
Python (355)
Hyperlinks in PDF documents are commonly used tools for navigating to internal or external related information. However, these links need to be accurate and up-to-date in order to be effective. Document editors are supposed to have the power to change or delete hyperlinks to update outdated references, rectify errors, comply with evolving web standards, or enhance accessibility. This article will demonstrate how to use Spire.PDF for Python to modify or remove hyperlinks in PDF documents to ensure accurate information dissemination, seamless navigation, and inclusive user experience.
- Update the Target Address of Hyperlinks in PDF Using Python
- Remove Hyperlinks in PDF Documents Using Python
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Update the Target Address of Hyperlinks in PDF Using Python
In PDF documents, hyperlinks are annotations displayed on the linked content on a page. Therefore, to modify hyperlinks in PDF documents, it is needed to retrieve all annotations on a page through PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget property. Then, a specific hyperlink annotation can be obtained from the annotation list and the target address can be updated through PdfTextWebLinkAnnotationWidget.Url property. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a page of the document using PdfDocument.Pages.get_Item() method.
- Get all annotations on the page through PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget property.
- Get a hyperlink annotation and cast it to a PdfTextWebLinkAnnotationWidget object.
- Set a new target address for the hyperlink annotation through PdfTextWebLinkAnnotationWidget.Url property.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get the first page of the document
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Get all annotations on the page
widgetCollection = page.AnnotationsWidget
# Get the second hyperlink annotation
annotation = widgetCollection.get_Item(1)
# Cast the hyperlink annotation to a PdfTextWebLinkAnnotationWidget object
link = PdfTextWebLinkAnnotationWidget(annotation)
# Set a new target address for the second hyperlink
link.Url = "https://www.mcafee.com/learn/understanding-trojan-viruses-and-how-to-get-rid-of-them/"
#Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/ModifyPDFHyperlink.pdf")
pdf.Close()

Remove Hyperlinks in PDF Documents Using Python
Spire.PDF for Python enables developers to effortlessly remove specific hyperlinks on a page using the PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.RemoveAt() method. Additionally, developers can also iterate through each page and its annotations to identify and eliminate all hyperlink annotations in the entire PDF document with the help of Spire.PDF for Python. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- To remove a specific hyperlink, get a page in the document using PdfDocument.Pages.get_Item() method and remove the hyperlink annotation using PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.RemoveAt() method.
- To remove all hyperlinks in the document, loop through the pages in the document to get the annotations on each page through PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget property.
- Loop through the annotations to check if each annotation is an instance of PdfTextWebLinkAnnotationWidget class. If it is, remove it using PdfAnnotationCollection.Remove() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import *
# # Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Remove the first hyperlink on the first page
#page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
#page.AnnotationsWidget.RemoveAt(0)
# Remove all hyperlinks
# Loop through the pages in the document
for j in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
# Get each page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(j)
# Get the annotations on each page
annotations = page.AnnotationsWidget
# Check if there is any annotations on a page
if annotations.Count > 0:
# Loop through the annotations
i = annotations.Count - 1
while i >=0:
# Get an annotation
annotation = annotations.get_Item(i)
# Check if each annotation is a hyperlink
if isinstance(annotation, PdfTextWebLinkAnnotationWidget):
# Remove hyperlink annotations
annotations.Remove(annotation)
i -= 1
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/RemovePDFHyperlink.pdf")
pdf.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
A PDF portfolio is a collection of files assembled into a single PDF document. It serves as a comprehensive and interactive showcase of various types of content, such as documents, images, presentations, videos, and more. Unlike a traditional PDF document, a PDF portfolio allows you to present multiple files in a cohesive and organized manner, providing a seamless browsing experience for the viewer. In this article, we will demonstrate how to create a PDF portfolio and how to identify if a PDF is a portfolio in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
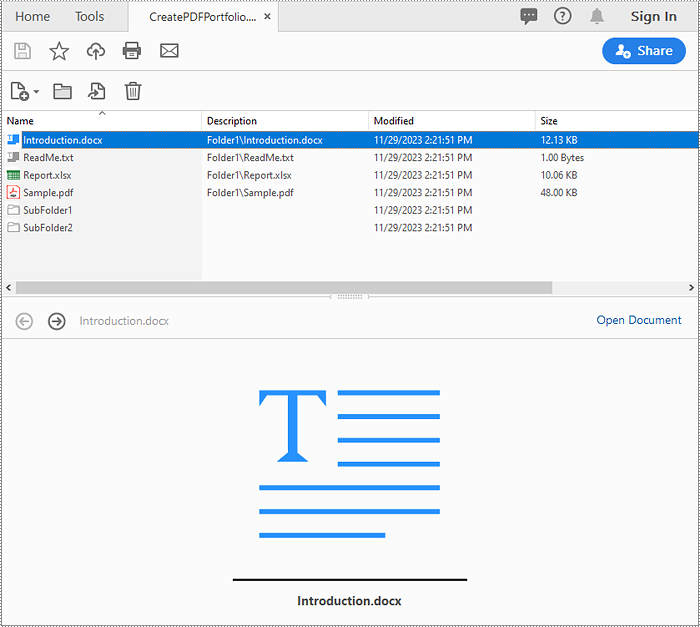
Create a PDF Portfolio with Python
Spire.PDF for Python allows you to generate a PDF portfolio by adding files to a PDF using the PdfDocument.Collection.AddFile() method. Furthermore, you can organize the files within the PDF portfolio by adding folders using the PdfDocument.Collection.Folders.CreateSubfolder() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Specify the output file path and the folders where the files to be included in the PDF portfolio are located.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Iterate through the files in the first folder and add them to the PDF portfolio using the PdfDocument.Collection.AddFile() method.
- Iterate through the files in the second folder. For each file, create a separate folder within the PDF portfolio using the PdfDocument.Collection.Folders.CreateSubfolder() method, and then add the file to the corresponding folder using the PdfFolder.AddFile() method.
- Save the resulting PDF portfolio using the PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
import glob
# Specify the folders where the files to be included in the PDF portfolio are located
input_folder1 = "Folder1/*"
input_folder2 = "Folder2/*"
# Specify the output file path
output_file = "CreatePDFPortfolio.pdf"
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Get the list of file paths in the first folder
files1 = glob.glob(input_folder1)
# Loop through the files in the list
for i, file in enumerate(files1):
# Add each file to the PDF portfolio
doc.Collection.AddFile(file)
# Get the list of file paths in the second folder
files2 = glob.glob(input_folder2)
# Loop through the files in the list
for j, file in enumerate(files2):
# Create a separate folder for each file
folder = doc.Collection.Folders.CreateSubfolder(f"SubFolder{j + 1}")
# Add the file to the folder
folder.AddFile(file)
# Save the resulting PDF portfolio to the specified file path
doc.SaveToFile(output_file)
# Close the PdfDocument object
doc.Close()
Identify if a PDF is a Portfolio with Python
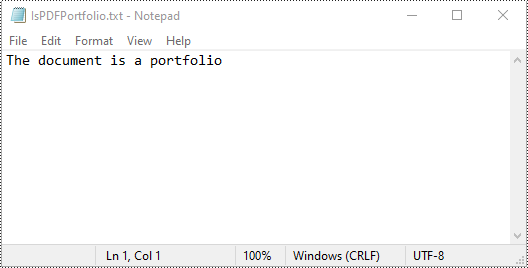
You can use the PdfDocument.IsPortfolio property to easily identify whether a PDF document is a portfolio or not. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Specify the input and output file paths.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document using the PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Identify whether the document is a portfolio or not using the PdfDocument.IsPortfolio property.
- Save the result to a text file.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Specify the input and output file paths
input_file = "CreatePDFPortfolio.pdf"
output_file = "IsPDFPortfolio.txt"
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile(input_file)
# Identify whether the document is a portfolio or not
if doc.IsPortfolio:
st = "The document is a portfolio"
else:
st = "The document is not a portfolio"
# Save the result to a text file
with open(output_file, "w") as text_file:
text_file.write(st)
# Close the PdfDocument object
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
In a PowerPoint document, the choice of fonts plays a significant role in enhancing the overall visual appeal and effectiveness of the presentation. Different fonts can be used to establish a visual hierarchy, allowing you to emphasize key points, headings, or subheadings in your presentation and guide the audience's attention. This article introduces how to set or change fonts in a PowerPoint document in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
- Set Fonts when Creating a New PowerPoint Document in Python
- Change Fonts in an Existing PowerPoint Document in Python
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Set Fonts when Creating a New PowerPoint Document in Python
Spire.Presentation for Python offers the TextRange class to represent a range of text. A paragraph can consist of one or more text ranges. To apply font formatting to the characters in a text range, you can use the properties like LatinFont, IsBold, IsItalic, and FontHeight of the TextRange class. The following are the steps to set fonts when creating a new PowerPoint document in Python.
- Create a Presentation object.
- Get the first slide through Presentation.Slides[0] property.
- Add a shape to the slide using ISlide.Shapes.AppendShape() method.
- Add text to the shape using IAutoShape.AppendTextFrame() method.
- Get TextRange object through IAutoShape.TextFrame.TextRange property.
- Set the font information such as font name, font size, bold, italic, underline, and text color through the properties under the TextRange object.
- Save the presentation to a PPTX file using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
import math
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Set slide size type
presentation.SlideSize.Type = SlideSizeType.Screen16x9
# Add a shape to the first slide
rec = RectangleF.FromLTRB (30, 100, 900, 250)
shape = presentation.Slides[0].Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, rec)
# Set line color and fill type of the shape
shape.ShapeStyle.LineColor.Color = Color.get_Transparent()
shape.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.none
# Add text to the shape
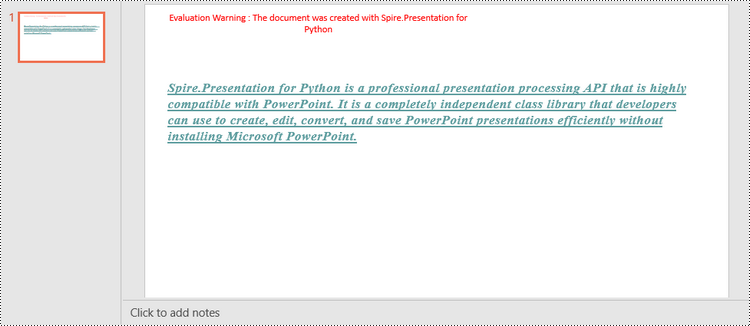
shape.AppendTextFrame("Spire.Presentation for Python is a professional presentation processing API that \
is highly compatible with PowerPoint. It is a completely independent class library that developers can \
use to create, edit, convert, and save PowerPoint presentations efficiently without installing Microsoft PowerPoint.")
# Get text of the shape as a text range
textRange = shape.TextFrame.TextRange
# Set font name
textRange.LatinFont = TextFont("Times New Roman")
# Set font style (bold & italic)
textRange.IsBold = TriState.TTrue
textRange.IsItalic = TriState.TTrue
# Set underline type
textRange.TextUnderlineType = TextUnderlineType.Single
# Set font size
textRange.FontHeight = 22
# Set text color
textRange.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
textRange.Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_CadetBlue()
# Set alignment
textRange.Paragraph.Alignment = TextAlignmentType.Left
# Set line spacing
textRange.LineSpacing = 0.5
# Save to file
presentation.SaveToFile("output/SetFont.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2019)
presentation.Dispose()
Change Fonts in an Existing PowerPoint Document in Python
To change the font for a specific paragraph, we need to get the paragraph from the document. Then, iterate through the text ranges in the paragraph and reset the font information for each text range. Below are the steps to change the font of a paragraph in an existing PowerPoint document using Spire.Presentation for Python.
- Create a Presentation object.
- Get a specific slide through Presentation.Slides[index] property.
- Get a specific shape through ISlide.Shapes[index] property.
- Get a specific paragraph of the shape through IAutoShape.TextFrame.Paragraphs[index] property.
- Iterate through the text ranges in the paragraph.
- Set the font information such as font name, font size, bold, italic, underline, and text color of a specific text range through the properties under the TextRange object.
- Save the presentation to a PPTX file using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint file
presentation.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.pptx")
# Get the first slide
slide = presentation.Slides[0]
"# Get the first shape on the slide
shape = (IAutoShape)(slide.Shapes[0])
# Get the first paragraph of the shape
paragraph = shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs[0]
# Get the first paragraph of the shape
paragraph = shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs[0]
# Create a font
newFont = TextFont("Times New Roman")
# Loop through the text ranges in the paragraph
for textRange in paragraph.TextRanges:
# Apply font to a specific text range
textRange.LatinFont = newFont
# Set font to Italic
textRange.Format.IsItalic = TriState.TTrue
# Set font size
textRange.FontHeight = 25
# Set font color
textRange.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
textRange.Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_Purple()
# Save to file
presentation.SaveToFile("output/ChangeFont.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2019)
presentation.Dispose()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Setting the background colors for paragraphs and text in Word documents can significantly enhance the presentation and readability of content. Customizing background color is an effective approach to emphasize key information, categorize content, and add a personalized touch, thereby making it easy to create polished and professional documents. By carefully selecting and applying background colors, documents can be transformed into visually appealing works that effectively convey information and engage the reader. This article shows how to use Spire.Doc for Python to set background colors for paragraphs and text in Word documents, unlocking new possibilities for document styling and customization.
- Set Background Colors for Paragraphs Using Python
- Set Background Colors for Selected Text Using Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Set Background Color for Paragraphs Using Python
By using Spire.Doc for Python, developers can get any paragraph in any section. After getting a paragraph, developers can apply a background color to it by assigning a Color object to Paragraph.Format.BackColor property. Below are the detailed steps:
- Create an instance of Document class and load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a section using Document.Sections.get_Item() method.
- Get a paragraph in the section using Section.Paragraphs.get_Item() method.
- Set the background color of the paragraph through Paragraph.Format.BackColor property.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an instance of Document class and load a Word document
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Get the first section
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get the fifth paragraph
paragraph = section.Paragraphs.get_Item(4)
# Set background color for the paragraph
paragraph.Format.BackColor = Color.get_DarkGreen()
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/ParagraphBackground.docx")
doc.Close()

Set Background Colors for Selected Text Using Python
Spire.Doc for Python enables developers to find all the occurrences of specific text in a Word document with Document.FindAllString() method. After getting the finding results, developers can set the background for them through TextRange.CharacterFormat.TextBackgroundColor property. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an instance of Document class and load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Find all the occurrences of specific text using Document.FindAllString() method.
- Loop through the occurrences, get each occurrence as a text range using TextSelection.GetAsOneRange(True) method, and set the background color of each occurrence through TextRange.CharacterFormat.TextBackgroundColor property. It is also possible to get only one occurrence from the result list and set the background color for the occurrence.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an instance of Document class and load a Word document
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Find text in the Word document
findResults = doc.FindAllString("advantages of LCD screens", False, False)
# Loop through the finding results to set background color for all occurrences
for text in findResults:
# Get an occurrence as a text range
textRange = text.GetAsOneRange(True)
# Set the background color of the text range
textRange.CharacterFormat.TextBackgroundColor = Color.get_LightCoral()
# Set the background color of a sepecified occurrence
# Get an occurrence as one text range
# textRange = findResults[1].GetAsOneRange()
# Set the background color of the text range
# textRange.CharacterFormat.BackgroundColor = Color.get_DarkCyan()
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/TextBackground.docx")
doc.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
To get the number of pages in a PDF file, you can open the file in a PDF viewer such as Adobe, which has a built-in page count feature. However, when there is a batch of PDF files, opening each file to check how many pages it contains is a time-consuming task. In this article, you will learn how to quicky count the number of pages in a PDF file through programming using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Count the Number of Pages in a PDF File in Python
Spire.PDF for Python offers the PdfDocument.Pages.Count property to quickly count the number of pages in a PDF file without opening it. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a sample PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Count the number of pages in the PDF document using PdfDocument.Pages.Count property.
- Write the result to a TXT file or print it out directly.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
def AppendText(fname: str, text: str):
fp = open(fname, "w")
fp.write(text + "\n")
fp.close()
# Specify the input and output files
inputFile = "contract.pdf"
outputFile = "GetNumberOfPages.txt"
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document from disk
pdf.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
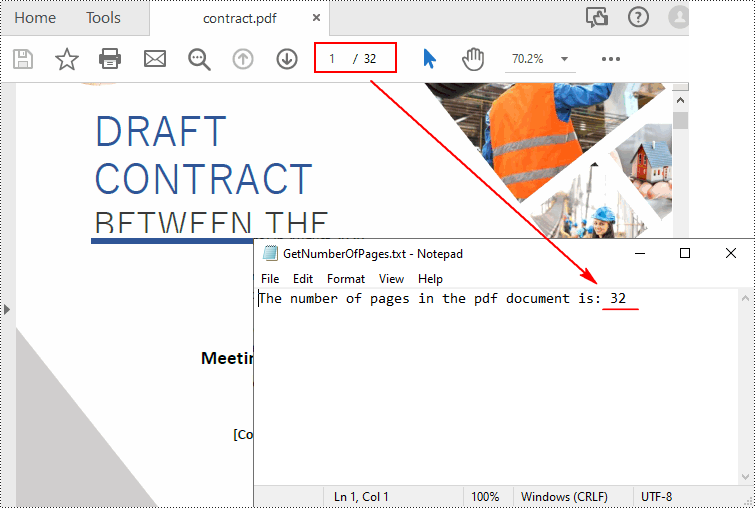
# Count the number of pages in the document
count = pdf.Pages.Count
# Print the result
print("Total Pages:", count)
# Write the result to a TXT file
AppendText(
outputFile, "The number of pages in the pdf document is: " + str(count))
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
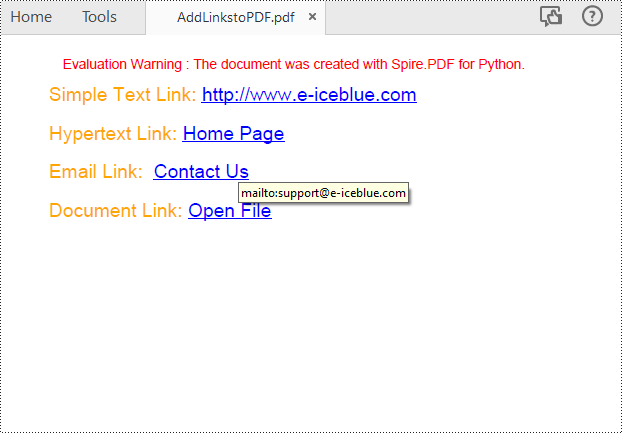
Hyperlinks in PDF are interactive elements that, when clicked, can jump to a specific location in the document, to an external website, or to other resources. By inserting hyperlinks in a PDF document, you can provide supplementary information and enhance the overall integrity of the document. This article will demonstrate how to add hyperlinks to PDF files in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Add Hyperlinks to a PDF Document in Python
With Spire.PDF for Python, you can add web links, email links and file links to a PDF document. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a pdf document and add a page to it.
- Specify a URL address and draw it directly on the page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Create a PdfTextWebLink object.
- Set the link's display text, URL address, and the font and brush used to draw it using properties of PdfTextWebLink class.
- Draw the link on the page using PdfTextWebLink.DrawTextWebLink() method.
- Create a PdfFileLinkAnnotation object and with a specified file.
- Add the file link to the page annotations using PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.Add(PdfFileLinkAnnotation) method.
- Draw hypertext of the file link using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Save the result file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a page
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
# Initialize x, y coordinates
y = 30.0
x = 10.0
# Create true type fonts
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 14.0,PdfFontStyle.Regular,True)
font1 = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 14.0, PdfFontStyle.Underline,True)
# Add a simply link
label = "Simple Text Link: "
format = PdfStringFormat()
format.MeasureTrailingSpaces = True
page.Canvas.DrawString(label, font, PdfBrushes.get_Orange(), 0.0, y, format)
x = font.MeasureString(label, format).Width
url = "http://www.e-iceblue.com"
page.Canvas.DrawString(url, font1, PdfBrushes.get_Blue(), x, y)
y = y + 28
# Add a hypertext link
label = "Hypertext Link: "
page.Canvas.DrawString(label, font, PdfBrushes.get_Orange(), 0.0, y, format)
x = font.MeasureString(label, format).Width
webLink = PdfTextWebLink()
webLink.Text = "Home Page"
webLink.Url = url
webLink.Font = font1
webLink.Brush = PdfBrushes.get_Blue()
webLink.DrawTextWebLink(page.Canvas, PointF(x, y))
y = y + 28
# Add an Email link
label = "Email Link: "
page.Canvas.DrawString(label, font, PdfBrushes.get_Orange(), 0.0, y, format)
x = font.MeasureString(label, format).Width
link = PdfTextWebLink()
link.Text = "Contact Us"
link.Url = "mailto:support@e-iceblue.com"
link.Font = font1
link.Brush = PdfBrushes.get_Blue()
link.DrawTextWebLink(page.Canvas, PointF(x, y))
y = y + 28
# Add a file link
label = "Document Link: "
page.Canvas.DrawString(label, font, PdfBrushes.get_Orange(), 0.0, y, format)
x = font.MeasureString(label, format).Width
text = "Open File"
location = PointF(x, y)
size = font1.MeasureString(text)
linkBounds = RectangleF(location, size)
fileLink = PdfFileLinkAnnotation(linkBounds,"C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Report.xlsx")
fileLink.Border = PdfAnnotationBorder(0.0)
page.AnnotationsWidget.Add(fileLink)
page.Canvas.DrawString(text, font1, PdfBrushes.get_Blue(), x, y)
#Save the result pdf file
pdf.SaveToFile("AddLinkstoPDF.pdf")
pdf.Close()
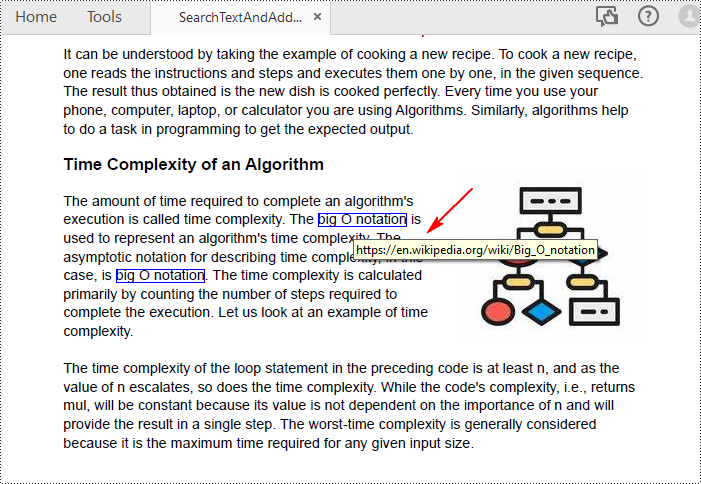
Insert Hyperlinks into Existing Text in PDF in Python
Adding a hyperlink to existing text in a PDF document requires locating the text first. Once the location has been obtained, an object of PdfUriAnnotation class with the link can be created and added to the position. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first page using PdfDocument.Pages property.
- Find all occurrences of the specified text on the page using PdfPageBase.FindText() method.
- Loop through all occurrences of the found text and create a PdfUriAnnotation instance based on the text bounds of each occurrence.
- Set the hyperlink URL, border, and border color using properties under PdfUriAnnotation class.
- Insert the hyperlink to the page annotations using PdfPageBase.AnnotationsWidget.Add(PdfUriAnnotation) method.
- Save the PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
pdf.LoadFromFile("input.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Find all occurrences of the specified text on the page
collection = page.FindText("big O notation", TextFindParameter.IgnoreCase)
# Loop through all occurrences of the specified text
for find in collection.Finds:
# Create a hyperlink annotation
uri = PdfUriAnnotation(find.Bounds)
# Set the URL of the hyperlink
uri.Uri = "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Big_O_notation"
# Set the border of the hyperlink annotation
uri.Border = PdfAnnotationBorder(1.0)
# Set the color of the border
uri.Color = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Blue())
# Add the hyperlink annotation to the page
page.AnnotationsWidget.Add(uri)
#Save the result file
pdf.SaveToFile("SearchTextAndAddHyperlink.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
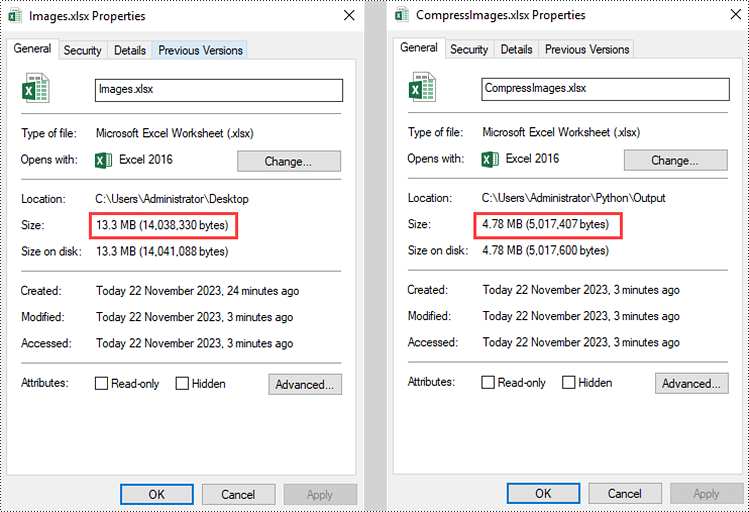
Excel provides various options to compress, resize, or move images, allowing users to effectively manage and optimize their spreadsheets. By utilizing these features, you can significantly reduce file size, adjust image dimensions to fit within cells, and effortlessly reposition images to enhance the visual appeal of your Excel documents. This article introduces how to programmatically compress, resize or move images in an Excel document in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Compress Images in an Excel Document in Python
- Resize an Image in an Excel Worksheet in Python
- Move an Image within the Same Worksheet in Python
- Move an Image from a Worksheet to Another in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Compress Images in an Excel Document in Python
To compress the quality of an image, Spire.XLS for Python offers the ExcelPicture.Compress() method. The following are the steps to compress images in an Excel document using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through the worksheets in the document, and get the images from a specific sheet through Worksheet.Pictures property.
- Get a specific image from the image collection and compress it using ExcelPicture.Compress() method.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Images.xlsx")
# Loop through the worksheets in the document
for sheet in workbook.Worksheets:
# Loop through the images in the worksheet
for picture in sheet.Pictures:
# Compress a specific image
picture.Compress(50)
# Save the file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/CompressImages.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Resize an Image in an Excel Worksheet in Python
The width and height of an image can be set or get through the ExcelPicture.Width property and the ExcelPicture.Height property. To resize an image in Excel, follow the steps below.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet though Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific image from the worksheet through Worksheet.Pictures[index] property.
- Reset the size of the image through ExcelPicture.Width property and ExcelPicture.Height property.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Image.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get a specific picture from the worksheet
picture = sheet.Pictures[0]
# Resize the picture
picture.Width = (int)(picture.Width / 2)
picture.Height = (int)(picture.Height / 2)
# Save to file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/ResizeImage.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()

Move an Image within the Same Worksheet in Python
The start position of an image can be set or get through the ExcelPicture.TopRow property and the ExcelPicture.LetColumn property. To move an image within the same worksheet, follow the steps below.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet though Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific image from the worksheet through Worksheet.Pictures[index] property.
- Reset the position of the image in the worksheet through ExcelPicture.TopRow property and ExcelPicture.LeftColumn property.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Image.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get a specific picture from the worksheet
picture = sheet.Pictures[0]
# Reset the position of the picture
picture.TopRow = 5
picture.LeftColumn = 6
# Save to file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/MoveImage.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()

Move an Image from a Worksheet to Another in Python
Besides moving images in the same worksheet, you can also move images in different worksheets of the workbook. First, you need to get the desired image from a worksheet and add it to a different worksheet using the Worksheet.Pictures.Add() method, and then delete the original image using the ExcelPicture.Remove() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet though Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific image from the worksheet through Worksheet.Pictures[index] property.
- Get another worksheet though Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Add the image to the target worksheet using Worksheet.Pictures.Add() method.
- Remove the image from the source worksheet using ExcelPicture.Remove() method.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Image.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the first picture from the worksheet
picture = sheet.Pictures[0]
# Get the second worksheet
sheet_two = workbook.Worksheets[1]
# Add the picture to the second worksheet
sheet_two.Pictures.Add(1, 1, picture.Picture)
# Remove the picture in the first worksheet
picture.Remove()
# Save to file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/MoveImage.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
The text highlighting feature in MS Word allows users to easily navigate and search for specific sections or content. By highlighting key paragraphs or keywords, users can quickly locate the desired information within the document. This feature is particularly useful when dealing with large documents, as it not only saves time but also minimizes the frustration associated with manual searching, enabling users to focus on the content that truly matters. In this article, we will demonstrate how to find and highlight text in a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Find and Highlight All Instances of a Specified Text in Word in Python
- Find and Highlight the First Instance of a Specified Text in Word in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Find and Highlight All Instances of a Specified Text in Word in Python
You can use the Document.FindAllString() method provided by Spire.Doc for Python to find all instances of a specified text in a Word document. Then you can loop through these instances and highlight each of them with a bright color using TextRange.CharacterFormat.HighlightColor property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Find all instances of a specific text in the document using Document.FindAllString() method.
- Loop through each found instance, and get it as a single text range using TextSelection.GetAsOneRange() method, then highlight the text range with color using TextRange.CharacterFormat.HighlightColor property.
- Save the resulting document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Specify the input and output file paths
inputFile = "Sample.docx"
outputFile = "HighlightAllInstances.docx"
# Create an object of the Document class
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Find all instances of a specific text
textSelections = document.FindAllString("Spire.Doc", False, True)
# Loop through all the instances
for selection in textSelections:
# Get the current instance as a single text range
textRange = selection.GetAsOneRange()
# Highlight the text range with a color
textRange.CharacterFormat.HighlightColor = Color.get_Yellow()
# Save the resulting document
document.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()

Find and Highlight the First Instance of a Specified Text in Word in Python
You can use the Document.FindString() method to find only the first instance of a specified text and then set a highlight color for it using TextRange.CharacterFormat.HighlightColor property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Find the first instance of a specific text using Document.FindString() method.
- Get the instance as a single text range using TextSelection.GetAsOneRange() method, and then highlight the text range with color using TextRange.CharacterFormat.HighlightColor property.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Specify the input and output file paths
inputFile = "Sample.docx"
outputFile = "HighlightTheFirstInstance.docx"
# Create an object of the Document class
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Find the first instance of a specific text
textSelection = document.FindString("Spire.Doc", False, True)
# Get the instance as a single text range
textRange = textSelection.GetAsOneRange()
# Highlight the text range with a color
textRange.CharacterFormat.HighlightColor = Color.get_Yellow()
# Save the resulting document
document.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
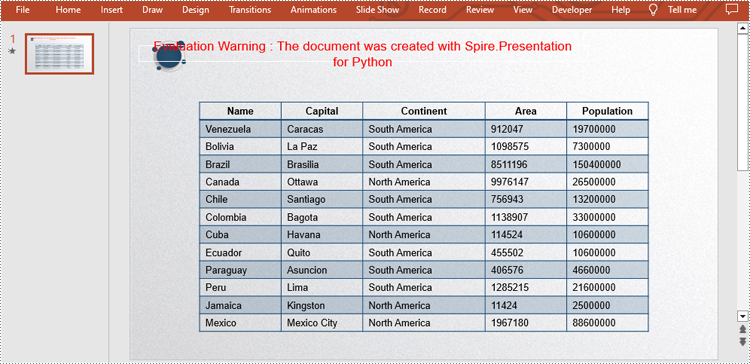
A table is a structured way of organizing and presenting data in rows and columns. It usually consists of horizontal rows and vertical columns, and each intersection can contain text, numbers, or other types of data. By inserting a table into a presentation, users can create or display structured data on slides to make the content more organized. In addition, compared to text forms, tabular data can be more intuitive to show the differences between data, which helps readers understand more, thus enhancing the professionalism and readability of the presentation. This article is going to show how to use Spire.Presentation for Python to create or edit a table in a PowerPoint Presentation in Python programs.
- Insert Tables into PowerPoint Presentations in Python
- Edit Tables in PowerPoint Presentations in Python
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Insert Tables into PowerPoint Presentations in Python
Spire.Presentation for Python provides the Presentation.Slides[].Shapes.AppendTable(x: float, y: float, widths: List[float], heights: List[float]) method to add a table to a PowerPoint presentation. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of Presentation class.
- Load a sample presentation from disk using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Define the dimensions of the table.
- Add a new table to the sample presentation by calling Presentation.Slides[].Shapes.AppendTable(x: float, y: float, widths: List[float], heights: List[float]) method.
- Define the table data as a two-dimensional string array.
- Loop through the arrays and fill each cell of the table with these data by ITable[columnIndex, rowIndex].TextFrame.Text property.
- Set font name and font size for these data.
- Set the alignment of the first row in the table to center.
- Apply a built-in style to the table using ITable.StylePreset property.
- Save the result file using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
import math
from spire.presentation import *
inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Sample.pptx"
outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/CreateTable.pptx"
#Create an object of Presentation class
presentation = Presentation()
#Load a sample presentation from disk
presentation.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
#Define the dimensions of the table
widths = [100, 100, 150, 100, 100]
heights = [15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15, 15]
#Add a new table to this presentation
left = math.trunc(presentation.SlideSize.Size.Width / float(2)) - 275
table = presentation.Slides[0].Shapes.AppendTable(left, 90, widths, heights)
#Define the table data as a two-dimensional string array
dataStr = [["Name", "Capital", "Continent", "Area", "Population"],
["Venezuela", "Caracas", "South America", "912047", "19700000"],
["Bolivia", "La Paz", "South America", "1098575", "7300000"],
["Brazil", "Brasilia", "South America", "8511196", "150400000"],
["Canada", "Ottawa", "North America", "9976147", "26500000"],
["Chile", "Santiago", "South America", "756943", "13200000"],
["Colombia", "Bagota", "South America", "1138907", "33000000"],
["Cuba", "Havana", "North America", "114524", "10600000"],
["Ecuador", "Quito", "South America", "455502", "10600000"],
["Paraguay", "Asuncion", "South America", "406576", "4660000"],
["Peru", "Lima", "South America", "1285215", "21600000"],
["Jamaica", "Kingston", "North America", "11424", "2500000"],
["Mexico", "Mexico City", "North America", "1967180", "88600000"]]
#Loop through the arrays
for i in range(0, 13):
for j in range(0, 5):
#Fill each cell of the table with these data
table[j,i].TextFrame.Text = dataStr[i][j]
#Set font name and font size
table[j,i].TextFrame.Paragraphs[0].TextRanges[0].LatinFont = TextFont("Arial")
table[j,i].TextFrame.Paragraphs[0].TextRanges[0].FontHeight = 12
#Set the alignment of the first row in the table to center
for i in range(0, 5):
table[i,0].TextFrame.Paragraphs[0].Alignment = TextAlignmentType.Center
#Apply a style to the table
table.StylePreset = TableStylePreset.LightStyle3Accent1
#Save the result file
presentation.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Pptx2010)
presentation.Dispose()
Edit Tables in PowerPoint Presentations in Python
You are also allowed to edit tables in the presentation as needed, such as replacing data, changing styles, highlighting data, and so on. Here are the detailed steps.
- Create an object of Presentation class.
- Load a sample presentation from disk using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Store the data used for replacement in a string.
- Loop through the shapes in the first slide, and determine if a certain shape is a table. If yes, convert it to an ITable object.
- Change the style of the table using ITable.StylePreset property.
- Replace the data in a specific cell range by using ITable[columnIndex, rowIndex].TextFrame.Text property.
- Highlight the new data using ITable[columnIndex, rowIndex].TextFrame.TextRange.HighlightColor.Color property.
- Save the result file using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/CreateTable.pptx"
outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/EditTable.pptx"
#Create an object of Presentation class
presentation = Presentation()
#Load a sample presentation from disk
presentation.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
#Store the data used in replacement in a string
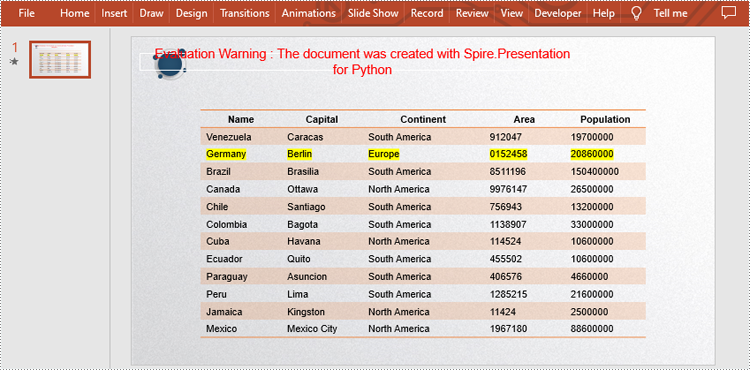
strs = ["Germany", "Berlin", "Europe", "0152458", "20860000"]
table = None
#Loop through shapes in the first slide to get the table
for shape in presentation.Slides[0].Shapes:
if isinstance(shape, ITable):
table = shape
#Change the style of the table
table.StylePreset = TableStylePreset.LightStyle1Accent2
for i, unusedItem in enumerate(table.ColumnsList):
#Replace the data in a specific cell range
table[i,2].TextFrame.Text = strs[i]
#Highlight the new data
table[i,2].TextFrame.TextRange.HighlightColor.Color = Color.get_Yellow()
#Save the result file
presentation.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Pptx2013)
presentation.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Grouping shapes in PowerPoint can greatly simplify the shape editing process, especially when dealing with complex arrangements of shapes. It allows you to modify the entire group collectively, saving time and effort compared to adjusting each shape individually. This is particularly beneficial when you need to apply consistent formatting or positioning to a set of shapes. Ungrouping shapes provides increased flexibility and customization options. By ungrouping a set of grouped shapes, you regain individual control over each shape. This allows you to make specific modifications, resize or reposition individual shapes, and apply unique formatting or styling as needed. In this article, we will explain how to group and ungroup shapes in PowerPoint in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Group Shapes in PowerPoint in Python
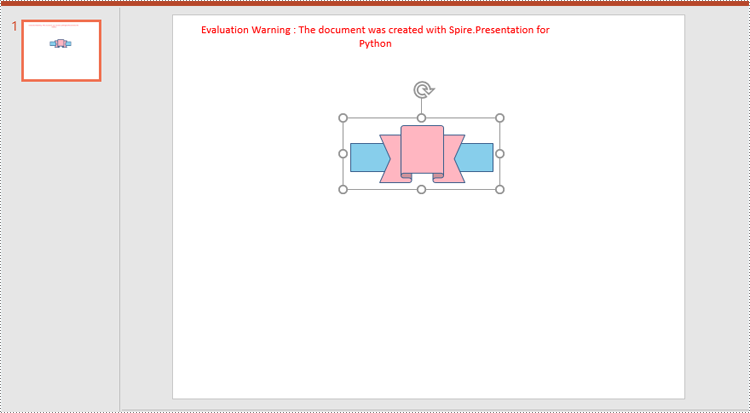
Spire.Presentation for Python provides the ISlide.GroupShapes(shapeList: List) method to group two or more shapes on a specific slide. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Get the first slide using Presentation.Slides[0] property.
- Add two shapes to the slide using ISlide.Shapes.AppendShape() method.
- Create a list to store the shapes that need to be grouped.
- Add the two shapes to the list.
- Group the two shapes using ISlide.GroupShapes(shapeList: List) method.
- Save the result document using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
ppt = Presentation()
# Get the first slide
slide = ppt.Slides[0]
# Add two shapes to the slide
rectangle = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, RectangleF.FromLTRB (250, 180, 450, 220))
rectangle.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
rectangle.Fill.SolidColor.KnownColor = KnownColors.SkyBlue
rectangle.Line.Width = 0.1
ribbon = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Ribbon2, RectangleF.FromLTRB (290, 155, 410, 235))
ribbon.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
ribbon.Fill.SolidColor.KnownColor = KnownColors.LightPink
ribbon.Line.Width = 0.1
# Add the two shapes to a list
shape_list = []
shape_list.append(rectangle)
shape_list.append(ribbon)
# Group the two shapes
slide.GroupShapes(shape_list)
# Save the resulting document
ppt.SaveToFile("GroupShapes.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
ppt.Dispose()
Ungroup Shapes in PowerPoint in Python
To ungroup the grouped shapes in a PowerPoint document, you need to iterate through all slides in the document and all shapes on each slide, find the grouped shapes and then ungroup them using ISlide.Ungroup(groupShape: GroupShape) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load the PowerPoint document using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through all slides in the document.
- Iterate through all shapes on each slide.
- Check if the current shape is of GroupShape type. If the result is True, ungroup it using ISlide.Ungroup(groupShape: GroupShape) method.
- Save the result document using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
ppt = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint document
ppt.LoadFromFile("GroupShapes.pptx")
# Iterate through all slides in the document
for i in range(ppt.Slides.Count):
slide = ppt.Slides[i]
# Iterate through all shapes on each slide
for j in range(slide.Shapes.Count):
shape = slide.Shapes[j]
# Check if the shape is a grouped shape
if isinstance(shape, GroupShape):
groupShape = shape
# Ungroup the grouped shape
slide.Ungroup(groupShape)
# Save the resulting document
ppt.SaveToFile("UngroupShapes.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
ppt.Dispose()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
