
Python (355)
Locking cells is often used to protect the contents of specific cell ranges in a spreadsheet from accidental modification, which is useful in situations such as sharing a worksheet or protecting specific data. When you lock a cell, no one else can edit it unless they know the password or have the appropriate permissions. This feature is important for data security and integrity. In this article, we will show you how to lock specific cells, columns or rows in Excel on python platforms by using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Lock Specific Cells in Python
Spire.XLS for Python supports users to lock a specified range of cells by setting the Worksheet.Range[].Style.Locked property to "True". Below are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook instance and load a sample excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Unlock all cells in the used range of the worksheet by setting the Worksheet.Range.Style.Locked property to "False".
- Set text for the specific cells using Worksheet.Range[].Text property and then lock them by setting the Worksheet.Range[].Style.Locked property to "True".
- Protect the worksheet using XlsWorksheetBase.Protect() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Sample.xlsx"
outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/LockSpecificCells.xlsx"
# Create a Workbook instance and load a sample file
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Unlock all cells in the used range of the worksheet
sheet.Range.Style.Locked = False
# Lock a specific cell in the sheet
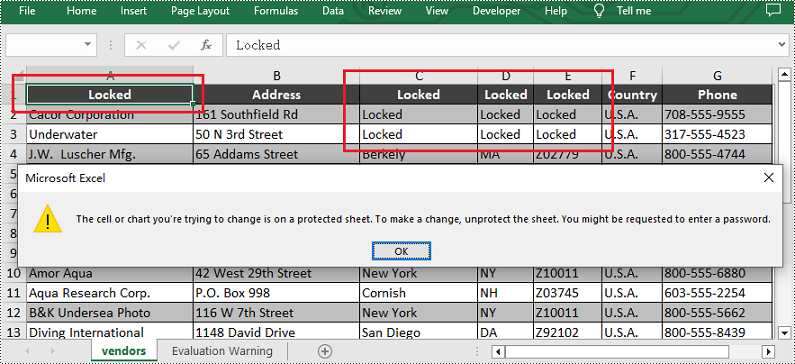
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "Locked"
sheet.Range["A1"].Style.Locked = True
# Lock a specific range of cells in the sheet
sheet.Range["C1:E3"].Text = "Locked"
sheet.Range["C1:E3"].Style.Locked = True
# Protect the worksheet with a password
sheet.Protect("123456", SheetProtectionType.All)
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Lock a Specific Column in Python
If you want to lock a specific column in the worksheet, please set the Worksheet.Columns[].Style.Locked property to "True". Other steps are similar to the above method. Below are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook instance and load a sample excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Unlock all cells in the used range of the worksheet by setting the Worksheet.Range.Style.Locked property to "False".
- Set text for the fourth column using the Worksheet.Columns[].Text property and then lock it by setting the Worksheet.Columns[].Style.Locked property to "True".
- Protect the worksheet with a password by calling XlsWorksheetBase.Protect() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Sample.xlsx"
outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/LockSpecificColumn.xlsx"
# Create a Workbook instance and load a sample file
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Unlock all cells in the used range of the worksheet
sheet.Range.Style.Locked = False
# Lock the fourth column in the sheet
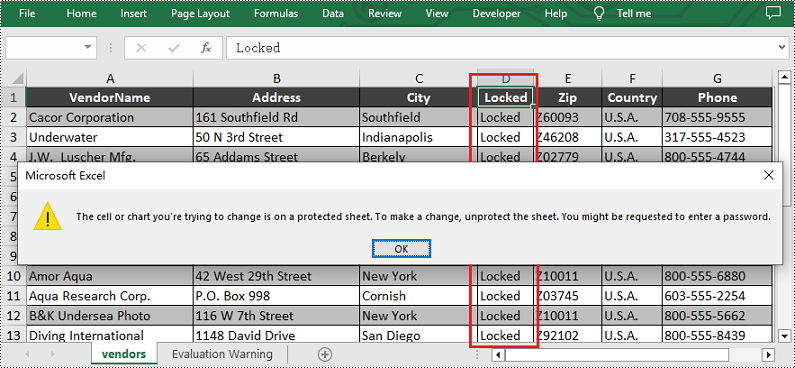
sheet.Columns[3].Text = "Locked"
sheet.Columns[3].Style.Locked = True
# Protect the worksheet with a password
sheet.Protect("123456", SheetProtectionType.All)
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Lock a Specific Row in Python
Similarly, if you want to lock a certain row, please set the Worksheet.Rows[].Style.Locked property to "True". Here are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook instance and load a sample excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Unlock all cells in the used range of the worksheet by setting the Worksheet.Range.Style.Locked property to "False".
- Set text for the third row using the Worksheet.Rows[].Text property and then lock it by setting the Worksheet.Rows[].Style.Locked property to "True".
- Protect the worksheet with a password using XlsWorksheetBase.Protect() method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Sample.xlsx"
outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/LockSpecificRow.xlsx"
# Create a Workbook instance and load a sample file
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Unlock all cells in the used range of the worksheet
sheet.Range.Style.Locked = False
# Lock the third row in the worksheet
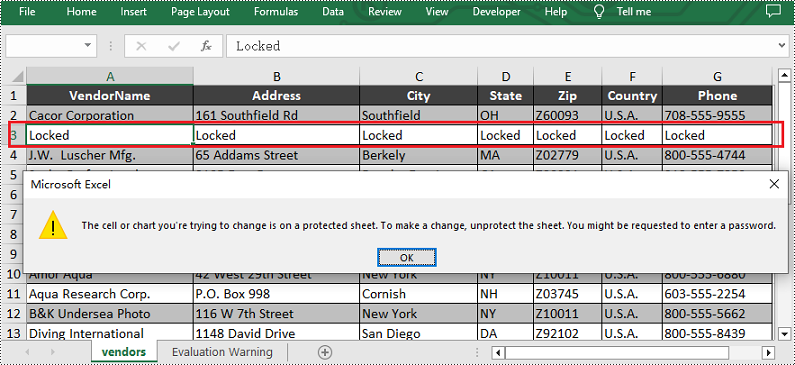
sheet.Rows[2].Text = "Locked"
sheet.Rows[2].Style.Locked = True
# Protect the worksheet with a password
sheet.Protect("123456", SheetProtectionType.All)
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
PDF files are designed to preserve the formatting and layout of the original document, making them ideal for sharing and printing. However, they are typically not editable without specialized software. Converting a PDF to a Word document allows you to make changes, add or delete text, modify formatting, and customize content as needed. This is particularly useful when you want to update or revise existing PDF files. In this article, we will explain how to convert PDF to Word DOC or DOCX formats in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Convert PDF to Word DOC or DOCX in Python
- Setting Document Properties While Converting PDF to Word in Python
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Convert PDF to Word DOC or DOCX in Python
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfDocument.SaveToFile(filename:str, fileFormat:FileFormat) method to convert PDF documents to a wide range of file formats, including Word DOC, DOCX, and more. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the PdfDocument class.
- Load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Convert the PDF document to a Word DOCX or DOC file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile(filename:str, fileFormat:FileFormat) method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create an object of the PdfDocument class
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Convert the PDF document to a Word DOCX file
doc.SaveToFile("ToDocx.docx", FileFormat.DOCX)
# Or convert the PDF document to a Word DOC file
doc.SaveToFile("ToDoc.doc", FileFormat.DOC)
# Close the PdfDocument object
doc.Close()
Setting Document Properties While Converting PDF to Word in Python
Document properties are attributes or information associated with a document that provide additional details about the file. These properties offer insights into various aspects of the document, such as its author, title, subject, version, keywords, category, and more.
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfToDocConverter class which allows developers to convert a PDF document to a Word DOCX file and set document properties for the file. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the PdfToDocConverter class.
- Set document properties, such as title, subject, comment and author, for the converted Word DOCX file using the properties of the PdfToDocConverter class.
- Convert the PDF document to a Word DOCX file using PdfToDocConverter.SaveToDocx() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create an object of the PdfToDocConverter class
converter = PdfToDocConverter("Sample.pdf")
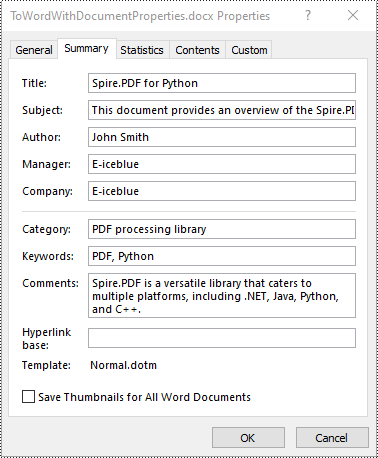
# Set document properties such as title, subject, author and keywords for the converted .DOCX file
converter.DocxOptions.Title = "Spire.PDF for Python"
converter.DocxOptions.Subject = "This document provides an overview of the Spire.PDF for Python product."
converter.DocxOptions.Tags = "PDF, Python"
converter.DocxOptions.Categories = "PDF processing library"
converter.DocxOptions.Commments = "Spire.PDF is a versatile library that caters to multiple platforms, including .NET, Java, Python, and C++."
converter.DocxOptions.Authors = "John Smith"
converter.DocxOptions.LastSavedBy = "Alexander Johnson"
converter.DocxOptions.Revision = 8
converter.DocxOptions.Version = "V4.0"
converter.DocxOptions.ProgramName = "Spire.PDF for Python"
converter.DocxOptions.Company = "E-iceblue"
converter.DocxOptions.Manager = "E-iceblue"
# Convert the PDF document to a Word DOCX file
converter.SaveToDocx("ToWordWithDocumentProperties.docx")
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
OLE enables users to incorporate diverse file types-such as images, charts, documents, and multimedia-directly into Excel workbooks, fostering a more dynamic and comprehensive representation of information. By inserting OLE objects, users can create interactive and engaging spreadsheets that integrate a variety of data formats to simplify analyses and presentations in a single Excel environment. In this article, you will learn how to insert linked or embedded OLE objects to Excel in Python as well as how to extract OLE objects from Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Insert a Linked OLE Object to Excel in Python
- Insert an Embedded Object to Excel in Python
- Extract OLE Objects from Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
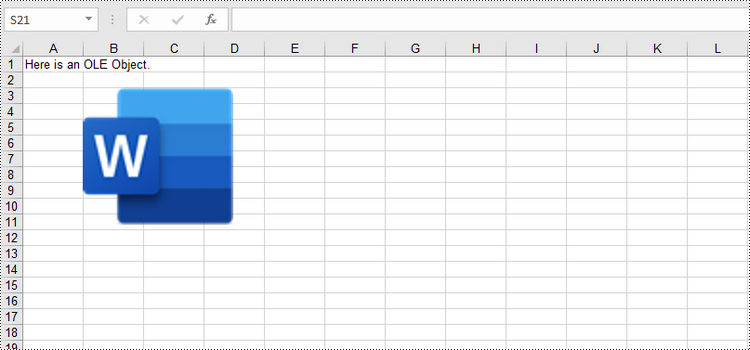
Insert a Linked OLE Object to Excel in Python
To insert an OLE object to a worksheet, you use the Worksheet.OleObjects.Add(fileName, image, linkType) method, in which:
- the fileName parameter specifies the path of an external file to be inserted,
- the image parameter specifies a thumbnail of the first page or a document icon that the OLE object will be displayed as,
- the linkType parameter determines whether the OLE object is inserted to the document as an embedded source or a linked source.
The following are the steps to insert a linked OEL object to Excel using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get the first worksheet through Workbook.Worksheet[index] property.
- Load an image using Image.FromFile() method.
- Insert an OLE object to the worksheet using Worksheet.OleObjects.Add() method, and specify the link type as OleLinkType.Link.
- Specify the OLE object location through IOleObject.Location property.
- Specify the OLE object type through IOleObject.ObjectType property.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Add text to A1
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "Here is an OLE Object."
# Load an image to be displayed as an icon of ole object
image = Image.FromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/word_icon.png")
with Stream() as stream:
image.Save(stream,ImageFormat.get_Png())
# Add an ole object to the worksheet that links to an external file
oleObject = sheet.OleObjects.Add("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/invoice.docx", stream, OleLinkType.Link)
# Specify ole object location
oleObject.Location = sheet.Range["B3"]
# Specify ole object type
oleObject.ObjectType = OleObjectType.WordDocument
# Save to file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/OleObject.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
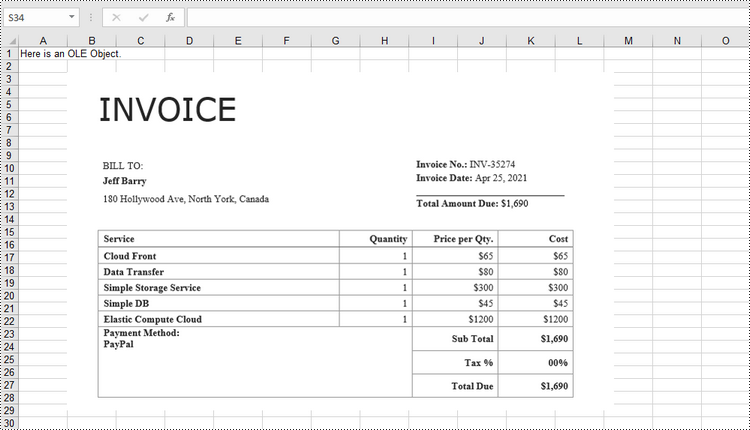
Insert an Embedded OLE Object to Excel in Python
To insert an embedded OEL object to Excel, you specify the link type as OleLinkType.Embed while invoking the Worksheet.OleObjects.Add() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get the first worksheet through Workbook.Worksheet[index] property.
- Load an image using Image.FromFile() method.
- Insert an OLE object to the worksheet using Worksheet.OleObjects.Add() method, and specify the link type as OleLinkType.Embed.
- Specify the OLE object location through IOleObject.Location property.
- Specify the OLE object type through IOleObject.ObjectType property.
- Save the workbook to an Excel file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Add text to A1
sheet.Range["A1"].Text = "Here is an OLE Object."
# Load an image that represents ole object
image = Image.FromFile("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/screenshot.png")
with Stream() as stream:
image.Save(stream,ImageFormat.get_Png())
# Add an ole object to the worksheet as embedded source
oleObject = sheet.OleObjects.Add("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/invoice.docx", stream, OleLinkType.Embed)
# Specify ole object location
oleObject.Location = sheet.Range["B3"]
# Specify ole object type
oleObject.ObjectType = OleObjectType.WordDocument
# Save to file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/OleObject.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
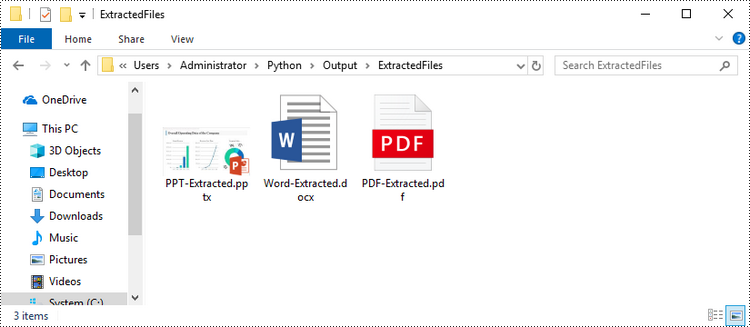
Extract OLE Objects from Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python provides the Worksheet.HasOleObjects property to determine whether a worksheet has OLE objects. If it does, get all the objects through the Worksheet.OleObjects property. Then, determine the type of a particular OEL object and save the OEL as a file of the appropriate document type. The following are the steps to extract OLE objects from Excel using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheet[index] property.
- Determine if the worksheet contains OLE objects through Worksheet.HasOleObjects property.
- Get all the OLE objects from the worksheet through Worksheet.OleObjects property.
- Determine the type of a particular OEL object and save the OEL as a file of the appropriate document type.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Write data to file
def WriteAllBytes(fname:str,data):
fp = open(fname,"wb")
for d in data:
fp.write(d)
fp.close()
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\OleObjects.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Determine if the worksheet has ole objects
if sheet.HasOleObjects:
# Iterate through the found objects
for obj in sheet.OleObjects:
# If the object type is a Word document, save it to a .docx file
type = obj.ObjectType
if type is OleObjectType.WordDocument:
WriteAllBytes("output/ExtractedFiles/Word-Extracted.docx", obj.OleData)
# If the object type is an Adobe Acrobat document, save it to a .pdf file
if type is OleObjectType.AdobeAcrobatDocument:
WriteAllBytes("output/ExtractedFiles/PDF-Extracted.pdf", obj.OleData)
# If the object type is a PowerPoint document, save it to a .pptx file
if type is OleObjectType.PowerPointPresentation:
WriteAllBytes("output/ExtractedFiles/PPT-Extracted.pptx", obj.OleData)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
When editing or updating a large presentation, manually locating and modifying specific text elements can be a tedious and time-consuming process. By using the replace feature in PowerPoint, you can quickly and accurately make updates throughout the presentation, ensuring that the information remains accurate and consistent. In this article, we will demonstrate how to replace text in PowerPoint presentations in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
- Replace the First Occurrence of a Specific Text in PowerPoint in Python
- Replace All Occurrences of a Specific Text in PowerPoint in Python
- Replace Text Using a Regular Expression in PowerPoint in Python
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Replace the First Occurrence of a Specific Text in PowerPoint in Python
To replace the first occurrence of a specific text in a PowerPoint document, you can loop through all slides in the document, and then call the ISlide.ReplaceFirstText() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint document using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Loop through all slides in the PowerPoint document.
- Replace the first occurrence of a specific text with new text using ISlide.ReplaceFirstText() method.
- Save the result document using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
ppt = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint document
ppt.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Loop through all slides in the document
for slide in ppt.Slides:
# Replace the first occurrence of "Spire.Presentation for Python" with "E-iceblue Product"
slide.ReplaceFirstText("Spire.Presentation for Python", "E-iceblue Product", False)
break
# Save the result document
ppt.SaveToFile("ReplaceFirstTextOccurrence.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
ppt.Dispose()
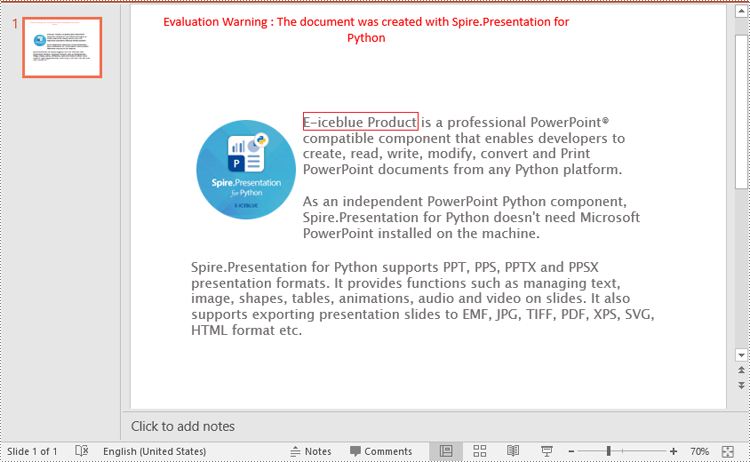
Replace All Occurrences of a Specific Text in PowerPoint in Python
To replace all occurrences of a specific text in a PowerPoint document, you can loop through all slides in the document, and then use the ISlide.ReplaceAllText() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint document using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Loop through all slides in the PowerPoint document.
- Replace all occurrences of a specific text with new text using ISlide.ReplaceAllText() method.
- Save the result document using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
ppt = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint document
ppt.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Loop through all slides in the document
for slide in ppt.Slides:
# Replace all occurrences of "Spire.Presentation for Python" with "E-iceblue Product"
slide.ReplaceAllText("Spire.Presentation for Python", "E-iceblue Product", False)
# Save the result document
ppt.SaveToFile("ReplaceAllTextOccurrences.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
ppt.Dispose()
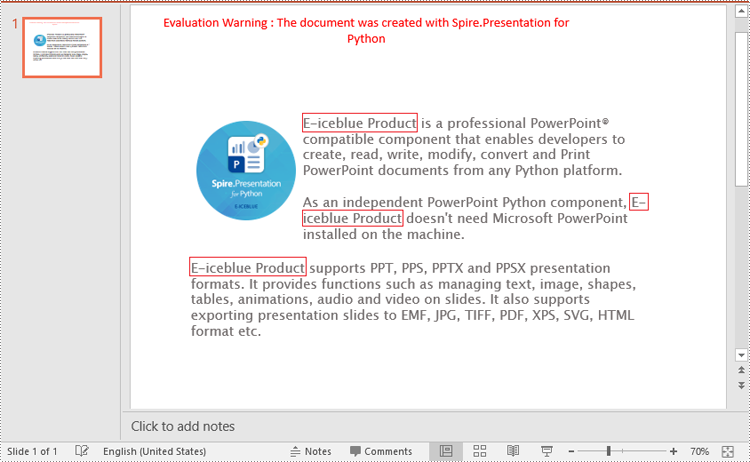
Replace Text Using a Regular Expression in PowerPoint in Python
Spire.Presentation for Python provides the IShape.ReplaceTextWithRegex() method to replace text matching a regular expression pattern. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint document using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Loop through all slides in the PowerPoint document.
- Loop through all shapes on each slide.
- Replace text matching a regular expression pattern using IShape.ReplaceTextWithRegex() method.
- Save the result document using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
ppt = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint document
ppt.LoadFromFile("Sample1.pptx")
# Loop through all slides in the document
for slide in ppt.Slides:
# Loop through all shapes on each slide
for shape in slide.Shapes:
# Replace text starting with # on the slide to "Monitor"
shape.ReplaceTextWithRegex(Regex("#\w+"), "Monitor")
# Save the result document
ppt.SaveToFile("ReplaceTextUsingRegex.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
ppt.Dispose()
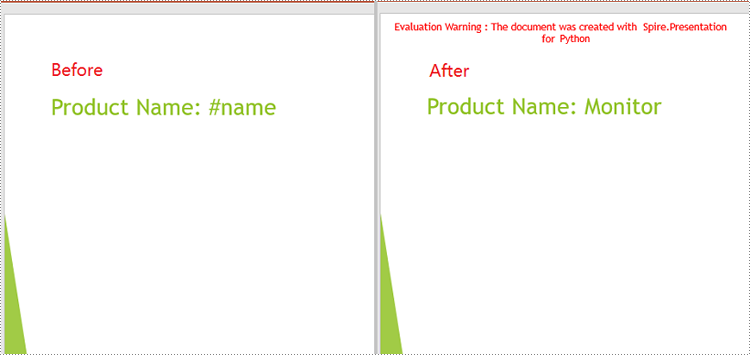
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Creating a form in PDF not only ensures a professional appearance but also allows users to fill out and submit data electronically, streamlining data entry processes. Whether you are collecting survey responses, gathering client information, or creating employment applications, the ability to generate interactive PDF forms offers a seamless and organized way to capture, store, and manage valuable data. In this article, you will learn how to create a fillable PDF form as well as how to fill in a PDF form using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Create a Fillable Form in PDF in Python
Spire.PDF for Python provides a range of helpful classes that enable programmers to generate and modify different types of form fields in PDF files. These include text boxes, check boxes, combo boxes, list boxes, and radio buttons. The table below lists some of the classes involved in this tutorial.
| Class | Description |
| PdfForm | Represents interactive form of the PDF document. |
| PdfField | Represents field of the PDF document's interactive form. |
| PdfTextBoxField | Represents text box field in the PDF form. |
| PdfCheckBoxField | Represents check box field in the PDF form. |
| PdfComboBoxField | Represents combo box field in the PDF Form. |
| PdfListBoxField | Represents list box field of the PDF form. |
| PdfListFieldItem | Represents an item of a list field. |
| PdfRadioButtonListField | Represents radio button field in the PDF form. |
| PdfRadioButtonListItem | Represents an item of a radio button list. |
| PdfButtonField | Represents button field in the PDF form. |
To generate a PDF form, start by creating an instance of the respective field class. Set the field's size and position in the document using the Bounds property, and finally, add it to the PDF using the PdfFormFieldCollection.Add() method. The following are the main steps to create various types of form fields in a PDF document using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Add a page using PdfDocuemnt.Pages.Add() method.
- Create a PdfTextBoxField object, set the properties of the field including Bounds, Font and Text, and then add it to the document using PdfFormFieldCollection.Add() method.
- Repeat the step 3 to add check box, combo box, list box, radio button, and button to the document.
- Save the document to a PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Add a page
page = doc.Pages.Add()
# Initialize x and y coordinates
baseX = 100.0
baseY = 30.0
# Create two brush objects
brush1 = PdfSolidBrush(PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Blue()))
brush2 = PdfSolidBrush(PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Black()))
# Create a font
font = PdfFont(PdfFontFamily.TimesRoman, 12.0, PdfFontStyle.Regular)
# Add a textbox
page.Canvas.DrawString("Name:", font, brush1, PointF(10.0, baseY))
tbxBounds = RectangleF(baseX, baseY, 150.0, 15.0)
textBox = PdfTextBoxField(page, "name")
textBox.Bounds = tbxBounds
textBox.Font = font
doc.Form.Fields.Add(textBox)
baseY += 30.0
# add two checkboxes
page.Canvas.DrawString("Gender:", font, brush1, PointF(10.0, baseY));
checkboxBound1 = RectangleF(baseX, baseY, 15.0, 15.0)
checkBoxField1 = PdfCheckBoxField(page, "male")
checkBoxField1.Bounds = checkboxBound1
checkBoxField1.Checked = False
page.Canvas.DrawString("Male", font, brush2, PointF(baseX + 20.0, baseY))
checkboxBound2 = RectangleF(baseX + 70.0, baseY, 15.0, 15.0)
checkBoxField2 = PdfCheckBoxField(page, "female")
checkBoxField2.Bounds = checkboxBound2
checkBoxField2.Checked = False
page.Canvas.DrawString("Female", font, brush2, PointF(baseX + 90.0, baseY))
doc.Form.Fields.Add(checkBoxField1)
doc.Form.Fields.Add(checkBoxField2)
baseY += 30.0
# Add a listbox
page.Canvas.DrawString("Country:", font, brush1, PointF(10.0, baseY))
listboxBound = RectangleF(baseX, baseY, 150.0, 50.0)
listBoxField = PdfListBoxField(page, "country")
listBoxField.Items.Add(PdfListFieldItem("USA", "usa"))
listBoxField.Items.Add(PdfListFieldItem("Canada", "canada"))
listBoxField.Items.Add(PdfListFieldItem("Mexico", "mexico"))
listBoxField.Bounds = listboxBound
listBoxField.Font = font
doc.Form.Fields.Add(listBoxField)
baseY += 60.0
# Add two radio buttons
page.Canvas.DrawString("Hobbies:", font, brush1, PointF(10.0, baseY))
radioButtonListField = PdfRadioButtonListField(page, "hobbies")
radioItem1 = PdfRadioButtonListItem("travel")
radioBound1 = RectangleF(baseX, baseY, 15.0, 15.0)
radioItem1.Bounds = radioBound1
page.Canvas.DrawString("Travel", font, brush2, PointF(baseX + 20.0, baseY))
radioItem2 = PdfRadioButtonListItem("movie")
radioBound2 = RectangleF(baseX + 70.0, baseY, 15.0, 15.0)
radioItem2.Bounds = radioBound2
page.Canvas.DrawString("Movie", font, brush2, PointF(baseX + 90.0, baseY))
radioButtonListField.Items.Add(radioItem1)
radioButtonListField.Items.Add(radioItem2)
doc.Form.Fields.Add(radioButtonListField)
baseY += 30.0
# Add a combobox
page.Canvas.DrawString("Degree:", font, brush1, PointF(10.0, baseY))
cmbBounds = RectangleF(baseX, baseY, 150.0, 15.0)
comboBoxField = PdfComboBoxField(page, "degree")
comboBoxField.Bounds = cmbBounds
comboBoxField.Items.Add(PdfListFieldItem("Bachelor", "bachelor"))
comboBoxField.Items.Add(PdfListFieldItem("Master", "master"))
comboBoxField.Items.Add(PdfListFieldItem("Doctor", "doctor"))
comboBoxField.Font = font
doc.Form.Fields.Add(comboBoxField)
baseY += 30.0
# Add a button
page.Canvas.DrawString("Button:", font, brush1, PointF(10.0, baseY))
btnBounds = RectangleF(baseX, baseY, 50.0, 15.0)
buttonField = PdfButtonField(page, "button")
buttonField.Bounds = btnBounds
buttonField.Text = "Submit"
buttonField.Font = font
submitAction = PdfSubmitAction("https://www.e-iceblue.com/getformvalues.php")
buttonField.Actions.MouseDown = submitAction
doc.Form.Fields.Add(buttonField)
# Save to file
doc.SaveToFile("output/Form.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
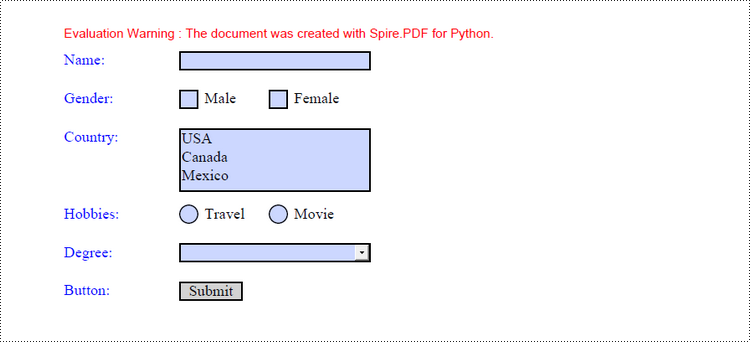
Fill in a PDF Form in Python
In order to fill in a form, the necessary steps include obtaining all form fields from the PDF document, locating a specific field based on its type and name, and subsequently entering or selecting a value from a predetermined list. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Load a sample PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the form from the document through PdfDocument.Form property.
- Get the form widget collection through PdfFormWidget.FieldsWidget property.
- Get a specific form field by its type and name.
- Enter a value or select a value from the predefined list for the field.
- Save the document to a PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document contaning form fields
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Form.pdf")
# Get form from the document
form = doc.Form
formWidget = PdfFormWidget(form)
# Get form widget collection
formWidgetCollection = formWidget.FieldsWidget
# If the collection is nut null
if formWidgetCollection.Count > 0:
# Loop through the elements in the form widget collection
for i in range(formWidgetCollection.Count):
# Get a specific field
field = formWidgetCollection.get_Item(i)
# Determine if a field is a textbox
if isinstance(field, PdfTextBoxFieldWidget):
textBoxField = field if isinstance(field, PdfTextBoxFieldWidget) else None
# Determine if the name of the text box is "name"
if textBoxField.Name == "name":
# Add text to the text box
textBoxField.Text = "Jackson Green"
# Choose an item from the list box
if isinstance(field, PdfListBoxWidgetFieldWidget):
listBoxField = field if isinstance(field, PdfListBoxWidgetFieldWidget) else None
if listBoxField.Name == "country":
index = [1]
listBoxField.SelectedIndex = index
# Choose an item from the combo box
if isinstance(field, PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget):
comBoxField = field if isinstance(field, PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget) else None
if comBoxField.Name == "degree":
items = [0]
comBoxField.SelectedIndex = items
# Select an item in the radio buttons
if isinstance(field, PdfRadioButtonListFieldWidget):
radioBtnField = field if isinstance(field, PdfRadioButtonListFieldWidget) else None
if radioBtnField.Name == "hobbies":
radioBtnField.SelectedIndex = 1
# Check the specified check box
if isinstance(field, PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget):
checkBoxField = field if isinstance(field, PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget) else None
if checkBoxField.Name == "male":
checkBoxField.Checked = True
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/FillForm.pdf")
doc.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Lists are a fundamental data structure in PDF documents as they allow users to efficiently store and arrange collections of items. The three most commonly utilized list types in PDFs are ordered lists, unordered lists (also known as bulleted lists), and nested lists. These lists facilitate the presentation of information in a well-organized and visually appealing manner within PDF documents. In this article, we will explore how to use Spire.PDF for Python to create ordered, unordered, and nested lists in PDF documents for generating professional-looking PDF documents.
- Create Ordered Lists in PDF with Python
- Create Unordered Lists with Symbol Markers in PDF Using Python
- Create Unordered Lists with Image Markers in PDF Using Python
- Create Nested Lists in PDF with Python
In Spire.PDF for Python, the PdfSortedList class and PdfList class are available for generating various types of lists in PDF documents, such as ordered lists, unordered lists, and nested lists. By utilizing the functionalities provided by Spire.PDF for Python, developers can easily format and incorporate these lists into their PDF pages. The following are the key classes and properties that are particularly useful for creating lists within PDF documents:
| Class or property | Description |
| PdfSortedList class | Represents an ordered list in a PDF document. |
| PdfList class | Represents an unordered list in a PDF document. |
| Brush property | Gets or sets a list's brush. |
| Font property | Gets or sets a list's font. |
| Indent property | Gets or sets a list's indent. |
| TextIndent property | Gets or sets the indent from the marker to the list item text. |
| Items property | Gets items of a list. |
| Marker property | Gets or sets the marker of a list. |
| Draw() method | Draw list on the canvas of a page at the specified location. |
| PdfOrderedMarker class | Represents the marker style of an ordered list, such as numbers, letters, and roman numerals. |
| PdfMarker class | Represents bullet style for an unordered list. |
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Create Ordered Lists in PDF with Python
Developers can use the PdfSortedList class in Spire.PDF for Python to create ordered lists and format them using the properties available under this class. Afterwards, the list can be drawn on a PDF page using the PdfSortedList.Draw() method. Here is a detailed step-by-step guide for how to create ordered lists in PDF documents:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Add a page to the document using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Create fonts and the brush for the title and the list and draw the list title on the page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Initialize an instance of PdfSortedList class to create an ordered list with specified items.
- Initialize an instance of PdfOrderedMarker class to create an ordered marker for the list.
- Set the font, item indent, text-indent, brush, and marker for the list using properties under PdfSortedList class.
- Draw the list on the page using PdfSortedList.Draw() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import *
# Create an object of PdfDocument class
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a page to the document with specified page size and margins
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
# Create tile font and list font
titleFont = PdfTrueTypeFont("HarmonyOS Sans SC", 14.0, 1, True)
listFont = PdfTrueTypeFont("HarmonyOS Sans SC", 12.0, 0, True)
# Create a brush to draw the list
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Black()
# Specify the initial coordinate
x = 10.0
y = 20.0
# Draw the title
title = "Introduction to Common Fruits:"
page.Canvas.DrawString(title, titleFont, brush, x, y)
# Create a numbered list
listItems = "Apples are fruits that are commonly eaten and come in various varieties.\n" \
+ "Bananas are tropical fruits that are rich in potassium and are a popular snack.\n" \
+ "Oranges are citrus fruits known for their high vitamin C content and refreshing taste.\n"\
+ "Grapes are small, juicy fruits that come in different colors, such as green, red, and purple."
list = PdfSortedList(listItems)
# Create a marker for the list
marker = PdfOrderedMarker(PdfNumberStyle.UpperRoman, listFont)
# Format the list
list.Font = listFont
list.Indent = 2
list.TextIndent = 4
list.Brush = brush
list.Marker = marker
# Draw the list on the page
list.Draw(page.Canvas, x, y + float(titleFont.MeasureString(title).Height + 5))
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/CreateNumberedList.pdf")
pdf.Close()

Create Unordered Lists with Symbol Markers in PDF Using Python
Creating an unordered list in a PDF document with Spire.PDF for Python involves PdfList class and the properties under this class. When creating an unordered list, developers need to set the marker style and font for the unordered list using the PdfList.Marker.Style and PdfList.Marker.Font properties. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Add a page to the document using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Create fonts and the brush for the title, the marker, and the list, and draw the list title on the page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Initialize an instance of PdfList class to create an unordered list with specified items.
- Set the font, item indent, text indent, and brush for the list using properties under PdfList class.
- Set the marker style and font through PdfList.Marker.Style property and PdfList.Marker.Font property.
- Draw the list on the page using PdfList.Draw() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import *
# Create an object of PdfDocument class
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a page to the document with specified page size and margins
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
# Create tile font and list font
titleFont = PdfTrueTypeFont("HarmonyOS Sans SC", 14.0, 1, True)
listFont = PdfTrueTypeFont("HarmonyOS Sans SC", 12.0, 0, True)
markerFont = PdfTrueTypeFont("HarmonyOS Sans SC", 8.0, 0, True)
# Create a brush to draw the list
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Black()
# Specify the initial coordinate
x = 10.0
y = 20.0
# Draw the title
title = "Colors:"
page.Canvas.DrawString(title, titleFont, brush, x, y)
# Create an unordered list
listContent = "Red is a vibrant color often associated with love, passion, and energy.\n" \
+ "Green is a color symbolizing nature, growth, and harmony.\n" \
+ "Pink is a color associated with femininity, love, and tenderness."
list = PdfList(listContent)
# Format the list
list.Font = listFont
list.Indent = 2
list.TextIndent = 4
list.Brush = brush
# Format the marker
list.Marker.Style = PdfUnorderedMarkerStyle.Asterisk
list.Marker.Font = markerFont
# Draw the list on the page
list.Draw(page.Canvas, x, float(y + titleFont.MeasureString(title).Height + 5))
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/CreateSymbolBulletedList.pdf")
pdf.Close()

Create Unordered Lists with Image Markers in PDF Using Python
Creating an unordered list with image markers follows similar steps to creating a list with symbol markers. Developers just need to set the item marker style to an image through PdfList.Marker.Style property. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Add a page to the document using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Create fonts and the brush for the title, the marker, and the list, and draw the list title on the page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Initialize an instance of PdfList class to create an unordered list with specified items.
- Set the font, item indent, text-indent, and brush for the list using properties under PdfList class.
- Load an image using PdfImage.LoadFromFile() method.
- Set the marker style as PdfUnorderedMarkerStyle.CustomImage through PdfList.Marker.Style property and set the loaded image as the marker through PdfList.Marker.Image property.
- Draw the list on the page using PdfList.Draw() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import *
# Create an object of PdfDocument class
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a page to the document with specified page size and margins
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
# Create tile font and list font
titleFont = PdfFont(PdfFontFamily.Helvetica, 14.0, PdfFontStyle.Bold)
listFont = PdfFont(PdfFontFamily.Helvetica, 12.0, PdfFontStyle.Regular)
# Create a brush to draw the list
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Black()
# Specify the initial coordinate
x = 10.0
y = 20.0
# Draw the title
title = "Colors:"
page.Canvas.DrawString(title, titleFont, brush, x, y)
# Create an unordered list
listContent = "Blue is a calming color often associated with tranquility, trust, and stability.\n" \
+ "Purple is a color associated with royalty, luxury, and creativity.\n" \
+ "Brown is a natural earthy color often associated with stability, reliability, and warmth."
list = PdfList(listContent)
# Format the list
list.Font = listFont
list.Indent = 2
list.TextIndent = 4
list.Brush = brush
# Load an image
image = PdfImage.FromFile("Marker.png")
# Set the marker as a custom image
list.Marker.Style = PdfUnorderedMarkerStyle.CustomImage
list.Marker.Image = image
# Draw the list on the page
list.Draw(page.Canvas, x, float(y + titleFont.MeasureString(title).Height + 5))
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/CreateImageBulletedList.pdf")
pdf.Close()

Create Nested Lists in PDF with Python
When creating a nested list, both the parent list and each level of sublists can be created as either unordered or ordered lists. Once the lists at each level are created, the PdfListItem.Sublist property can be used to set a list as the sublist of a corresponding item in the parent list. Here are the steps to create a nested list:
- Create an object of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Add a page to the document using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Create fonts and the brush for the title, the marker, and the list, and draw the list title on the page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Create an unordered list as the parent list and format the list and the marker.
- Create three sublists for the items in the parent list and format the list.
- Get an item in the parent list using PdfList.Items.get_Item() method.
- Set a specified list as the sublist of the item through PdfListItem.SubList property.
- Draw the list on the page using PdfList.Draw() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.pdf.common import *
# Create an object of PdfDocument class
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a page to the document with specified page size and margins
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
# Create tile font and list font
titleFont = PdfTrueTypeFont("HarmonyOS Sans SC", 14.0, 1, True)
listFont = PdfTrueTypeFont("HarmonyOS Sans SC", 12.0, 0, True)
markerFont = PdfTrueTypeFont("HarmonyOS Sans SC", 12.0, 0, True)
# Create brushs to draw the title and lists
titleBrush = PdfBrushes.get_Blue()
firstListBrush = PdfBrushes.get_Purple()
secondListBrush = PdfBrushes.get_Black()
# Specify the initial coordinate
x = 10.0
y = 20.0
# Draw the title
title = "Nested List:"
page.Canvas.DrawString(title, titleFont, titleBrush, x, y)
# Create a parent list
parentListContent = "Fruits:\n" + "Colors:\n" + "Days of the week:"
parentList = PdfList(parentListContent)
# Format the parent list
indent = 4
textIndent = 4
parentList.Font = listFont
parentList.Indent = indent
parentList.TextIndent = textIndent
# Set the parent list marker
parentList.Marker.Style = PdfUnorderedMarkerStyle.Square
parentList.Marker.Font = markerFont
# Create nested sublists and format them
subListMarker = PdfOrderedMarker(PdfNumberStyle.LowerLatin, markerFont)
subList1Content = "Apples\n" + "Bananas\n" + "Oranges"
subList1 = PdfSortedList(subList1Content, subListMarker)
subList1.Font = listFont
subList1.Indent = indent * 2
subList1.TextIndent = textIndent
subList2Content = "Red\n" + "Green"
subList2 = PdfSortedList(subList2Content, subListMarker)
subList2.Font = listFont
subList2.Indent = indent * 2
subList2.TextIndent = textIndent
subList3Content = "Monday\n" + "Tuesday\n" + "Wednesday"
subList3 = PdfSortedList(subList3Content, subListMarker)
subList3.Font = listFont
subList3.Indent = indent * 2
subList3.TextIndent = textIndent
# Set the created list as the nested sublist of each item in the parent list
item1 = parentList.Items.get_Item(0)
item1.SubList = subList1
item2 = parentList.Items.get_Item(1)
item2.SubList = subList2
item3 = parentList.Items.get_Item(2)
item3.SubList = subList3
# Draw the list
parentList.Draw(page.Canvas, x, float(y + titleFont.MeasureString(title).Height + 5))
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/CreateNestedList.pdf")
pdf.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
The Find and Replace feature in Excel allows you to quickly find specific values and perform targeted replacements based on specific requirements. With it, all occurrences of a specific value can be updated at once, which can significantly improve productivity when working with large data sets. In this article, you will learn how to programmatically find and replace data in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Find and Replace Data in a Worksheet in Excel
- Find and Replace Data in a Specific Cell Range in Excel
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Find and Replace Data in an Excel Worksheet in Python
Spire.XLS for Python offers the Worksheet.FindAllString() method to find the cells containing specific data values in an Excel worksheet. Once the cells are found, you can use the CellRange.Text property to update their values with new values. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Find the cells containing a specific value in the worksheet using Worksheet.FindAllString() method.
- Iterate through the found cells.
- Replace the value of each found cell with another value using CellRange.Text property.
- Set a background color to highlight the cell using CellRange.Style.Color property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.common import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document from disk
workbook.LoadFromFile("input.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Find the cells with the specific string value “Total” in the worksheet
ranges = worksheet.FindAllString("Total", False, False)
# Iterate through the found cells
for range in ranges:
# Replace the value of the cell with another value
range.Text = "Sum"
# Set a background color for the cell
range.Style.Color = Color.get_Yellow()
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("FindAndReplaceData.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
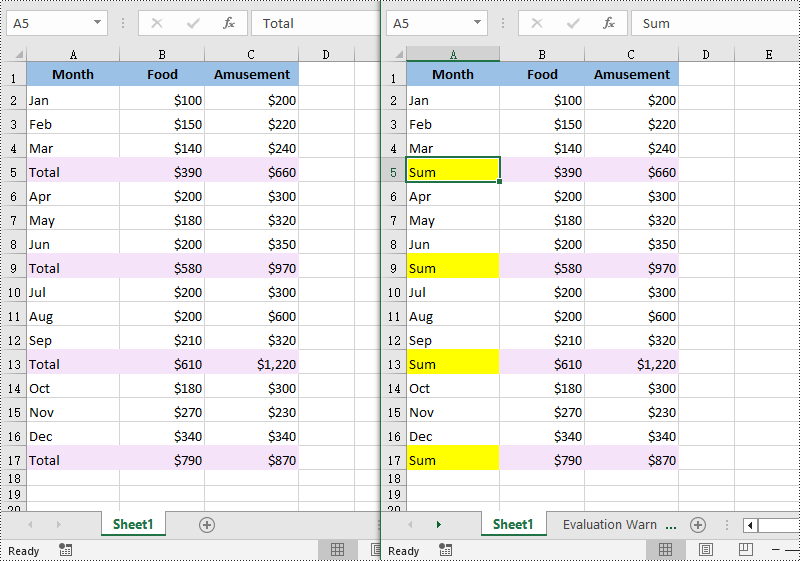
Find and Replace Data in a Specific Cell Range in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python also allows you to find the cells containing a specific value in a cell range through the CellRange.FindAllString() method. Then you can update the value of each found cell with another value using the CellRange.Text property. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Get a specific cell range of the worksheet using Worksheet.Range[] property.
- Find the cells with a specific value in the cell range using CellRange.FindAllString() method.
- Iterate through the found cells.
- Replace the value of each found cell with another value using CellRange.Text property.
- Set a background color to highlight the cell using CellRange.Style.Color property.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document from disk
workbook.LoadFromFile("input.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get a specific cell range
range = sheet.Range["A6:C13"]
# Find the cells with the specific value "Total" in the cell range
cells = range.FindAllString("Total", False, False)
# Iterate through the found cells
for cell in cells:
# Replace the value of the cell with another value
cell.Text = "Sum"
# Set a background color for the cell
cell.Style.Color = Color.get_Yellow()
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("ReplaceDataInCellRange.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
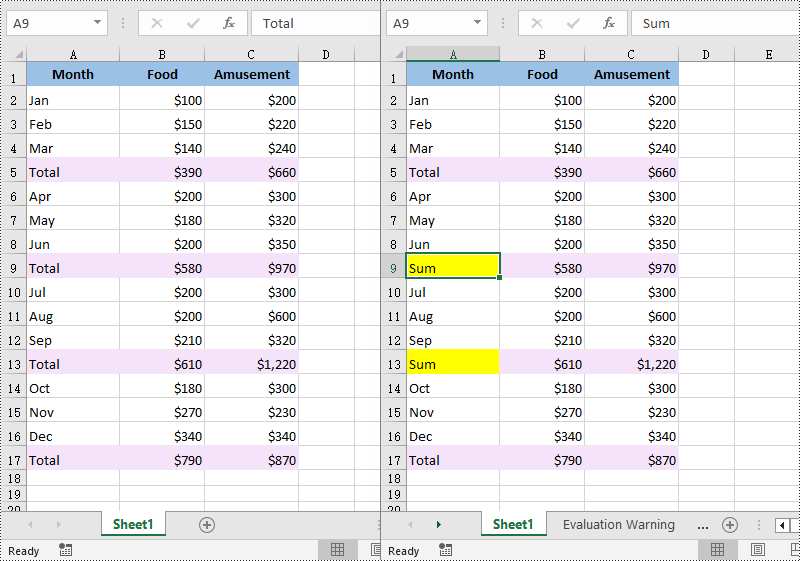
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Deleting rows and columns from Excel is crucial for maintaining clean and organized data. For example, when a worksheet accumulates blank rows or columns that serve no purpose and clutter the data, removing them becomes necessary. By deleting these blank rows and columns, you can effectively reduce the file size and enhance the spreadsheet's readability. In this article, we will explain how to delete rows and columns from Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Delete a Specific Row and Column from Excel in Python
- Delete Multiple Rows and Columns from Excel in Python
- Delete Blank Rows and Columns from Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Delete a Specific Row and Column from Excel in Python
The Worksheet.DeleteRow(rowIndex) and Worksheet.DeleteColumn(columnIndex) methods provided by Spire.XLS for Python enable you to delete a specific row and column from an Excel worksheet. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the desired worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Delete the desired row from the worksheet by its index (1-based) using Worksheet.DeleteRow(rowIndex) method.
- Delete the desired column from the worksheet by its index (1-based) using Worksheet.DeleteColumn(columnIndex) method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Input.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Delete the 9th row
sheet.DeleteRow(9)
# Delete the 3rd column
sheet.DeleteColumn(3)
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("DeleteSpecificRowAndColumn.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Delete Multiple Rows and Columns from Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python enables you to delete multiple adjacent rows and columns from an Excel worksheet at once by using the Worksheet.DeleteRow(startRowIndex, rowCount) and Worksheet.DeleteColumn(startColumnIndex, columnCount) methods. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the desired worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Delete the desired rows from the worksheet using Worksheet.DeleteRow(startRowIndex, rowCount) method.
- Delete the desired columns from the worksheet using Worksheet.DeleteColumn(startColumnIndex, columnCount) method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Input.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Delete the 5th, 6th and 7th rows
sheet.DeleteRow(5, 3)
# Delete the 3rd and 4th columns
sheet.DeleteColumn(3, 2)
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("DeleteMultipleRowsAndColumns.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Delete Blank Rows and Columns from Excel in Python
You can use the Worksheet.Row[rowIndex].IsBlank and Worksheet.Column[columnIndex].IsBlank properties to detect whether a specific row and column are blank or not. If the result is True, you can remove them from your woeksheet using the Worksheet.DeleteRow(rowIndex) and Worksheet.DeleteColumn(columnIndex) methods.
The following steps show how to delete the blank rows and columns from an Excel worksheet.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the desired worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Loop through the used rows in the worksheet.
- Find the blank rows using Worksheet.Row[rowIndex].IsBlank property and then delete them from the worksheet using Worksheet.DeleteRow(rowIndex) method.
- Loop through the used columns in the worksheet.
- Find the blank columns using Worksheet.Column[columnIndex].IsBlank property and then delete them from the worksheet using Worksheet.DeleteColumn(columnIndex) method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Input1.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Delete blank rows from the worksheet
for i in range(sheet.Rows.Length - 1, -1, -1):
if sheet.Rows[i].IsBlank:
sheet.DeleteRow(i + 1)
# Delete blank columns from the worksheet
for j in range(sheet.Columns.Length - 1, -1, -1):
if sheet.Columns[j].IsBlank:
sheet.DeleteColumn(j + 1)
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("DeleteBlankRowsAndColumns.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
If you need to display or interact with the contents of an Excel spreadsheet on a web page, converting Excel to HTML is a good choice. This conversion allows users to view and manipulate the table data directly on the web page without having to download the Excel file, providing a more convenient way to share and display the data. When needed, you can also convert the HTML file back to Excel format for better data editing. In this article, we will show you how to convert Excel to HTML and HTML to Excel in Python by using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Convert Excel to HTML in Python
- Convert Excel to HTML with Images Embedded in Python
- Convert HTML to Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
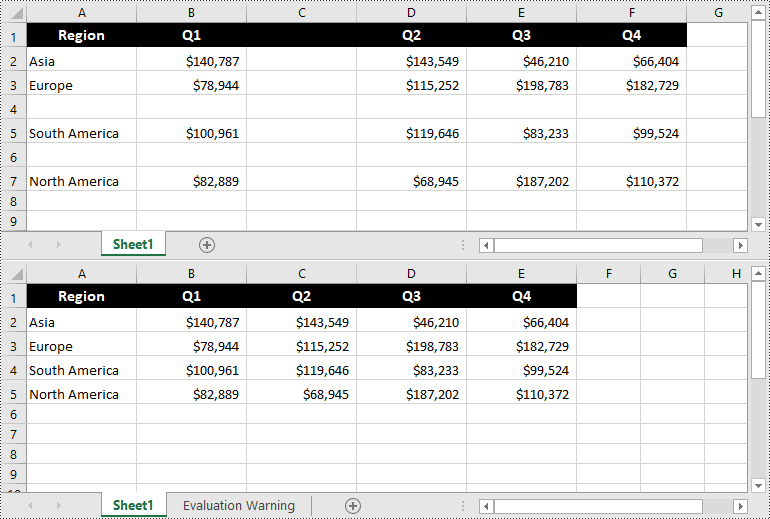
Convert Excel to HTML in Python
Spire.XLS for Python supports converting a specific Excel worksheet to HTML using Worksheet.SaveToHtml() method. Detailed steps are listed below.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Save the worksheet as an HTML file using Worksheet.SaveToHtml() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Sample_1.xlsx" outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/ToHtml.html" # Create a Workbook instance workbook = Workbook() # Load a sample Excel file workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get the first sheet of this file sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] # Save the worksheet to HTML sheet.SaveToHtml(outputFile) workbook.Dispose()
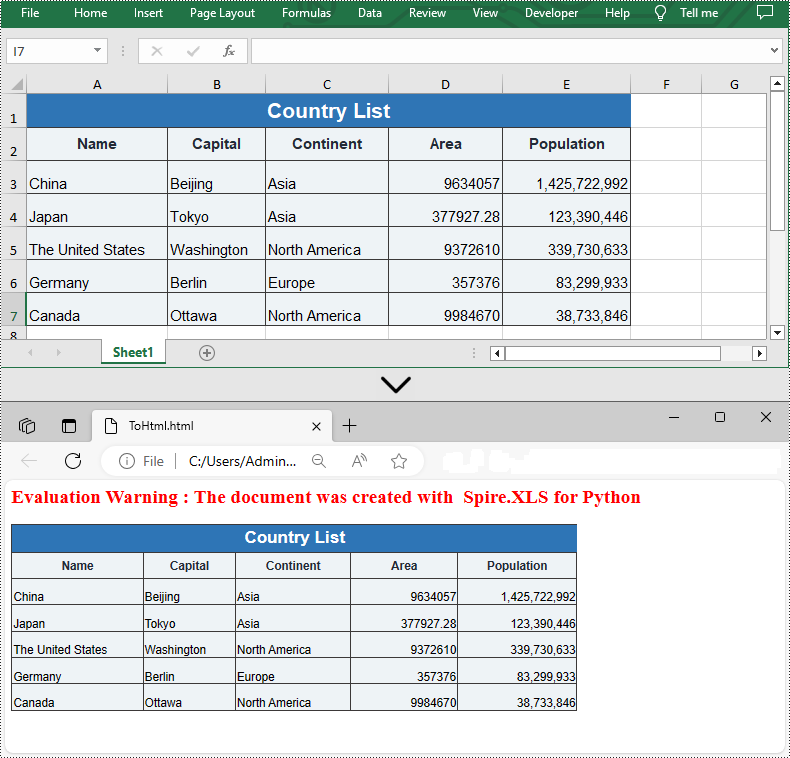
Convert Excel to HTML with Images Embedded in Python
If the Excel file you want to convert contains images, you can embed the images into the HTML file by setting the ImageEmbedded property to "True". Detailed steps are listed below.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Create an HTMLOptions instance.
- Set the ImageEmbedded as “True” to embed images to HTML.
- Save the worksheet as an HTML file using Worksheet.SaveToHtml() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Sample_2.xlsx" outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/ToHtmlwithImages.html" # Create a Workbook instance workbook = Workbook() # Load a sample Excel file workbook.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get the first sheet of this file sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0] # Create an HTMLOptions instance options = HTMLOptions() # Embed images to HTML options.ImageEmbedded = True # Save the worksheet to HTML sheet.SaveToHtml(outputFile, options) workbook.Dispose()
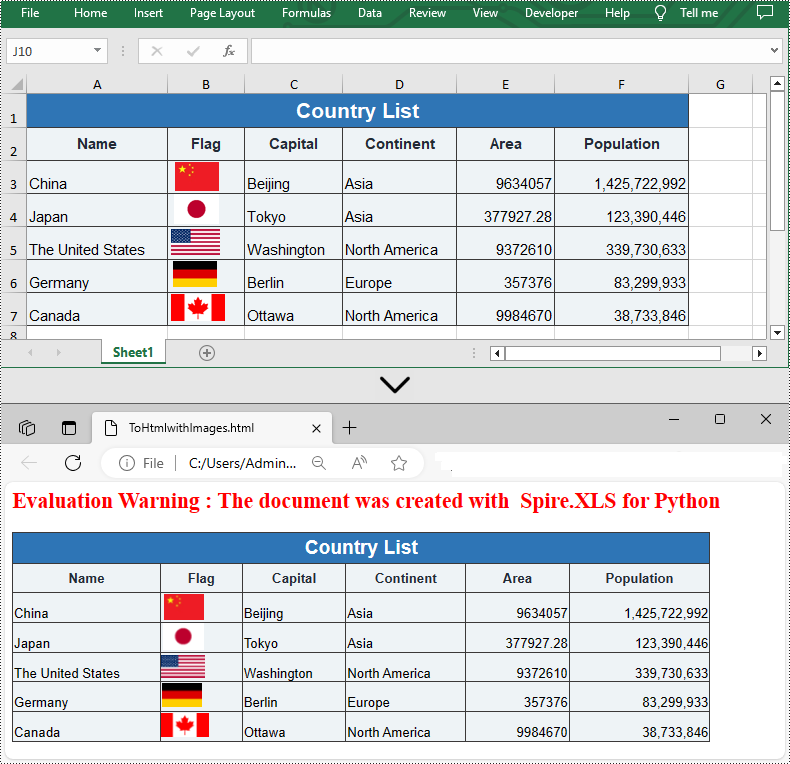
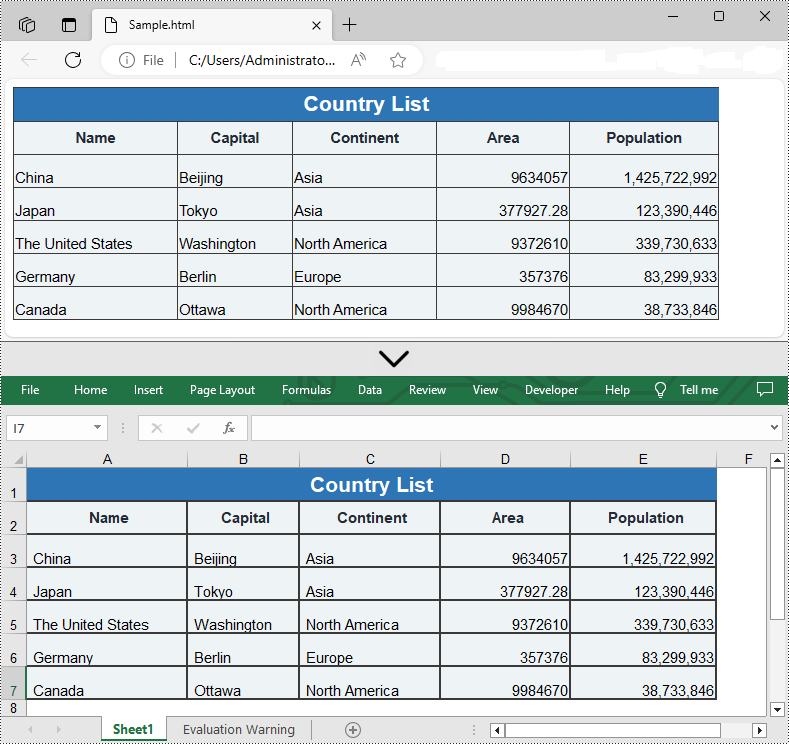
Convert HTML to Excel in Python
You are also allowed to convert an HTML back to an Excel file by calling the Workbook.SaveToFile() method provided by Spire.XLS for Python. Detailed steps are listed below.
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load an HTML file from disk using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Save the HTML file to an Excel file by using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import * from spire.xls.common import * inputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Sample.html" outputFile = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/ToExcel.xlsx" # Create a Workbook instance workbook = Workbook() # Load an HTML file from disk workbook.LoadFromHtml(inputFile) # Save the HTML file to an Excel file workbook.SaveToFile(outputFile, ExcelVersion.Version2013) workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Hiding or unhiding rows and columns in Excel gives you precise control over the visibility of specific data within a worksheet. By hiding rows or columns, you can temporarily remove irrelevant information from view, reducing visual clutter and creating a cleaner workspace. This makes it easier to work with the data that truly matters and enhances your productivity. On the other hand, unhiding rows or columns allows you to restore visibility and regain access to previously hidden information whenever you need it. This is advantageous when you have hidden data that requires further review, modification, or analysis. In this article, we will explain how to hide or unhide rows and columns in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Hide Specific Rows and Columns in Excel in Python
- Unhide Specific Hidden Rows and Columns in Excel in Python
- Hide Multiple Rows and Columns at Once in Excel in Python
- Unhide All Hidden Rows and Columns in Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
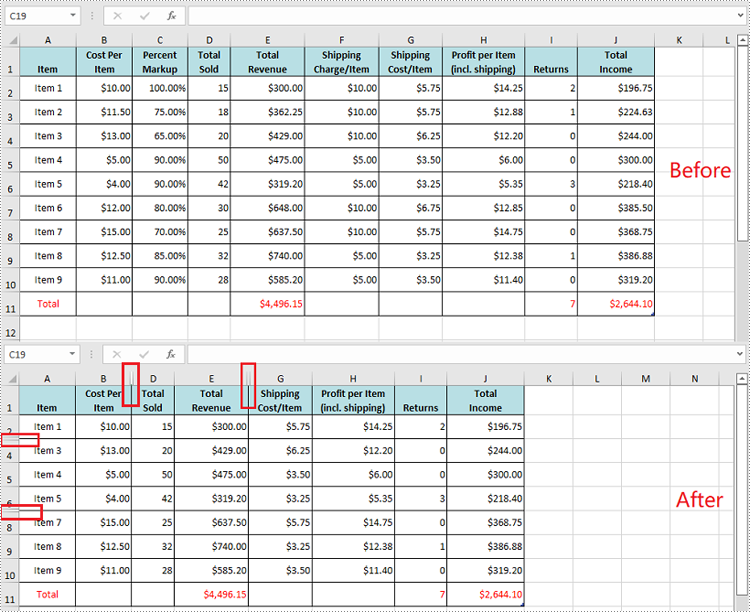
Hide Specific Rows and Columns in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python offers the Worksheet.HideRow(rowIndex) and Worksheet.HideColumn(columnIndex) methods to hide a specific row and column in an Excel worksheet. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Hide specific rows in the worksheet using Worksheet.HideRow(rowIndex) method.
- Hide Specific columns in the worksheet using Worksheet.HideColumn(columnIndex) method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Input.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Hide the 3rd and the 7th rows
sheet.HideRow(3)
sheet.HideRow(7)
# Hide the 3rd and the 6th columns
sheet.HideColumn(3)
sheet.HideColumn(6)
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("HideRowsAndColumns.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Unhide Specific Hidden Rows and Columns in Excel in Python
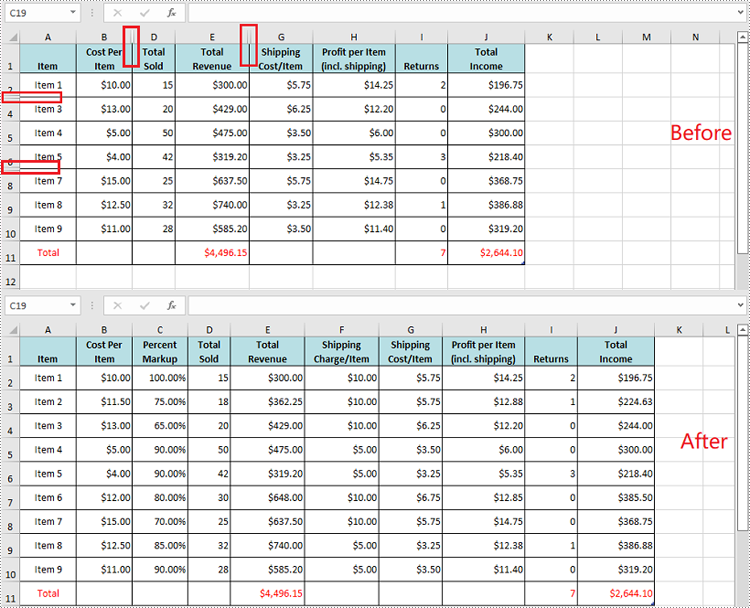
You can use the Worksheet.ShowRow(rowIndex) and Worksheet.ShowColumn(columnIndex) methods to unhide a specific hidden row and column. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Unhide specific hidden rows in the worksheet using Worksheet.ShowRow(rowIndex) method.
- Unhide specific hidden columns in the worksheet using Worksheet.ShowColumn(columnIndex) method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("HideRowsAndColumns.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Unhide the 3rd and the 7th rows
sheet.ShowRow(3)
sheet.ShowRow(7)
# Unhide the 3rd and the 6th columns
sheet.ShowColumn(3)
sheet.ShowColumn(6)
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("ShowRowsAndColumns.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Hide Multiple Rows and Columns at Once in Excel in Python
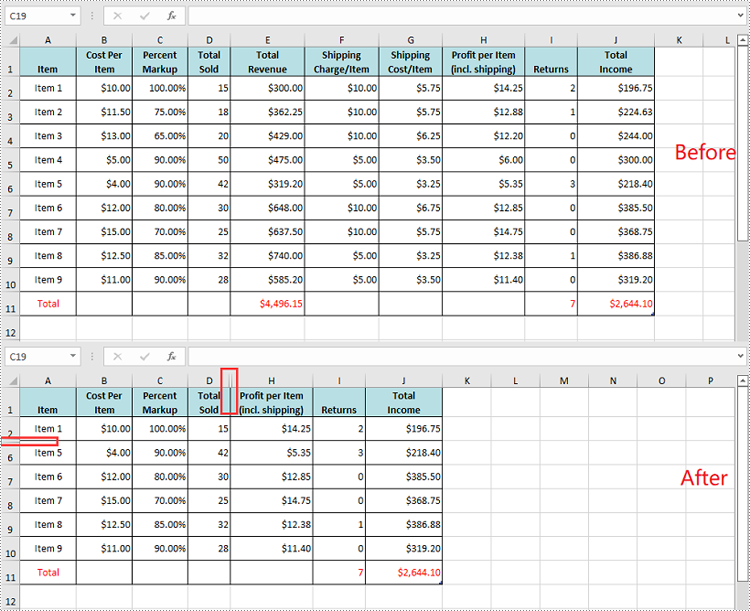
To hide multiple rows and columns at once, you can use the Worksheet.HideRows(startRowIndex, rowCount) and Worksheet.HideColumns(startColumnIndex, columnCount) methods. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Hide multiple rows in the worksheet using the Worksheet.HideRows(startRowIndex, rowCount) method.
- Hide multiple columns in the worksheet using Worksheet.HideColumns(startColumnIndex, columnCount) method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Input.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Hide 3, 4 and 5 rows
sheet.HideRows(3, 3)
# Hide 5, 6 and 7 columns
sheet.HideColumns(5, 3)
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("HideMultipleRowsAndColumns.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Unhide All Hidden Rows and Columns in Excel in Python
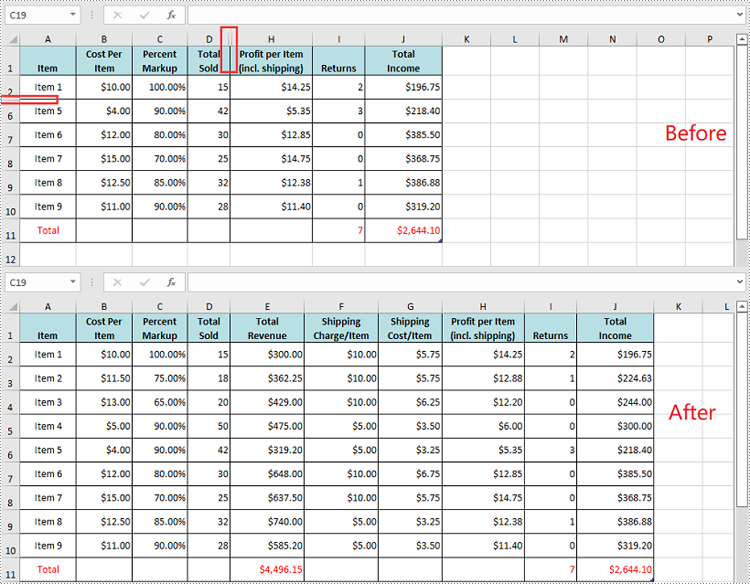
To unhide all hidden rows and columns, you first need to loop through the used rows and columns in the worksheet. Next, find the hidden rows and columns using Worksheet.GetRowIsHide(rowIndex) and Worksheet.GetColumnIsHide(columnIndex) methods, and then unhide them using Worksheet.ShowRow(rowIndex) and Worksheet.ShowColumn(columnIndex) methods. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet through Workbook.Worksheets[sheetIndex] property.
- Iterate through the used rows in the worksheet and find the hidden rows using Worksheet.GetRowIsHide(rowIndex) method.
- Unhide every hidden row using Worksheet.ShowRow(rowIndex) method.
- Iterate through the used columns in the worksheet and find the hidden columns using Worksheet.GetColumnIsHide(columnIndex) method.
- Unhide every hidden column using Worksheet.ShowColumn(columnIndex) method.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("HideMultipleRowsAndColumns.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Iterate through the used rows in the worksheet
for i in range(1, sheet.LastRow + 1):
# Check if the current row is hidden
if sheet.GetRowIsHide(i):
# Unhide the hidden row
sheet.ShowRow(i)
# Iterate through the used columns in the worksheet
for j in range(1, sheet.LastColumn + 1):
# Check if the current column is hidden
if sheet.GetColumnIsHide(j):
# Unhide the hidden column
sheet.ShowColumn(j)
# Save the result file
workbook.SaveToFile("ShowAllHiddenRowsAndColumns.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
