
Python (355)
XML (Extensible Markup Language) is widely used for its structured format and readability on different platforms and systems. Its self-descriptive tags enable you to process data more easily. Meanwhile, Word XML focuses specifically on storing and exchanging Microsoft Word documents. It allows Word documents to transfer without loss. They both show flexibility under various scenarios that Word documents cannot achieve.
On the page, you will learn how to convert Word to XML and Word XML formats using Python with Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows.
Convert Word to XML in Python with Spire.Doc for Python
This part will explain how to convert Word documents to XML in Python with step-by-step instructions and a code example. Spire.Doc for Python provides the Document.SaveToFile() method to make it easy to save Word as XML. Check out the steps below and start processing your Word documents without effort!
Steps to Convert Word to XML:
- Create a new Document object.
- Load the Word document that you wish to be operated using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Covert it to XML by calling Document.SaveToFile() method.
Here's the code example:
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Word document object
document = Document()
# Load the file from the disk
document.LoadFromFile("sample.docx")
# Save the document to an XML file
document.SaveToFile("WordtoXML.xml", FileFormat.Xml)
document.Close()

Convert Word to Word XML in Python
To convert Word to Word XML, you can utilize the Document.SaveToFile() method provided by Spire.Doc for Python. It not only helps to convert Word documents to Word XML but also to many other formats, such as PDF, XPS, HTML, RTF, etc.
Steps to Convert Word to Word XML:
- Create a new Document object.
- Load the Word document by Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Convert it to Word XML using Document.SaveToFile() method.
Here's the code example for you:
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Word document object
document = Document()
# Load the file from the disk
document.LoadFromFile("sample.docx")
# For Word 2003
document.SaveToFile("WordtoWordML.wordml", FileFormat.WordML)
# For Word 2007-2013
document.SaveToFile("WordtoWordXML.wordxml", FileFormat.WordXml)
document.Close()

Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
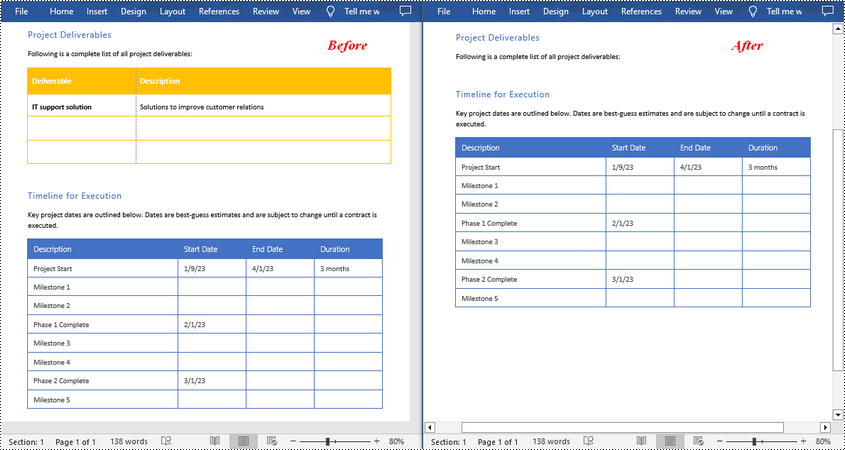
Formatting plays a crucial role in making your Excel spreadsheets clean, organized, and visually appealing. Often, you may want to apply the same formatting to multiple cells or ranges in your workbook. Instead of manually formatting each cell individually, Excel provides a convenient feature called "Copy Cell Formatting" that allows you to quickly replicate the formatting from one cell to others.
Here in this article, you will learn how to programmatically copy cell formatting in Excel using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your system through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Copy Formatting from One Cell to Another in Python
You can access a specific cell by using the Worksheet.Range[row:int, column:int] property. The formatting of that cell can be retrieved through the CellRange.Style property, and this formatting can then be applied to a different cell.
The steps to copy formatting from one to cell to anther are as follows.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document from a give path.
- Get a specific worksheet within the workbook.
- Get a specific cell through Worksheet.Range[row:int, column:int] property.
- Get the cell formatting through CellRange.Style property, and apply it to another cell through the same property.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file.
This code example loads an existing Excel document, copies the formatting (style) from the cells in the second column to the cells in the fourth column for rows 2 through 14, and then saves the modified workbook to a new Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Loop through the selected rows
for i in range(2, 15):
# Get style (formatting) of a specific cell
style = worksheet.Range[i, 2].Style
# Apply the style to a different cell
worksheet.Range[i, 4].Style = style
# Save the workbook to file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/CopyFormatting.xlsx",ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
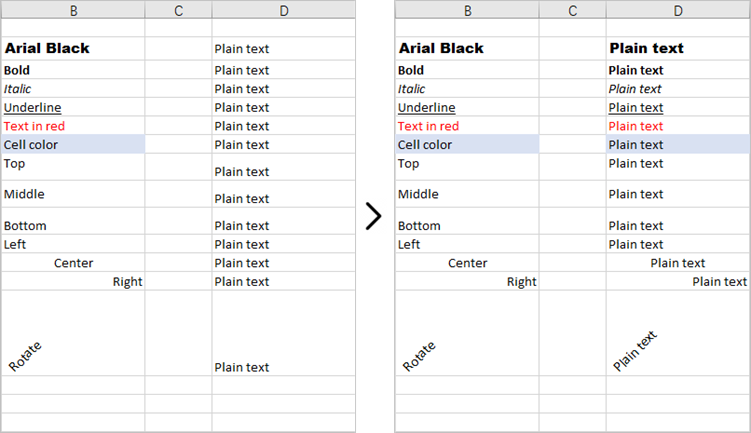
Copy Formatting from One Cell to a Cell Range in Python
Once you get the style (formatting) of a certain cell, you can apply it to a cell rang which is retrieved through the Worksheet.Range[row:int, column:int, endRow:int, endColumn:int] property.
Here are the steps to copy formatting from once cell to a cell range.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel document from a give path.
- Get a specific worksheet within the workbook.
- Get a specific cell through Worksheet.Range[row:int, column:int] property.
- Get the formatting of the cell through CellRange.Style property.
- Get a cell range through Worksheet.Range[row:int, column:int, endRow:int, endColumn:int] property.
- Apply the formatting to the cell range through CellRange.Style property.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file.
This code example loads an existing Excel document, retrieves the style of a cell located in the third row and first column, and then applies that style to a range of cells from the third row, fourth column to the fourth row, sixth column.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get style (formatting) of a specific cell
style = worksheet.Range[3, 1].Style
# Apply the style to a cell range
worksheet.Range[3, 4, 4, 6].Style = style
# Save the workbook to file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/ApplyFormatToCellRange.xlsx",ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
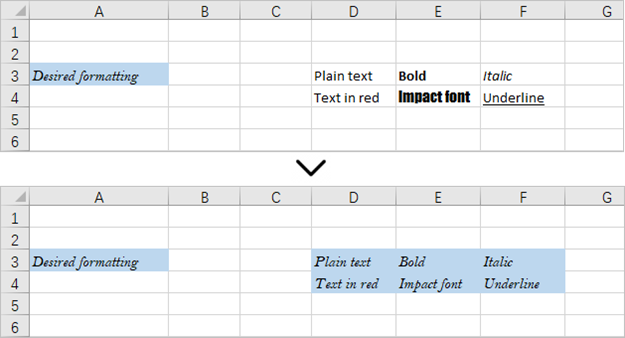
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
When creating a new PDF document, you can add information about the company, icons, and page numbers as the header and footer to enhance the appearance and professionalism of PDF documents.
This detailed guide will introduce how to add a header and footer when creating a new PDF Document in Python with Spire.PDF for Python effortlessly. Read on.
- Add Header with Python When Creating a PDF Document
- Add Footer with Python When Creating a PDF Document
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows.
Background Knowledge
Spire.PDF for Python offers the PdfPageTemplateElement class for defining page template elements. It provides users with PdfPageTemplateElement.Graphics.DrawString(), PdfPageTemplateElement.Graphics.DrawLine(), PdfPageTemplateElement.Graphics.DrawImage(), and more to draw text, lines, and images. Furthermore, Spire.PDF for Python supports drawing automatic fields like PdfPageCountField and PdfPageNumberField to the template element by PdfGraphicsWidget.Draw() method.
To draw content on the PdfPageTemplateElement template element, the coordinate system settings are as follows:
- The coordinates system's origin is positioned at the top left corner of the template.
- The x-axis extends to the right, and the y-axis extends downward.
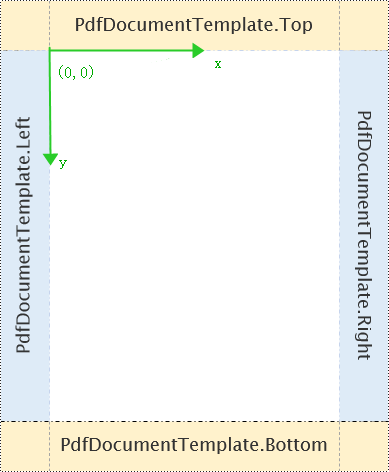
Spire.PDF for Python provides PdfDocumentTemplate class to design the entire page templates of a PDF. The defined PdfPageTemplateElement page template elements above can be applied to the PdfDocumentTemplate page template directly.
PdfDocumentTemplate can apply one or more PdfPageTemplateElement page template elements. For example, apply them to PdfDocumentTemplate.Top and PdfDocumentTemplate.Bottom page templates to create a header and footer in the PDF.
The new page generated by Spire.PDF contains margins by default. The initialization coordinates for the PdfDocumentTemplate page template are set as follows:
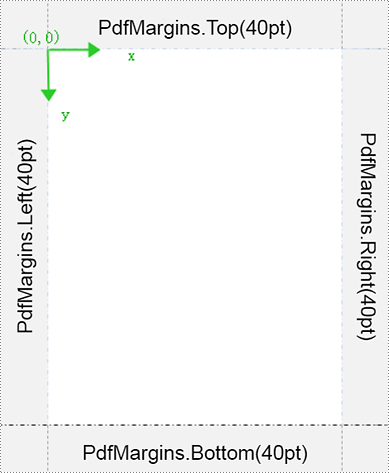
Content cannot be drawn in the margins. To apply PdfPageTemplateElement to PdfDocumentTemplate for the header and footer, you can reset the PDF margins to 0. This way, the coordinate system of the PdfDocumentTemplate page template on the new page will adjust based on the size set by the PdfPageTemplateElement. For example:
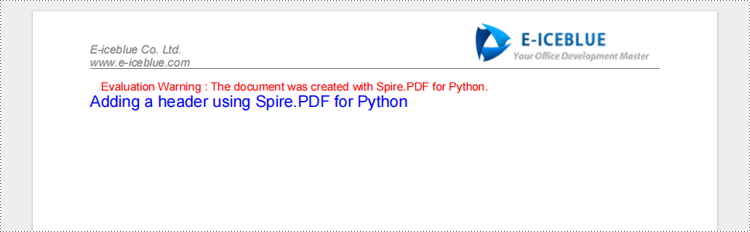
Add a Header with Python When Creating a PDF Document
The following explains how to add text, images, and lines to the header using Spire.PDF for Python when creating a new PDF.
Part 1: Design the header template elements by customizing the CreateHeaderTemplate() method.
- Create PdfPageTemplateElement objects.
- Set the font, brush, pen, and text alignment format for drawing the content of the header by defining PdfTrueTypeFont, PdfBrushes, PdfPen, and PdfTextAlignment.
- Load images to be drawn in the header with PdfImage.FromFile() method.
- Draw text, lines, and images at specified positions in the header template elements using PdfPageTemplateElement.Graphics.DrawString(), PdfPageTemplateElement.Graphics.DrawLine(), and PdfPageTemplateElement.Graphics.DrawImage() methods.
Part 2: Create PDF document objects and call the custom method above to add the header
- Create a new PdfDocument object.
- Set page size by PdfDocoment.PageSettings.Size. Reset the top, bottom, left, and right margins to 0 using PageSettings.Margins.
- Create a new PdfMargins object to set the sizes of the header, the footer, and the left and right templates.
- Call the custom method CreateHeaderTemplate() to add a header.
- Add pages using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Define PdfTrueTypeFont and PdfBrushes to set font and brushes for drawing the main content.
- Draw content in the specified area on the newly created page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Save the resulting file with PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Define CreateHeaderTemplate()
def CreateHeaderTemplate(doc, pageSize, margins):
#Create a header template with a specified size
headerSpace = PdfPageTemplateElement(pageSize.Width, margins.Top)
headerSpace.Foreground = True
doc.Template.Top = headerSpace
# Initialize the x and y coordinate points
x = margins.Left
y = 0.0
# Set font, brush, pen, and ext alignment format
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 10.0, PdfFontStyle.Italic, True)
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Gray()
pen = PdfPen(PdfBrushes.get_Gray(), 1.0)
leftAlign = PdfTextAlignment.Left
# Load the header image and get its height and width values
headerImage = PdfImage.FromFile("E:\Administrator\Python1\header.png")
width = headerImage.Width
height = headerImage.Height
unitCvtr = PdfUnitConvertor()
pointWidth = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(width, PdfGraphicsUnit.Pixel, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point)
pointFeight = unitCvtr.ConvertUnits(height, PdfGraphicsUnit.Pixel, PdfGraphicsUnit.Point)
# Draw a header image at the specified position
headerSpace.Graphics.DrawImage(headerImage, headerSpace.Width-x-pointWidth, headerSpace.Height-pointFeight)
# Draw the header text at the specified place
headerSpace.Graphics.DrawString("E-iceblue Co. Ltd.\nwww.e-iceblue.com", font, brush, x, headerSpace.Height-font.Height*2, PdfStringFormat(leftAlign))
# Draw the header line at the specified position
headerSpace.Graphics.DrawLine(pen, x, margins.Top, pageSize.Width - x, margins.Top)
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Set the page size and margins
pageSize =PdfPageSize.A4()
doc.PageSettings.Size = pageSize
doc.PageSettings.Margins = PdfMargins(0.0)
# Create a new PdfMargins object to set the size of the header, footer, and left and right templates
margins = PdfMargins(50.0, 50.0, 50.0, 50.0)
doc.Template.Left = PdfPageTemplateElement(margins.Left, pageSize.Height-margins.Bottom-margins.Top)
doc.Template.Right = PdfPageTemplateElement(margins.Right, pageSize.Height-margins.Bottom-margins.Top)
doc.Template.Bottom = PdfPageTemplateElement(pageSize.Width, margins.Bottom)
# Call CreateHeaderTemplate() to add a header
CreateHeaderTemplate(doc, pageSize, margins)
# Add pages according to the settings above
page = doc.Pages.Add()
# Define the font and brush to be used for the page content
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 14.0, PdfFontStyle.Regular, True)
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Blue()
# Draw text on the page
text = "Adding a header using Spire.PDF for Python"
page.Canvas.DrawString(text, font, brush, 0.0, 20.0)
# Save the document as PDF
doc.SaveToFile("output/result.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
# Dispose document objects
doc.Close()
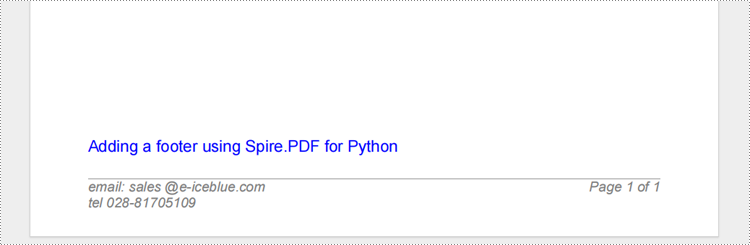
Adding A Footer When Creating A New PDF Document with Python
The following is about how to add text, lines, and page content to the footer by Spire.PDF for Python when creating a new PDF:
Part 1: Customize CreateFooterTemplate() to design footer template elements
- Create a PdfPageTemplateElement object.
- Define PdfTrueTypeFont, PdfBrushes, PdfPen, and PdfTextAlignment to set font, brush, pen, and the text alignment format for drawing the content of footers.
- Draw lines and text in the footer template element using PdfPageTemplateElement Graphics.DrawString() and PdfPageTemplateElement Graphics.DrawLine() methods.
- Create PdfPageNumberField () and PdfPageCountField() objects.
- Create a PdfCompositeField() object to set the composite format and convert it to a PdfGraphicsWidget type. Use PdfGraphicsWidget.Draw() method to draw the page number field content.
Part 2: Create PDF document objects and call the custom method above to add the footer
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Set page size using PdfDocoment.PageSettings.Size. Reset the top, bottom, left, and right margins to 0 by PageSettings.Margins.
- Create a new PdfMargins object to set the sizes of the header, footer, and left and right templates.
- Call the custom method CreateFooterTemplate() to add a Footer.
- Add pages using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Define PdfTrueTypeFont and PdfBrushes to set font and brushes for drawing the main content.
- Draw content in the specified area on the newly created page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Save the resulting file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Define CreateFooterTemplate()
def CreateFooterTemplate(doc, pageSize, margins):
# Create a footer template with specified sizes
footerSpace = PdfPageTemplateElement(pageSize.Width, margins.Bottom)
footerSpace.Foreground = True
doc.Template.Bottom = footerSpace
# Initialize the x and y coordinate points
x = margins.Left
y = 0.0
# Set font, brush, pen, and ext alignment format
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 12.0, PdfFontStyle.Italic, True)
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Gray()
pen = PdfPen(PdfBrushes.get_Gray(), 1.0)
leftAlign = PdfTextAlignment.Left
# Draw footer lines at the specified place
footerSpace.Graphics.DrawLine(pen, x, y, pageSize.Width - x, y)
# Draw footer text at the specified position
footerSpace.Graphics.DrawString("email: sales @e-iceblue.com\ntel:028-81705109 ", font, brush, x, y, PdfStringFormat(leftAlign))
# Create fields for page number and total page count
number = PdfPageNumberField()
count = PdfPageCountField()
listAutomaticField = [number, count]
# Create a composite field and set string formatting for drawing
compositeField = PdfCompositeField(font, PdfBrushes.get_Gray(), "Page {0} of {1}", listAutomaticField)
compositeField.StringFormat = PdfStringFormat(PdfTextAlignment.Right, PdfVerticalAlignment.Top)
size = font.MeasureString(compositeField.Text)
compositeField.Bounds = RectangleF(pageSize.Width -x-size.Width, y, size.Width, size.Height)
newTemplate = compositeField
templateGraphicsWidget = PdfGraphicsWidget(newTemplate.Ptr)
templateGraphicsWidget.Draw(footerSpace.Graphics)
# Create a PdfDocument object
doc = PdfDocument()
# Set page sizes and the margin
pageSize =PdfPageSize.A4()
doc.PageSettings.Size = pageSize
doc.PageSettings.Margins = PdfMargins(0.0)
# Create a new PdfMargins object for setting sizes of the header, footer, and left and right templates
margins = PdfMargins(50.0, 50.0, 50.0, 50.0)
doc.Template.Left = PdfPageTemplateElement(margins.Left, pageSize.Height-margins.Top-margins.Bottom)
doc.Template.Right = PdfPageTemplateElement(margins.Right, pageSize.Height-margins.Top-margins.Bottom)
doc.Template.Top = PdfPageTemplateElement(pageSize.Width, margins.Top)
# Call CreateFooterTemplate() to add a footer
CreateFooterTemplate(doc, pageSize, margins)
# Add pages according to the settings above
page = doc.Pages.Add()
# Create font and brush for page content
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 14.0, PdfFontStyle.Regular, True)
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Blue()
# Draw text on the page
text = "Adding a footer using Spire.PDF for Python"
page.Canvas.DrawString(text, font, brush, 0.0, pageSize.Height-margins.Bottom-margins.Top-font.Height-20)
# Save the document as PDF
doc.SaveToFile("output/result.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
# Dispose document object
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Merge tables in Word can be useful when you want to combine data from multiple tables into a single, larger table to create a more comprehensive view of the information. On the contrary, split tables can help you divide a large table into smaller, more manageable sections so you can focus on specific data sets. This article will demonstrate how to merge or split tables in Word in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Merge Tables in Word in Python
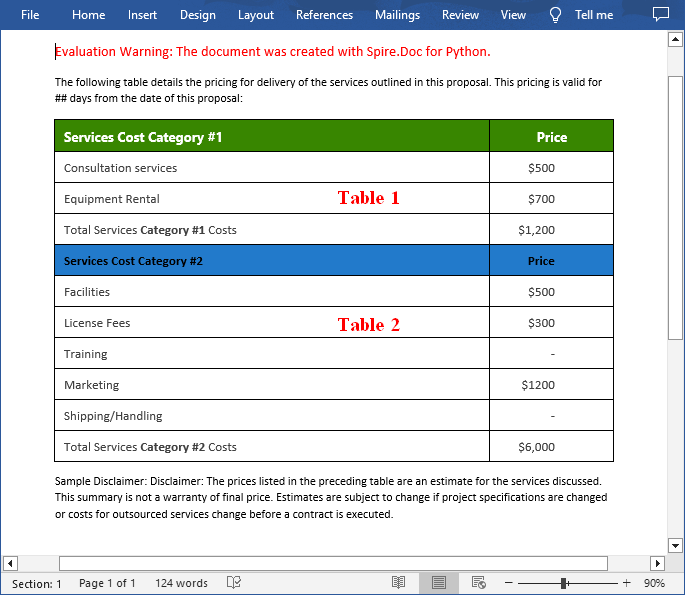
With Spire.Doc for Python, you can combine two or more tables into one by copying all rows from other tables to the target table and then deleting the other tables. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section using Document.Sections[] property.
- Get two tables in the section using Section.Tables[] property.
- Iterate through all rows in the second table and copy them using Table.Rows[].Clone() method.
- Add the rows of the second table to the first table using Table.Rows.Add() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
inputFile = "Cost.docx"
outputFile = "CombineTables.docx"
# Create a Document instance
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get the first section
section = doc.Sections[0]
# Get the first and second table in the section
table1 = section.Tables[0] if isinstance(section.Tables[0], Table) else None
table2 = section.Tables[1] if isinstance(section.Tables[1], Table) else None
# Add rows of the second table to the first table
for i in range(table2.Rows.Count):
table1.Rows.Add(table2.Rows[i].Clone())
# Remove the second table
section.Tables.Remove(table2)
# Save the result document
section.Document.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx2013)
doc.Close()
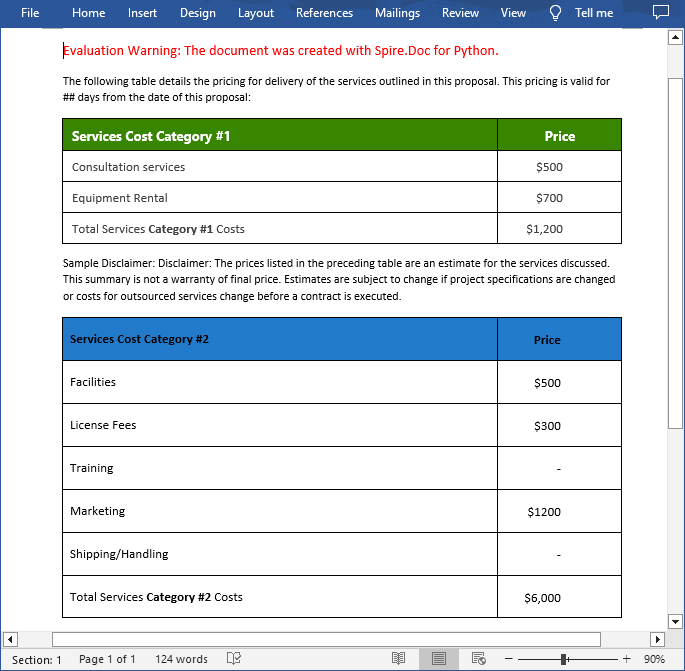
Spilt a Table in Word in Python
To split a table into two or more tables, you need to create a new table, then copy the specified rows from the original table to the new table, and then delete those rows from the original table. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section using Document.Sections[] property.
- Get a specified table in the section using Section.Tables[] property.
- Specify the row index where the table will be split.
- Create a new instance of the Table class.
- Iterate through the specified rows in the original table and copy them using Table.Rows[].Clone() method.
- Add the specified rows to the new table using Table.Rows.Add() method.
- Iterate through the copied rows and remove each row from the original table using Table.Rows.RemoveAt() method.
- Add the new table to the section using Section.Tables.Add() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
inputFile = "CombineTables.docx"
outputFile = "SplitTable.docx"
# Create a Document instance
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get the first section
section = doc.Sections[0]
# Get the first table in the section
table = section.Tables[0] if isinstance(section.Tables[0], Table) else None
# Specify to split the table from the fifth row
splitIndex = 4
# Create a new table
newTable = Table(section.Document, True)
# Adds rows (from the 5th to the last row) to the new table
for i in range(splitIndex, table.Rows.Count):
newTable.Rows.Add(table.Rows[i].Clone())
# Delete rows from the original table
for i in range(table.Rows.Count - 1, splitIndex - 1, -1):
table.Rows.RemoveAt(i)
# Add the new table to the section
section.Tables.Add(newTable)
# Save the result document
section.Document.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx2013)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
The inclusion of line numbers in Word documents serves as a critical tool for enhancing readability, facilitating reference, and streamlining collaborative editing processes. Whether you're a lawyer marking up contracts, a researcher annotating scientific papers, or a student revising a thesis, line numbers provide a precise way to cite specific lines, making discussions and revisions more efficient.
The powerful Python programming language enables users to batch add or remove line numbers in Word documents, providing a robust means to automate document preparation workflows. This article will demonstrate how to utilize Spire.Doc for Python to add or remove line numbers in Word documents with Python code.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Add Line Numbers to Word Documents with Python
Spire.Doc for Python provides properties under PageSetup class for line number formatting. The properties and their functions are as follows:
- LineNumberingStep: Used to set the interval of the line number display.
- LineNumberingStartValue: Used to set the start number of the line number.
- LineNumberingDistanceFromText: Used to set the distance between the line number and the text.
- LineNumberingRestartMode: Used to set when the line number restarts, like every page, every section, or continuously without restarting.
It is important to note that line numbers will only be displayed when the PageSetup.LineNumberingStep property is set to a value greater than 0.
The detailed steps for adding line numbers to Word documents are as follows:
- Create an instance of Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through the sections in the document:
- Get the current section using Document.Sections.get_Item() method.
- Get the page setup of the section through Section.PageSetup property.
- Set the display interval of the line numbers through PageSetup.LineNumberingStep property.
- Set the start number of the line numbers through PageSetup.LineNumberingStartValue property.
- Set the distance between line numbers and text through PageSetup.LineNumberingDistanceFromText property.
- Set the restarting mode of the line numbers through PageSetup.LineNumberingRestartMode property.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an instance of Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Iterate through the sections
for i in range(0, doc.Sections.Count):
# Get the current section
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(i)
# Get the page setup of the section
pageSetup = section.PageSetup
# Set the interval of the line numbering
pageSetup.LineNumberingStep = 2
# Set the start number of the line numbering
pageSetup.LineNumberingStartValue = 1
# Set the distance between the line number and text
pageSetup.LineNumberingDistanceFromText = 20
# Set the restarting mode of the line number
pageSetup.LineNumberingRestartMode = LineNumberingRestartMode.Continuous
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/AddLineNumberWord.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()

Remove Line Numbers from Word Documents with Python
Since the value of the PageSetup.LineNumberingStep property directly determines the display of line numbers, developers can simply set the value to 0 to remove the line numbers from Word documents.
The detailed steps for removing line numbers from a Word document are as follows:
- Create an instance of Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through the sections in the document:
- Get the current section using Document.Sections.get_Item() method.
- Set the display interval of the line numbers to 0 through Section.PageSetup.LineNumberingStep property to remove the line numbers.
- Save the document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an instance of Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("output/AddLineNumberWord.docx")
# Iterate through the sections
for i in range(0, doc.Sections.Count):
# Get the current section
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(i)
# Set the interval of the line numbering to 0 to remove the line numbering
section.PageSetup.LineNumberingStep = 0
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/RemoveLineNumberWord.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
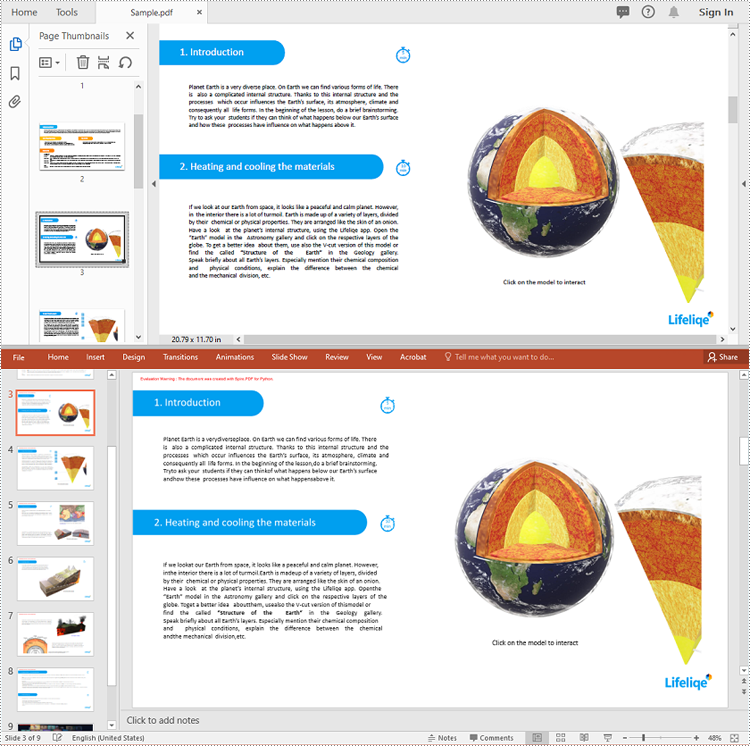
PDF (Portable Document Format) files are widely used for sharing and distributing documents due to their consistent formatting and broad compatibility. However, when it comes to presentations, PowerPoint remains the preferred format for many users. PowerPoint offers a wide range of features and tools that enable the creation of dynamic, interactive, and visually appealing slideshows. Unlike static PDF documents, PowerPoint presentations allow for the incorporation of animations, transitions, multimedia elements, and other interactive components, making them more engaging and effective for delivering information to the audience.
By converting PDF to PowerPoint, you can transform a static document into a captivating and impactful presentation that resonates with your audience and helps to achieve your communication goals. In this article, we will explain how to convert PDF files to PowerPoint format in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Convert PDF to PowerPoint in Python
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfDocument.SaveToFile(filename:str, FileFormat.PPTX) method to convert a PDF document into a PowerPoint presentation. With this method, each page of the original PDF document will be converted into a single slide in the output PPTX presentation.
The detailed steps to convert a PDF document to PowerPoint format are as follows:
- Create an object of the PdfDocument class.
- Load a sample PDF document using the PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Save the PDF document as a PowerPoint PPTX file using the PdfDocument.SaveToFile(filename:str, FileFormat.PPTX) method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create an object of the PdfDocument class
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a sample PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Save the PDF document as a PowerPoint PPTX file
pdf.SaveToFile("PdfToPowerPoint.pptx", FileFormat.PPTX)
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Tables in Word documents can sometimes disrupt the flow of text or the visual balance of a page. Removing these tables can help in creating a more aesthetically pleasing document, which is crucial for reports, presentations, or publications where appearance is important. In this article, you will learn how to remove tables from a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Remove a Specified Table in Word in Python
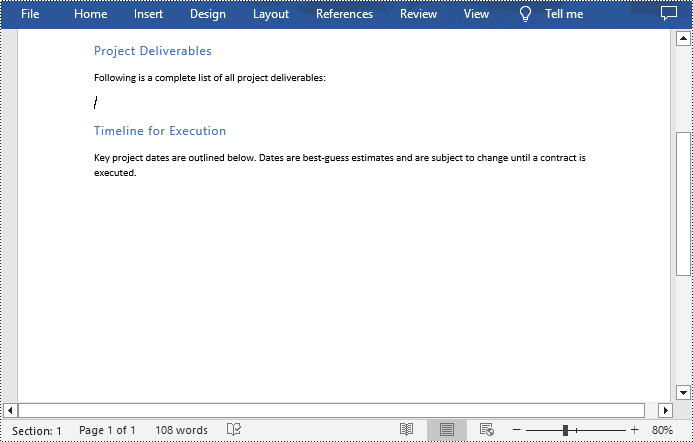
Spire.Doc for Python provides the Section.Tables.RemoveAt(int index) method to delete a specified table in a Word document by index. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section using Document.Sections[] property.
- Delete a specified table by index using Section.Tables.RemoveAt() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import * from spire.doc.common import * inputFile = "Tables.docx" outputFile = "RemoveTable.docx" # Create a Document instance doc = Document() # Load a Word document doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get the first section in the document sec = doc.Sections[0] # Remove the first table in the section sec.Tables.RemoveAt(0) # Save the result document doc.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx) doc.Close()
Remove All Tables in Word in Python
To delete all tables from a Word document, you need to iterate through all sections in the document, then iterate through all tables in each section and remove them through the Section.Tables.Remove() method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through all sections in the document.
- Iterate through all tables in each section.
- Delete the tables using Section.Tables.Remove() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
inputFile = "Tables.docx"
outputFile = "RemoveAllTables.docx"
# Create a Document instance
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Iterate through all sections in the document
for i in range(doc.Sections.Count):
sec = doc.Sections.get_Item(i)
# Iterate through all tables in each section
for j in range(sec.Tables.Count):
table = sec.Tables.get_Item(j)
# Remove the table
sec.Tables.Remove(table)
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
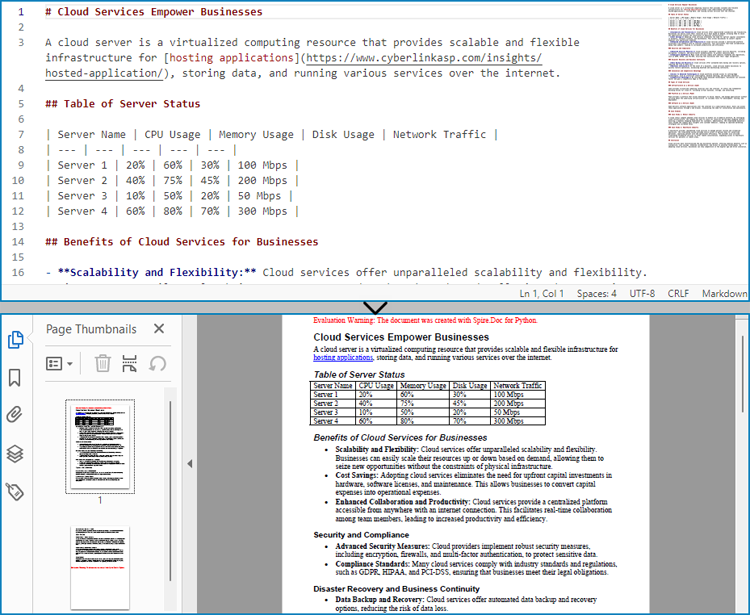
Markdown has become a popular choice for writing structured text due to its simplicity and readability, making it widely used for documentation, README files, and note-taking. However, sometimes there arises a need to present this content in a more universal and polished format, such as PDF, which is compatible across various devices and platforms without formatting inconsistencies. Converting Markdown files to PDF documents not only enhances portability but also adds a professional touch, enabling easier distribution for reports, manuals, or sharing content with non-technical audiences who may not be familiar with Markdown syntax.
This article will demonstrate how to convert Markdown files to PDF documents using Spire.Doc for Python to automate the conversion process.
- Convert Markdown Files to PDF Documents with Python
- Convert Markdown to PDF and Customize Page Settings
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Convert Markdown Files to PDF Documents with Python
With Spire.Doc for Python, developers can load Markdown files using Document.LoadFromFile(string: fileName, FileFormat.Markdown) method, and then save the files to PDF documents using Document.SaveToFile(string: fileName, FileFormat.PDF) method. Besides, developers can also convert Markdown files to HTML, XPS, and SVG formats by specifying enumeration items of the FileFormat enumeration class.
The detailed steps for converting a Markdown file to a PDF document are as follows:
- Create an instance of Document class.
- Load a Markdown file using Document.LoadFromFile(string: fileName, FileFormat.Markdown) method.
- Convert the Markdown file to a PDF document and save it using Document.SaveToFile(string: fileName, FileFormat.PDF) method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Markdown file
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.md", FileFormat.Markdown)
# Save the file to a PDF document
doc.SaveToFile("output/MarkdownToPDF.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Dispose()
Convert Markdown to PDF and Customize Page Settings
Spire.Doc for Python supports performing basic page setup before converting Markdown files to formats like PDF, allowing for control over the appearance of the converted document.
The detailed steps to convert a Markdown file to a PDF document and customize the page settings are as follows:
- Create an instance of Document class.
- Load a Markdown file using Document.LoadFromFile(string: fileName, FileFormat.Markdown) method.
- Get the default section using Document.Sections.get_Item() method.
- Get the page settings through Section.PageSetup property and set the page size, orientation, and margins through properties under PageSetup class.
- Convert the Markdown file to a PDF document and save it using Document.SaveToFile(string: fileName, FileFormat.PDF) method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an instance of Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.md", FileFormat.Markdown)
# Get the default section
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get the page settings
pageSetup = section.PageSetup
# Customize the page settings
pageSetup.PageSize = PageSize.A4()
pageSetup.Orientation = PageOrientation.Landscape
pageSetup.Margins.All = 50
# Save the Markdown document to a PDF file
doc.SaveToFile("output/MarkdownToPDFPageSetup.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Dispose()
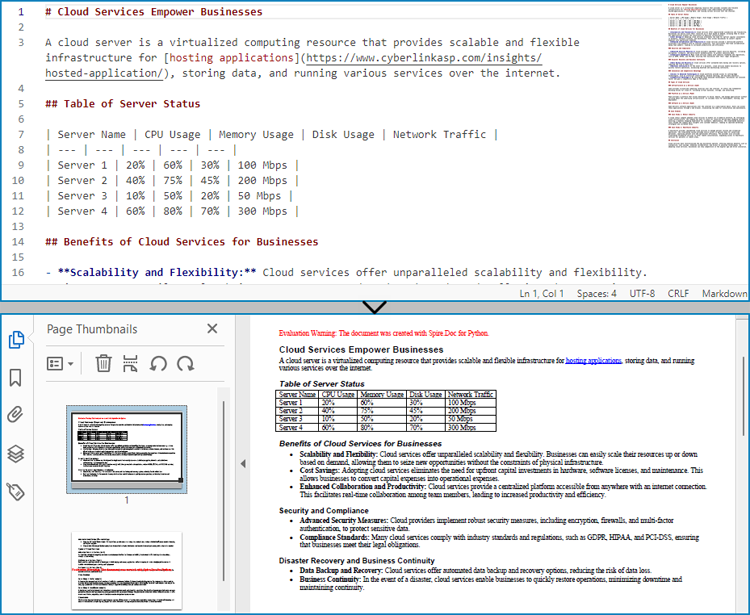
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Markdown is a lightweight markup language that is becoming increasingly popular for writing content on the web. It offers a simple and human-readable syntax for formatting text, adding links, images, lists, and more. Many websites and content management systems support Markdown, as it can be easily converted to HTML. On the other hand, Microsoft Word is a widely used word-processing software that utilizes its own proprietary file format. While Word offers robust formatting options, its files are not always compatible with other platforms or content management systems.
In certain scenarios, it is useful to convert between Word and Markdown file formats. It allows you to take advantage of Word's advanced editing tools while also being able to publish your content in a web-friendly Markdown format. In this article, we will demonstrate how to convert Markdown to Word DOC or DOCX and convert Word DOC or DOCX to Markdown in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Convert Markdown to Word in Python
You can load a Markdown file using the Document.LoadFromFile(fileName, FileFormat.Markdown) method and then convert it to Word DOC or DOCX format using the Document.SaveToFile(fileName, FileFormat.Doc) or Document.SaveToFile(fileName, FileFormat.Docx) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Markdown file using the Document.LoadFromFile(fileName, FileFormat.Markdown) method.
- Save the Markdown file to a Word DOC or DOCX file using Document.SaveToFile(fileName, FileFormat.Doc) or Document.SaveToFile(fileName, FileFormat.Docx) method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of the Document class
document = Document()
# Load a Markdown file
document.LoadFromFile("input.md")
# Save the Markdown file to a Word DOCX file
document.SaveToFile("MdToDocx.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
# Save the Markdown file to a Word DOC file
document.SaveToFile("MdToDoc.doc", FileFormat.Doc)
document.Close()

Convert Word to Markdown in Python
You are also able to convert a Word DOC or DOCX file to Markdown format using the Document.SaveToFile(fileName, FileFormat.Markdown) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word DOC or DOCX file using the Document.LoadFromFile(fileName) method.
- Save the Word DOC or DOCX file to a Markdown file using Document.SaveToFile(fileName, FileFormat.Markdown) method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of the Document class
document = Document()
# Load a Word DOCX file
document.LoadFromFile("input.docx")
# Or load a Word DOC file
#document.LoadFromFile("input.doc")
# Save the Word file to a Markdown file
document.SaveToFile("WordToMarkdown.md", FileFormat.Markdown)
document.Close()
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Converting a document from Word to TIFF can be useful when you need to share the content as an image file, such as for electronic forms, presentations, or publishing. The TIFF format preserves the visual layout and appearance of the document. Conversely, converting a TIFF image to a Word document can be helpful when you want to present information in the Word format.
This article demonstrates how to convert Word to TIFF and TIFF to Word (non-editable) using Python and the Spire.Doc for Python library.
Install the Required Libraries
This situation relies on the combination of Spire.Doc for Python and Pillow (PIL). Spire.Doc is used to read, create and convert Word documents, while the PIL library is used for handling TIFF files and accessing their frames.
The libraries can be easily installed on your device through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc pip install pillow
Convert Word to TIFF in Python
To convert a Word document into a TIFF image, the initial step is to use the Spire.Doc library to load the Word document and transform the individual pages into image data streams. Then, you can leverage the functionality provided by the PIL to merge these separate image streams into a unified TIFF image.
The following are the steps to convert Word to TIFF using Python.
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document from a specified file path.
- Iterate through the pages in the document.
- Convert each page into an image stream using Document.SaveImageToSteams() method.
- Convert the image stream into a PIL image.
- Combine these PIL images into a single TIFF image.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
from PIL import Image
from io import BytesIO
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.docx")
# Create an empty list to store PIL Images
images = []
# Iterate through pages in the document
for i in range(doc.GetPageCount()):
# Convert a specific page to image stream
with doc.SaveImageToStreams(i, ImageType.Bitmap) as imageData:
# Open a specific image stream as a PIL image
img = Image.open(BytesIO(imageData.ToArray()))
# Append the PIL image to list
images.append(img)
# Save the PIL Images as a multi-page TIFF file
images[0].save("Output/ToTIFF.tiff", save_all=True, append_images=images[1:])
# Dispose resources
doc.Dispose()

Convert TIFF to Word in Python
By utilizing PIL library, you can load a TIFF file and break it down into separate PNG images for each frame. You can then utilize the Spire.Doc library to incorporate these separate PNG files as distinct pages within a Microsoft Word document.
To convert a TIFF image to a Word document using Python, follow these steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section to it and set the page margins to zero.
- Load a TIFF image.
- Iterate though the frames in the TIFF image.
- Get a specific frame, and save it as a PNG file.
- Add a paragraph to the section.
- Append the image file to the paragraph.
- Set the page size to be the same as the image size.
- Save the document to a Word file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
from PIL import Image
import io
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Add a section
section = doc.AddSection()
# Set margins to 0
section.PageSetup.Margins.All = 0.0
# Load a TIFF image
tiff_image = Image.open("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\TIFF.tiff")
# Iterate through the frames in it
for i in range(tiff_image.n_frames):
# Go to the current frame
tiff_image.seek(i)
# Extract the image of the current frame
frame_image = tiff_image.copy()
# Save the image to a PNG file
frame_image.save(f"temp/output_frame_{i}.png")
# Add a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
# Append image to the paragraph
image = paragraph.AppendPicture(f"temp/output_frame_{i}.png")
# Get image width and height
width = image.Width
height = image.Height
# Set the page size to be the same as the image size
section.PageSetup.PageSize = SizeF(width, height)
# Save the document to a Word file
doc.SaveToFile("Output/ToWord.docx",FileFormat.Docx2019)
# Dispose resources
doc.Dispose()

Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
