Python (355)
How to Read PDF Files in Python – Text, Tables, Images, and More
2025-06-06 08:07:20 Written by zaki zou
Reading PDF files using Python is essential for tasks like document automation, content analysis, and data scraping. Whether you're working with contracts, reports, invoices, or scientific papers, being able to programmatically access PDF content saves time and enables powerful workflows.
To reliably read PDF content in Python — including text, tables, images, and metadata — you need a reliable Python PDF reader. In this guide, we’ll show you how to read PDFs in Python using Spire.PDF for Python, a professional and easy-to-use library that supports full-featured PDF reading without relying on any third-party tools.
Here's what's covered:
- Preparing Your Environment
- Load a PDF File in Python
- Read Text from PDF Pages in Python
- Read Table Data from PDFs in Python
- Read Images from PDFs in Python
- Read PDF Metadata (Title, Author, etc.)
- Common Questions on Reading PDFs
Environment Setup for Reading PDFs in Python
Spire.PDF for Python is a powerful Python PDF reader that allows users to read PDF content with simple Python code, including text, tables, images, and metadata. It offers a developer-friendly interface and supports a wide range of PDF reading operations:
- Read PDF files from disk or memory
- Access text, tables, metadata, and images
- No need for third-party tools
- High accuracy for structured data reading
- Free version available
It’s suitable for developers who want to read and process PDFs with minimal setup.
You can install Spire.PDF for Python via pip:
pip install spire.pdf
Or the free version Free Spire.PDF for Python for small tasks:
pip install spire.pdf.free
Load a PDF File in Python
Before accessing content, the first step is to load the PDF into memory. Spire.PDF lets you read PDF files from a path on disk or directly from in-memory byte streams — ideal for reading from web uploads or APIs.
Read PDF from File Path
To begin reading a PDF in Python, load the file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile(). This creates a document object you can use to access content.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
Read PDF from Bytes (In-Memory)
To read a PDF file from memory without saving it to disk, you can first load its byte content and then initialize a PdfDocument using a Stream object. This method is especially useful when handling PDF files received from web uploads, APIs, or temporary in-memory data.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, Stream
# Read the PDF file to a byte array
with open("sample.pdf", "rb") as f:
byte_data = f.read()
# Create a stream using the byte array
pdfStream = Stream(byte_data)
# Create a PdfDocument using the stream
pdf = PdfDocument(pdfStream)
To go further, check out this guide: Loading and Saving PDFs via Byte Streams in Python
Read Text from PDF Pages in Python
Reading text from a PDF file is one of the most common use cases in document automation. With Spire.PDF, you can easily retrieve all visible text from the entire PDF or from individual pages using simple methods.
Read All Text from PDF
To extract all text from a PDF, loop through each page and call PdfTextExtractor.ExtractText() to collect visible text content.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTextExtractor, PdfTextExtractOptions
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
all_text = ""
# Loop through each page
for pageIndex in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(pageIndex)
# Create a PdfTextExtract instance
text_extractor = PdfTextExtractor(page)
# Configure extracting options
options = PdfTextExtractOptions()
options.IsExtractAllText = True
options.IsSimpleExtraction = True
# Extract text from the current page
all_text += text_extractor.ExtractText(options)
print(all_text)
Sample text content retrieved:

Read Text from Specific Area of a Page
You can also read text from a defined region of a page using a bounding box. This is useful when only a portion of the layout contains relevant information.
from spire.pdf import RectangleF, PdfDocument, PdfTextExtractor, PdfTextExtractOptions
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Create a PdfTextExtractor instance
textExtractor = PdfTextExtractor(page)
# Set the area to extract text by configuring the PdfTextExtractOptions
options = PdfTextExtractOptions()
area = RectangleF.FromLTRB(0, 200, page.Size.Width, 270) # x, y, width, height
options.ExtractArea = area
options.IsSimpleExtraction = True
# Extract text from the area
text = textExtractor.ExtractText(options)
print(text)
The text read from the PDF page area:
Read Table Data from PDFs in Python
PDF tables are often used in reports, invoices, and statements. With Spire.PDF, you can read PDF tables in Python by extracting structured tabular content using its layout-aware table extractor, making it ideal for financial and business documents. Use PdfTableExtractor.ExtractTable() to detect tables page by page and output each row and cell as structured text.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTableExtractor
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
# Create a PdfTableExtractor instance
table_extractor = PdfTableExtractor(pdf)
# Extract the table from the first page
tables = table_extractor.ExtractTable(0)
for table in tables:
# Get the number of rows and columns
row_count = table.GetRowCount()
column_count = table.GetColumnCount()
# Iterate all rows
for i in range(row_count):
table_row = []
# Iterate all columns
for j in range(column_count):
# Get the cell
cell_text = table.GetText(i, j)
table_row.append(cell_text)
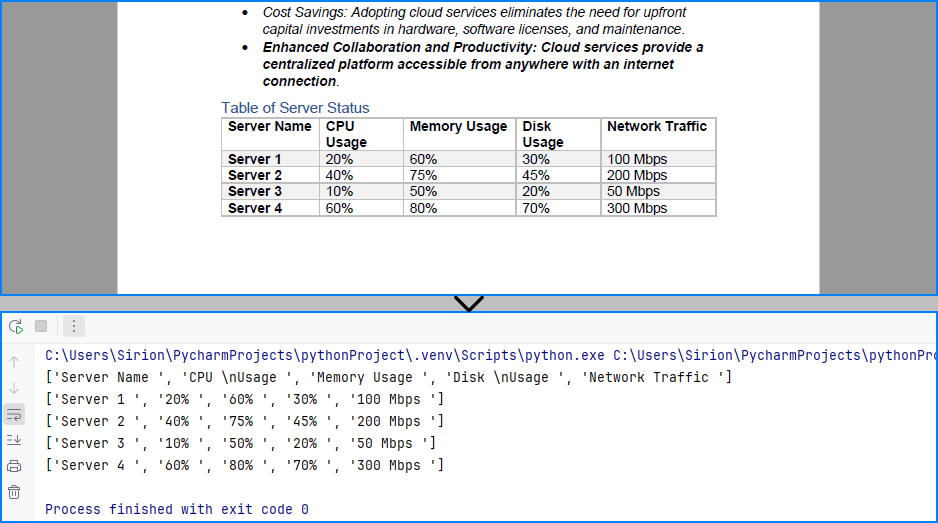
print(table_row)
Table content extracted using the code above:
Want to extract text from scanned PDFs using OCR? Read this guide on OCR with Python
Read Images from PDF in Python
PDF files often contain logos, scanned pages, or embedded images. Spire.PDF allows you to read and export these images, which is helpful for working with digitized documents or preserving visual content. Use PdfImageHelper.GetImagesInfo() on each page to retrieve and save all embedded images.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfImageHelper
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Create a PdfImageHelper object
image_helper = PdfImageHelper()
# Get the image information from the page
images_info = image_helper.GetImagesInfo(page)
# Save the images from the page as image files
for i in range(len(images_info)):
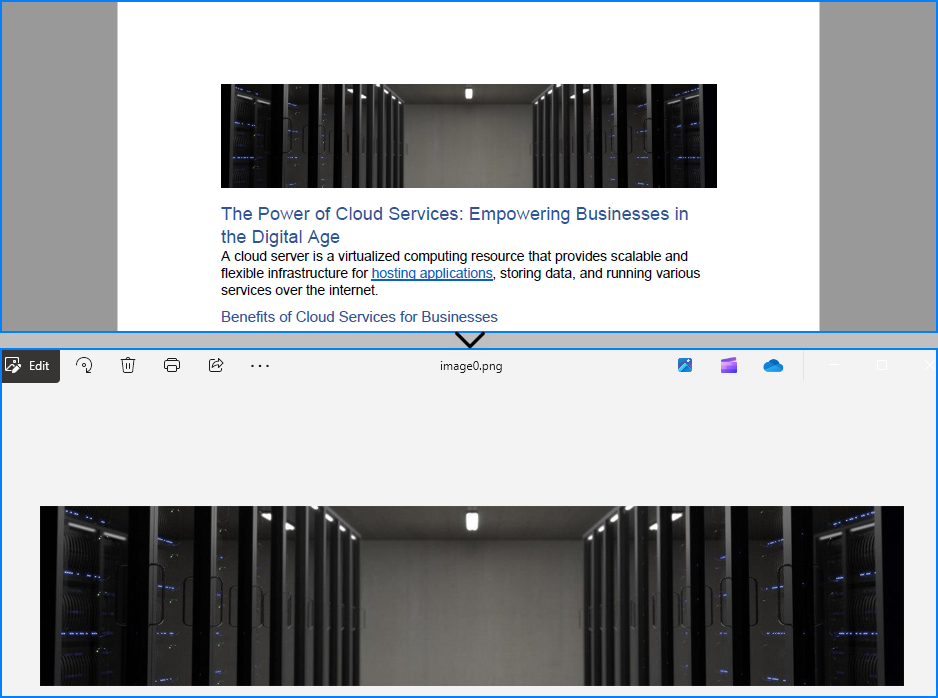
images_info[i].Image.Save("output/Images/image" + str(i) + ".png")
The image read from the PDF file:
Read PDF Metadata (Title, Author, etc.)
Sometimes you may want to access document metadata like author, subject, and title. This can be helpful for indexing or organizing files. Use the ocumentInformation property to read metadata fields.
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("sample.pdf")
# Get the document properties
properties = pdf.DocumentInformation
print("Title: " + properties.Title)
print("Author: " + properties.Author)
print("Subject: " + properties.Subject)
print("Keywords: " + properties.Keywords)
The metadata read from the PDF document:

Common Questions on Reading PDFs
Can Python parse a PDF file?
Yes. Libraries like Spire.PDF for Python allow you to read PDF text, extract tables, and access embedded images or metadata. It supports methods like PdfTextExtractor.ExtractText() and PdfTableExtractor.ExtractTable() for structured content parsing.
How do I read a PDF in Jupyter?
Spire.PDF works seamlessly in Jupyter Notebooks. Just install it via pip and use its API to read PDF files, extract text, or parse tables and images directly in your notebook environment.
How to read text from a PDF file?
Use the PdfTextExtractor.ExtractText() method on each page after loading the PDF with Spire.PDF. This lets you read PDF file to text in Python and retrieve visible content for processing or analysis.
Can I read a PDF file without saving it to disk?
Yes. You can use LoadFromStream() to read PDF content as bytes and load it directly from memory. This is useful for processing PDFs received from web APIs or file uploads.
Conclusion
With Spire.PDF for Python, you can easily read a PDF in Python — including reading PDF text, tables, images, and metadata — and even read a PDF file to text for further processing or automation. This makes it an ideal solution for document automation, data ingestion, and content parsing in Python.
Need to process large PDF files or unlock all features? Request a free license and take full advantage of Spire.PDF for Python today!
How to Convert CSV to Excel (XLSX) in Python – Single & Batch Guide
2025-06-06 08:04:25 Written by zaki zouWhile working with CSV files is common in data processing, Excel (XLSX) often provides more advantages when it comes to data sharing, visualization, and large-scale analysis. In this guide, you’ll learn how to convert CSV to Excel in Python, including both single file and batch conversion methods. Whether you're automating reports or preparing data for further analysis, this guide will help you handle the conversion efficiently.

- Why Convert CSV to Excel
- Install Required Python Libraries
- Convert Single CSV to Excel
- Batch Convert CSV to XLSX
- FAQs
Why Convert CSV to Excel?
While CSV files are widely used for data storage and exchange due to their simplicity, they come with several limitations—especially when it comes to formatting, presentation, and usability. Converting CSV to Excel can bring several advantages:
Benefits of Converting CSV to Excel
- Better formatting support: Excel allows rich formatting options like fonts, colors, borders, and cell merging, making your data easier to read and present.
- Multiple worksheets: Unlike CSV files that support only a single sheet, Excel files can store multiple worksheets in one file, which is better for large datasets.
- Built-in formulas and charts: You can apply Excel formulas, pivot tables, and charts to analyze and visualize your data.
- Improved compatibility for business users: Excel is the preferred tool for many non-technical users, making it easier to share and collaborate on data.
Limitations of CSV Files
- No styling or formatting (plain text only)
- Single-sheet structure only
- Encoding issues (e.g., with non-English characters)
- Not ideal for large datasets or advanced reporting If your workflow involves reporting, data analysis, or sharing data with others, converting CSV to Excel is often a more practical and flexible choice.
Install Required Python Libraries
This guide demonstrates how to effortlessly convert CSV to Excel using Spire.XLS for Python. Spire.XLS is a powerful and professional Python Excel library that allows you to read, edit, and convert Excel files (both .xlsx and .xls) without relying on Microsoft Excel. Installing this CSV to Excel converter on your device is simple — just run the following command:
pip install Spire.XLS
Alternatively, you can download the Spire.XLS package manually for custom installation.
How to Convert CSV to Excel in Python: Single File
Now let’s get to the main part — how to convert a single CSV file to Excel using Python. With the help of Spire.XLS, this task becomes incredibly simple. All it takes is three easy steps: create a new workbook, load the CSV file, and save it as an Excel (.xlsx) file. Below is a detailed walkthrough along with a complete code example — let’s take a look!
Steps to convert a single CSV to Excel in Python:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Load a sample CSV file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Save the CSV file as Excel through Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
Below is the Python code to convert a CSV file to Excel. It also ignores parsing errors and automatically adjusts the column widths for better readability.
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Load a csv file
workbook.LoadFromFile("/sample csv.csv", ",", 1, 1)
# Set ignore error options
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
sheet.Range["D2:E19"].IgnoreErrorOptions = IgnoreErrorType.NumberAsText
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns()
# Save the document and launch it
workbook.SaveToFile("/CSVToExcel1.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
Warm Note: If you're only working with small files or doing some light testing, you can also use the free Spire.XLS. It's a great option for getting started quickly.
How to Batch Convert CSV to XLSX in Python
Another common scenario is when you need to convert multiple CSV files to Excel. Instead of manually replacing the file path and name for each one, there's a much more efficient approach. Simply place all the CSV files in the same folder, then use Python to loop through each file and convert them to Excel using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method. Let’s walk through the detailed steps below!
Steps to batch convert CSVs to Excel files in Python:
- Specify the file paths of input and output folders.
- Loop through all CSV files in the input folder.
- Create an object of Workbook class.
- Load each CSV file from the input folder with Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Save the current CSV as an Excel file through Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
Here's the Python code to batch convert CSV to Excel (.XLSX):
import os
from spire.xls import *
input_folder = r"E:input\New folder"
output_folder = r"output\New folder"
# Loop through each CSV file
for csv_file in os.listdir(input_folder):
if csv_file.endswith(".csv"):
input_path = os.path.join(input_folder, csv_file)
output_name = os.path.splitext(csv_file)[0] + ".xlsx"
output_path = os.path.join(output_folder, output_name)
# Create a Workbook instance and load CSV files
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile(input_path, ",", 1, 1)
# Save each CSV file as an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile(output_path, ExcelVersion.Version2013)
The Conclusion
This guide showed you how to convert CSV to Excel in Python with step-by-step instructions and complete code examples. Whether you're working with a single CSV file or multiple files, Spire.XLS makes the process simple, fast, and hassle-free. Need help with more advanced scenarios or other Excel-related tasks? Feel free to contact us anytime!
FAQs about Converting CSV to Excel
Q1: How to convert CSV to Excel in Python without pandas?
A: You can use libraries like Spire.XLS, openpyxl, or xlsxwriter to convert CSV files without relying on pandas. These tools provide simple APIs to load .csv files and export them as xlsx—no Microsoft Excel installation required.
Q2: What is the easiest way to convert multiple CSV files to Excel in Python?
A: Just place all CSV files in one folder, then loop through them in Python and convert each using Workbook.SaveToFile(). This approach is ideal for batch processing. Alternatively, online converters can be a quick fix for occasional use.
Q3: How to auto-adjust column width when converting CSV to Excel in Python?
A: After loading the CSV, call worksheet.autoFitColumns() in Spire.XLS to automatically resize columns based on content before saving the Excel file.

Text files (.txt) are a common way to store data due to their simplicity, but they lack the structure and analytical power of Excel spreadsheets. Converting TXT files to Excel allows for better data organization, visualization, and manipulation.
While manual import text file to Excel works for small datasets, automating this process saves time and reduces errors. Python, with its powerful libraries, offers an efficient solution. In this guide, you’ll learn how to convert TXT to Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python, a robust API for Excel file manipulation.
Prerequisites
Install Python and Spire.XLS
- Install Python on your machine from python.org.
- Install the Spire.XLS for Python library via PyPI. Open your terminal and run the following command:
pip install Spire.XLS
Prepare a TXT File
Ensure your TXT file follows a consistent structure, typically with rows separated by newlines and columns separated by delimiters (e.g., commas, tabs, or spaces). For example, a sample text file might look like this: 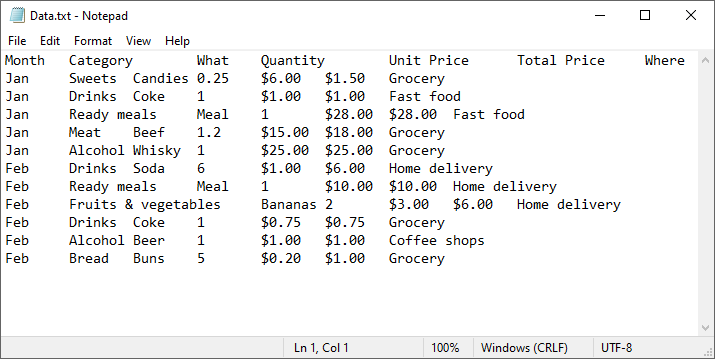
Step-by-Step Guide to Convert Text File to Excel
Step 1: Import Required Modules
In your Python script, import the necessary classes from Spire.XLS:
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
Step 2: Read and Parse the TXT File
Read the text file and split it into rows and columns using Python’s built-in functions. Define your delimiter (tab, in this case):
with open("Data.txt", "r") as file:
lines = file.readlines()
data = [line.strip().split("\t") for line in lines]
Note: If different delimiter was used, replace the parameter "\t" of the split() method (e.g., spaces: split(" ")).
Step 3: Create an Excel Workbook
Initialize a workbook object and access the first worksheet:
workbook = Workbook()
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
Step 4: Write Data to the Worksheet
Loop through the parsed data and populate the Excel cells.
for row_num, row_data in enumerate(data):
for col_num, cell_data in enumerate(row_data):
sheet.Range[row_num + 1, col_num + 1].Value = cell_data
sheet.Range[1, col_num + 1].Style.Font.IsBold = True
Step 5: Save the Excel File
Export the workbook as an XLSX file (you can also use .xls for older formats):
workbook.SaveToFile("TXTtoExcel.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
TXT to Excel Full Code Example
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Read TXT data
with open("Data.txt", "r") as file:
lines = file.readlines()
# Split data by delimiter
data = [line.strip().split("\t") for line in lines]
# Create an Excel workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Iterate through each row and column in the list
for row_num, row_data in enumerate(data):
for col_num, cell_data in enumerate(row_data):
# Write the data into the corresponding Excel cells
sheet.Range[row_num + 1, col_num + 1].Value = cell_data
# Set the header row to bold
sheet.Range[1, col_num + 1].Style.Font.IsBold = True
# Autofit column width
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns()
# Save as Excel (.xlsx or.xls) file
workbook.SaveToFile("TXTtoExcel.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
The Excel workbook converted from a text file:
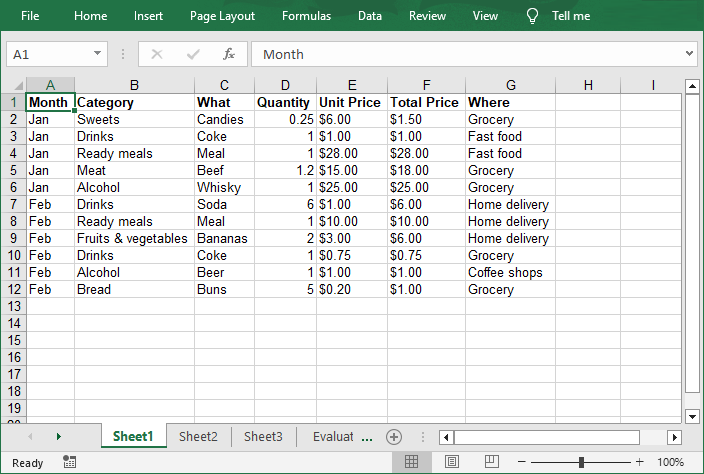
Conclusion
Converting TXT files to Excel in Python using Spire.XLS automates data workflows, saving time and reducing manual effort. Whether you’re processing logs, survey results, or financial records, this method ensures structured, formatted outputs ready for analysis.
Pro Tip: Explore Spire.XLS’s advanced features—such as charts, pivot tables, and encryption—to further enhance your Excel files.
FAQs
Q1: Can Spire.XLS convert large TXT files?
Yes, the Python Excel library is optimized for performance and can process large files efficiently. However, ensure your system has sufficient memory for very large datasets (e.g., millions of rows). For optimal results, process data in chunks or use batch operations.
Q2: Can I convert Excel back to TXT using Spire.XLS?
Yes, Spire.XLS allows to read Excel cells and write their values to a text file. A comprehensive guide is available at: Convert Excel to TXT in Python
Q3: How to handle the encoding issues during conversion?
Specify encoding if the text file uses non-standard characters (e.g., utf-8):
with open("Data.txt", "r", encoding='utf-8') as file:
lines = file.readlines()
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.XLS for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
How to Count Word Frequency in a Word Document Using Python
2025-05-22 09:16:03 Written by AdministratorWant to count the frequency of words in a Word document? Whether you're analyzing content, generating reports, or building a document tool, Python makes it easy to find how often a specific word appears—across the entire document, within specific sections, or even in individual paragraphs. In this guide, you’ll learn how to use Python to count word occurrences accurately and efficiently, helping you extract meaningful insights from your Word files without manual effort.

- Count Frequency of Words in an Entire Word Document
- Count Word Frequency by Section
- Count Word Frequency by Paragraph
- To Wrap Up
- FAQ
In this tutorial, we’ll use Spire.Doc for Python, a powerful and easy-to-use library for Word document processing. It supports a wide range of features like reading, editing, and analyzing DOCX files programmatically—without requiring Microsoft Office.
You can install it via pip:
pip install spire.doc
Let’s see how it works in practice, starting with counting word frequency in an entire Word document.
How to Count Frequency of Words in an Entire Word Document
Let’s start by learning how to count how many times a specific word or phrase appears in an entire Word document. This is a common task—imagine you need to check how often the word "contract" appears in a 50-page file.
With the FindAllString() method from Spire.Doc for Python, you can quickly search through the entire document and get an exact count in just a few lines of code—saving you both time and effort.
Steps to count the frequency of a word in the entire Word document:
- Create an object of Document class and read a source Word document.
- Specify the keyword to find.
- Find all occurrences of the keyword in the document using Document.FindAllString() method.
- Count the number of matches and print it out.
The following code shows how to count the frequency of the keyword "AI-Generated Art" in the entire Word document:
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("E:/Administrator/Python1/input/AI-Generated Art.docx")
# Customize the keyword to find
keyword = "AI-Generated Art"
# Find all matches (False: distinguish case; True: full text search)
textSelections = document.FindAllString(keyword, False, True)
# Count the number of matches
count = len(textSelections)
# Print the result
print(f'"{keyword}" appears {count} times in the entire document.')
# Close the document
document.Close()
How to Count Word Frequency by Section in a Word Document Using Python
A Word document is typically divided into multiple sections, each containing its own paragraphs, tables, and other elements. Sometimes, instead of counting a word's frequency across the entire document, you may want to know how often it appears in each section. To achieve this, we’ll loop through all the document sections and search for the target word within each one. Let’s see how to count word frequency by section using Python.
Steps to count the frequency of a word by section in Word documents:
- Create a Document object and load the Word file.
- Define the target keyword to search.
- Loop through all sections in the document. Within each section, loop through all paragraphs.
- Use regular expressions to count keyword occurrences.
- Accumulate and print the count for each section and the total count.
This code demonstrates how to count how many times "AI-Generated Art" appears in each section of a Word document:
import re
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object and load a Word file
document = Document()
document.LoadFromFile("E:/Administrator/Python1/input/AI.docx")
# Specify the keyword
keyword = "AI-Generated Art"
# The total count of the keyword
total_count = 0
# Get all sections
sections = document.Sections
# Loop through each section
for i in range(sections.Count):
section = sections.get_Item(i)
paragraphs = section.Paragraphs
section_count = 0
print(f"\n=== Section {i + 1} ===")
# Loop through each paragraph in the section
for j in range(paragraphs.Count):
paragraph = paragraphs.get_Item(j)
text = paragraph.Text
# Find all matches using regular expressions
count = len(re.findall(re.escape(keyword), text, flags=re.IGNORECASE))
section_count += count
total_count += count
print(f'Total in Section {i + 1}: {section_count} time(s)')
print(f'\n=== Total occurrences in all sections: {total_count} ===')
# Close the document
document.Close()
How to Count Word Frequency by Paragraph in a Word Document
When it comes to tasks like sensitive word detection or content auditing, it's crucial to perform a more granular analysis of word frequency. In this section, you’ll learn how to count word frequency by paragraph in a Word document, which gives you deeper insight into how specific terms are distributed across your content. Let’s walk through the steps and see a code example in action.
Steps to count the frequency of words by paragraph in Word files:
- Instantiate a Document object and load a Word document from files.
- Specify the keyword to search for.
- Loop through each section and each paragraph in the document.
- Find and count the occurrence of the keyword using regular expressions.
- Print out the count for each paragraph where the keyword appears and the total number of occurrences.
Use the following code to calculate the frequency of "AI-Generated Art" by paragraphs in a Word document:
import re
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("E:/Administrator/Python1/input/AI.docx")
# Customize the keyword to find
keyword = "AI-Generated Art"
# Initialize variables
total_count = 0
paragraph_index = 1
# Loop through sections and paragraphs
sections = document.Sections
for i in range(sections.Count):
section = sections.get_Item(i)
paragraphs = section.Paragraphs
for j in range(paragraphs.Count):
paragraph = paragraphs.get_Item(j)
text = paragraph.Text
# Find all occurrences of the keyword while ignoring case
count = len(re.findall(re.escape(keyword), text, flags=re.IGNORECASE))
# Print the result
if count > 0:
print(f'Paragraph {paragraph_index}: "{keyword}" appears {count} time(s)')
total_count += count
paragraph_index += 1
# Print the total count
print(f'\nTotal occurrences in all paragraphs: {total_count}')
document.Close()
To Wrap Up
The guide demonstrates how to count the frequency of specific words across an entire Word document, by section, and by paragraph using Python. Whether you're analyzing long reports, filtering sensitive terms, or building smart document tools, automating the task with Spire.Doc for Python can save time and boost accuracy. Give them a try in your own projects and take full control of your Word document content.
FAQs about Counting the Frequency of Words
Q1: How to count the number of times a word appears in Word?
A: You can count word frequency in Word manually using the “Find” feature, or automatically using Python and libraries like Spire.Doc. This lets you scan the entire document or target specific sections or paragraphs.
Q2: Can I analyze word frequency across multiple Word files?
A: Yes. By combining a loop in Python to load multiple documents, you can apply the same word-count logic to each file and aggregate the results—ideal for batch processing or document audits.
How to Convert PDF to CSV in Python (Fast & Accurate Table Extraction)
2025-05-19 03:43:16 Written by Administrator
Working with PDFs that contain tables, reports, or invoice data? Manually copying that information into spreadsheets is slow, error-prone, and just plain frustrating. Fortunately, there's a smarter way: you can convert PDF to CSV in Python automatically — making your data easy to analyze, import, or automate.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to use Python for PDF to CSV conversion by directly extracting tables with Spire.PDF for Python — a pure Python library that doesn’t require any external tools.
✅ No Adobe or third-party tools required
✅ High-accuracy table recognition
✅ Ideal for structured data workflows
In this guide, we’ll cover:
- Convert PDF to CSV in Python Using Table Extraction
- Related Use Cases
- Why Use Spire.PDF for PDF to CSV Conversion in Python?
- Frequently Asked Questions
Convert PDF to CSV in Python Using Table Extraction
The best way to convert PDF to CSV using Python is by extracting tables directly — no need for intermediate formats like Excel. This method is fast, clean, and highly effective for documents with structured data such as invoices, bank statements, or reports. It gives you usable CSV output with minimal code and high accuracy, making it ideal for automation and data analysis workflows.
Step 1: Install Spire.PDF for Python
Before writing code, make sure to install the required library. You can install Spire.PDF for Python via pip:
pip install spire.pdfYou can also install Free Spire.PDF for Python if you're working on smaller tasks:
pip install spire.pdf.freeStep 2: Python Code — Extract Table from PDF and Save as CSV
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTableExtractor
import csv
import os
# Load the PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Create a table extractor
extractor = PdfTableExtractor(pdf)
# Ensure output directory exists
os.makedirs("output/Tables", exist_ok=True)
# Loop through each page in the PDF
for page_index in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
# Extract tables on the current page
tables = extractor.ExtractTable(page_index)
for table_index, table in enumerate(tables):
table_data = []
# Extract all rows and columns
for row in range(table.GetRowCount()):
row_data = []
for col in range(table.GetColumnCount()):
# Get cleaned cell text
cell_text = table.GetText(row, col).replace("\n", "").strip()
row_data.append(cell_text)
table_data.append(row_data)
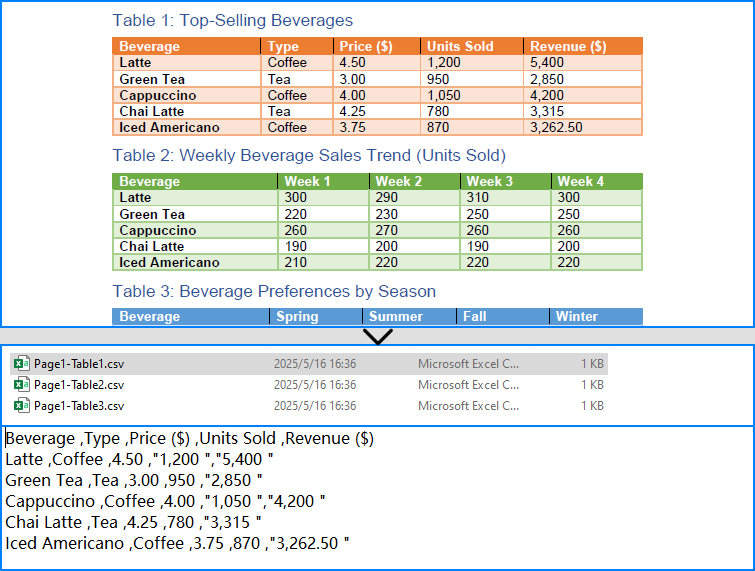
# Write the table to a CSV file
output_path = os.path.join("output", "Tables", f"Page{page_index + 1}-Table{table_index + 1}.csv")
with open(output_path, "w", newline="", encoding="utf-8") as csvfile:
writer = csv.writer(csvfile)
writer.writerows(table_data)
# Release PDF resources
pdf.Dispose()The conversion result:
What is PdfTableExtractor?
PdfTableExtractor is a utility class provided by Spire.PDF for Python that detects and extracts table structures from PDF pages. Unlike plain text extraction, it maintains the row-column alignment of tabular data, making it ideal for converting PDF tables to CSV with clean structure.
Best for:
- PDFs with structured tabular data
- Automated Python PDF to CSV conversion
- Fast Python-based data workflows
Relate Article: How to Convert PDFs to Excel XLSX Files with Python
Related Use Cases
If your PDF doesn't contain traditional tables — such as when it's formatted as paragraphs, key-value pairs, or scanned as an image — the following approaches can help you convert such PDFs to CSV using Python effectively:
Useful when data is in paragraph or report form — format it into table-like CSV using Python logic.
Perfect for image-based PDFs — use OCR to detect and export tables to CSV.
Why Choose Spire.PDF for Python?
Spire.PDF for Python is a robust PDF SDK tailored for developers. Whether you're building automated reports, analytics tools, or ETL pipelines — it just works.
Key Benefits:
- Accurate Table Recognition
Smartly extracts structured data from tables
- Pure Python, No Adobe Needed
Lightweight and dependency-free
- Multi-Format Support
Also supports conversion to text, images, Excel, and more
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I convert PDF to CSV using Python?
Yes, you can convert PDF to CSV in Python using Spire.PDF. It supports both direct table extraction to CSV and an optional workflow that converts PDFs to Excel first. No Adobe Acrobat or third-party tools are required.
What's the best way to extract tables from PDFs in Python?
The most efficient way is using Spire.PDF’s PdfTableExtractor class. It automatically detects tables on each page and lets you export structured data to CSV with just a few lines of Python code — ideal for invoices, reports, and automated processing.
Why would I convert PDF to Excel before CSV?
You might convert PDF to Excel first if the layout is complex or needs manual review. This gives you more control over formatting and cleanup before saving as CSV, but it's slower than direct extraction and not recommended for automation workflows.
Does Spire.PDF work without Adobe Acrobat?
Yes. Spire.PDF for Python is a 100% standalone library that doesn’t rely on Adobe Acrobat or any external software. It's a pure Python solution for converting, extracting, and manipulating PDF content programmatically.
Conclusion
Converting PDF to CSV in Python doesn’t have to be a hassle. With Spire.PDF for Python, you can:
- Automatically extract structured tables to CSV
- Build seamless, automated workflows in Python
- Handle both native PDFs and scanned ones (with OCR)
Get a Free License
Spire.PDF for Python offers a free edition suitable for basic tasks. If you need access to more features, you can also apply for a free license for evaluation use. Simply submit a request, and a license key will be sent to your email after approval.
How to Filter Excel Pivot Tables with Python: Step-by-Step Guide
2025-05-16 10:01:44 Written by Administrator
Introduction
Pivot Tables in Excel are versatile tools that enable efficient data summarization and analysis. They allow users to explore data, uncover insights, and generate reports dynamically. One of the most powerful features of Pivot Tables is filtering, which lets users focus on specific data subsets without altering the original data structure.
What This Tutorial Covers
This tutorial provides a detailed, step-by-step guide on how to programmatically apply various types of filters to a Pivot Table in Excel using Python with the Spire.XLS for Python library. It covers the following topics:
- Benefits of Filtering Data in Pivot Tables
- Install Python Excel Library – Spire.XLS for Python
- Add Report Filter to Pivot Table
- Apply Row Field Filter in Pivot Table
- Apply Column Field Filter in Pivot Table
- FAQs
- Conclusion
Benefits of Filtering Data in Pivot Tables
Filtering is an essential feature of Pivot Tables that provides the following benefits:
- Enhanced Data Analysis: Quickly focus on specific segments or categories of your data to draw meaningful insights.
- Dynamic Data Updates: Filters automatically adjust to reflect changes when the underlying data is refreshed, keeping your analysis accurate.
- Improved Data Organization: Display only relevant data in your reports without altering or deleting the original dataset, preserving data integrity.
Install Python Excel Library – Spire.XLS for Python
Before working with Pivot Tables in Excel using Python, ensure the Spire.XLS for Python library is installed. The quickest way to do this is using pip, Python’s package manager. Simply run the following command in your terminal or command prompt:
pip install spire.xlsOnce installed, you’re ready to start automating Pivot Table filtering in your Python projects.
Add Report Filter to Pivot Table
A report filter allows you to filter the entire Pivot Table based on a particular field and value. This type of filter is useful when you want to display data for a specific category or item globally across the Pivot Table, without changing the layout.
Steps to Add a Report Filter
- Initialize the Workbook: Create a Workbook object to manage your Excel file.
- Load the Excel File: Use Workbook.LoadFromFile() to load an existing file containing a Pivot Table.
- Access the Worksheet: Use Workbook.Worksheets[] to select the desired worksheet.
- Locate the Pivot Table: Use Worksheet.PivotTables[] to access the specific Pivot Table.
- Define the Report Filter: Create a PivotReportFilter object specifying the field to filter.
- Apply the Report Filter: Add the filter to the Pivot Table using XlsPivotTable.ReportFilters.Add().
- Save the Updated File: Use Workbook.SaveToFile() to save your changes.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.xls import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an existing Excel file containing a Pivot Table
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Access the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Access the first Pivot Table in the worksheet
pt = sheet.PivotTables[0]
# Create a report filter for the field "Product"
reportFilter = PivotReportFilter("Product", True)
# Add the report filter to the pivot table
pt.ReportFilters.Add(reportFilter)
# Save the updated workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("AddReportFilter.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()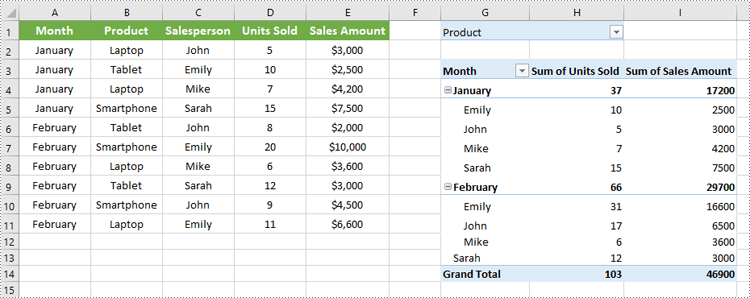
Apply Row Field Filter in Pivot Table
Row field filters allow you to filter data displayed in the row fields of an Excel Pivot Table. These filters can be based on labels (specific text values) or values (numeric criteria).
Steps to Add a Row Field Filter
- Initialize the Workbook: Create a Workbook object to manage the Excel file.
- Load the Excel File: Use Workbook.LoadFromFile() to load your target file containing a Pivot Table.
- Access the Worksheet: Select the desired worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[].
- Locate the Pivot Table: Access the specific Pivot Table using Worksheet.PivotTables[].
- Add a Row Field Filter: Add a label filter or value filter using
XlsPivotTable.RowFields[].AddLabelFilter() or
XlsPivotTable.RowFields[].AddValueFilter().
- Calculate Pivot Table Data: Use XlsPivotTable.CalculateData() to calculate the pivot table data.
- Save the Updated File: Save your changes using Workbook.SaveToFile().
Code Example
- Python
from spire.xls import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the first pivot table
pt = sheet.PivotTables[0]
# Add a value filter to the first row field in the pivot table
pt.RowFields[0].AddValueFilter(PivotValueFilterType.GreaterThan, pt.DataFields[0], Int32(5000), None)
# Or add a label filter to the first row field in the pivot table
# pt.RowFields[0].AddLabelFilter(PivotLabelFilterType.Equal, "Mike", None)
# Calculate the pivot table data
pt.CalculateData()
# Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile("AddRowFieldFilter.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()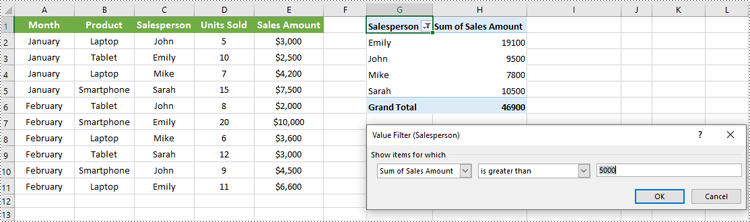
Apply Column Field Filter in Pivot Table
Column field filters in Excel Pivot Tables allow you to filter data displayed in the column fields. Similar to row field filters, column field filters can be based on labels (text values) or values (numeric criteria).
Steps to Add Column Field Filter
- Initialize the Workbook: Create a Workbook object to manage your Excel file.
- Load the Excel File: Use Workbook.LoadFromFile() to open your file containing a Pivot Table.
- Access the Worksheet: Select the target worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[].
- Locate the Pivot Table: Use Worksheet.PivotTables[] to access the desired Pivot Table.
- Add a Column Field Filter: Add a label filter or value filter using
XlsPivotTable.ColumnFields[].AddLabelFilter() or
XlsPivotTable.ColumnFields[].AddValueFilter().
- Calculate Pivot Table Data: Use XlsPivotTable.CalculateData() to calculate the Pivot Table data.
- Save the Updated File: Save your changes using Workbook.SaveToFile().
Code Example
- Python
from spire.xls import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Access the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Access the first Pivot Table
pt = sheet.PivotTables[0]
# Add a label filter to the first column field
pt.ColumnFields[0].AddLabelFilter(PivotLabelFilterType.Equal, String("Laptop"), None)
# # Or add a value filter to the first column field
# pt.ColumnFields[0].AddValueFilter(PivotValueFilterType.Between, pt.DataFields[0], Int32(5000), Int32(10000))
# Calculate the pivot table data
pt.CalculateData()
# Save the updated workbook
workbook.SaveToFile("AddColumnFieldFilter.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()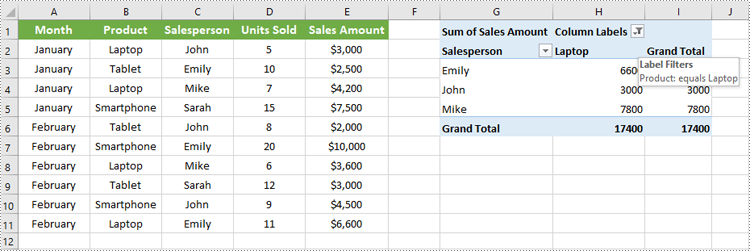
Conclusion
Filtering Pivot Tables in Excel is crucial for effective data analysis, allowing users to zoom in on relevant information without disrupting the table’s structure. Using Spire.XLS for Python, developers can easily automate adding, modifying, and managing filters on Pivot Tables programmatically. This tutorial covered the primary filter types—report filters, row field filters, and column field filters—with detailed code examples to help you get started quickly.
FAQs
Q: Can I add multiple filters to the same Pivot Table?
A: Yes, you can add multiple report filters, row filters, and column filters simultaneously to customize your data views with Spire.XLS.
Q: Do filters update automatically if the source data changes?
A: Yes, after refreshing the Pivot Table or recalculating with CalculateData(), filters will reflect the latest data.
Q: Can I filter based on custom conditions?
A: Spire.XLS supports many filter types including label filters (equals, begins with, contains) and value filters (greater than, less than, between).
Q: Is it possible to remove filters programmatically?
A: Yes, you can remove filters by clearing or resetting the respective filter collections or fields.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.XLS for .NET without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.

Barcodes are essential in inventory management, retail systems, logistics, and many other data-driven fields. For Python developers, generating barcodes in Python can be complex—especially when working with multiple formats or large-scale automation. That’s why a reliable Python barcode generator library is necessary to ensure flexible and efficient barcode creation, with support for various barcode types and batch processing.
This article provides an accurate and efficient approach to generating barcodes in Python using Spire.Barcode for Python.
- Get Started with Spire.Barcode for Python
- How to Generate Barcode in Python
- Supported Barcode Types
- Frequently Asked Questions
Get Started with Spire.Barcode for Python
Why Choose Spire.Barcode?
Spire.Barcode for Python is a professional and user-friendly Python Barcode API designed for developers who want to add barcode generation or reading features to their Python applications. Here’s why it stands out:
- Supports multiple barcode symbologies including Code 128, QR Code, EAN-13, UPC, and more
- High-quality image output with complete customization settings
- Comprehensive and easy-to-integrate API
- No need for third-party dependencies
- One library to generate and scan barcodes
Installation and Importing
To install Spire.Barcode for Python, simply run:
pip install spire.barcodeYou can also install Free Spire.Barcode for Python for simple barcode generating tasks:
pip install spire.barcode.freeHow to Generate Barcode in Python
To generate a barcode in Python, you typically need to define the barcode type (such as Code 128 or QR Code) and the content to encode. Using a library like Spire.Barcode, you can configure them in just a few lines of code.
Key Classes and Methods:
- BarcodeSettings: Defines properties such as type, data, color, text, etc.
- BarCodeGenerator: Generates barcode images based on settings.
- GenerateImage(): Outputs barcode as an image stream.
Step 1: Import the Required Modules
To start coding your Python barcode generator, import the necessary classes.
- Python
from spire.barcode import BarcodeSettings, BarCodeType, BarCodeGenerator, Code128SetMode, FontStyle, ColorStep2: Configure Barcode Settings
Create a BarcodeSettings object and define barcode properties:
- Python
# Create a BarcodeSettings object
barcodeSettings = BarcodeSettings()
# Set the barcode type
barcodeSettings.Type = BarCodeType.Code128
# Set the barcode data
barcodeSettings.Data = "ABC123456789"
# Set the barcode code128 set mode
barcodeSettings.Code128SetMode = Code128SetMode.Auto
# Choose the data display position
barcodeSettings.ShowTextOnBottom = True
# Set the bottom text and style
barcodeSettings.BottomText = "Code 128 Example"
barcodeSettings.SetTextFont("Arial", 12.0, FontStyle.Regular)
barcodeSettings.ShowBottomText = True
# Set the background color
barcodeSettings.BackColor = Color.get_Beige()Step 3: Generate the Barcode Image
Create a BarCodeGenerator object using the configured BarcodeSettings, then generate the barcode image as a stream and save it to a local file:
- Python
# Create a BarCodeGenerator object
barcodeGenerator = BarCodeGenerator(barcodeSettings)
# Generate the barcode image
barcodeImage = barcodeGenerator.GenerateImage()
# Save the image
with open("output/Code 128.png", "wb") as fp:
fp.write(barcodeImage)The generated barcode:

This script allows you to generate a Code 128 barcode and save it as an image. Just replace the BarCodeType and Data value to customize.
Generating Other Barcode Types
Spire.Barcode for Python supports a wide range of barcode symbologies, including the most commonly used types such as Code 39, UPC, QR Code, and EAN-13. This ensures developers can generate barcodes for various applications with compatibility and ease.
Barcode Type Support Overview
| Barcode Category | Barcode Types (Examples) | Free Version | Paid Version |
| 1D Linear Barcodes | Codabar, Code11, Code25, Interleaved25, Code39, Code39Extended, Code93, Code93Extended, Code128, EAN8, EAN13, EAN128, EAN14, UPCA, UPCE, MSI, PostNet, Planet, SCC14, SSCC18, ITF14, ITF6, PZN, OPC | ✅ (Partial) | ✅ (All) |
| 2D Barcodes | QRCode, DataMatrix, Pdf417, Pdf417Macro, Aztec, MicroQR | ✅ (QRCode only) | ✅ (All) |
| Stacked/Composite Codes | RSS14, RSS14Truncated, RSSLimited, RSSExpanded | ❌ | ✅ |
| Postal Barcodes | USPS, SwissPostParcel, DeutschePostIdentcode, DeutschePostLeitcode, RoyalMail4State, SingaporePost4State | ❌ | ✅ |
Advanced: Generate Barcodes in Bulk
You can easily generate multiple barcodes in bulk using Spire.Barcode for Python. This is especially useful for inventory management, batch labeling, or automated systems where each item requires a unique barcode.
Code Example
- Python
# Create a list of barcode data
data = ["Barcode 1", "Barcode 2", "Barcode 3"]
# Loop through the data to generate barcodes
for barcode_data in data:
# Create a BarcodeSettings object
settings = BarcodeSettings()
# Set the barcode type and data
settings.Type = BarCodeType.Code39
settings.Data = barcode_data
# Create a BarCodeGenerator object
generator = BarCodeGenerator(settings)
# Save the barcode image
barcode_stream = generator.GenerateImage()
with open(f"output/{barcode_data}.png", "wb") as file:
file.write(barcode_stream)This Python script generates and saves a barcode image for each entry in the list, streamlining barcode creation workflow.
Conclusion
Generating barcodes in Python is simple and efficient with Spire.Barcode for Python. Whether you’re creating a single Code 128 barcode or automating batch QR code generation, this robust and flexible library gives you the control and quality needed for professional barcode integration. From supporting various symbologies to delivering high-quality output with minimal code, this Python barcode generator is an excellent tool for developers across industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How to create a barcode in Python?
You can create a barcode using libraries like Spire.Barcode for Python, which supports a variety of symbologies like Code 128, QR Code, and more. Just install the package, configure barcode settings, and save the output image.
Q: How is barcode generated?
Barcodes are generated by encoding data into a visual pattern of bars or modules. With Python, this is done through barcode libraries like Spire.Barcode, which translate string input into a corresponding image.
Q: How to create a code generator in Python?
If you're referring to a barcode generator, define the barcode type (e.g., Code 128), provide the data, and use a library like Spire.Barcode to generate and save the image. You can automate this process using loops and functions.
Q: How to generate QR code by Python?
You can use Spire.Barcode for Python to generate QR codes quickly and efficiently. Here's a full example that creates a QR code with embedded data:
- Python
from spire.barcode import BarcodeSettings, BarCodeGenerator, BarCodeType
# Create a BarcodeSettings object
barcodeSettings = BarcodeSettings()
# Set the barcode type to QRCode
barcodeSettings.Type = BarCodeType.QRCode
# Set the barcode data
barcodeSettings.Data = "ABC123456"
# Generate the barcode
barcodeGenerator = BarCodeGenerator(barcodeSettings)
barcodeGenerator.GenerateImage()
with open("output/QRCode.png", "wb") as f:
f.write(barcodeGenerator.GenerateImage())Result:

This enables you to embed URLs, text, or IDs into scannable QR images.
See Also: How to Generate and Scan QR Codes with Python
Get a Free License
Spire.Barcode for Python offers a free trial license that removes limitations and watermarking. Get a free license today and explore the full capabilities of this powerful Python barcode library.
Edit PDF Using Python: A Practical Guide to PDF Modification
2025-05-06 03:42:04 Written by Administrator
PDFs are widely used in reports, invoices, and digital forms due to their consistent formatting across platforms. However, their fixed layout makes editing difficult without specialized tools. For developers looking to edit PDF using Python, Spire.PDF for Python provides a comprehensive and easy-to-use solution. This Python PDF editor enables you to modify PDF files programmatically—changing text, replacing images, adding annotations, handling forms, and securing files—without relying on Adobe Acrobat or any external software.
In this article, we will explore how to use Spire.PDF for Python to programmatically edit PDFs in Python applications.
- Why Use Python and Spire.PDF to Edit PDF Documents?
- Getting Started with Spire.PDF for Python
- How to Edit an Existing PDF Using Spire.PDF for Python
- Frequently Asked Questions
Why Use Python and Spire.PDF to Edit PDF Documents?
Python is a highly versatile programming language that provides an excellent platform for automating and managing PDF documents. When it comes to edit PDF Python tasks, Spire.PDF for Python stands out as a comprehensive and easy-to-use solution for all your PDF manipulation needs.
Benefits of Using Python for PDF Editing
- Automation and Batch Processing: Streamline repetitive PDF editing tasks efficiently.
- Cost-Effective: Reduce manual work, saving time and resources when you Python-edit PDF files.
- Integration: Seamlessly incorporate PDF editing into existing Python-based systems and workflows.
Advantages of Spire.PDF for Python
Spire.PDF for Python is a standalone library that enables developers to create, read, edit, convert, and save PDF files without relying on external software. As a trusted Python PDF editor, it offers powerful features such as:
- Text and Image Editing
- Annotations and Bookmark Management
- Form Field Handling
- Security Settings (Encryption and Permissions)
- Conversion to Word, Excel, HTML, and Images
To learn more about these specific features, visit the Spire.PDF for Python tutorials.
With its intuitive API design, Spire.PDF makes it easier than ever to edit PDF files in Python quickly and effectively, ensuring a smooth development experience.
Getting Started with Spire.PDF for Python
Installation:
To install Spire.PDF for Python, simply run the following pip command:
pip install spire.pdf
Alternatively, you can install Free Spire.PDF for Python, a free version suitable for small projects, by running:
pip install spire.pdf.free
You can also download the library manually from the links.
Basic Setup Example:
The following example demonstrates how to create a simple PDF using Spire.PDF for Python:
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfFont, PdfBrushes, PdfFontFamily, PdfFontStyle
# Create a new PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a new page to the document
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
# Create a font
font = PdfFont(PdfFontFamily.TimesRoman, 28.0, PdfFontStyle.Bold)
# Create a brush
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Black()
# Draw the string using the font and brush
page.Canvas.DrawString("Hello, World", font, brush, 100.0, 100.0)
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/NewPDF.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result: The generated PDF displays the text "Hello, World" using Times Roman Bold.

With Spire.PDF installed, you're now ready to edit PDFs using Python. The sections below explain how to manipulate structure, content, security, and metadata.
How to Edit an Existing PDF Using Spire.PDF for Python
Spire.PDF for Python provides a simple yet powerful way to edit PDF using Python. With its intuitive API, developers can automate a wide range of PDF editing tasks including modifying document structure, page content, security settings, and properties. This section outlines the core categories of editing and their typical use cases.
Edit PDF Pages and Structure with Python
Structure editing lets you manipulate PDF page order, merge files, or insert/delete pages—ideal for document assembly workflows.
- Insert or Delete Pages
Use the Pages.Insert() and Pages.RemoveAt() methods of the PdfDocument class to insert or delete pages at specific positions.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfPageSize, PdfMargins, PdfPageRotateAngle
# Load a PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Insert and delete pages
# Insert at beginning
pdf.Pages.Insert(0, PdfPageSize.A4(), PdfMargins(50.0, 60.0), PdfPageRotateAngle.RotateAngle90)
# Delete second page
pdf.Pages.RemoveAt(1)
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/InsertDeletePage.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
- Merge Two PDF Files
The AppendPage() method allows you to combine PDFs by inserting pages from one document into another.
Code Example
- Python
import os
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
# Specify the PDF file path
pdfPath = "PDFs/"
# Read the PDF file names from the path and add them to a list
files = [pdfPath + file for file in os.listdir(pdfPath) if file.endswith(".pdf")]
# Load the first PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile(files[0])
# Iterate through the other PDF files
for i in range(1, len(files)):
# Load the current PDF file
pdf2 = PdfDocument()
pdf2.LoadFromFile(files[i])
# Append the pages from the current PDF file to the first PDF file
pdf.AppendPage(pdf2)
# Save the merged PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/MergePDFs.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
You may also like: Splitting PDF Files with Python Code
Edit PDF Content with Python
As a Python PDF editor, Spire.PDF supports a variety of content-level operations, including modifying text, images, annotations, and interactive forms.
- Replace Text in a PDF
The PdfTextReplacer class can be used to find and replace text from a page. Note that precise replacement may require case and layout-aware handling.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTextReplacer, ReplaceActionType, Color
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Iterate through the pages
for i in range(pdf.Pages.Count):
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Create a PdfTextReplacer object
replacer = PdfTextReplacer(page)
# Set the replacement options
replacer.Options.ReplaceType = ReplaceActionType.IgnoreCase
# Replace the text
replacer.ReplaceAllText("drones", "ROBOTS", Color.get_Aqua()) # Setting the color is optional
# Save the merged PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/ReplaceText.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:

- Replace Images in a PDF
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfImageHelper class to help you replace images in a PDF file with ease. By retrieving image information from a specific page, you can use the ReplaceImage() method to directly substitute the original image with a new one.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfImageHelper, PdfImage
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get a page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Create a PdfImageHelper instance
imageHelper = PdfImageHelper()
# Get the image info of the first image on the page
imageInfo = imageHelper.GetImagesInfo(page)[0]
# Load a new image
newImage = PdfImage.FromFile("Image.png")
# Replace the image
imageHelper.ReplaceImage(imageInfo, newImage)
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/ReplaceImage.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:

- Add Comments or Notes
To add comments or notes with Python, use the PdfTextMarkupAnnotation class and add it to the page’s AnnotationsWidget collection.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfTextFinder, PdfTextMarkupAnnotation, PdfRGBColor, Color
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get a page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
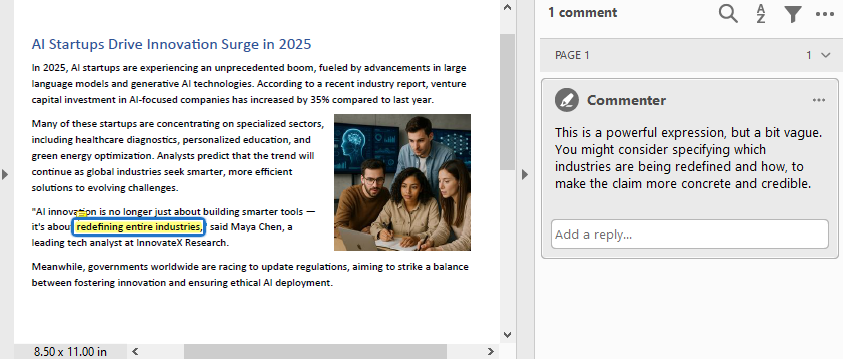
#Create a PdfTextFinder instance and set the options
finder = PdfTextFinder(page)
finder.Options.Parameter.IgnoreCase = False
finder.Options.Parameter.WholeWord = True
# Find the text to comment
text = finder.Find("redefining entire industries")[0]
# Get the bound of the text
bound = text.Bounds[0]
# Add comment
commentText = ("This is a powerful expression, but a bit vague. "
"You might consider specifying which industries are "
"being redefined and how, to make the claim more "
"concrete and credible.")
comment = PdfTextMarkupAnnotation("Commenter", commentText, bound)
comment.TextMarkupColor = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Yellow())
page.AnnotationsWidget.Add(comment)
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/CommentNote.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
- Edit or Read Form Fields
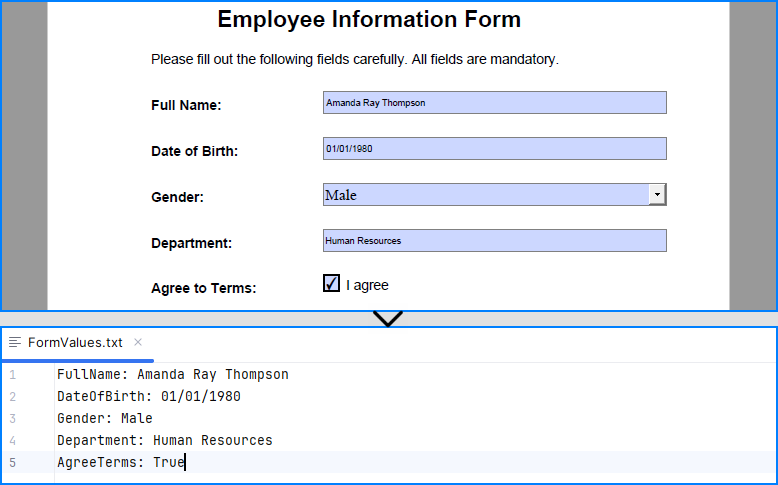
Spire.PDF for Python allows you to programmatically fill out and read form fields in a PDF document. By accessing the FieldsWidget property of a PdfFormWidget object, you can iterate through all interactive form elements, such as text boxes, combo boxes, and checkboxes, and update or extract their values.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfFormWidget, PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget, PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget, PdfTextBoxFieldWidget
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("EmployeeInformationForm.pdf")
forms = pdf.Form
formWidgets = PdfFormWidget(forms).FieldsWidget
# Fill the forms
for i in range(formWidgets.Count):
formField = formWidgets.get_Item(i)
if formField.Name == "FullName":
textBox = PdfTextBoxFieldWidget(formField)
textBox.Text = "Amanda Ray Thompson"
elif formField.Name == "DateOfBirth":
textBox = PdfTextBoxFieldWidget(formField)
textBox.Text = "01/01/1980"
elif formField.Name == "Gender":
comboBox = PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget(formField)
comboBox.SelectedIndex = [ 1 ]
elif formField.Name == "Department":
formField.Value = "Human Resources"
elif formField.Name == "AgreeTerms":
checkBox = PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget(formField)
checkBox.Checked = True
# Read the forms
formValues = []
for i in range(formWidgets.Count):
formField = formWidgets.get_Item(i)
if isinstance(formField, PdfTextBoxFieldWidget):
formValues.append(formField.Name + ": " + formField.Text)
elif isinstance(formField, PdfComboBoxWidgetFieldWidget):
formValues.append(formField.Name + ": " + formField.SelectedValue)
elif isinstance(formField, PdfCheckBoxWidgetFieldWidget):
formValues.append(formField.Name + ": " + str(formField.Checked))
# Write the form values to a file
with open("output/FormValues.txt", "w") as file:
file.write("\n".join(formValues))
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/FilledForm.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
Explore more: How to Insert Page Numbers to PDF Using Python
Manage PDF Security with Python
PDF security editing is essential when dealing with sensitive documents. Spire.PDF supports encryption, password protection, digital signature handling, and permission settings.
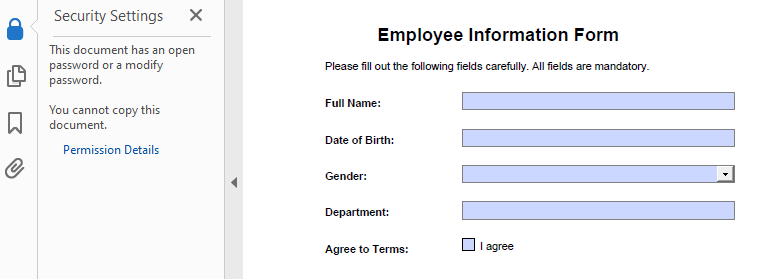
- Add a Password and Set Permissions
The Encrypt() method lets you secure a PDF with user/owner passwords and define allowed actions like printing or copying.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfEncryptionAlgorithm, PdfDocumentPrivilege, PdfPasswordSecurityPolicy
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("EmployeeInformationForm.pdf")
# Create a PdfSecurityPolicy object and set the passwords and encryption algorithm
securityPolicy = PdfPasswordSecurityPolicy("userPSD", "ownerPSD")
securityPolicy.EncryptionAlgorithm = PdfEncryptionAlgorithm.AES_128
# Set the document privileges
pdfPrivileges = PdfDocumentPrivilege.ForbidAll()
pdfPrivileges.AllowPrint = True
pdfPrivileges.AllowFillFormFields = True
# Apply the document privileges
securityPolicy.DocumentPrivilege = pdfPrivileges
# Encrypt the PDF with the security policy
pdf.Encrypt(securityPolicy)
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/EncryptedForm.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result
- Remove the Password from a PDF
To open a protected file, provide the user password when calling LoadFromFile(), use Decrypt() to decrypt the document, and save it again unprotected.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
# Load the encrypted PDF file with the owner password
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("output/EncryptedForm.pdf", "ownerPSD")
# Decrypt the PDF file
pdf.Decrypt()
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/DecryptedForm.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Recommended for you: Use Python to Add and Remove Digital Signature in PDF
Edit PDF Properties with Python
Use Spire.PDF to read and edit PDF metadata and viewer preferences—key features for document presentation and organization.
- Update Document Metadata
Update metadata such as title, author, or subject via the DocumentInformation property of the PDF document.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("EmployeeInformationForm.pdf")
# Set document metadata
pdf.DocumentInformation.Author = "John Doe"
pdf.DocumentInformation.Title = "Employee Information Form"
pdf.DocumentInformation.Producer = "Spire.PDF"
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/EditProperties.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
- Set View Preferences
The ViewerPreferences property allows you to customize the viewing mode of a PDF (e.g., two-column layout).
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument, PdfPageLayout, PrintScalingMode
# Load the PDF file
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("EmployeeInformationForm.pdf")
# Set the viewer preferences
pdf.ViewerPreferences.DisplayTitle = True
pdf.ViewerPreferences.HideToolbar = True
pdf.ViewerPreferences.HideWindowUI = True
pdf.ViewerPreferences.FitWindow = False
pdf.ViewerPreferences.HideMenubar = True
pdf.ViewerPreferences.PrintScaling = PrintScalingMode.AppDefault
pdf.ViewerPreferences.PageLayout = PdfPageLayout.OneColumn
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("output/EditViewerPreference.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Result:
Similar topic: Change PDF Version Easily with Python Code
Conclusion
Editing PDFs using Python is both practical and efficient with Spire.PDF for Python. Whether you're building automation tools, editing digital forms, or securing sensitive reports, Spire.PDF equips you with a comprehensive suite of editing features—all accessible via clean and simple Python code.
With capabilities that span content editing, form interaction, document structuring, and security control, this Python PDF editor is a go-to solution for developers and organizations aiming to streamline their PDF workflows.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can I edit a PDF using Python?
A: Yes, Python offers powerful libraries like Spire.PDF for Python that enable you to edit text, images, forms, annotations, and even security settings in a PDF file.
Q: How to edit a PDF using coding?
A: By using libraries such as Spire.PDF for Python, you can load an existing PDF, modify its content or structure programmatically, and save the changes with just a few lines of code.
Q: What is the Python library for PDF editor?
A: Spire.PDF for Python is a popular choice. It offers comprehensive functionalities for creating, reading, editing, converting, and securing PDF documents without the need for additional software.
Q: Can I modify a PDF for free?
A: Yes, you can use the free edition of Spire.PDF for Python to edit PDF files, although it comes with some limitations, such as processing up to 10 pages per document. Additionally, you can apply for a 30-day temporary license that removes all limitations and watermarks for full functionality testing.
PDF documents may occasionally include blank pages. These pages can affect the reading experience, increase the file size and lead to paper waste during printing. To improve the professionalism and usability of a PDF document, detecting and removing blank pages is an essential step.
This article shows how to accurately detect and remove blank pages—including those that appear empty but actually contain invisible elements—using Python, Spire.PDF for Python, and Pillow.
Install Required Libraries
This tutorial requires two Python libraries:
- Spire.PDF for Python: Used for loading PDFs and detecting/removing blank pages.
- Pillow: A library for image processing that helps detect visually blank pages, which may contain invisible content.
You can easily install both libraries using pip:
pip install Spire.PDF Pillow
Need help installing Spire.PDF? Refer to this guide:
How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
How to Effectively Detect and Remove Blank Pages from PDF Files in Python
Spire.PDF provides a method called PdfPageBase.IsBlank() to check if a page is completely empty. However, some pages may appear blank but actually contain hidden content like white text, watermarks, or background images. These cannot be reliably detected using the PdfPageBase.IsBlank() method alone.
To ensure accuracy, this tutorial adopts a two-step detection strategy:
- Use the PdfPageBase.IsBlank() method to identify and remove fully blank pages.
- Convert non-blank pages to images and analyze them using Pillow to determine if they are visually blank.
⚠️ Important:
If you don’t use a valid license during the PDF-to-image conversion, an evaluation watermark will appear on the image, potentially affecting the blank page detection.
Contact the E-iceblue sales team to request a temporary license for proper functionality.
Steps to Detect and Remove Blank Pages from PDF in Python
Follow these steps to implement blank page detection and removal in Python:
1. Define a custom is_blank_image() Method
This custom function uses Pillow to check whether the converted image of a PDF page is blank (i.e., if all pixels are white).
2. Load the PDF Document
Load the PDF using the PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
3. Iterate Through Pages
Loop through each page to check if it’s blank using two methods:
- If the PdfPageBase.IsBlank() method returns True, remove the page directly.
- If not, convert the page to an image using the PdfDocument.SaveAsImage() method and analyze it with the custom is_blank_image() method.
4. Save the Result PDF
Finally, save the PDF with blank pages removed using the PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
Code Example
- Python
import io
from spire.pdf import PdfDocument
from PIL import Image
# Custom function: Check if the image is blank (whether all pixels are white)
def is_blank_image(image):
# Convert to RGB mode and then get the pixels
img = image.convert("RGB")
# Get all pixel points and check if they are all white
white_pixel = (255, 255, 255)
return all(pixel == white_pixel for pixel in img.getdata())
# Load the PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample1111.pdf")
# Iterate through each page in reverse order to avoid index issues when deleting
for i in range(pdf.Pages.Count - 1, -1, -1):
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Check if the current page is completely blank
if page.IsBlank():
# If it's completely blank, remove it directly from the document
pdf.Pages.RemoveAt(i)
else:
# Convert the current page to an image
with pdf.SaveAsImage(i) as image_data:
image_bytes = image_data.ToArray()
pil_image = Image.open(io.BytesIO(image_bytes))
# Check if the image is blank
if is_blank_image(pil_image):
# If it's a blank image, remove the corresponding page from the document
pdf.Pages.RemoveAt(i)
# Save the resulting PDF
pdf.SaveToFile("RemoveBlankPages.pdf")
pdf.Close()

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is considered a blank page in a PDF file?
A: A blank page may be truly empty or contain hidden elements such as white text, watermarks, or transparent objects. This solution detects both types using a dual-check strategy.
Q2: Can I use this method without a Spire.PDF license?
A: Yes, you can run it without a license. However, during PDF-to-image conversion, an evaluation watermark will be added to the output images, which may affect the accuracy of blank page detection. It's best to request a free temporary license for testing.
Q3: What versions of Python are compatible with Spire.PDF?
A: Spire.PDF for Python supports Python 3.7 and above. Ensure that Pillow is also installed to perform image-based blank page detection.
Q4: Can I modify the script to only detect blank pages without deleting them?
A: Absolutely. Just remove or comment out the pdf.Pages.RemoveAt(i) line and use print() or logging to list detected blank pages for further review.
Conclusion
Removing unnecessary blank pages from PDF files is an important step in optimizing documents for readability, file size, and professional presentation. With the combined power of Spire.PDF for Python and Pillow, developers can precisely identify both completely blank pages and pages that appear empty but contain invisible content. Whether you're generating reports, cleaning scanned files, or preparing documents for print, this Python-based solution ensures clean and efficient PDFs.
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.PDF for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Introduction
Digital signatures help verify the authenticity and integrity of PDF documents. However, if a signing certificate expires or is revoked, the signature alone may no longer be considered valid. To solve this, a timestamp can be added to the digital signature, proving that the document was signed at a specific point in time-validated by a trusted Time Stamp Authority (TSA).
In this tutorial, we will introduce how to use the Spire.PDF for Python library to digitally sign a PDF document with a timestamp in Python.
Prerequisites
To follow this tutorial, ensure you have the following:
- Spire.PDF for Python library
- A valid digital certificate (.pfx file)
- A sample PDF file
- An image to display as the signature appearance (optional)
- A reliable Time Stamp Authority (TSA) URL
pip install Spire.PDF
How to Digitally Sign a PDF with a Timestamp in Python
In Spire.PDF for Python, the Security_PdfSignature class is used to create a digital signature, and the ConfigureTimestamp(tsaUrl) method in this class is used to embed a timestamp into the signature. The tsaUrl parameter specifies the address of the TSA server.
Steps to Add a Timestamped Digital Signature
Follow these steps to add a timestamped digital signature to a PDF in Python using Spire.PDF for Python:
- Create a PdfDocument instance and use the LoadFromFile() method to load the PDF you want to sign.
- Create a Security_PdfSignature object, specifying the target page, certificate file path, certificate password, and signature name.
- Configure the signature's appearance, including its position, size, display labels, and signature image.
- Embed a timestamp by calling the ConfigureTimestamp(tsaUrl) method with a valid Time Stamp Authority (TSA) URL.
- Save the signed PDF using the SaveToFile() method.
Code Example
- Python
from spire.pdf import * inputFile = "Sample.pdf" inputFile_pfx = "gary.pfx" inputImage = "E-iceblueLogo.png" outputFile = "SignWithTimestamp.pdf" # Create a PdfDocument instance and load the PDF file to be signed doc = PdfDocument() doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Create a digital signature object by specifying the document, target page, certificate file path, certificate password, and signature name signature = Security_PdfSignature(doc, doc.Pages.get_Item(0), inputFile_pfx, "e-iceblue", "signature") # Define the position and size of the signature on the page (unit: point) signature.Bounds = RectangleF(PointF(90.0, 600.0), SizeF(180.0, 90.0)) # Set the labels and content for the signature details signature.NameLabel = "Digitally signed by: " signature.Name = "Gary" signature.LocationInfoLabel = "Location: " signature.LocationInfo = "CN" signature.ReasonLabel = "Reason: " signature.Reason = "Ensure authenticity" signature.ContactInfoLabel = "Contact Number: " signature.ContactInfo = "028-81705109" # Set document permissions: allow form filling, forbid further changes signature.DocumentPermissions = PdfCertificationFlags.AllowFormFill.value | PdfCertificationFlags.ForbidChanges.value # Set the graphic mode to include both image and signature details, # and set the signature image signature.GraphicsMode = Security_GraphicMode.SignImageAndSignDetail signature.SignImageSource = PdfImage.FromFile(inputImage) # Embed a timestamp into the signature using a Time Stamp Authority (TSA) server url = "http://tsa.cesnet.cz:3161/tsa" signature.ConfigureTimestamp(url) # Save the signed PDF and close the document doc.SaveToFile(outputFile) doc.Close()
View the Timestamp in PDF
When you open the signed PDF in a viewer like Adobe Acrobat, you can click the Signature Panel to view both the digital signature and the timestamp, which confirm the document’s validity and the signing time:
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.PDF for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Conclusion
Timestamping enhances the reliability of digital signatures by proving when a PDF was signed-even after the certificate has expired. With Spire.PDF for Python, implementing a timestamped digital signature is a straightforward process. Whether you're handling contracts, invoices, or confidential records, this approach ensures long-term document validity and compliance.