
Python (355)
Modern workflows often span multiple platforms-while analysts work with data in Excel, polished reports are created in Word. Manually copying data between these documents can lead to errors, version conflicts, and inconsistent formatting. Python-driven automation provides an efficient solution by seamlessly integrating Excel's data capabilities with Word's formatting strengths. This integration ensures data integrity, reduces repetitive formatting, and accelerates report creation for financial, academic, and compliance-related tasks.
This article explores how to use Spire.Office for Python to insert Excel tables into Word documents using Python code.
- Read Excel Data and Insert It into Word Documents
- Copy Data and Formatting from Excel to Word
- Integrate Excel Worksheets as OLE into Word Documents
Install Spire.Office for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Office for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Office
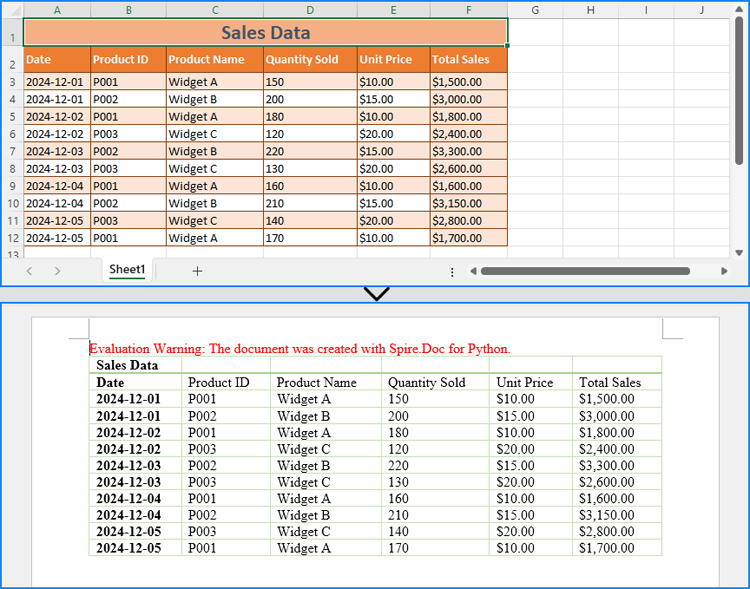
Read Excel Data and Insert It into Word Documents
With Spire.XLS for Python, developers can extract data from Excel worksheets while preserving number formatting using the CellRange.NumberText property. The extracted data can then be inserted into a Word table created using Spire.Doc for Python. This method is ideal for simple Excel worksheets and cases requiring table reformatting.
Steps to Read Excel Data and Insert It into Word:
- Create an instance of the Workbook class and load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Retrieve the worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method and obtain the used cell range with the Worksheet.AllocatedRange property.
- Initialize a Document instance to create a Word document.
- Add a section using the Document.AddSection() method and insert a table using the Section.AddTable() method.
- Define the number of rows and columns based on the used cell range with the Table.ResetCells() method.
- Iterate through the rows and columns of the used cell range.
- Retrieve the corresponding table cell using the Table.Rows.get_Item().Cells.get_Item() method and add a paragraph using the TableCell.AddParagraph() method.
- Extract the cell value using the CellRange.get_Item().NumberText property and append it to the paragraph using the Paragraph.AppendText() method.
- Apply the required formatting to the Word table.
- Save the Word document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import Document, AutoFitBehaviorType, FileFormat, DefaultTableStyle
from spire.xls import Workbook
# Specify the file names
excel_file = "Sample.xlsx"
word_file = "output/ExcelDataToWord.docx"
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile(excel_file)
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Get the used cell range in the first worksheet
allocatedRange = sheet.AllocatedRange
# Create a Document instance
doc = Document()
# Add a section to the document and add a table to the section
section = doc.AddSection()
table = section.AddTable()
# Reset the number of rows and columns in the Word table to match the number of rows and columns in the Excel worksheet
table.ResetCells(allocatedRange.RowCount, allocatedRange.ColumnCount)
# Loop through each row and column in the used cell range
for rowIndex in range(allocatedRange.RowCount):
# Loop through each column in the row
for colIndex in range(allocatedRange.ColumnCount):
# Add a cell to the Word table and add a paragraph to the cell
cell = table.Rows.get_Item(rowIndex).Cells.get_Item(colIndex)
paragraph = cell.AddParagraph()
# Append the cell value to the Word table
paragraph.AppendText(allocatedRange.get_Item(rowIndex + 1, colIndex + 1).NumberText)
# Auto-fit the table to the window and apply a table style
table.AutoFit(AutoFitBehaviorType.AutoFitToWindow)
table.ApplyStyle(DefaultTableStyle.GridTable1LightAccent6)
# Save the Word document
doc.SaveToFile(word_file, FileFormat.Docx2019)
# Dispose resources
doc.Dispose()
workbook.Dispose()
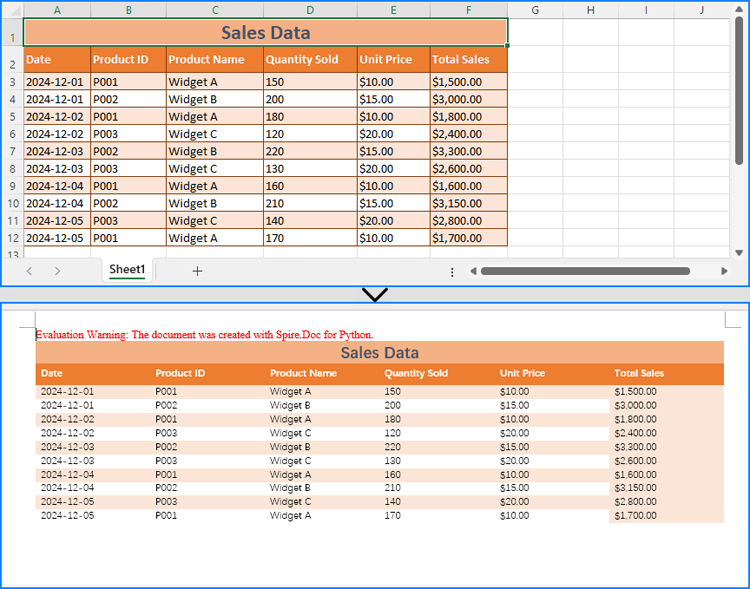
Copy Data and Formatting from Excel to Word
Spire.XLS for Python and Spire.Doc for Python can also be used together to copy both data and formatting from Excel to Word, preserving the table's original structure and appearance.
To handle format preservation, two helper methods are needed:
- MergeCells: Merges table cells in Word according to the merged cells in the Excel worksheet.
- CopyFormatting: Copies Excel cell formatting (font style, background color, horizontal and vertical alignment) to the Word table.
Steps to Copy Data and Formatting:
- Create a Workbook instance and load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Retrieve a worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Initialize a Document instance and add a section with the Document.AddSection() method.
- Insert a table using the Section.AddTable() method.
- Adjust the table’s structure based on the worksheet using the Table.ResetCells() method.
- Apply cell merging using the MergeCells() method.
- Iterate through each worksheet row and set row heights using the Table.Rows.get_Item().Height property.
- For each column in a row:
- Retrieve worksheet cells using the Worksheet.Range.get_Item() method and table cells using the TableRow.Cells.get_Item() method.
- Extract cell data using the CellRange.NumberText property and append it to the table cell using the TableCell.AddParagraph().AppendText() method.
- Apply formatting using the CopyFormatting() method.
- Save the Word document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import Workbook, HorizontalAlignType, ExcelPatternType, VerticalAlignType
from spire.doc import Document, Color, HorizontalAlignment, VerticalAlignment, PageOrientation, FileFormat
def MergeCells(worksheet, wordTable):
# Check if there are merged cells
if not worksheet.HasMergedCells:
return
for cell_range in worksheet.MergedCells:
start_row, start_col = cell_range.Row, cell_range.Column
row_count, col_count = cell_range.RowCount, cell_range.ColumnCount
# Process horizontal merging
if col_count > 1:
for row in range(start_row, start_row + row_count):
wordTable.ApplyHorizontalMerge(row - 1, start_col - 1, start_col - 1 + col_count - 1)
# Process vertical merging
if row_count > 1:
wordTable.ApplyVerticalMerge(start_col - 1, start_row - 1, start_row - 1 + row_count - 1)
def CopyFormatting(tableTextRange, excelCell, wordCell):
# Copy font styles
font = excelCell.Style.Font
tableTextRange.CharacterFormat.TextColor = Color.FromRgb(font.Color.R, font.Color.G, font.Color.B)
tableTextRange.CharacterFormat.FontSize = float(font.Size)
tableTextRange.CharacterFormat.FontName = font.FontName
tableTextRange.CharacterFormat.Bold = font.IsBold
tableTextRange.CharacterFormat.Italic = font.IsItalic
# Copy background colors
if excelCell.Style.FillPattern != ExcelPatternType.none:
wordCell.CellFormat.BackColor = Color.FromRgb(excelCell.Style.Color.R, excelCell.Style.Color.G,
excelCell.Style.Color.B)
# Copy the horizontal alignment
hAlignMap = {
HorizontalAlignType.Left: HorizontalAlignment.Left,
HorizontalAlignType.Center: HorizontalAlignment.Center,
HorizontalAlignType.Right: HorizontalAlignment.Right
}
if excelCell.HorizontalAlignment in hAlignMap:
tableTextRange.OwnerParagraph.Format.HorizontalAlignment = hAlignMap[excelCell.HorizontalAlignment]
# Copy the vertical alignment
vAlignMap = {
VerticalAlignType.Top: VerticalAlignment.Top,
VerticalAlignType.Center: VerticalAlignment.Middle,
VerticalAlignType.Bottom: VerticalAlignment.Bottom
}
if excelCell.VerticalAlignment in vAlignMap:
wordCell.CellFormat.VerticalAlignment = vAlignMap[excelCell.VerticalAlignment]
# Specify the file names
excelFileName = "Sample.xlsx"
wordFileName = "output/ExcelDataFormatToWord.docx"
# Create a Workbook instance and load the Excel file
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile(excelFileName)
# Get a worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Create a Document instance
doc = Document()
# Add a section to the document and set the page orientation
section = doc.AddSection()
section.PageSetup.Orientation = PageOrientation.Landscape
# Add a table to the section
table = section.AddTable()
# Set the number of rows and columns according to the number of rows and columns in the Excel worksheet
table.ResetCells(sheet.LastRow, sheet.LastColumn)
# Execute the MergeCells method to merge cells
MergeCells(sheet, table)
# Iterate through each row and column in the Excel worksheet
for r in range(1, sheet.LastRow + 1):
tableRow = table.Rows.get_Item(r - 1)
tableRow.Height = float(sheet.Rows.get_Item(r - 1).RowHeight)
for c in range(1, sheet.LastColumn + 1):
# Get the corresponding cell in the Excel worksheet and the cell in the Word table
eCell = sheet.Range.get_Item(r, c)
wCell = table.Rows.get_Item(r - 1).Cells.get_Item(c - 1)
# Append the cell value to the Word table
textRange = wCell.AddParagraph().AppendText(eCell.NumberText)
# Copy the cell formatting
CopyFormatting(textRange, eCell, wCell)
# Save the Word document
doc.SaveToFile(wordFileName, FileFormat.Docx2019)
doc.Dispose()
workbook.Dispose()
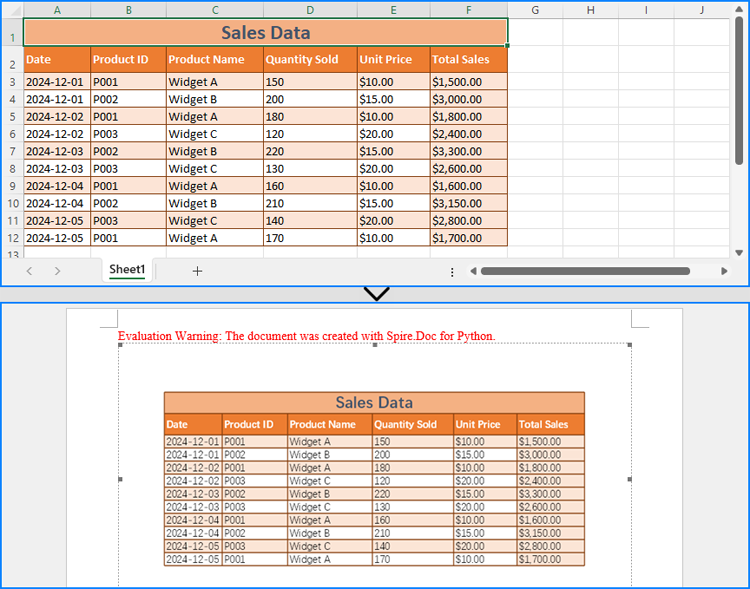
Integrate Excel Worksheets as OLE into Word Documents
Beyond copying data and formatting, Excel worksheets can be embedded as OLE objects in Word documents. This approach enables full worksheet visualization and allows users to edit Excel data directly from the Word document.
Using the Paragraph.AppendOleObject(str: filename, DocPicture, OleObjectType.ExcelWorksheet) method, developers can easily insert an Excel file as an OLE object.
Steps to Insert an Excel Worksheet as an OLE Object:
- Create a Workbook instance and load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Retrieve a worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method and save it as an image using the Worksheet.ToImage().Save() method.
- Initialize a Document instance to create a Word document.
- Add a section using the Document.AddSection() method and insert a paragraph using the Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Create a DocPicture instance and load the saved image using the DocPicture.LoadImage() method.
- Resize the image according to the page layout using the DocPicture.Width property.
- Insert the Excel file as an OLE object into the paragraph using the Paragraph.AppendOleObject() method.
- Set the DocOleObject.DisplayAsIcon property to False to ensure that the OLE object updates dynamically after worksheet edits.
- Save the Word document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import Document, DocPicture, FileFormat, OleObjectType from spire.xls import Workbook # Specify the file path and names excelFileName = "Sample.xlsx" wordFileName = "output/ExcelOleToWord.docx" tempImageName = "SheetImage.png" # Create a Workbook instance and load the Excel file workbook = Workbook() workbook.LoadFromFile(excelFileName) # Save the first worksheet as an image sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0) sheet.ToImage(1, 1, sheet.LastRow, sheet.LastColumn).Save(tempImageName) # Initialize a Document instance to create a Word document doc = Document() # Add a section to the document and add a paragraph to the section section = doc.AddSection() paragraph = section.AddParagraph() # Create a DocPicture instance and load the image pic = DocPicture(doc) pic.LoadImage(tempImageName) # Set the image width pic.Width = section.PageSetup.PageSize.Width - section.PageSetup.Margins.Left - section.PageSetup.Margins.Right # Insert the Excel file into the Word document as an OLE object and set the saved image as the display image ole = paragraph.AppendOleObject(excelFileName, pic, OleObjectType.ExcelWorksheet) # Set to not display the OLE object as an icon ole.DisplayAsIcon = False # Save the Word document doc.SaveToFile(wordFileName, FileFormat.Docx2019) workbook.Dispose() doc.Dispose()
Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Install Spire.Office for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Word documents often contain extensive text, and applying emphasis marks is an effective way to highlight key information. Whether you need to accentuate important terms or enhance text clarity with styled formatting, emphasis marks can make your content more readable and professional. Instead of manually adjusting formatting, this guide demonstrates how to use Spire.Doc for Python to efficiently apply emphasis to text in Word with Python, saving time while ensuring a polished document.
- Apply Emphasis Marks to First Matched Text
- Apply Emphasis Marks to All Matched Text
- Apply Emphasis Marks to Text with Regular Expression
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows.
Apply Emphasis Marks to First Matched Text in Word Documents
When crafting a Word document, highlighting keywords or phrases can improve readability and draw attention to important information. With Spire.Doc's CharacterFormat.EmphasisMark property, you can easily apply emphasis marks to any text, ensuring clarity and consistency.
Steps to apply emphasis marks to the first matched text in a Word document:
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a source Word document from files using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Find the text that you want to emphasize with Document.FindString() method.
- Apply emphasis marks to the text through CharacterFormat.EmphasisMark property.
- Save the updated Word document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
Below is the code example showing how to emphasize the first matching text of "AI-Generated Art" in a Word document:
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("/AI-Generated Art.docx")
# Customize the text that you want to apply an emphasis mark to
matchingtext = doc.FindString("AI-Generated Art", True, True)
# Apply the emphasis mark to the matched text
matchingtext.GetAsOneRange().CharacterFormat.EmphasisMark = Emphasis.CommaAbove
# Save the document as a new one
doc.SaveToFile("/ApplyEmphasisMark_FirstMatch.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
doc.Close()

Apply Emphasis Marks to All Matched Text in Word Files
In the previous section, we demonstrated how to add an emphasis mark to the first matched text. Now, let's take it a step further—how can we emphasize all occurrences of a specific text? The solution is simple: use the Document.FindAllString() method to locate all matches and then apply emphasis marks using the CharacterFormat.EmphasisMark property. Below, you'll find detailed steps and code examples to guide you through the process.
Steps to apply emphasis marks to all matched text:
- Create an instance of Document class.
- Read a Word file through Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Find all the matching text using Document.FindAllString() method.
- Loop through all occurrences and apply the emphasis effect to the text through CharacterFormat.EmphasisMark property.
- Save the modified Word document through Document.SaveToFile() method.
The following code demonstrates how to apply emphasis to all occurrences of "AI-Generated Art" while ignoring case sensitivity:
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("/AI-Generated Art.docx")
# Customize the text that you want to apply an emphasis mark to
textselections = doc.FindAllString("AI-Generated Art", False, True)
# Loop through the text selections and apply the emphasis mark to the text
for textselection in textselections:
textselection.GetAsOneRange().CharacterFormat.EmphasisMark = Emphasis.CircleAbove
# Save the document as a new one
doc.SaveToFile("/ApplyEmphasisMark_AllMatch.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
doc.Close()

Apply Emphasis Marks to Text in Word Documents with Regular Expression
Sometimes, the text you want to highlight may vary but follow a similar structure, such as email addresses, phone numbers, dates, or patterns like two to three words followed by special symbols (#, *, etc.). The best way to identify such text is by using regular expressions. Once located, you can apply emphasis marks using the same method. Let's go through the steps!
Steps to apply emphasis marks to text using regular expressions:
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document from the local storage using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Find text that you want to emphasize with Document.FindAllPattern() method.
- Iterate through all occurrences and apply the emphasis effect to the text through CharacterFormat.EmphasisMark property.
- Save the resulting Word file through Document.SaveToFile() method.
The code example below shows how to emphasize "AI" and the word after it in a Word document:
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("/AI-Generated Art.docx")
# Match "AI" and the next word using regular expression
pattern = Regex(r"AI\s+\w+")
# Find all matching text
textSelections = doc.FindAllPattern(pattern)
# Loop through all the matched text and apply an emphasis mark
for selection in textSelections:
selection.GetAsOneRange().CharacterFormat.EmphasisMark = Emphasis.DotBelow
# Save the document as a new one
doc.SaveToFile("/ApplyEmphasisMark_Regex.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
doc.Close()

Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Adding borders to specific text and paragraphs in Word documents is an effective way to highlight key information and improve the document's structure. Whether it's important terms or entire sections, borders help them stand out. In this guide, we'll show you how to use Spire.Doc for Python to add borders to text and paragraphs in Word with Python, boosting both the readability and professionalism of your document while saving you time from manual formatting.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows.
Add a Border to Text in Word Documents with Python
In Word documents, important information like technical terms, company names, or legal clauses can be highlighted with borders to draw readers' attention. Using Python, you can locate the required text with the Document.FindAllString() method and apply borders using the CharacterFormat.Border.BorderType property. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you do this efficiently.
Steps to add borders to all matched text in a Word document:
- Create an object of Document class.
- Read a source Word document from files using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Find all occurrences of the specified text through Document.FindAllString() method.
- Loop through all matched text and get the text as a text range.
- Add a border to the text with CharacterFormat.Border.BorderType property.
- Customize the color of the border through CharacterFormat.Border.Color property.
- Save the modified document with Document.SaveToFile() method.
The code example below shows how to add a border to all occurrences of "AI-Generated Art":
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("/AI-Generated Art.docx")
# Set the target text
target_text = "AI-Generated Art"
# Create a TextSelection object and find all matches
text_selections = doc.FindAllString(target_text, False, True)
# Loop through the text selections
for selection in text_selections:
text_range = selection.GetAsOneRange()
# Add a border to the text
text_range.CharacterFormat.Border.BorderType = BorderStyle.Single
# Set the border color
text_range.CharacterFormat.Border.Color = Color.get_Blue()
# Save the resulting document
doc.SaveToFile("/AddBorder_Text.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
doc.Close()

Add a Border to Paragraphs in Word Files Using Python
Important clauses or legal statements in contracts, summaries in reports, and quotations in papers often require adding borders to paragraphs for emphasis or distinction. Unlike text borders, adding a border to a paragraph involves finding the target paragraph by its index and then using the Format.Borders.BorderType property. Let's check out the detailed instructions.
Steps to add a border to paragraphs in Word documents:
- Create a Document instance.
- Read a Word document through Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the specified paragraph with Document.Sections[].Paragraphs[] property.
- Add a border to the paragraph using Format.Borders.BorderType property.
- Set the type and color of the border.
- Save the resulting Word file through Document.SaveToFile() method.
Here is an example showing how to add a border to the fourth paragraph in a Word document:
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("/AI-Generated Art.docx")
# Get the fourth paragraph
paragraph = doc.Sections[0].Paragraphs[3]
# Add a border to the paragraph
borders = paragraph.Format.Borders
borders.BorderType(BorderStyle.DotDotDash)
borders.Color(Color.get_Blue())
# Save the updated document
doc.SaveToFile("/AddBorder_Paragraph.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
doc.Close()

Get a Free License
To fully experience the capabilities of Spire.Doc for Python without any evaluation limitations, you can request a free 30-day trial license.
Applying styles is one of the simplest ways to enhance the professionalism and readability of Excel spreadsheets. Excel provides a wide range of built-in styles that allow users to quickly format cells, ranges, or worksheets. Additionally, users can create custom styles to specify fonts, colors, borders, number formats, and more, tailored to their individual preferences. Whether you're designing professional reports, sales presentations, or project management plans, knowing how to use styles effectively helps make data more visually appealing and easier to understand.
In this guide, you will learn how to apply styles to cells or worksheets in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Apply a Built-in Style to Cells in Excel in Python
- Apply a Custom Style to Cells in Excel in Python
- Apply a Custom Style to a Worksheet in Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Apply a Built-in Style to Cells in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python offers the CellRange.BuiltInStyle property, which enables developers to apply built-in styles, such as Title, Heading 1, and Heading 2 to individual cells or ranges in Excel. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get the desired cell or range of cells using the Worksheet.Range[] property.
- Apply a built-in style to the cell or range of cells using the CellRange.BuiltInStyle property.
- Save the resulting file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first sheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the desired cell range
range = sheet.Range["A1:H1"]
# Apply a built-in style to the cell range
range.BuiltInStyle = BuiltInStyles.Heading2
# Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile("ApplyBuiltinStyle.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply a Custom Style to Cells in Excel in Python
Developers can use the Workbook.Styles.Add() method to create a custom style, which can then be applied to individual cells or ranges using the CellRange.Style property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get the desired cell or range of cells using the Worksheet.Range[] property.
- Add a custom style to the workbook using the Workbook.Styles.Add() method.
- Define the formatting, such as the font size, font color, text alignment, cell borders and cell background color, using the properties of the CellStyle class.
- Apply the custom style to the cell or range of cells using the CellRange.Style property.
- Save the resulting file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first sheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the desired cell range
range = sheet.Range["A1:H1"]
# Add a custom style to the workbook
style = workbook.Styles.Add("CustomCellStyle")
# Set the font size
style.Font.Size = 13
# Set the font color
style.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
# Bold the text
style.Font.IsBold = True
# Set the vertical text alignment
style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Bottom
# Set the horizontal text alignment
style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Left
# Set the bottom border color
style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].Color = Color.get_GreenYellow()
# Set the bottom border type
style.Borders[BordersLineType.EdgeBottom].LineStyle = LineStyleType.Medium
# Set the background color
style.Color = Color.get_CornflowerBlue()
# Apply the custom style to the cell range
range.Style = style
# Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile("ApplyCustomStyle.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
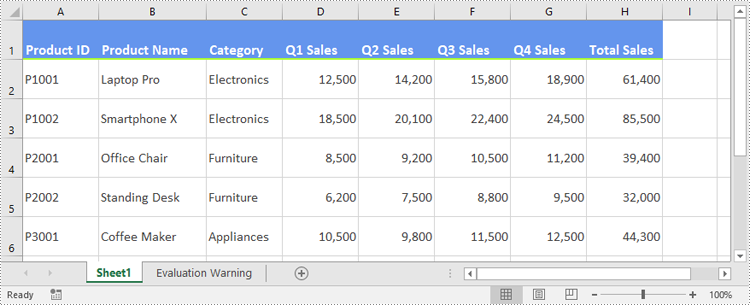
Apply a Custom Style to a Worksheet in Excel in Python
In certain cases, it may be necessary to apply a custom style to an entire worksheet rather than to specific cells or ranges. This can be accomplished using the Worksheet.ApplyStyle() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet by its index using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Add a custom style to the workbook using the Workbook.Styles.Add() method.
- Define the formatting, such as the font size, font color, and cell background color, using the properties of the CellStyle class.
- Apply the custom style to the worksheet using the Worksheet.ApplyStyle() method.
- Save the resulting file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first sheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Add a custom style to the workbook
style = workbook.Styles.Add("CustomSheetStyle")
# Set the font size
style.Font.Size = 12
# Set the font color
style.Font.Color = Color.FromRgb(91, 155, 213)
# Set the cell background color
style.Color = Color.FromRgb(242, 242, 242)
# Apply the custom style to the worksheet
sheet.ApplyStyle(style)
# Save the resulting file
workbook.SaveToFile("ApplyCustomStyleToSheet.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Check if a PDF is Password Protected and Determine the Correct Password
2025-03-19 01:06:07 Written by KoohjiWhen working with PDF files, you may encounter documents that are password protected. This means that you cannot view or edit the content without entering the correct password. Understanding how to check if a PDF is password protected and determining the correct password is essential for accessing important information. In this guide, we will introduce how to check if a PDF is password protected and determine the correct password using Python and the Spire.PDF for Python library.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Check if a PDF is Password Protected
Spire.PDF for Python offers the PdfDocument.IsPasswordProtected(fileName: str) method to check if a PDF file is password protected. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Specify the input and output file paths.
- Check if the PDF file is password protected or not using the PdfDocument.IsPasswordProtected() method.
- Save the result to a text file.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
# Specify the input and output file paths
inputFile = "Secured.pdf"
outputFile = "CheckPasswordProtection.txt"
# Check if the input PDF file is password protected
isProtected = PdfDocument.IsPasswordProtected(inputFile)
# Write the result into a text file
with open(outputFile, "w") as fp:
fp.write("The PDF is " + ("password protected!" if isProtected else "not password protected!"))
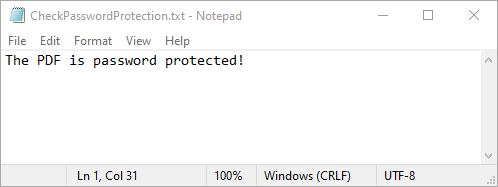
Determine the Correct Password for a PDF
While Spire.PDF for Python does not provide a direct method to check if a password is correct, you can achieve this by attempting to load the PDF with the password and catching exceptions. If the password is incorrect, an exception will be thrown. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Specify the input and output file paths.
- Create a list of potential passwords to test.
- Iterate through the list and load the PDF with each password using the PdfDocument.LoadFromFile(filename: str, password: str) method.
- If no exception is thrown, the password is correct. Otherwise, the password is incorrect.
- Save the results to a text file.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
# Specify the input and output file paths
inputFile = "Secured.pdf"
outputFile = "DetermineCorrectPassword.txt"
# Create a list of potential passwords to test
passwords = ["password1", "password2", "password3", "test", "sample"]
# Create a text file to store the results
with open(outputFile, "w") as fp:
for value in passwords:
try:
# Load the PDF with the current password
doc = PdfDocument()
doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile, value)
# If successful, write that the password is correct
fp.write(f'Password "{value}" is correct\n')
except SpireException:
# If an exception occurs, write that the password is not correct
fp.write(f'Password "{value}" is not correct\n')
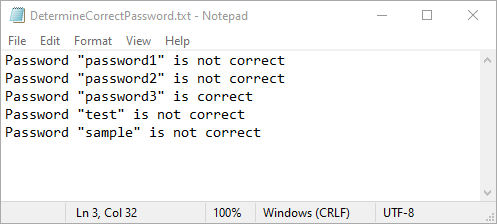
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Verifying digital signatures in a PDF is essential for ensuring the authenticity and integrity of electronically signed documents. It confirms that the signature is valid and that the document has not been altered since signing. Additionally, extracting signature images from a PDF allows you to retrieve and save the visual representation of a signature, making it easier to verify and archive for legal or record-keeping purposes. In this article, we will demonstrate how to verify and extract digital signatures in PDF in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
- Verify Digital Signatures in PDF in Python
- Detect Whether a Signed PDF Has Been Modified in Python
- Extract Signature Images from PDF in Python
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Verify Signatures in PDF in Python
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfDocument.VerifySignature(signName: str) method to check the validity of a digital signature in a PDF document. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the PdfDocument class.
- Load a PDF file using the PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the form of the PDF file using the PdfDocument.Form property.
- Iterate through all fields in the form and find the signature field.
- Get the name of the signature field using the PdfSignatureFieldWidget.FullName property.
- Verify the validity of the signature using the PdfSignature.VerifySignature(signName: str) method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Load a PDF document
doc = PdfDocument()
doc.LoadFromFile("Signature.pdf")
# Access the form in the document
pdfform = doc.Form
formWidget = PdfFormWidget(pdfform)
# Check if there are any fields in the form
if formWidget.FieldsWidget.Count > 0:
# Loop through all fields in the form
for i in range(formWidget.FieldsWidget.Count):
field = formWidget.FieldsWidget.get_Item(i)
# Check if the field is a PdfSignatureFieldWidget
if isinstance(field, PdfSignatureFieldWidget):
# Typecast the field to a PdfSignatureFieldWidget instance
signatureField = PdfSignatureFieldWidget(field)
# Get the name of the signature field
fullName = signatureField.FullName
# Verify the signature
valid = doc.VerifySignature(fullName)
# Determine the validation status text based on the verification result
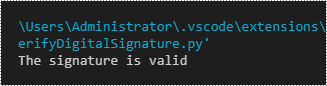
if valid:
print("The signature is valid")
else:
print("The signature is invalid")
doc.Close()
Detect Whether a Signed PDF Has Been Modified in Python
To determine whether a PDF document has been modified after signing, use the Security_PdfSignature.VerifyDocModified() method. This method returns a Boolean value: True indicates that the document has been altered and the signature is no longer valid, while False confirms that the document remains unchanged since it was signed. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the PdfDocument class.
- Load a PDF file using the PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the form of the PDF file using the PdfDocument.Form property.
- Iterate through all fields in the form and find the signature field.
- Get the signature using the PdfSignatureFieldWidget.Signature property.
- Verify if the document has been modified since it was signed using the Security_PdfSignature.VerifyDocModified() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Load a PDF document
doc = PdfDocument()
doc.LoadFromFile("Signature.pdf")
# Access the form in the document
pdfform = doc.Form
formWidget = PdfFormWidget(pdfform)
# Check if there are any fields in the form
if formWidget.FieldsWidget.Count > 0:
# Loop through all fields in the form
for i in range(formWidget.FieldsWidget.Count):
field = formWidget.FieldsWidget.get_Item(i)
# Check if the field is a PdfSignatureFieldWidget
if isinstance(field, PdfSignatureFieldWidget):
# Typecast the field to a PdfSignatureFieldWidget instance
signatureField = PdfSignatureFieldWidget(field)
# Get the signature
signature = signatureField.Signature
# Verify if the document has been modified since it was signed
modified = signature.VerifyDocModified()
# Determine the validation status text based on the verification result
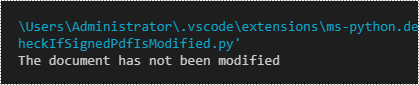
if modified:
print("The document has been modified")
else:
print("The document has not been modified")
doc.Close()
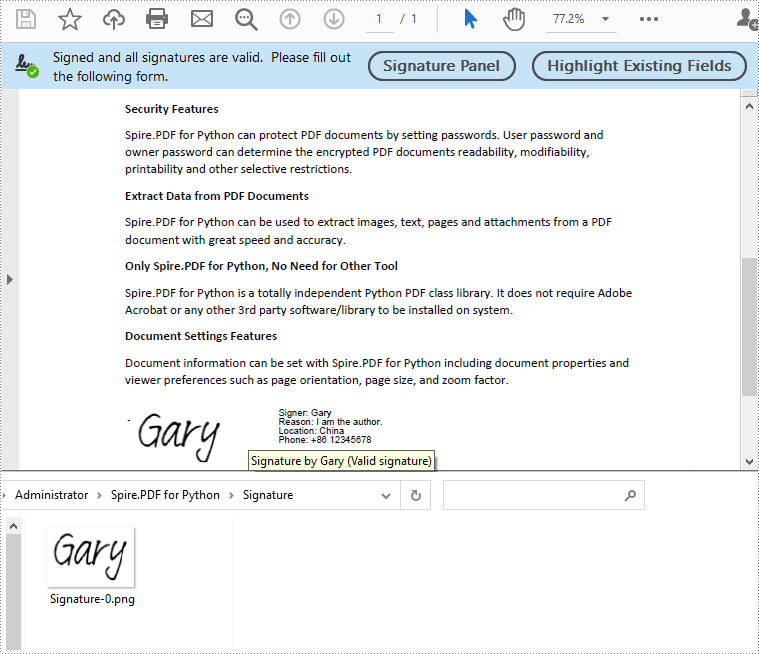
Extract Signature Images from PDF in Python
Spire.PDF for Python allows extracting all signature images from a PDF document using the PdfFormWidget.ExtractSignatureAsImages property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the PdfDocument class.
- Load a PDF file using the PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the form of the PDF file using the PdfDocument.Form property.
- Extract signature images from the form using the PdfFormWidget.ExtractSignatureAsImages property.
- Save the extracted images to image files.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Load a PDF document
doc = PdfDocument()
doc.LoadFromFile("Signature.pdf")
# Access the form in the document
pdfform = doc.Form
formWidget = PdfFormWidget(pdfform)
i = 0
# Extract signature images from the form and save them to files
for image in formWidget.ExtractSignatureAsImages:
filename = "Signature/" + f"Image-{i}.png"
# Save the image to a file
image.Save(filename)
i = i + 1
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
When working with Word documents, managing fonts can be a tedious task, especially when dealing with large files or multiple documents. Whether you're looking to standardize fonts across a document or fix inconsistencies, knowing how to retrieve and replace fonts efficiently is a valuable skill. In this guide, you will learn how to use Spire.Doc for Python to automate font retrieval and replacement processes.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Retrieve Fonts in a Word Document
To retrieve font information from a Word document, you will need to iterate through the document's sections, paragraphs, and their child objects. As you check each child object, look for instances of TextRange. If a TextRange is found, you can extract the font details such as the font name and size from its CharacterFormat properties.
The following are the steps to retrieve font information from a Word document using Python:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through each section and paragraph.
- For each child object, check if it’s an instance of TextRange.
- If it is, get the font name and size using the TextRange.CharacterFormat.FontName and TextRange.CharacterFormat.FontSize properties.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Function to write string to a txt file
def WriteAllText(fname:str,text:List[str]):
fp = open(fname,"w")
for s in text:
fp.write(s)
# Customize a FontInfo class
class FontInfo:
def __init__(self):
self._m_name = ''
self._m_size = None
def __eq__(self,other):
if isinstance(other,FontInfo):
return self._m_name == other.get_name() and self._m_size == other.get_size()
return False
def get_name(self):
return self._m_name
def set_name(self, value):
self._m_name = value
def get_size(self):
return self._m_size
def set_size(self, value):
self._m_size = value
# Declare variables
fontImformations = ""
font_infos = []
# Create a Document instance
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx")
# Iterate through the sections
for i in range(document.Sections.Count):
# Get a specific section
section = document.Sections.get_Item(i)
# Iterate through the paragraphs
for j in range(section.Body.Paragraphs.Count):
# Get a specific paragraph
paragraph = section.Body.Paragraphs.get_Item(j)
# Iterate through the child objects
for k in range(paragraph.ChildObjects.Count):
# Get a specific paragraph
obj = paragraph.ChildObjects.get_Item(k)
# Determine if a child object is a text range
if isinstance(obj, TextRange):
# Get a specific text range
txtRange = obj if isinstance(obj, TextRange) else None
# Get the font name and size
fontName = txtRange.CharacterFormat.FontName
fontSize = txtRange.CharacterFormat.FontSize
# Get text color
textColor = txtRange.CharacterFormat.TextColor.Name
# Store the font information in the fontInformations variable
fontInfo = FontInfo()
fontInfo.set_name(fontName)
fontInfo.set_size(fontSize)
if fontInfo not in font_infos:
font_infos.append(fontInfo)
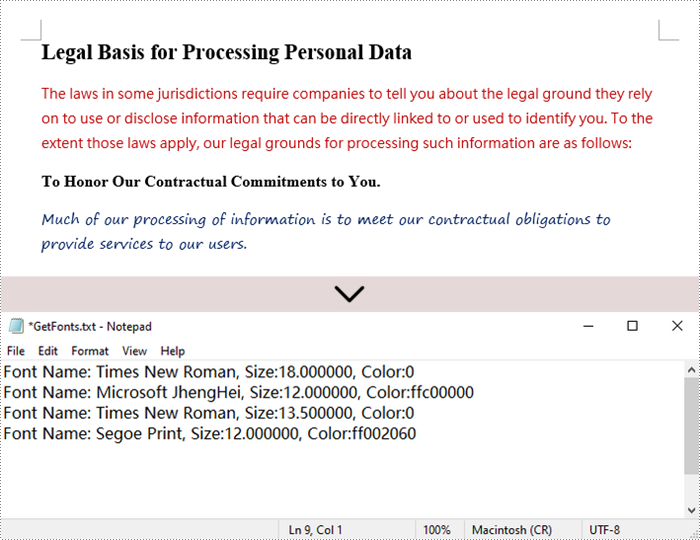
str = "Font Name: {0:s}, Size:{1:f}, Color:{2:s}".format(fontInfo.get_name(), fontInfo.get_size(), textColor)
fontInformations += str
fontInformations += '\r'
# Write font information to a txt file
WriteAllText("output/GetFonts.txt", fontInformations)
# Dispose resources
document.Dispose()
Replace Fonts in a Word Document
Once you retrieve the font name of a specific text range, you can easily replace it with a different font. To do this, utilize the TextRange.CharacterFormat.FontName property to assign a new font. Additionally, you can modify the font size and text color using the corresponding properties in the TextRange class.
The following are the steps to replace a specific font in a Word document using Python:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through each section and paragraph.
- For each child object, check if it’s an instance of TextRange.
- If it is, get the font name using the TextRange.CharacterFormat.FontName property.
- Check if the font name is the specified font.
- If it is, set a new font name for the text range using the TextRange.CharacterFormat.FontName property.
- Save the changes to a different Word file using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document instance
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx")
# Iterate through the sections
for i in range(document.Sections.Count):
# Get a specific section
section = document.Sections.get_Item(i)
# Iterate through the paragraphs
for j in range(section.Body.Paragraphs.Count):
# Get a specific paragraph
paragraph = section.Body.Paragraphs.get_Item(j)
# Iterate through the child objects
for k in range(paragraph.ChildObjects.Count):
# Get a specific paragraph
obj = paragraph.ChildObjects.get_Item(k)
# Determine if a child object is a text range
if isinstance(obj, TextRange):
# Get a specific text range
txtRange = obj if isinstance(obj, TextRange) else None
# Get the font name
fontName = txtRange.CharacterFormat.FontName
# Determine if the font name is Microsoft JhengHei
if (fontName == "Microsoft JhengHei"):
# Replace the font with another font
txtRange.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Segoe Print"
# Save the document to a different file
document.SaveToFile("output/ReplaceFonts.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
# Dispose resources
document.Dispose()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
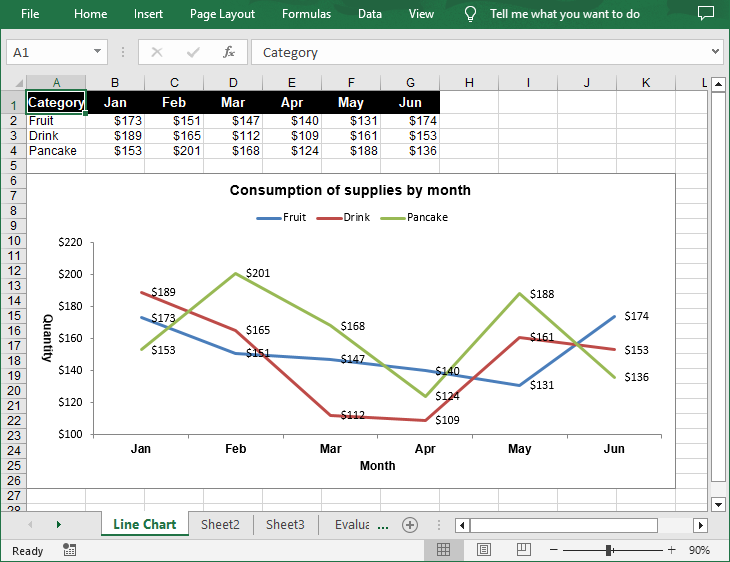
A line chart is a type of chart that displays information as a series of data points connected by straight line segments. It's particularly useful for showing changes over time. For example, if you're tracking monthly sales figures, a line chart can help you identify trends, peaks, and troughs. In this article, you will learn how to create a line chart in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Create a Simple Line Chart in Excel in Python
Spire.XLS for Python provides the Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Line) method to add a simple line chart to an Excel worksheet. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Add the chart data to specified cells and set the cell styles.
- Add a simple line chart to the worksheet using Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Line) method.
- Set data range for the chart using Chart.DataRange property.
- Set the position, title, axis and other attributes of the chart.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first sheet and set its name
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
sheet.Name = "Line Chart"
# Add chart data to specified cells
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Category"
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "Fruit"
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "Drink"
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "Pancake"
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Jan"
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 173
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 189
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 153
sheet.Range["C1"].Value = "Feb"
sheet.Range["C2"].NumberValue = 151
sheet.Range["C3"].NumberValue = 165
sheet.Range["C4"].NumberValue = 201
sheet.Range["D1"].Value = "Mar"
sheet.Range["D2"].NumberValue = 147
sheet.Range["D3"].NumberValue = 112
sheet.Range["D4"].NumberValue = 168
sheet.Range["E1"].Value = "Apr"
sheet.Range["E2"].NumberValue = 140
sheet.Range["E3"].NumberValue = 109
sheet.Range["E4"].NumberValue = 124
sheet.Range["F1"].Value = "May"
sheet.Range["F2"].NumberValue = 131
sheet.Range["F3"].NumberValue = 161
sheet.Range["F4"].NumberValue = 188
sheet.Range["G1"].Value = "Jun"
sheet.Range["G2"].NumberValue = 174
sheet.Range["G3"].NumberValue = 153
sheet.Range["G4"].NumberValue = 136
# Set cell styles
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].RowHeight = 20
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.Color = Color.get_Black()
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.Font.IsBold = True
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.Font.Size = 11
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["B2:G4"].Style.NumberFormat = "\"$\"#,##0"
# Add a line chart to the worksheet
chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Line)
# Set data range for the chart
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:G4"]
# Set position of chart
chart.LeftColumn = 1
chart.TopRow = 6
chart.RightColumn = 12
chart.BottomRow = 27
# Set and format chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Consumption of supplies by month"
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 12
# Set the category axis of the chart
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Title = "Month"
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Font.IsBold = True
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = True
# Set the value axis of the chart
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.Title = "Quantity"
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = False
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.TitleArea.TextRotationAngle = 90
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.MinValue = 100
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = True
# Set series colors and data labels
for cs in chart.Series:
cs.Format.Options.IsVaryColor = True
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = True
# Set legend position
chart.Legend.Position = LegendPositionType.Top
# Save the document
workbook.SaveToFile("LineChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
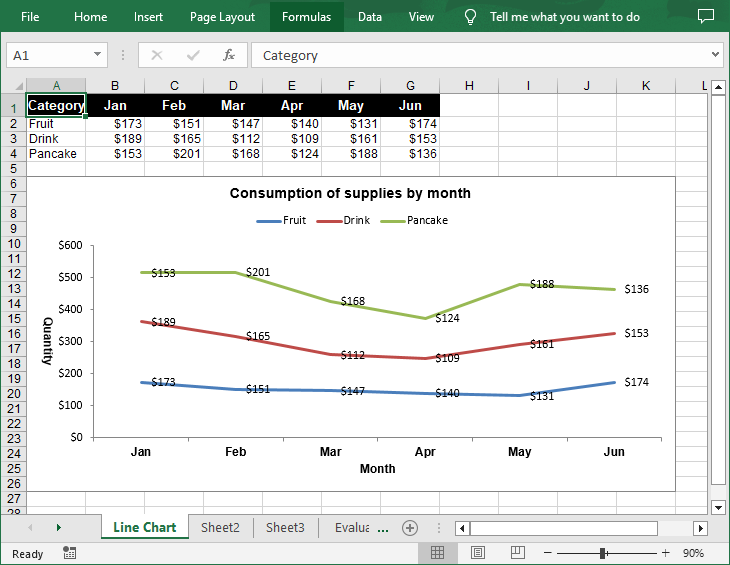
Create a Stacked Line Chart in Excel in Python
A stacked line chart stacks the values of each category on top of each other. This makes it easier to visualize how each data series contributes to the overall trend. The following are the steps to create a stacked line chart using Python:
- Create a Workbook instance.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Add the chart data to specified cells and set the cell styles.
- Add a stacked line chart to the worksheet using Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.LineStacked) method.
- Set data range for the chart using Chart.DataRange property.
- Set the position, title, axis and other attributes of the chart.
- Save the result file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook instance
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first sheet and set its name
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
sheet.Name = "Line Chart"
# Add chart data to specified cells
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Category"
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "Fruit"
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "Drink"
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "Pancake"
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Jan"
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 173
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 189
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 153
sheet.Range["C1"].Value = "Feb"
sheet.Range["C2"].NumberValue = 151
sheet.Range["C3"].NumberValue = 165
sheet.Range["C4"].NumberValue = 201
sheet.Range["D1"].Value = "Mar"
sheet.Range["D2"].NumberValue = 147
sheet.Range["D3"].NumberValue = 112
sheet.Range["D4"].NumberValue = 168
sheet.Range["E1"].Value = "Apr"
sheet.Range["E2"].NumberValue = 140
sheet.Range["E3"].NumberValue = 109
sheet.Range["E4"].NumberValue = 124
sheet.Range["F1"].Value = "May"
sheet.Range["F2"].NumberValue = 131
sheet.Range["F3"].NumberValue = 161
sheet.Range["F4"].NumberValue = 188
sheet.Range["G1"].Value = "Jun"
sheet.Range["G2"].NumberValue = 174
sheet.Range["G3"].NumberValue = 153
sheet.Range["G4"].NumberValue = 136
# Set cell styles
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].RowHeight = 20
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.Color = Color.get_Black()
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.Font.IsBold = True
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.Font.Size = 11
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1:G1"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["B2:G4"].Style.NumberFormat = "\"$\"#,##0"
# Add a stacked line chart to the worksheet
chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.LineStacked)
# Set data range for the chart
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["A1:G4"]
# Set position of chart
chart.LeftColumn = 1
chart.TopRow = 6
chart.RightColumn = 12
chart.BottomRow = 27
# Set and format chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Consumption of supplies by month"
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 12
# Set the category axis of the chart
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Title = "Month"
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.Font.IsBold = True
chart.PrimaryCategoryAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = True
# Set the value axis of the chart
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.Title = "Quantity"
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.HasMajorGridLines = False
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.TitleArea.TextRotationAngle = 90
chart.PrimaryValueAxis.TitleArea.IsBold = True
# Set series colors and data labels
for cs in chart.Series:
cs.Format.Options.IsVaryColor = True
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = True
# Set legend position
chart.Legend.Position = LegendPositionType.Top
# Save the document
workbook.SaveToFile("StackedLineChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Editing an Excel document involves a variety of actions, such as inputting and formatting text, applying formulas, generating visualizations, and organizing data for clarity and insight. Being able to edit Excel documents programmatically is a crucial skill that empowers developers to enhance their data management capabilities.
In this article, you will learn how to edit an existing Excel document in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Read and Write Excel Files in Python
- Apply Formatting to Excel Cells in Python
- Find and Replace Text in Excel in Python
- Add Formulas and Charts to Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
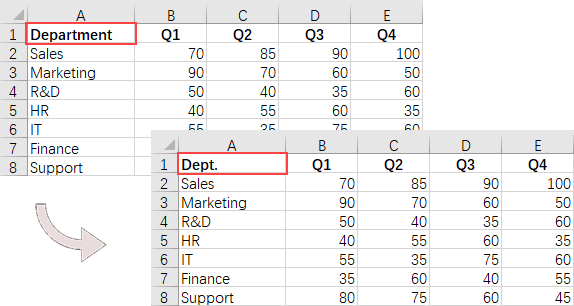
Read and Write Excel Files in Python
A key task when handling Excel files in Python is the efficient reading and writing of data, which is essential for numerous applications such as data analysis and report generation. Spire.XLS for Python simplifies this process by offering the CellRange.Value property. This feature allows developers to easily retrieve values from individual cells and reassign them as needed.
Here are the steps to read and write an Excel file using Python:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file from a given file path.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific cell using the Worksheet.Range property
- Get or set the cell value using the CellRange.Value property.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get a specific cell
cell = worksheet.Range["A1"]
# Read the cell value
cellValue = cell.Value
# Determine if the cell value is "Department"
if (cellValue == "Department"):
# Update the cell value
cell.Value = "Dept."
# Save the workbook to a different
workbook.SaveToFile("ModifyExcel.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
Apply Formatting to Excel Cells in Python
Formatting Excel documents is essential for producing professional-looking reports that effectively communicate information. Spire.XLS for Python offers a comprehensive suite of APIs within the CellRange class, empowering developers to manage various formatting options seamlessly. This includes adjusting font styles, selecting cell colors, aligning text, and modifying row heights and column widths.
Here are the steps to apply styles and formats to Excel cells using Python:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file from a given file path.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get all located range using the Worksheet.AllocatedRange property.
- Get a specific row using the CellRange.Rows[index] property, and set the cell color, text color, text alignment, and row height using the properties under the CellRange object.
- Get a specific column using the CellRange.Columns[index] property, and set the column width using the ColumnWidth property under the CellRange object.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get all located range from the worksheet
allocatedRange = worksheet.AllocatedRange
#Iterate through the rows
for rowNum in range(0, allocatedRange.RowCount):
if rowNum == 0:
# Apply cell color to the header row
allocatedRange.Rows[rowNum].Style.Color = Color.get_Black()
# Change the font color of the header row
allocatedRange.Rows[rowNum].Style.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
else:
# Apply alternate colors to other rows
if rowNum % 2 == 1:
allocatedRange.Rows[rowNum].Style.Color = Color.get_LightGray()
else:
allocatedRange.Rows[rowNum].Style.Color = Color.get_White()
# Align text to center
allocatedRange.Rows[rowNum].HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
allocatedRange.Rows[rowNum].VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
# Set the row height
allocatedRange.Rows[rowNum].RowHeight = 20
# Iterate through the columns
for columnNum in range(0, allocatedRange.ColumnCount):
if (columnNum > 0):
# Set the column width
allocatedRange.Columns[columnNum].ColumnWidth = 10
# Save the workbook to a different
workbook.SaveToFile("FormatExcel.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()

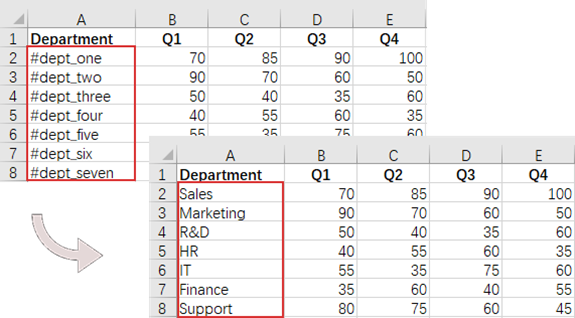
Find and Replace Text in Excel in Python
The find and replace functionality in Excel enables users to swiftly locate specific text within their spreadsheets and substitute it with new content, which is particularly useful for data corrections and updates. With Spire.XLS for Python, you can efficiently locate a cell containing a specific string using the Worksheet.FindString() method. Once identified, you can easily replace its value using the CellRange.Value property.
Here are the steps to find and replace text in Excel using Python:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file from a given file path.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Find the cell that contains a specified string using the Worksheet.FindString() method.
- Update the cell value using the CellRange.Value property.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Define a list of department names for replacement
departments = ["Sales", "Marketing", "R&D", "HR", "IT", "Finance", "Support"]
# Define a list of placeholders that will be replaced in the Excel sheet
placeholders = ["#dept_one", "#dept_two", "#dept_three", "#dept_four", "#dept_five", "#dept_six", "#dept_seven"]
# Iterate through the placeholder strings
for i in range (0, len(placeholders)):
# Find the cell containing the current placeholder string
cell = worksheet.FindString(placeholders[i], False, False)
# Replace the value in the found cell with the corresponding department name
cell.Value = departments[i]
# Save the workbook to a different
workbook.SaveToFile("ReplaceText.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
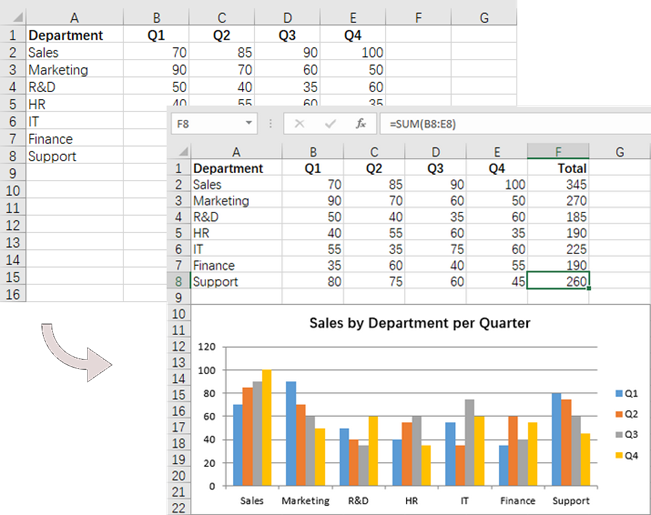
Add Formulas and Charts to Excel in Python
In addition to basic file operations, Spire.XLS for Python provides a variety of advanced techniques for working with Excel files. For example, you can insert formulas into cells using the CellRange.Formula property, which allows for real-time calculations and data analysis directly within your spreadsheet. Furthermore, it allows you to create visually appealing data presentations by adding charts to your worksheets using the Worksheet.Charts.Add() method.
Here are the steps to add formulas and charts to Excel using Python:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load an Excel file from a given file path.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get a specific cell using the Worksheet.Range property.
- Add a formula to the cell using the CellRange.Formula property.
- Add a column chart to the worksheet using the Worksheet.Charts.Add() method.
- Set the chart data range, position, title and other attributes using the properties under the Chart object.
- Save the workbook to a different Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get all located range
allocatedRange = worksheet.AllocatedRange
#Iterate through the rows
for rowNum in range(0, allocatedRange.RowCount):
if (rowNum == 0):
# Write text to cell G1
worksheet.Range[rowNum + 1, 6].Text = "Total"
# Apply style to the cell
worksheet.Range[rowNum + 1, 6].Style.Font.IsBold = True
worksheet.Range[rowNum + 1, 6].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Right
else:
# Add formulas to the cells from G2 to G8
worksheet.Range[rowNum + 1, 6].Formula = f"=SUM(B{rowNum + 1}:E{rowNum + 1})"
# Add a clustered column chart
chart = worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.ColumnClustered)
# Set data range for the chart
chart.DataRange = worksheet.Range["A1:E8"]
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = False
# Set position of the chart
chart.LeftColumn = 1
chart.TopRow = 10
chart.RightColumn = 8
chart.BottomRow = 23
# Set and format chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Sales by Department per Quarter"
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 13
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = True
# Save the workbook to a different
workbook.SaveToFile("AddFormulaAndChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
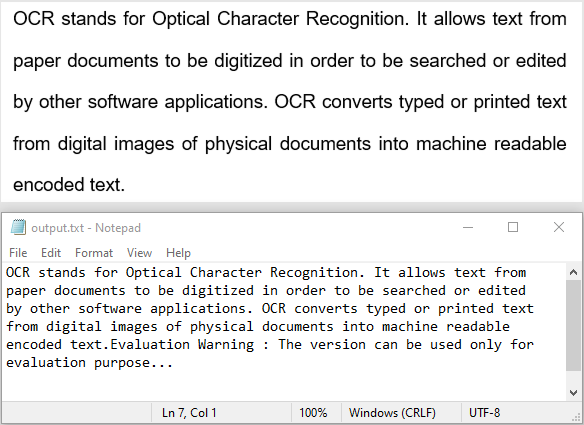
In today's digital world, extracting text from images has become essential for many fields, including business, education, and data analysis. OCR (Optical Character Recognition) technology makes this process effortless by converting text in images into editable and searchable formats quickly and accurately. Whether it's turning handwritten notes into digital files or pulling key information from scanned documents, OCR simplifies tasks and makes work more efficient. In this article, we will demonstrate how to recognize text from images in Python using Spire.OCR for Python.
Install Spire.OCR for Python
This scenario requires Spire.OCR for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.OCR
Download the Model of Spire.OCR for Python
Spire.OCR for Python provides different recognition models for different operating systems. Download the model suited to your system from one of the links below:
- Windows: win-x64.zip
- Linux: linux.zip
- macOS: mac.zip
- linux_aarch: linux_aarch.zip
After downloading, extract the package and save it to a specific directory on your system.
Recognize Text from Images in Python
Spire.OCR for Python offers the OcrScanner.Scan() method to recognize text from images. Once the recognition is complete, you can use the OcrScanner.Text property to retrieve the recognized text and then save it to a file for further use. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an instance of the OcrScanner class to handle OCR operations.
- Create an instance of the ConfigureOptions class to configure the OCR settings.
- Specify the file path to the model and the desired recognition language through the ConfigureOptions.ModelPath and ConfigureOptions.Language properties.
- Apply the configuration settings to the OcrScanner instance using the OcrScanner.ConfigureDependencies() method.
- Call the OcrScanner.Scan() method to perform text recognition on the image.
- Retrieve the recognized text using the OcrScanner.Text property.
- Save the extracted text to a file for further use.
- Python
from spire.ocr import *
# Create an instance of the OcrScanner class
scanner = OcrScanner()
# Configure OCR settings
configureOptions = ConfigureOptions()
# Set the file path to the model
configureOptions.ModelPath = r'D:\OCR\win-x64'
# Set the recognition language. Supported languages include English, Chinese, Chinesetraditional, French, German, Japanese, and Korean.
configureOptions.Language = 'English'
# Apply the settings to the OcrScanner instance
scanner.ConfigureDependencies(configureOptions)
# Recognize text from the image
scanner.Scan(r'Sample.png')
# Retrieve the recognized text and save it to a file
text = scanner.Text.ToString() + '\n'
with open('output.txt', 'a', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.write(text + '\n')
Recognize Text with Coordinates from Images in Python
In scenarios where you need the exact position of text in an image, such as for layout analysis or advanced data processing, extracting coordinate information is essential. With Spire.OCR for Python, you can retrieve recognized text block by block. Each text block includes detailed positional data such as the x and y coordinates, width, and height. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an instance of the OcrScanner class to handle OCR operations.
- Create an instance of the ConfigureOptions class to configure the OCR settings.
- Specify the file path to the model and the desired recognition language through the ConfigureOptions.ModelPath and ConfigureOptions.Language properties.
- Apply the configuration settings to the OcrScanner instance using the OcrScanner.ConfigureDependencies() method.
- Call the OcrScanner.Scan() method to perform text recognition on the image.
- Retrieve the recognized text using the OcrScanner.Text property.
- Iterate through the text blocks in the recognized text. For each block, use the IOCRTextBlock.Text property to get the text and the IOCRTextBlock.Box property to retrieve positional details (x, y, width, and height).
- Save the results to a text file for further analysis.
- Python
from spire.ocr import *
# Create an instance of the OcrScanner class
scanner = OcrScanner()
# Configure OCR settings
configureOptions = ConfigureOptions()
# Set the file path to the model
configureOptions.ModelPath = r'D:\OCR\win-x64'
# Set the recognition language. Supported languages include English, Chinese, Chinesetraditional, French, German, Japanese, and Korean.
configureOptions.Language = 'English'
# Apply the settings to the OcrScanner instance
scanner.ConfigureDependencies(configureOptions)
# Recognize text from the image
scanner.Scan(r'sample.png')
# Retrieve the recognized text
text = scanner.Text
# Iterate through the text blocks in the recognized text. For each text block, retrieve its text and positional data (x, y, width, and height)
block_text = ""
for block in text.Blocks:
rectangle = block.Box
block_info = f'{block.Text} -> x: {rectangle.X}, y: {rectangle.Y}, w: {rectangle.Width}, h: {rectangle.Height}'
block_text += block_info + '\n'
# Save the results to a file
with open('output.txt', 'a', encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.write(block_text + '\n')

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
