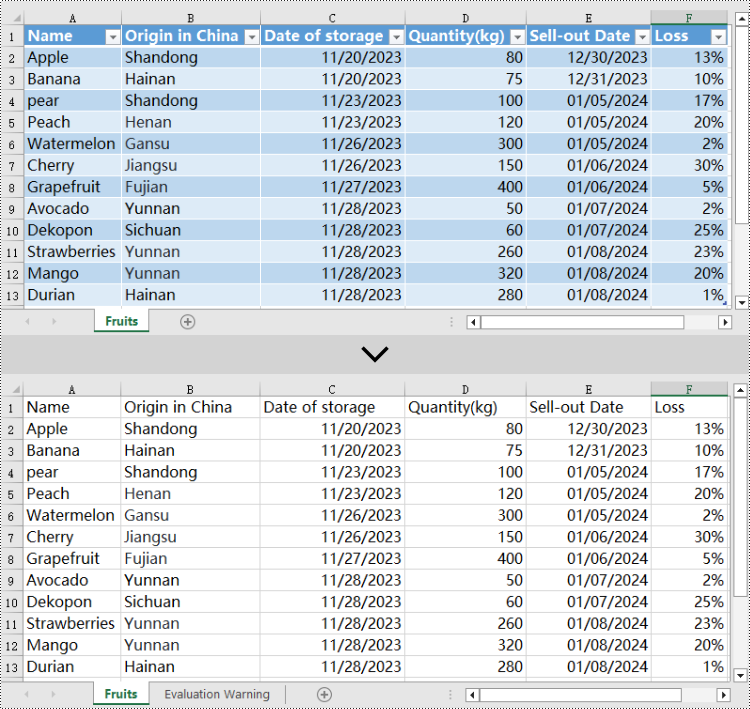
# Create PdfAttachment objects based on external files
attachment_one = PdfAttachment("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Data.xlsx")
attachment_two = PdfAttachment("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\logo.png")
# Add the attachments to PDF
doc.Attachments.Add(attachment_one)
doc.Attachments.Add(attachment_two)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/Attachment.pdf")
Attach Files as Annotations in PDF in Python
An annotation attachment is represented by the PdfAttachmentAnnotation class. Create an instance of this class, specify its attributes such as bounds, flag and text, and then add it to a specified page using the PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.Add() method.
Below are the steps to attach files as annotations in PDF using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific page to add annotation through PdfDocument.Pages[] property.
- Create a PdfAttachmentAnnotation object based on an external file.
- Add the annotation attachment to the page using PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.Add() method.
- Save the document to a different PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a sample PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.pdf")
# Get a specific page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(1)
# Draw a string on PDF
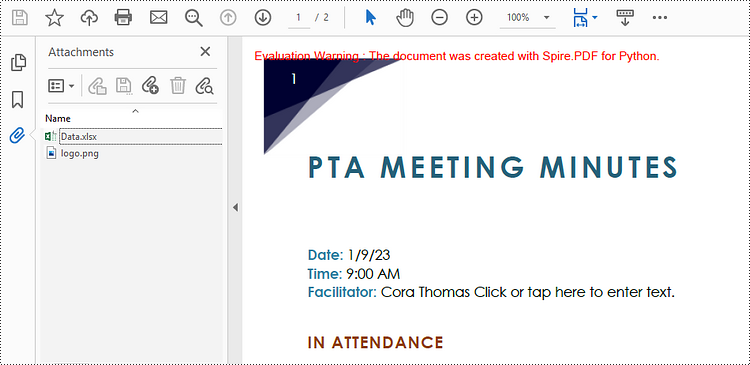
str = ""Here is the report:""
font = PdfTrueTypeFont(""Times New Roman"", 16.0, PdfFontStyle.Bold, True)
x = 50.0
y = doc.Pages.get_Item(0).ActualSize.Height - 300.0
page.Canvas.DrawString(str, font, PdfBrushes.get_Blue(), x, y)
# Create a PdfAttachmentAnnotation object based on an external file
data = Stream("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Data.xlsx")
size = font.MeasureString(str);
bounds = RectangleF((x + size.Width + 5.0), y, 10.0, 15.0)
annotation = PdfAttachmentAnnotation(bounds, "Report.docx", data);
# Set color, flag, icon and text of the annotation
annotation.Color = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Blue())
annotation.Flags = PdfAnnotationFlags.Default
annotation.Icon = PdfAttachmentIcon.Graph
annotation.Text = "Click to open the file"
# Add the attachment annotation to PDF
page.AnnotationsWidget.Add(annotation)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/AnnotationAttachment.pdf")
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Content controls play an important role in Excel, providing powerful functionality for data input, display, and user interaction. These controls include text boxes, radio buttons, checkboxes, drop-down lists, and more. They offer users more efficient, intuitive, and flexible ways of handling data, making Excel a powerful tool for data management and analysis. This article will introduce how to use Spire.XLS for Python to add content controls to Excel documents or edit content controls in Excel documents using Python.
- Add Content Controls to an Excel document in Python
- Edit Content Controls in an Excel document in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Add Content Controls to an Excel document in Python
Spire.XLS for Python allows you to add content controls supported by Excel, such as text boxes, radio buttons, drop-down lists (also known as combo boxes), checkboxes, and more. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Use the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method to load an Excel data document.
- Use the Workbook.Worksheets[] property to retrieve the desired worksheet.
- Add a text box using the Worksheet.TextBoxes.AddTextBox() method.
- Add a radio button using the Worksheet.RadioButtons.Add() method.
- Add a combo box using the Worksheet.ComboBoxes.AddComboBox() method.
- Add a checkbox using the Worksheet.CheckBoxes.AddCheckBox() method.
- Use the Workbook.SaveToFile() method to save the resulting file.
- Python
from spire.xls.common import *
from spire.xls import *
# Create a new Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an existing Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Data/Sample01.xlsx")
# Select the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set the height of the text box (unit: points)
height = 40
# Add a text box to the worksheet
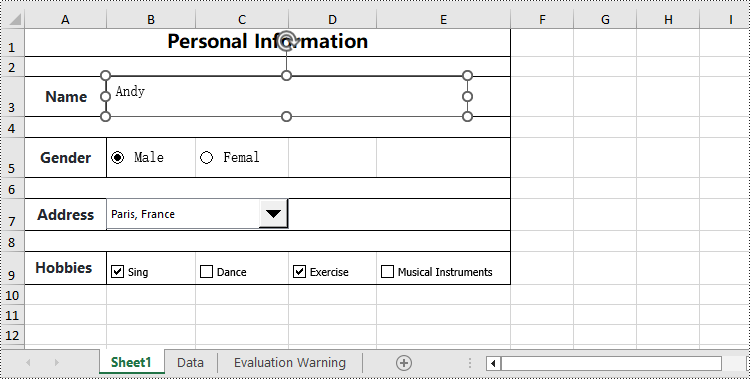
textbox = worksheet.TextBoxes.AddTextBox(3, 2, height, 400)
textbox.Line.ForeKnownColor = ExcelColors.Black
textbox.Text = "Andy"
# Add radio buttons to the worksheet
radioButton1 = worksheet.RadioButtons.Add(5, 2, height, 60)
radioButton1.Text = "Male"
radioButton1.CheckState=CheckState.Checked
radioButton2 = worksheet.RadioButtons.Add(5, 3, height, 60)
radioButton2.Text = "Female"
# Assign a data range from another worksheet to a combo box
dataSheet = workbook.Worksheets[1]
comboBoxShape = worksheet.ComboBoxes.AddComboBox(7, 2, 30, 200)
comboBoxShape.ListFillRange = dataSheet.Range["A1:A7"]
comboBoxShape.SelectedIndex=1
# Add check boxes to the worksheet
checkBox = worksheet.CheckBoxes.AddCheckBox(9, 2, height, 60)
checkBox.CheckState = CheckState.Checked
checkBox.Text = "Sing"
checkBox = worksheet.CheckBoxes.AddCheckBox(9, 3, height, 60)
checkBox.CheckState = CheckState.Unchecked
checkBox.Text = "Dance"
checkBox = worksheet.CheckBoxes.AddCheckBox(9, 4, height, 60)
checkBox.CheckState = CheckState.Checked
checkBox.Text = "Exercise"
checkBox = worksheet.CheckBoxes.AddCheckBox(9, 5, height, 100)
checkBox.CheckState = CheckState.Unchecked
checkBox.Text = "Musical Instruments"
# Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("AddContentControls.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Clean up and release the workbook object
workbook.Dispose()
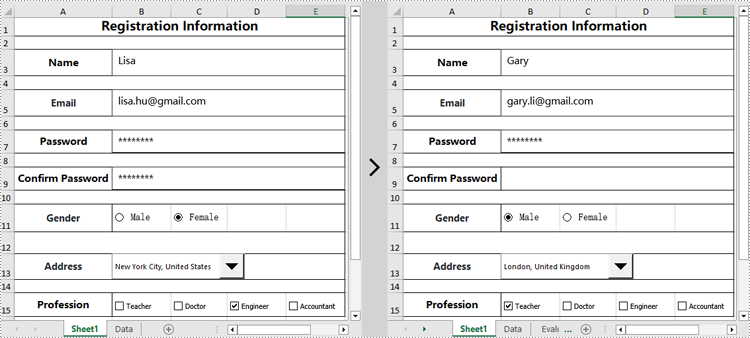
Edit Content Controls in an Excel document in Python
Spire.XLS for Python can also modify the properties of existing content controls in an Excel document, such as changing the text of a text box, resetting the selected item of a drop-down list, hiding a specific content control, and more. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Use the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method to load an Excel document.
- Use the Workbook.Worksheets[] property to retrieve the desired worksheet.
- Modify the display content of a text box using the Worksheet.TextBoxes[].Text property.
- Set whether to display a specific text box using the Worksheet.TextBoxes[].Visible property.
- Set whether a radio button is checked using the Worksheet.RadioButtons[].CheckState property.
- Set the selected item of a combo box using the Worksheet.ComboBoxes[].SelectedIndex property.
- Set whether a checkbox is checked using the Worksheet.CheckBoxes[].CheckState property.
- Use the Workbook.SaveToFile() method to save the resulting file.
- Python
from spire.xls.common import *
from spire.xls import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load Excel data from file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Data/Sample02.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set the text content of the first textbox to "Gary"
worksheet.TextBoxes[0].Text = "Gary"
# Set the text content of the second textbox to "gary.li@gmail.com"
worksheet.TextBoxes[1].Text = "gary.li@gmail.com"
# Hide the fourth textbox
worksheet.TextBoxes[3].Visible = False
# Check the first radio button
worksheet.RadioButtons[0].CheckState = CheckState.Checked
# Set the selected index of the first combobox to 0 (the first option)
worksheet.ComboBoxes[0].SelectedIndex = 0
# Check the first checkbox
worksheet.CheckBoxes[0].CheckState = CheckState.Checked
# Uncheck the third checkbox
worksheet.CheckBoxes[2].CheckState = CheckState.Unchecked
# Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("EditContentControls.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Clean up and release the workbook object
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Sometimes, when dealing with PDF documents, there is a need to split a page into different sections based on content or layout. For instance, splitting a mixed-layout page with both horizontal and vertical content into two separate parts. This type of splitting is not commonly available in basic PDF management functions but can be important for academic papers, magazine ads, or mixed-layout designs. This article explains how to use Spire.PDF for Python to perform horizontal or vertical PDF page splitting.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Split PDF Page Horizontally or Vertically with Python
Spire.PDF for Python not only supports splitting a PDF document into multiple PDF documents, but also allows splitting a specific page within a PDF into two or more pages. Here are the detailed steps to split a page:
- Create an instance of the PdfDocument class.
- Load the source PDF document using the PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Retrieve the page(s) to be split using PdfDocument.Pages[].
- Create a new PDF document and set its page margins to 0.
- Set the width or height of the new document to half of the source document.
- Add a page to the new PDF document using the PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Create a template for the source document's page using the PdfPageBase.CreateTemplate() method.
- Draw the content of the source page onto the new page using the PdfTemplate.Draw() method.
- Save the split document using the PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load the PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("Terms of service.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Create a new PDF document and remove the page margins
newpdf = PdfDocument()
newpdf.PageSettings.Margins.All=0
# Horizontal splitting: Set the width of the new document's page to be the same as the width of the first page of the original document, and the height to half of the first page's height
newpdf.PageSettings.Width=page.Size.Width
newpdf.PageSettings.Height=page.Size.Height/2
'''
# Vertical splitting: Set the width of the new document's page to be half of the width of the first page of the original document, and the height to the same as the first page's height
newpdf.PageSettings.Width=page.Size.Width/2
newpdf.PageSettings.Height=page.Size.Height
'''
# Add a new page to the new PDF document
newPage = newpdf.Pages.Add()
# Set the text layout format
format = PdfTextLayout()
format.Break=PdfLayoutBreakType.FitPage
format.Layout=PdfLayoutType.Paginate
# Create a template based on the first page of the original document and draw it onto the new page of the new document, automatically paginating when the page is filled
page.CreateTemplate().Draw(newPage, PointF(0.0, 0.0), format)
# Save the document
newpdf.SaveToFile("HorizontalSplitting.pdf")
# Close the objects
newpdf.Close()
pdf.Close()
The result of horizontal splitting is as follows:
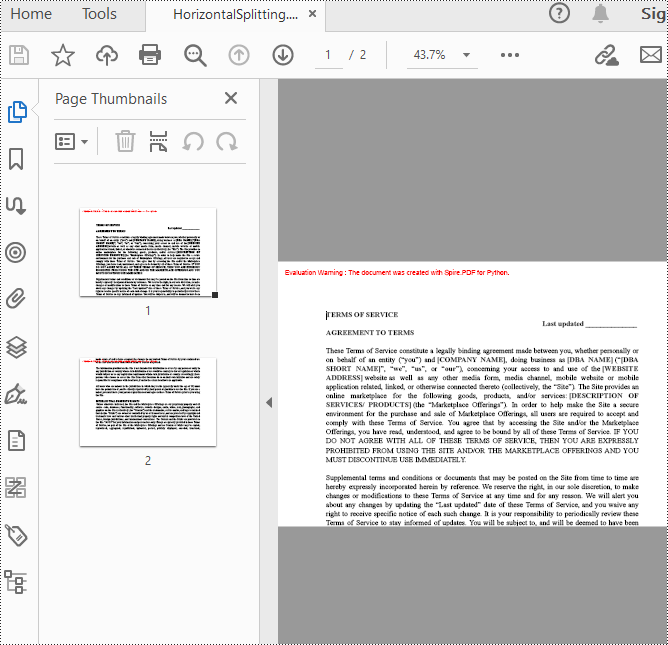
The result of vertical splitting is as follows:

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Using lists in PowerPoint allows you to present information in a structured and visually appealing way. They help break down complex ideas into digestible points, making it easier for your audience to understand and retain key concepts. Whether you're creating a slide deck for a business presentation, educational workshop, or conference talk, incorporating lists can enhance the visual appeal and effectiveness of your content. In this article, we will demonstrate how to create numbered lists and bulleted lists in PowerPoint presentations in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
- Create a Numbered List in PowerPoint in Python
- Create a Bulleted List with Symbol Bullets in PowerPoint in Python
- Create a Bulleted List with Image Bullets in PowerPoint in Python
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
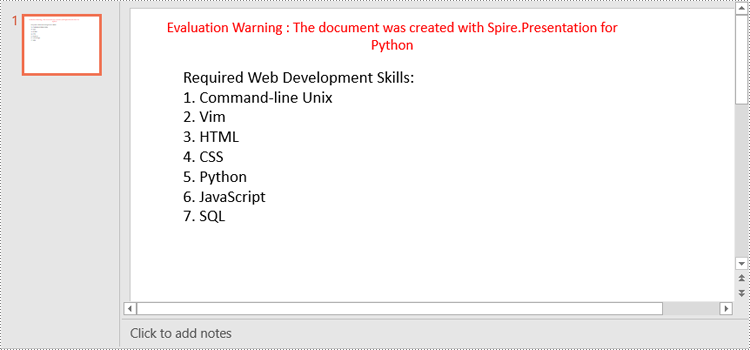
Create a Numbered List in PowerPoint in Python
Spire.Presentation supports adding numerals or bullet points in front of paragraphs to create a numbered or bulleted list. To specify the bullet type, you can use the ParagraphProperties.BulletType property. The following are the steps to create a numbered list in a PowerPoint slide using Spire.Presentation for Python.
- Create a Presentation object.
- Get the first slide using Presentation.Slides[0] property.
- Append a shape to the slide using ISlide.Shapes.AppendShape() method and set the shape style.
- Specify the items of the numbered list inside a list.
- Create paragraphs based on the list items, and set the bullet type of these paragraphs to Numbered using ParagraphProperties.BulletType property.
- Set the numbered bullet style of these paragraphs using ParagraphProperties.BulletStyle property.
- Add these paragraphs to the shape using IAutoShape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Append() method.
- Save the document to a PowerPoint file using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
presentation = Presentation()
# Get the first slide
slide = presentation.Slides[0]
# Add a shape to the slide and set the shape style
shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, RectangleF(50.0, 50.0, 300.0, 200.0))
shape.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.none
shape.Line.FillType= FillFormatType.none
# Add text to the default paragraph
paragraph = shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs[0]
paragraph.Text = "Required Web Development Skills:"
paragraph.Alignment = TextAlignmentType.Left
paragraph.TextRanges[0].Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
paragraph.TextRanges[0].Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_Black()
# Specify the list items
listItems = [
" Command-line Unix",
" Vim",
" HTML",
" CSS",
" Python",
" JavaScript",
" SQL"
]
# Create a numbered list
for item in listItems:
textParagraph = TextParagraph()
textParagraph.Text = item
textParagraph.Alignment = TextAlignmentType.Left
textParagraph.TextRanges[0].Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
textParagraph.TextRanges[0].Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_Black()
textParagraph.BulletType = TextBulletType.Numbered
textParagraph.BulletStyle = NumberedBulletStyle.BulletArabicPeriod
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Append(textParagraph)
# Save the result document
presentation.SaveToFile("NumberedList.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
presentation.Dispose()
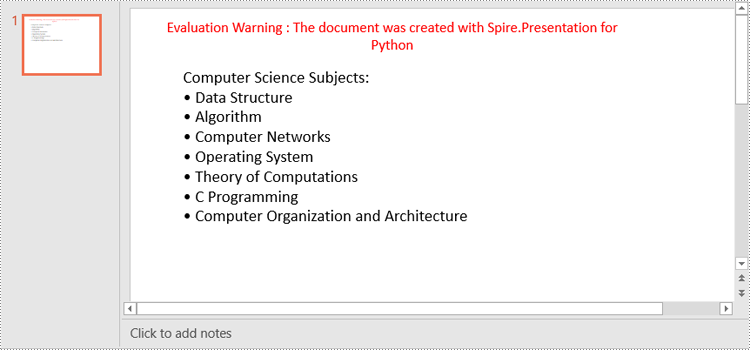
Create a Bulleted List with Symbol Bullets in PowerPoint in Python
The process of creating a bulleted list with symbol bullets is very similar to that of creating a numbered list. The only difference is that you need to set the bullet type of the paragraphs to Symbol. The following are the steps.
- Create a Presentation object.
- Get the first slide using Presentation.Slides[0] property.
- Append a shape to the slide using ISlide.Shapes.AppendShape() method and set the shape style.
- Specify the items of the bulleted list inside a list.
- Create paragraphs based on the list items, and set the bullet type of these paragraphs to Symbol using ParagraphProperties.BulletType property.
- Add these paragraphs to the shape using IAutoShape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Append() method.
- Save the document to a PowerPoint file using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
presentation = Presentation()
# Get the first slide
slide = presentation.Slides[0]
# Add a shape to the slide and set the shape style
shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, RectangleF(50.0, 50.0, 350.0, 200.0))
shape.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.none
shape.Line.FillType = FillFormatType.none
# Add text to the default paragraph
paragraph = shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs[0]
paragraph.Text = "Computer Science Subjects:"
paragraph.Alignment = TextAlignmentType.Left
paragraph.TextRanges[0].Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
paragraph.TextRanges[0].Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_Black()
# Specify the list items
listItems = [
" Data Structure",
" Algorithm",
" Computer Networks",
" Operating System",
" Theory of Computations",
" C Programming",
" Computer Organization and Architecture"
]
# Create a symbol bulleted list
for item in listItems:
textParagraph = TextParagraph()
textParagraph.Text = item
textParagraph.Alignment = TextAlignmentType.Left
textParagraph.TextRanges[0].Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
textParagraph.TextRanges[0].Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_Black()
textParagraph.BulletType = TextBulletType.Symbol
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Append(textParagraph)
# Save the result document
presentation.SaveToFile("SymbolBulletedList.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
presentation.Dispose()
Create a Bulleted List with Image Bullets in PowerPoint in Python
To use an image as bullets, you need to set the bullet type of the paragraphs to Picture and then set the image as bullet points using the ParagraphProperties.BulletPicture.EmbedImage property. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Presentation object.
- Get the first slide using Presentation.Slides[0] property.
- Append a shape to the slide using ISlide.Shapes.AppendShape() method and set the shape style.
- Specify the items of the bulleted list inside a list.
- Create paragraphs based on the list items, and set the bullet type of these paragraphs to Picture using ParagraphProperties.BulletType property.
- Set an image as bullet points using ParagraphProperties.BulletPicture.EmbedImage property.
- Add these paragraphs to the shape using IAutoShape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Append() method.
- Save the document to a PowerPoint file using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
presentation = Presentation()
# Get the first slide
slide = presentation.Slides[0]
# Add a shape to the slide and set the shape style
shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, RectangleF(50.0, 50.0, 400.0, 180.0))
shape.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.none
shape.Line.FillType = FillFormatType.none
# Add text to the default paragraph
paragraph = shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs[0]
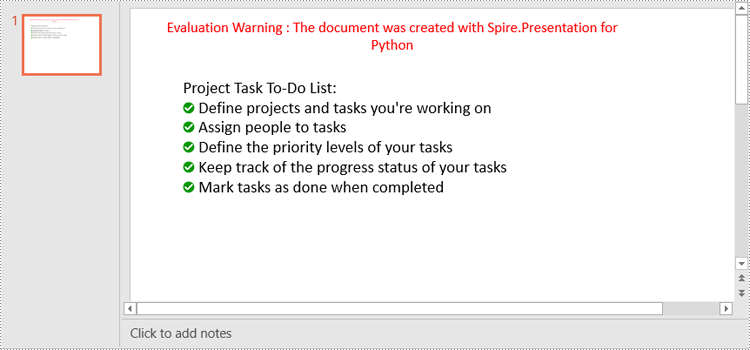
paragraph.Text = "Project Task To-Do List:"
paragraph.Alignment = TextAlignmentType.Left
paragraph.TextRanges[0].Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
paragraph.TextRanges[0].Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_Black()
# Specify the list items
listItems = [
" Define projects and tasks you're working on",
" Assign people to tasks",
" Define the priority levels of your tasks",
" Keep track of the progress status of your tasks",
" Mark tasks as done when completed"
]
# Create an image bulleted list
for item in listItems:
textParagraph = TextParagraph()
textParagraph.Text = item
textParagraph.Alignment = TextAlignmentType.Left
textParagraph.TextRanges[0].Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
textParagraph.TextRanges[0].Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_Black()
textParagraph.BulletType = TextBulletType.Picture
stream = Stream("icon.png")
imageData = presentation.Images.AppendStream(stream)
textParagraph.BulletPicture.EmbedImage = imageData
shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs.Append(textParagraph)
stream.Close()
# Save the result document
presentation.SaveToFile("ImageBulletedList.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
presentation.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
In Excel, document properties refer to the metadata or information associated with an Excel file. These properties provide details about the workbook itself, such as author, title, subject, keywords, and other descriptive information. Document properties are useful for organizing and categorizing Excel files, making it easier to search, sort, and manage a collection of workbooks. In this article, you will learn how to add document properties in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Add Built-in Document Properties in Excel in Python
- Add Custom Document Properties in Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Add Built-in Document Properties in Excel in Python
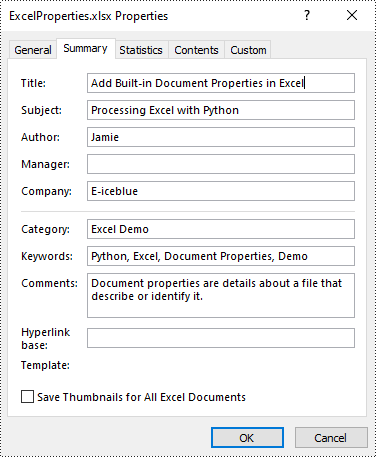
Built-in document properties are basic information about a document such as title, subject, author, category, etc. The names of these properties are predefined that cannot be edited, but Spire.XLS for Python allows you to set specific values for these properties. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the built-in document properties of the document using Workbook.DocumentProperties property.
- Set specific document properties such as title, author, keywords and comments using the properties of BuiltInDocumentProperties class.
- Save the result document using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "sample.xlsx" outputFile = "ExcelProperties.xlsx" # Create a Workbook object workbook = Workbook() # Load a sample Excel document workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Set built-in document properties for the Excel workbook workbook.DocumentProperties.Author = "Jamie" workbook.DocumentProperties.Title = "Add Built-in Document Properties in Excel" workbook.DocumentProperties.Subject = "Processing Excel with Python" workbook.DocumentProperties.Keywords = "Python, Excel, Document Properties, Demo" workbook.DocumentProperties.Category = "Excel Demo" workbook.DocumentProperties.Company = "E-iceblue" workbook.DocumentProperties.Comments = "Document properties are details about a file that describe or identify it." # Save the result document workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Version2016) workbook.Dispose()
Add Custom Document Properties in Excel in Python
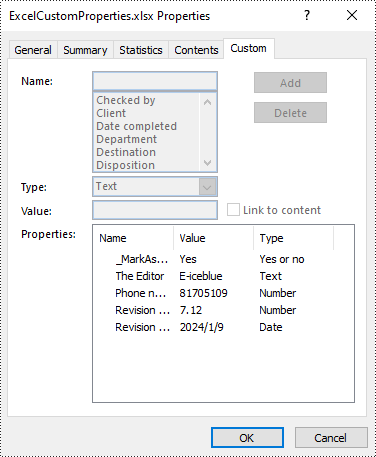
Custom document properties are additional properties that you can define for an Excel document. With Spire.XLS for Python, you can add custom properties with specified names and values through the ICustomDocumentProperties.Add() method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the custom document properties of the document using Workbook.CustomDocumentProperties property.
- Add custom document properties with different data types to the document using ICustomDocumentProperties.Add() method.
- Save the result document using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
inputFile = "sample.xlsx"
outputFile = "ExcelCustomProperties.xlsx"
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load a sample Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Add a custom property to make the document as final
workbook.CustomDocumentProperties.Add("_MarkAsFinal", True)
# Add other custom properties to the document
workbook.CustomDocumentProperties.Add("The Editor", "E-iceblue")
workbook.CustomDocumentProperties.Add("Phone number", 81705109)
workbook.CustomDocumentProperties.Add("Revision number", 7.12)
workbook.CustomDocumentProperties.Add("Revision date", DateTime.get_Now())
# Save the result document
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
PDF bookmarks are key tools for optimizing reading navigation. When expanded, users can click on the titles to jump to the corresponding chapters and display sub-level directories, enabling intuitive access and positioning within the document's deep structure. Collapsing bookmarks, on the other hand, allows users to hide all sub-bookmark information at the current level with a single click, simplifying the view and focusing on higher-level structure. These two operations work together to significantly enhance the efficiency and experience of reading complex, multi-level PDF documents. This article will introduce how to programmatically expand and collapse bookmarks in a PDF using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Expand or Collapse all Bookmarks in Python
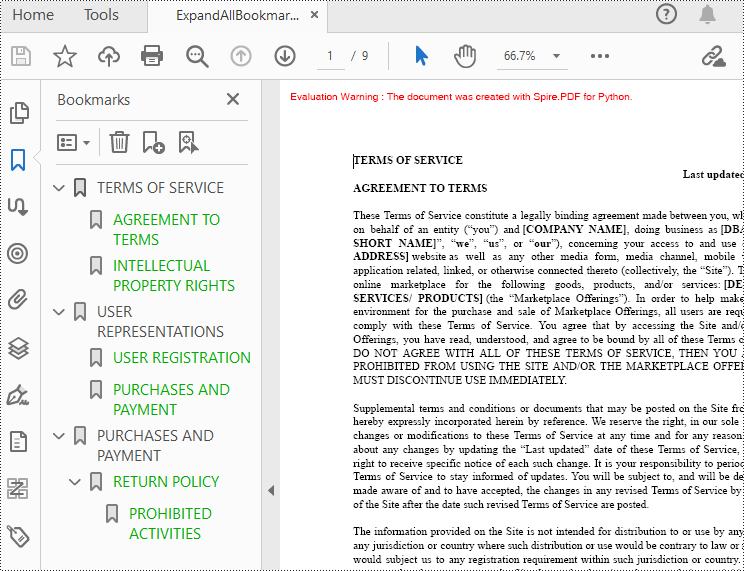
Spire.PDF for Python provides the property BookMarkExpandOrCollapse to expand or collapse bookmarks, when set to True, it expands all bookmarks. Conversely, setting it to False will collapses all bookmarks. The following are the detailed steps for expanding bookmarks in a PDF document.
- Create a PdfDocument class instance.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Expand all bookmarks using BookMarkExpandOrCollapse property.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("Terms of service.pdf")
# Set BookMarkExpandOrCollapse as True to expand all bookmarks, set False to collapse all bookmarks
doc.ViewerPreferences.BookMarkExpandOrCollapse = True
# Save the document
outputFile="ExpandAllBookmarks.pdf"
doc.SaveToFile(outputFile)
# Close the document
doc.Close()
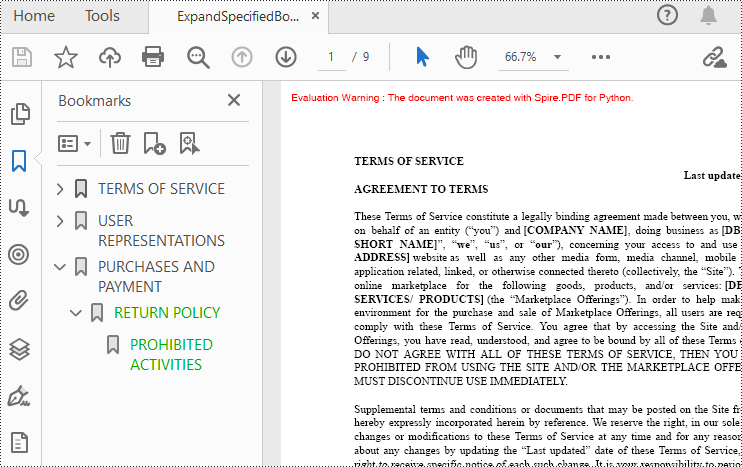
Expand or Collapse a specific Bookmark in Python
If you need to expand or collapse only a specific bookmark, you can use the property ExpandBookmark. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument class instance.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific bookmark using PdfDocument.Bookmarks.get_Item() method.
- Expand the bookmark using ExpandBookmark property.
- Save the result document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
doc.LoadFromFile("Terms of service.pdf")
# Set ExpandBookmark as True for the third bookmark
doc.Bookmarks.get_Item(2).ExpandBookmark = True
# Save the document
outputFile="ExpandSpecifiedBookmarks.pdf"
doc.SaveToFile(outputFile)
# Close the document
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Creating a fillable form in Word allows you to design a document that can be easily completed and customized by others. Whether you need to collect information, gather feedback, or create an interactive document, fillable forms provide a convenient way to capture data electronically. By adding various elements such as text fields, checkboxes, dropdown menus, and more, you can tailor the form to your specific requirements.
To create a fillable form in Word, you probably need to use the following tools.
- Content Controls: The areas where users input information in a form.
- Tables: Tables are used in forms to align text and form fields, and to create borders and boxes.
- Protection: Allows users to populate fields but not to make changes to the rest of the document.
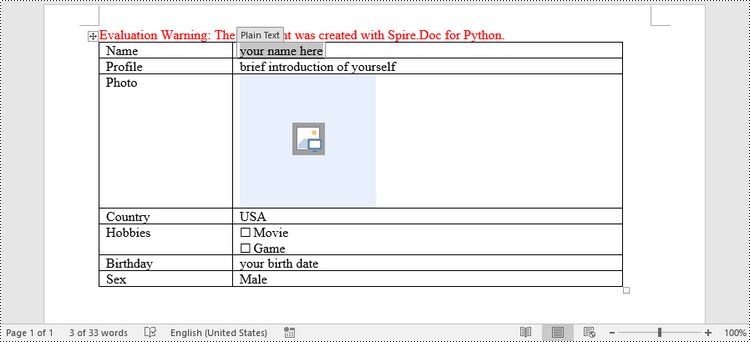
In Word, content controls serve as containers for structured documents, allowing users to organize content within a document. Word 2013 provides ten types of content controls. This article introduces how to create a fillable form in Word that includes the following seven commonly-used content controls using Spire.Doc for Python.
| Content Control | Description |
| Plain Text | A text field limited to plain text, so no formatting can be included. |
| Rich Text | A text field that can contain formatted text or other items, such as tables, pictures, or other content controls. |
| Picture | Accepts a single picture. |
| Drop-Down List | A drop-down list displays a predefined list of items for the user to choose from. |
| Combo Box | A combo box enables users to select a predefined value in a list or type their own value in the text box of the control. |
| Check Box | A check box provides a graphical widget that allows the user to make a binary choice: yes (checked) or no (not checked). |
| Date Picker | Contains a calendar control from which the user can select a date. |
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Create a Fillable Form in Word in Python
Spire.Doc for Python offers the StructureDocumentTagInline class, which is utilized to generate structured document tags within a paragraph. By utilizing the SDTProperties property and SDTContent property of this class, one can define the properties and content of the current structured document tag. Below are the step-by-step instructions for creating a fill form in a Word document in Python.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Add a table using Section.AddTable() method.
- Add a paragraph to a specific table cell using TableCell.AddParagraph() method.
- Create an instance of StructureDocumentTagInline class, and add it to the paragraph as a child object using Paragraph.ChildObjects.Add() method.
- Specify the type, content and other attributes of the structured document tag through the SDTProperties property and the SDTContent property of the StructureDocumentTagInline object.
- Prevent users from editing content outside form fields using Document.Protect() method.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Add a table
table = section.AddTable(True)
table.ResetCells(7, 2)
table.SetColumnWidth(0, 120, CellWidthType.Point)
table.SetColumnWidth(1, 350, CellWidthType.Point)
# Add text to the cells of the first column
paragraph = table.Rows.get_Item(0).Cells.get_Item(0).AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Name")
paragraph = table.Rows[1].Cells[0].AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Profile")
paragraph = table.Rows[2].Cells[0].AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Photo")
paragraph = table.Rows[3].Cells[0].AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Country")
paragraph = table.Rows[4].Cells[0].AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Hobbies")
paragraph = table.Rows[5].Cells[0].AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Birthday")
paragraph = table.Rows[6].Cells[0].AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Sex")
# Add a plain text content control to the cell (0,1)
paragraph = table.Rows[0].Cells[1].AddParagraph()
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.Text
sdt.SDTProperties.Alias = "Plain Text"
sdt.SDTProperties.Tag = "Plain Text"
sdt.SDTProperties.IsShowingPlaceHolder = True
text = SdtText(True)
text.IsMultiline = False
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = text
textRange = TextRange(doc)
textRange.Text = "your name here"
sdt.SDTContent.ChildObjects.Add(textRange)
# Add a rich text content control to the cell (1,1)
paragraph = table.Rows[1].Cells[1].AddParagraph()
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.RichText
sdt.SDTProperties.Alias = "Rich Text"
sdt.SDTProperties.Tag = "Rich Text"
sdt.SDTProperties.IsShowingPlaceHolder = True
text = SdtText(True)
text.IsMultiline = False
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = text
textRange = TextRange(doc)
textRange.Text = "brief introduction of yourself"
sdt.SDTContent.ChildObjects.Add(textRange )
# Add a picture content control to the cell (2,1)
paragraph = table.Rows[2].Cells[1].AddParagraph()
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.Picture
sdt.SDTProperties.Alias = "Picture"
sdt.SDTProperties.Tag = "Picture"
sdtPicture = SdtPicture(True)
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = sdtPicture
pic = DocPicture(doc)
pic.LoadImage("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\placeHolder.png")
sdt.SDTContent.ChildObjects.Add(pic)
# Add a dropdown list content control to the cell (3,1)
paragraph = table.Rows[3].Cells[1].AddParagraph();
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.DropDownList
sdt.SDTProperties.Alias = "Dropdown List"
sdt.SDTProperties.Tag = "Dropdown List"
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
stdList = SdtDropDownList()
stdList.ListItems.Add(SdtListItem("USA", "1"))
stdList.ListItems.Add(SdtListItem("China", "2"))
stdList.ListItems.Add(SdtListItem("Briza", "3"))
stdList.ListItems.Add(SdtListItem("Austrilia", "4"))
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = stdList;
textRange = TextRange(doc)
textRange .Text = stdList.ListItems[0].DisplayText
sdt.SDTContent.ChildObjects.Add(textRange )
# Add two check box content controls to the cell (4,1)
paragraph = table.Rows[4].Cells[1].AddParagraph()
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.CheckBox
sdtCheckBox = SdtCheckBox()
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = sdtCheckBox
textRange = TextRange(doc)
sdt.ChildObjects.Add(textRange)
sdtCheckBox.Checked = False
paragraph.AppendText(" Movie")
paragraph = table.Rows[4].Cells[1].AddParagraph();
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.CheckBox
sdtCheckBox = SdtCheckBox()
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = sdtCheckBox
textRange = TextRange(doc)
sdt.ChildObjects.Add(textRange)
sdtCheckBox.Checked = False
paragraph.AppendText(" Game")
# Add a date picker content control to the cell (5,1)
paragraph = table.Rows[5].Cells[1].AddParagraph()
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.DatePicker
sdt.SDTProperties.Alias = "Date Picker"
sdt.SDTProperties.Tag = "Date Picker"
stdDate = SdtDate()
stdDate.CalendarType = CalendarType.Default
stdDate.DateFormat = "yyyy.MM.dd"
stdDate.FullDate = DateTime.get_Now()
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = stdDate
textRange = TextRange(doc)
textRange.Text = "your birth date"
sdt.SDTContent.ChildObjects.Add(textRange)
# Add a combo box content control to the cell (6,1)
paragraph = table.Rows[6].Cells[1].AddParagraph()
sdt = StructureDocumentTagInline(doc)
paragraph.ChildObjects.Add(sdt)
sdt.SDTProperties.SDTType = SdtType.ComboBox
sdt.SDTProperties.Alias = "Combo Box"
sdt.SDTProperties.Tag = "Combo Box"
stdComboBox = SdtComboBox()
stdComboBox.ListItems.Add(SdtListItem("Male"))
stdComboBox.ListItems.Add(SdtListItem("Female"))
sdt.SDTProperties.ControlProperties = stdComboBox
textRange = TextRange(doc)
textRange.Text = stdComboBox.ListItems[0].DisplayText
sdt.SDTContent.ChildObjects.Add(textRange)
# Allow users to edit the form fields only
doc.Protect(ProtectionType.AllowOnlyFormFields, "permission-psd")
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/Form.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
PDF forms are commonly used to collect user information, and extracting form values programmatically allows for automated processing of submitted data, ensuring accurate data collection and analysis. After extraction, you can generate reports based on form field values or migrate them to other systems or databases. In this article, you will learn how to extract form field values from PDF with Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Extract Form Field Values from PDF with Python
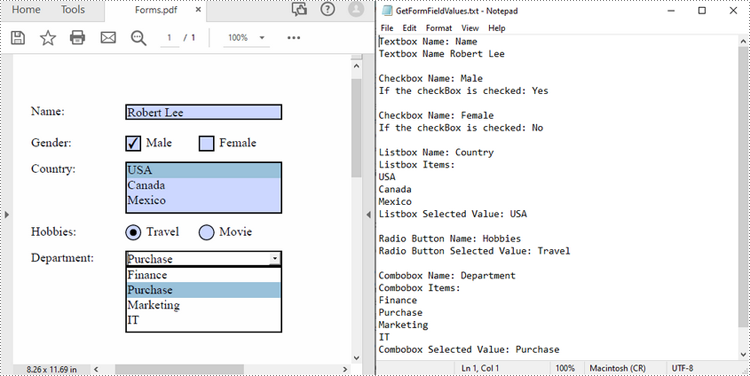
Spire.PDF for Python supports various types of PDF form fields, including:
- Text box field (represented by the PdfTextBoxFieldWidget class)
- Check box field (represented by the PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget class)
- Radio button field (represented by the PdfRadioButtonListFieldWidget class)
- List box field (represented by the PdfListBoxWidgetFieldWidget class)
- Combo box field (represented by the PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget class)
Before extracting data from the PDF forms, it is necessary to determine the specific type of each form field first, and then you can use the properties of the corresponding form field class to extract their values accurately. The following are the detailed steps.
- Initialize an instance of the PdfDocument class.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the form in the PDF document using PdfDocument.Form property.
- Create a list to store the extracted form field values.
- Iterate through all fields in the PDF form.
- Determine the types of the form fields, then get the names and values of the form fields using the corresponding properties.
- Write the results to a text file.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
inputFile = "Forms.pdf"
outputFile = "GetFormFieldValues.txt"
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get PDF forms
pdfform = pdf.Form
formWidget = PdfFormWidget(pdfform)
sb = []
# Iterate through all fields in the form
if formWidget.FieldsWidget.Count > 0:
for i in range(formWidget.FieldsWidget.Count):
field = formWidget.FieldsWidget.get_Item(i)
# Get the name and value of the textbox field
if isinstance(field, PdfTextBoxFieldWidget):
textBoxField = field if isinstance(field, PdfTextBoxFieldWidget) else None
name = textBoxField.Name
value = textBoxField.Text
sb.append("Textbox Name: " + name + "\r")
sb.append("Textbox Name " + value + "\r\n")
# Get the name of the listbox field
if isinstance(field, PdfListBoxWidgetFieldWidget):
listBoxField = field if isinstance(field, PdfListBoxWidgetFieldWidget) else None
name = listBoxField.Name
sb.append("Listbox Name: " + name + "\r")
# Get the items of the listbox field
sb.append("Listbox Items: \r")
items = listBoxField.Values
for i in range(items.Count):
item = items.get_Item(i)
sb.append(item.Value + "\r")
# Get the selected item of the listbox field
selectedValue = listBoxField.SelectedValue
sb.append("Listbox Selected Value: " + selectedValue + "\r\n")
# Get the name of the combo box field
if isinstance(field, PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget):
comBoxField = field if isinstance(field, PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget) else None
name = comBoxField.Name
sb.append("Combobox Name: " + name + "\r");
# Get the items of the combo box field
sb.append("Combobox Items: \r");
items = comBoxField.Values
for i in range(items.Count):
item = items.get_Item(i)
sb.append(item.Value + "\r")
# Get the selected item of the combo box field
selectedValue = comBoxField.SelectedValue
sb.append("Combobox Selected Value: " + selectedValue + "\r\n")
# Get the name and selected item of the radio button field
if isinstance(field, PdfRadioButtonListFieldWidget):
radioBtnField = field if isinstance(field, PdfRadioButtonListFieldWidget) else None
name = radioBtnField.Name
selectedValue = radioBtnField.SelectedValue
sb.append("Radio Button Name: " + name + "\r");
sb.append("Radio Button Selected Value: " + selectedValue + "\r\n")
# Get the name and status of the checkbox field
if isinstance(field, PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget):
checkBoxField = field if isinstance(field, PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget) else None
name = checkBoxField.Name
sb.append("Checkbox Name: " + name + "\r")
state = checkBoxField.Checked
stateValue = "Yes" if state else "No"
sb.append("If the checkBox is checked: " + stateValue + "\r\n")
# Write the results to a text file
f2=open(outputFile,'w', encoding='UTF-8')
for item in sb:
f2.write(item)
f2.close()
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
