
Python (355)
PowerPoint presentations often contain hyperlinks that guide audiences to additional resources or locations within the presentations. While these links can be useful for providing further information and easy navigation, there are instances where they may detract from the presentation's flow or compromise its professional appearance. Those invalid or unnecessary links in slides can be easily removed using Python, enhancing the overall quality of the presentations.
This article will show how Spire.Presentation for Python can be utilized to remove hyperlinks from PowerPoint presentations efficiently.
- Remove Hyperlinks from Text in PowerPoint Slides
- Remove Hyperlinks from All Shapes in PowerPoint Slides
- Remove Hyperlinks from Specific Types of Shapes in PowerPoint Slides
- Remove Hyperlinks from Table Text in PowerPoint Slides
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Remove Hyperlinks from Text in PowerPoint Slides
The normal text in a PowerPoint presentation is contained in auto shapes. Developers can access the text ranges within these shapes using the IAutoShape.TextFrame.Paragraphs[].TextRanges[] property and read or set the hyperlinks on them using the TextRange.ClickAction property. Hyperlinks on text can be removed by setting the TextRange.ClickAction property to None.
The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an instance of Presentation class and load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through the slides in the presentation and then iterate through the shapes in the slides.
- Check if the shape is an instance of IAutoShape. If it is, iterate through the paragraphs in the shape, and then the text ranges in the paragraphs.
- Check if the TextRange.ClickAction property of a text range is None. If it is not, remove the hyperlink by setting TextRange.ClickAction property to None.
- Save the presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import Presentation, IAutoShape, FileFormat
# Create an instance of Presentation
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Iterate through the slides in the presentation
for slide in presentation.Slides:
# Iterate through the shapes
for shape in slide.Shapes:
# Check if the shape is an AutoShape instance
if isinstance(shape, IAutoShape):
# Iterate through the paragraphs in the shape
for paragraph in shape.TextFrame.Paragraphs:
# Iterate through the text ranges in the paragraph
for textRange in paragraph.TextRanges:
# Check if the text range has a hyperlink
if textRange.ClickAction is not None:
# Remove the hyperlink
textRange.ClickAction = None
# Save the presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("output/RemoveSlideTextHyperlink.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
presentation.Dispose()

Remove Hyperlinks from All Shapes in PowerPoint Slides
The IShape class represents all types of shapes in a presentation slide, such as auto shapes, images, tables, and more. The hyperlink on all these shapes can be removed by setting the value obtained from the IShape.Click.get_NoAction() method as the value of the shapes’ IShape.Click property. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an instance of Presentation class and load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through the slides in the presentation and then iterate through the shapes in the slides.
- Check if the IShape.Click property is None. If it is not, remove the hyperlink by setting the property to the result of IShape.Click.get_NoAction() method.
- Save the presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import Presentation, FileFormat
# Create an instance of Presentation
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Iterate through the slides in the presentation
for slide in presentation.Slides:
# Iterate through the shapes in the slide
for shape in slide.Shapes:
# Check if the shape has a hyperlink
if shape.Click is not None:
# Remove the click action
shape.Click = shape.Click.get_NoAction()
# Save the presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("output/RemoveSlideShapeHyperlink.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
presentation.Dispose()

Remove Hyperlinks from Specific Types of Shapes in PowerPoint Slides
In addition to directly removing hyperlinks for all shapes, we can also determine the shape type before removing the hyperlinks to find and remove hyperlinks from shapes of the specified type. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an instance of Presentation class and load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through the slides in the presentation and then iterate through the shapes in the slides.
- Check if the shape is an instance of IEmbedImage, ITable, or IChart. If it is, check if the IShape.Click property of the shape is None. If it is not, remove the hyperlink by setting the property to the result of IShape.Click.get_NoAction() method.
- Save the presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import Presentation, FileFormat, IEmbedImage, ITable, IChart
# Create an instance of Presentation
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Iterate through the slides in the presentation
for slide in presentation.Slides:
# Iterate through the shapes in the slide
for shape in slide.Shapes:
# Check if the shape is an embedded image
if isinstance(shape, (IEmbedImage, ITable, IChart)):
# check if the click action is not None
if shape.Click is not None:
# Remove the click action
shape.Click = shape.Click.get_NoAction()
# Save the presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("output/RemoveSlideShapeTypeHyperlink.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
presentation.Dispose()
Remove Hyperlinks from Table Text in PowerPoint Slides
To remove hyperlinks from text within a table, it is necessary to iterate through the table's cells and the text ranges within each cell. Afterward, the hyperlinks on the text ranges in each cell can be removed by setting the TextRange.ClickAction property to None. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an instance of Presentation class and load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through the slides in the presentation and then iterate through the shapes in the slides.
- Check if a shape is an instance of ITable class. If it is, iterate through the rows in the table and then the cells in the rows.
- Iterate through the paragraphs in the cells and then the text ranges in the paragraphs.
- Check if the TextRange.ClickAction property of a text range is None. If it is not, remove the hyperlink by setting the value of the property to None.
- Save the presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import Presentation, ITable, FileFormat
# Create an instance of Presentation
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Iterate through the slides in the presentation
for slide in presentation.Slides:
# Iterate through the shapes in the slide
for shape in slide.Shapes:
# Check if the shape is a table
if isinstance(shape, ITable):
# Get the table
table = ITable(shape)
# Iterate through the rows in the table
for row in table.TableRows:
# Iterate through the cells in the row
for cell in row:
# Iterate through the paragraphs in the cell
for para in cell.TextFrame.Paragraphs:
# Iterate through the text ranges in the paragraph
for range in para.TextRanges:
# Check if the text run contains a hyperlink
if range.ClickAction is not None:
# Remove the hyperlink
range.ClickAction = None
presentation.SaveToFile("output/RemoveSlideTableTextHyperlink.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
presentation.Dispose()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Barcodes in PDFs can facilitate quicker data retrieval and processing. You can add barcodes to PDF files that contain detailed information such as the document's unique identifier, version number, creator, or even the entire document content. When scanned, all information is decoded immediately. This instant access is invaluable for businesses dealing with large volumes of documents, as it minimizes the time and effort required for manual searching and data entry. In this article, you will learn how to add barcodes to PDF in Python using Spire.PDF for Python and Spire.Barcode for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and Spire.Barcode for Python. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF pip install Spire.Barcode
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Add Barcodes to PDF in Python
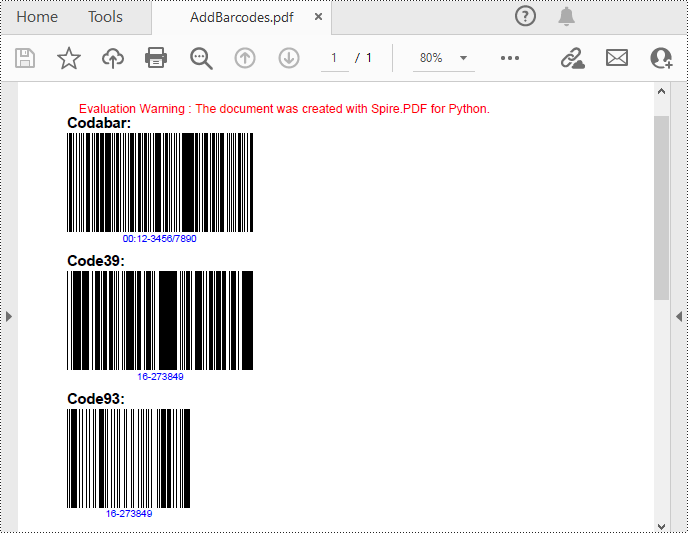
Spire.PDF for Python support several 1D barcode types represented by different classes, such as PdfCodabarBarcode, PdfCode11Barcode, PdfCode32Barcode, PdfCode39Barcode, PdfCode93Barcode.
Each class provides corresponding properties for setting the barcode text, size, color, etc. The following are the steps to draw the common Codabar, Code39 and Code93 barcodes at the specified locations on a PDF page.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Add a PDF page using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Create a PdfTextWidget object and draw text on the page using PdfTextWidget.Draw() method.
- Create PdfCodabarBarcode, PdfCode39Barcode, PdfCode93Barcode objects.
- Set the gap between the barcode and the displayed text through the BarcodeToTextGapHeight property of the corresponding classes.
- Sets the barcode text display location through the TextDisplayLocation property of the corresponding classes.
- Set the barcode text color through the TextColor property of the corresponding classes.
- Draw the barcodes at specified locations on the PDF page using the Draw(page: PdfPageBase, location: PointF) method of the corresponding classes.
- Save the result PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PDF document
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a page
page = pdf.Pages.Add(PdfPageSize.A4())
# Initialize y-coordinate
y = 20.0
# Create a true type font
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 12.0, PdfFontStyle.Bold, True)
# Draw text on the page
text = PdfTextWidget()
text.Font = font
text.Text = "Codabar:"
result = text.Draw(page, 0.0, y)
page = result.Page
y = result.Bounds.Bottom + 2
# Draw Codabar barcode on the page
Codabar = PdfCodabarBarcode("00:12-3456/7890")
Codabar.BarcodeToTextGapHeight = 1.0
Codabar.EnableCheckDigit = True
Codabar.ShowCheckDigit = True
Codabar.TextDisplayLocation = TextLocation.Bottom
Codabar.TextColor = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Blue())
Codabar.Draw(page, PointF(0.0, y))
y = Codabar.Bounds.Bottom + 6
# Draw text on the page
text.Text = "Code39:"
result = text.Draw(page, 0.0, y)
page = result.Page
y = result.Bounds.Bottom + 2
# Draw Code39 barcode on the page
Code39 = PdfCode39Barcode("16-273849")
Code39.BarcodeToTextGapHeight = 1.0
Code39.TextDisplayLocation = TextLocation.Bottom
Code39.TextColor = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Blue())
Code39.Draw(page, PointF(0.0, y))
y = Code39.Bounds.Bottom + 6
# Draw text on the page
text.Text = "Code93:"
result = text.Draw(page, 0.0, y)
page = result.Page
y = result.Bounds.Bottom + 2
# Draw Code93 barcode on the page
Code93 = PdfCode93Barcode("16-273849")
Code93.BarcodeToTextGapHeight = 1.0
Code93.TextDisplayLocation = TextLocation.Bottom
Code93.TextColor = PdfRGBColor(Color.get_Blue())
Code93.QuietZone.Bottom = 5.0
Code93.Draw(page, PointF(0.0, y))
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("AddBarcodes.pdf")
pdf.Close()
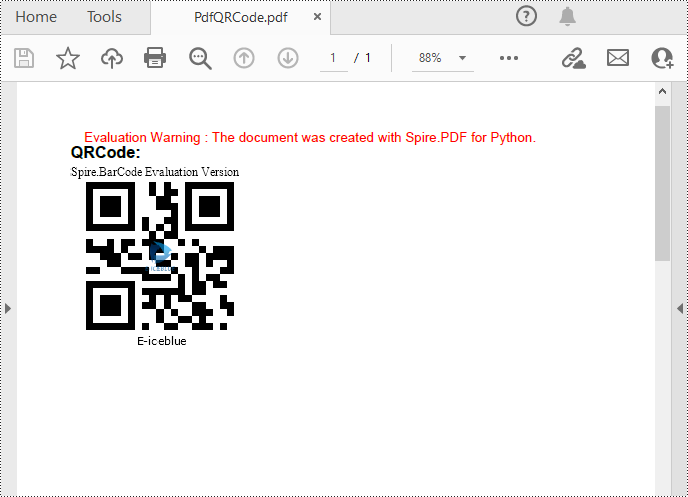
Add QR Codes to PDF in Python
To add 2D barcodes to a PDF file, the Spire.Barcode for Python library is required to generate QR code first, and then you can add the QR code image to the PDF file with the Spire.PDF for Python library. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument object.
- Add a PDF page using PdfDocument.Pages.Add() method.
- Create a BarcodeSettings object.
- Call the corresponding properties of the BarcodeSettings class to set the barcode type, data, error correction level and width, etc.
- Create a BarCodeGenerator object based on the settings.
- Generate QR code image using BarCodeGenerator.GenerateImage() method.
- Save the QR code image to a PNG file.
- Draw the QR code image at a specified location on the PDF page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawImage() method.
- Save the result PDF file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
from spire.barcode import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Add a page
page = pdf.Pages.Add()
# Create a BarcodeSettings object
settings = BarcodeSettings()
# Set the barcode type to QR code
settings.Type = BarCodeType.QRCode
# Set the data of the QR code
settings.Data = "E-iceblue"
settings.Data2D = "E-iceblue"
# Set the width of the QR code
settings.X = 2
# Set the error correction level of the QR code
settings.QRCodeECL = QRCodeECL.M
# Set to show QR code text at the bottom
settings.ShowTextOnBottom = True
# Generate QR code image based on the settings
barCodeGenerator = BarCodeGenerator(settings)
QRimage = barCodeGenerator.GenerateImage()
# Save the QR code image to a .png file
with open("QRCode.png", "wb") as file:
file.write(QRimage)
# Initialize y-coordinate
y = 20.0
# Create a true type font
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 12.0, PdfFontStyle.Bold, True)
# Draw text on the PDF page
text = PdfTextWidget()
text.Font = font
text.Text = "QRCode:"
result = text.Draw(page, 0.0, y)
page = result.Page
y = result.Bounds.Bottom + 2
# Draw QR code image on the PDF page
pdfImage = PdfImage.FromFile("QRCode.png")
page.Canvas.DrawImage(pdfImage, 0.0, y)
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("PdfQRCode.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
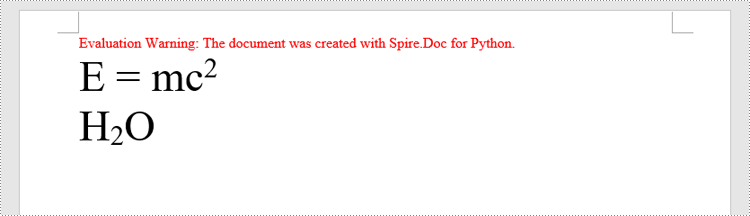
Superscript and subscript are formatting options that allow you to raise or lower characters in relation to the main text. Superscript is typically used for mathematical expressions, footnotes, ordinal indicators (such as "1st" or "2nd"), and chemical formulas. Subscript is commonly employed in chemical equations, mathematical notation, and certain linguistic elements. By adding superscripts and subscripts, you can enhance the readability and professionalism of your documents, especially in scientific, mathematical, and technical writing. In this article, we will demonstrate how to add superscripts and subscripts to Word documents in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Add Superscript and Subscript Text to Word in Python
- Apply Superscript and Subscript Formatting to Existing Text in Word in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Add Superscript and Subscript Text to Word in Python
You can add text to a paragraph using the Paragraph.AppentText() method. After that, you can apply superscript or subscript formatting to the text through the TextRange.CharacterFormat.SubSuperScript property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Add a section to the document using Document.AddSection() method.
- Add a paragraph to the section using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Add normal text to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendText() method.
- Add superscript or subscript text to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendText() method.
- Apply superscript or subscript formatting to the superscript or subscript text using TextRange.CharacterFormat.SubSuperScript property.
- Save the resulting document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document instance
document = Document()
# Add a section to the document
section = document.AddSection()
# Add a paragraph to the section
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
# Add normal text to the paragraph
paragraph.AppendText("E = mc")
# Add superscript text to the paragraph
superscript_text = paragraph.AppendText("2")
# Apply superscript formatting to the superscript text
superscript_text.CharacterFormat.SubSuperScript = SubSuperScript.SuperScript
# Start a new line
paragraph.AppendBreak(BreakType.LineBreak)
# Add normal text to the paragraph
paragraph.AppendText("H")
# Add subscript text to the paragraph
subscript_text = paragraph.AppendText("2")
# Apply subscript formatting to the subscript text
subscript_text.CharacterFormat.SubSuperScript = SubSuperScript.SubScript
# Add normal text to the paragraph
paragraph.AppendText("O")
# Set the font size for the text in the paragraph
for i in range(paragraph.Items.Count):
item = paragraph.Items[i]
if isinstance(item, TextRange):
text_range = item
text_range.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 36
# Save the resulting document
document.SaveToFile("AddSuperscriptAndSubscriptText.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
document.Close()
Apply Superscript and Subscript Formatting to Existing Text in Word in Python
To apply superscript or subscript formatting to a specific text, you need to search for the text using the Document.FindAllString() method, then apply superscript or subscript formatting to the instances of that text through the TextRange.CharacterFormat.SubSuperScript property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Find a specific text in the document using Document.FindAllString() method. This method will return a list of TextSelection objects, each representing an instance of the text in the document.
- Get the first instance of the text as a single text range using TextSelection.GetAsOneRange() method, then apply superscript formatting to the text range by setting the TextRange.CharacterFormat.SubSuperScript property to SubSuperScript.SuperScript.
- Get the second instance of the text as a single text range using TextSelection.GetAsOneRange() method, then apply subscript formatting to the text range by setting the TextRange.CharacterFormat.SubSuperScript property to SubSuperScript.SubScript.
- Save the resulting document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document instance
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Find a specific number in the document
text_selections = document.FindAllString("2", False, False)
# Apply superscript formatting to the first instance of the number
superscript_text = text_selections[0].GetAsOneRange()
superscript_text.CharacterFormat.SubSuperScript = SubSuperScript.SuperScript
# Apply subscript formatting to the second instance of the number
subscript_text = text_selections[1].GetAsOneRange()
subscript_text.CharacterFormat.SubSuperScript = SubSuperScript.SubScript
# Save the resulting document
document.SaveToFile("ApplySuperscriptAndSubscriptFormatting.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
document.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Insert, Rotate, Resize, Reposition, and Reorder Shapes in PowerPoint
2024-08-15 00:52:47 Written by KoohjiShapes are the fundamental building blocks that bring your PowerPoint slides to life. From simple geometric forms to complex icons and illustrations, these versatile visual elements enable you to add interest, highlight key information, and craft visually striking layouts. Whether you are creating professional-looking slides from scratch or enhancing existing ones, knowing how to insert and manipulate shapes is an essential skill. In this guide, we'll cover how to insert, rotate, resize, reposition, and reorder shapes in PowerPoint presentations in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
- Insert Shapes in PowerPoint in Python
- Rotate Shapes in PowerPoint in Python
- Resize and Reposition Shapes in PowerPoint in Python
- Reorder Shapes in PowerPoint in Python
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Insert Shapes in PowerPoint in Python
Spire.Presentation for Python enables you to add various types of shapes such as rectangles, circles, triangles, arrows, and eclipses to a PowerPoint slide by using the ISlide.Shapes.AppendShape() method.
Here are the steps to insert shapes in PowerPoint using Spire.Presentation for Python:
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific slide in the presentation using Presentation.Slides[index] property.
- Add various types of shapes to the slide using ISlide.Shapes.AppendShape() method and then set styles for the shapes.
- Save the resulting presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
ppt = Presentation()
# Get the first slide
slide = ppt.Slides[0]
# Add a triangle shape to the slide
shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Triangle, RectangleF.FromLTRB (115, 130, 215, 230))
shape.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
shape.Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_LightGreen()
shape.ShapeStyle.LineColor.Color = Color.get_White()
# Add an ellipse shape to the slide
shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Ellipse, RectangleF.FromLTRB (290, 130, 440, 230))
shape.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
shape.Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_LightSkyBlue()
shape.ShapeStyle.LineColor.Color = Color.get_White()
# Add a heart shape to the slide
shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Heart, RectangleF.FromLTRB (470, 130, 600, 230))
shape.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
shape.Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_Red()
shape.ShapeStyle.LineColor.Color = Color.get_LightGray()
# Add a five-pointed star shape to the slide
shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.FivePointedStar, RectangleF.FromLTRB (90, 270, 240, 420))
shape.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Gradient
shape.Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_Black()
shape.ShapeStyle.LineColor.Color = Color.get_White()
# Add a rectangle shape to the slide
shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.Rectangle, RectangleF.FromLTRB (320, 290, 420, 410))
shape.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
shape.Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_Pink()
shape.ShapeStyle.LineColor.Color = Color.get_LightGray()
# Add an arrow shape to the slide
shape = slide.Shapes.AppendShape(ShapeType.BentUpArrow, RectangleF.FromLTRB (470, 300, 580, 400))
shape.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Gradient
shape.Fill.Gradient.GradientStops.AppendByKnownColors(1, KnownColors.Olive)
shape.Fill.Gradient.GradientStops.AppendByKnownColors(0, KnownColors.PowderBlue)
shape.ShapeStyle.LineColor.Color = Color.get_Red()
# Save the resulting presentation to a new file
ppt.SaveToFile("InsertShapes.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2010)
ppt.Dispose()
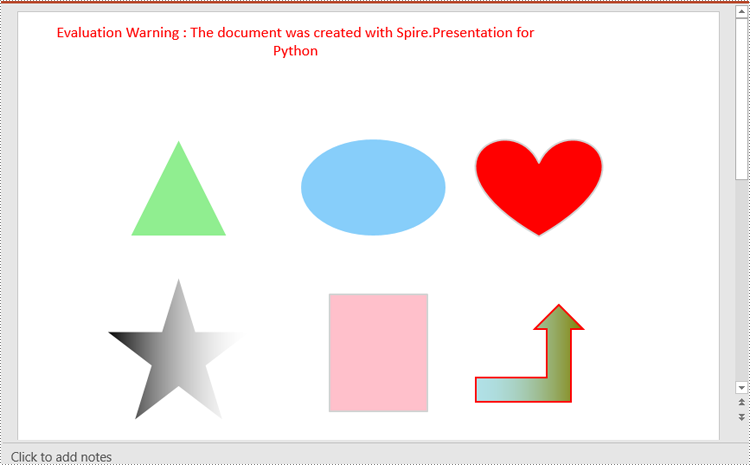
Rotate Shapes in PowerPoint in Python
The IShape.Rotation property in Spire.Presentation for Python is used to rotate a shape on a PowerPoint slide. Setting this property to a positive value will rotate the shape clockwise, while setting it to a negative value will rotate the shape counterclockwise.
Here are the steps to rotate a shape in PowerPoint using Spire.Presentation for Python:
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific slide in the presentation using Presentation.Slides[index] property.
- Get a specific shape on the slide using ISlide.Shapes[index] property.
- Rotate the shape by specific degrees using IShape.Rotation property.
- Save the resulting presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
ppt = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
ppt.LoadFromFile("ShapeTemplate1.pptx")
# Get the first slide
slide = ppt.Slides[0]
# Get the first shape on the slide
shape = slide.Shapes[0] if isinstance(slide.Shapes[0], IAutoShape) else None
# Rotate the shape 180 degrees clockwise
shape.Rotation = 180
# Save the resulting presentation to a new file
ppt.SaveToFile("RotateShape.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
ppt.Dispose()
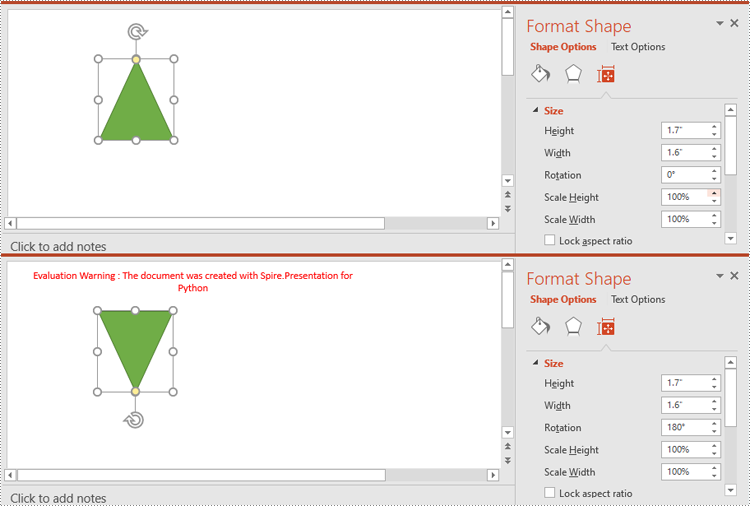
Resize and Reposition Shapes in PowerPoint in Python
The size and position of a shape can be reset through the IShape.Height, IShape.Width and IShape.Left, IShape.Top properties.
Here are the steps to reset the size and position of shapes in PowerPoint using Spire.Presentation for Python:
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the original slide height and width using Presentation.SlideSize.Size.Height and Presentation.SlideSize.Size.Width properties.
- Change the slide size using Presentation.SlideSize.Type property, and then get the new slide height and width.
- Calculate the ratio for resetting the size and position of the shapes based on the original and new slide heights and widths.
- Iterate through the slides in the presentation and the shapes on each slide.
- Reset the size and position of each shape based on the specified ratio using IShape.Height, IShape.Width, IShape.Left and IShape.Top properties.
- Save the resulting presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
ppt = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
ppt.LoadFromFile("ShapeTemplate.pptx")
# Get the original slide height and width
currentHeight = ppt.SlideSize.Size.Height
currentWidth = ppt.SlideSize.Size.Width
# Change the slide size to A3
ppt.SlideSize.Type = SlideSizeType.A3
# Get the new slide height and width
newHeight = ppt.SlideSize.Size.Height
newWidth = ppt.SlideSize.Size.Width
# Calculate the ratio for resizing shapes based on the original and new slide heights and widths
ratioHeight = newHeight / currentHeight
ratioWidth = newWidth / currentWidth
# Iterate through the slides in the presentation
for slide in ppt.Slides:
# Iterate through the shapes on the slide
for shape in slide.Shapes:
if isinstance(shape, IAutoShape):
# Reset the size of the shape based on the specified ratio
shape.Height = shape.Height * ratioHeight
shape.Width = shape.Width * ratioWidth
# Reset the position (x and y coordinates) of the shape based on the specified ratio
shape.Top = shape.Top * ratioHeight
shape.Left = shape.Left * ratioWidth
# Save the resulting presentation to a new file
ppt.SaveToFile("ResizeAndRepositionShapes.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
ppt.Dispose()
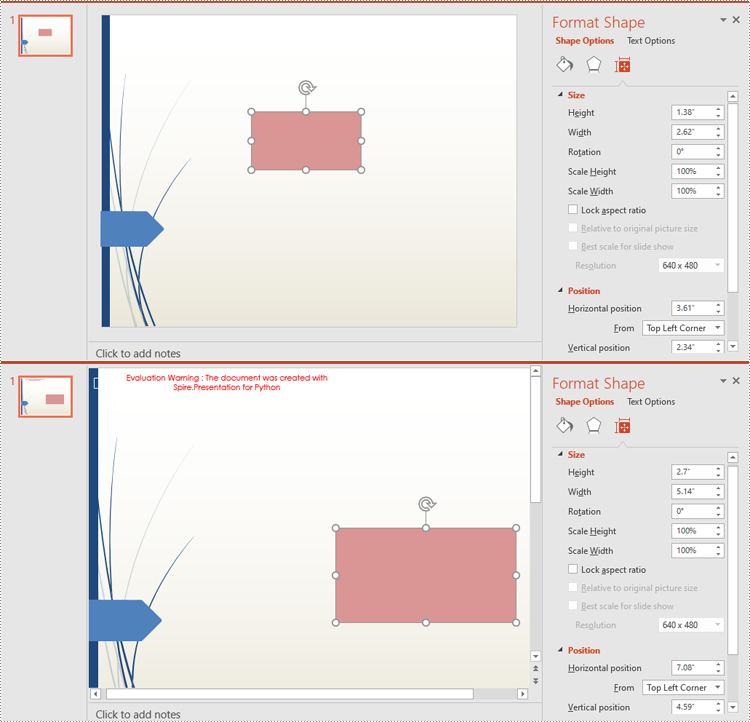
Reorder Shapes in PowerPoint in Python
The order in which shapes are arranged determines which shapes appear in front of or behind others. Using the ISlide.Shapes.ZOrder() method, you can easily change the order of multiple overlapping shapes on a PowerPoint slide.
Here are the steps to change the order of shapes in PowerPoint using Spire.Presentation for Python:
- Create an object of the Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific slide in the presentation using Presentation.Slides[index] property.
- Get a specific shape on the slide using ISlide.Shapes[index] property.
- Change the stacking order of the shape using ISlide.Shapes.ZOrder() method.
- Save the resulting presentation using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an object of the Presentation class
ppt = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint presentation
ppt.LoadFromFile("ShapeTemplate3.pptx")
# Get the first slide
slide = ppt.Slides[0]
# Get the first shape on the slide
shape = slide.Shapes[0] if isinstance(slide.Shapes[0], IAutoShape) else None
# Change the stacking order of the shape
slide.Shapes.ZOrder(1, shape)
# Save the resulting presentation to a new file
ppt.SaveToFile("ReorderShapes.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2016)
ppt.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
When preparing multiple PowerPoint presentations with similar themes, copying slides helps to maintain consistency in terms of design, layout and content. This ensures that all presentations have a uniform appearance, which can enhance the aesthetics of your document. In this article, you will learn how to copy or clone slides in PowerPoint presentations in Python using Spire.Presentation for Python.
- Copy Slides Within the Same Presentation with Python
- Copy Slides to Another Presentation with Python
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
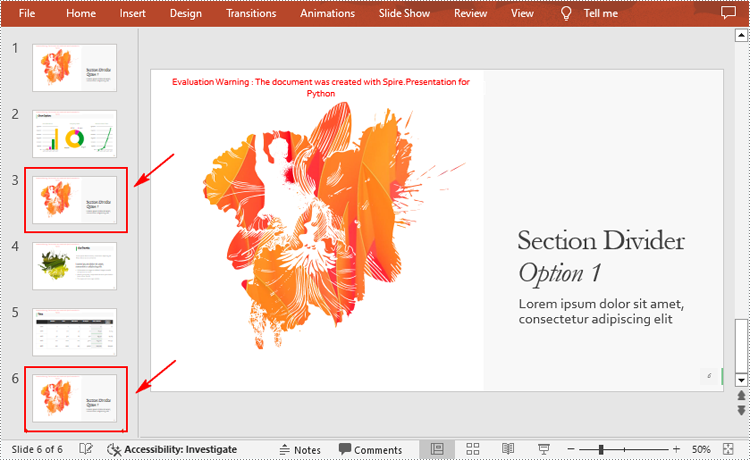
Copy Slides Within the Same Presentation with Python
You can clone a slide either at a specified location or at the end of a PowerPoint presentation through the Presentation.Slides.Insert(Index: int, slide: ISlide) or Presentation.Slides.AppendBySlide(slide: ISlide) methods. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Presentation instance.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified slide using Prenstion.Slides[] property.
- Clone the slide to the end of the same presentation using Presentation.Slides.AppendBySlide() method.
- Clone the slide to a specific position within the same presentation using Presentation.Slides.Insert() method.
- Save the result file using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import * from spire.presentation import * inputFile ="Input1.pptx" outputFile ="CloneSlidesWithinTheSame.pptx" # Create a Presentation instance ppt = Presentation() #Load a PowerPoint presentation ppt.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get the first slide in the presentation slide = ppt.Slides[0] # Clone the slide to the end of the presentation ppt.Slides.AppendBySlide(slide) # Clone the slide to the third position within the presentation ppt.Slides.Insert(2, slide) # Save the result file ppt.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Pptx2016) ppt.Dispose()
Copy Slides to Another Presentation with Python
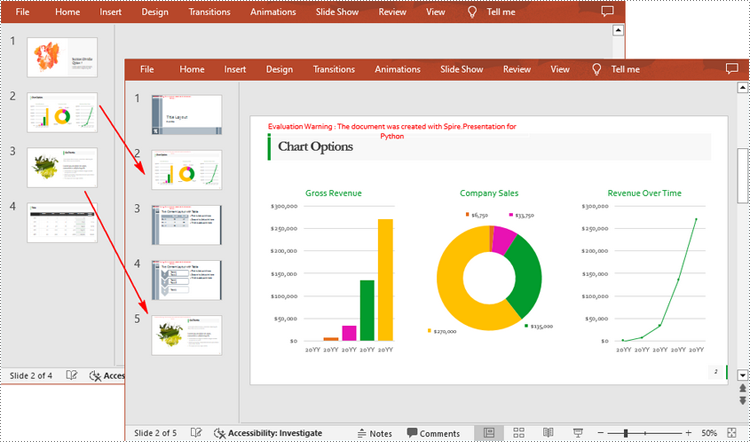
Spire.Presentation for Python also allows you to load two PowerPoint files and then clone the slides from one presentation to another presentation. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Presentation instance.
- Load two PowerPoint presentations using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get two slides in the first presentation using Prenstion.Slides[] property.
- Clone the first slide to a specific position in the second presentation using Presentation.Slides.Insert() method.
- Clone the second slide to the end of the second presentation using Presentation.Slides.AppendBySlide() method.
- Save the result file using Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import * from spire.presentation import * inputFile_1 = "Input1.pptx" inputFile_2 = "Input2.pptx" outputFile ="CloneSlidesToAnother.pptx" # Load the first PowerPoint presentation sourcePPT = Presentation() sourcePPT.LoadFromFile(inputFile_1) # Load the second PowerPoint presentation destPPT = Presentation() destPPT.LoadFromFile(inputFile_2) # Get two slides in the first presentation slide1 =sourcePPT.Slides[1] slide2 =sourcePPT.Slides[2] # Clone slide1 to the second position in the second presentation destPPT.Slides.Insert(1, slide1) # Clone slide2 to the end of the second presentation destPPT.Slides.AppendBySlide(slide2) # Save the second presentation destPPT.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Pptx2016) destPPT.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Charts and shapes in Excel are vital tools for clear and effective data presentation. Sometimes, it's beneficial to convert these visual elements into images. Perhaps you need to include a specific chart in a report or presentation outside of Excel. Or maybe you want to use an Excel-created infographic on your company's website. Regardless of the use case, knowing how to export these visuals as standalone image files can be invaluable. In this guide, we will explore how to convert charts and shapes in Excel to images in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Convert a Specific Chart in an Excel Worksheet to Image in Python
- Convert All Charts in an Excel Worksheet to Images in Python
- Convert a Chart Sheet in Excel to Image in Python
- Convert Shapes in Excel to Images in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
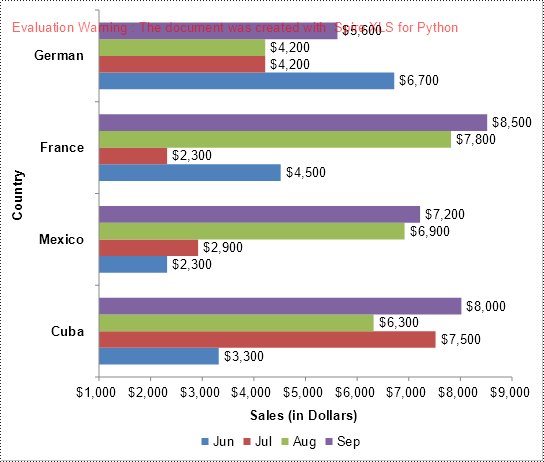
Convert a Specific Chart in an Excel Worksheet to Image in Python
Spire.XLS for Python offers the Workbook.SaveChartAsImage(worksheet: Worksheet, chartIndex: int) method, allowing you to convert a specific chart within a worksheet into an image stream. This image stream can then be saved as an image file in various formats, including PNG, JPG, BMP, and more. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet in the file using the Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Save a specific chart in the worksheet to an image stream using the Workbook.SaveChartAsImage(worksheet: Worksheet, chartIndex: int) method.
- Save the image stream to an image file using the Stream.Save() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Charts.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Save the first chart in the worksheet to an image stream
image_stream = workbook.SaveChartAsImage(sheet, 0)
# Save the image stream to a PNG image file
image_stream.Save("Output/chart.png")
workbook.Dispose()
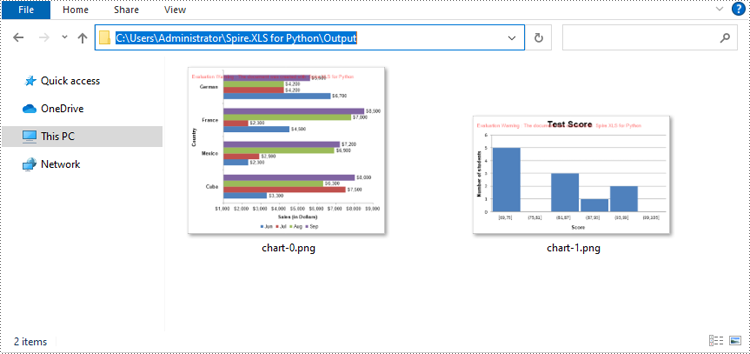
Convert All Charts in an Excel Worksheet to Images in Python
To convert all charts in an Excel worksheet to images, you can use the Workbook.SaveChartAsImage(worksheet: Worksheet) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet in the file using the Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Save all charts in the worksheet to a list of image streams using the Workbook.SaveChartAsImage(worksheet: Worksheet) method.
- Iterate through the image streams in the list and save them to separate image files.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Charts.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
image_streams = []
# Save the charts in the worksheet to a list of image streams
image_streams = workbook.SaveChartAsImage(sheet)
# Save the image streams to PNG image files
for i, image_stream in enumerate(image_streams):
image_stream.Save(f"Output/chart-{i}.png")
workbook.Dispose()
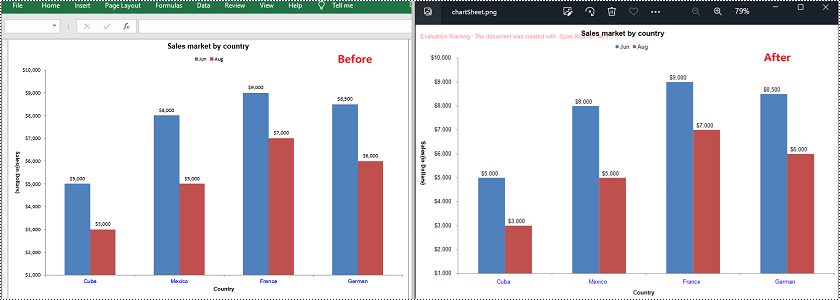
Convert a Chart Sheet in Excel to Image in Python
In Microsoft Excel, a chart sheet is a special type of sheet that is dedicated to displaying a single chart or graph. You can convert a chart sheet in an Excel workbook to an image using the Workbook.SaveChartAsImage(chartSheet: ChartSheet) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific chart sheet in the file using the Workbook.Chartsheets[] property.
- Save the chart sheet to an image stream using the Workbook.SaveChartAsImage(chartSheet: ChartSheet) method.
- Save the image stream to an image file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("ChartSheet.xlsx")
# Get the first chart sheet
chart_sheet = workbook.Chartsheets[0]
# Save the chart sheet to an image stream
image_stream = workbook.SaveChartAsImage(chart_sheet)
# Save the image stream to a PNG image file
image_stream.Save("Output/chartSheet.png")
workbook.Dispose()
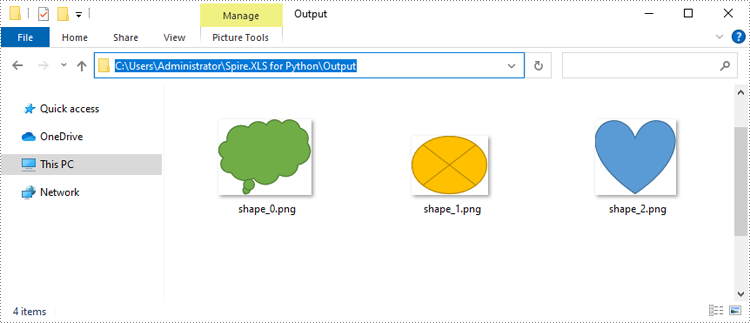
Convert Shapes in Excel to Images in Python
In addition to converting charts or chart sheets to images, you can also convert shapes in an Excel worksheet to images by using the XlsShape.SaveToImage() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet in the file using the Workbook.Worksheets[] property.
- Iterate through all the shapes in the worksheet.
- Typecast the shape to an XlsShape object.
- Save the shape to an image stream using the XlsShape.SaveToImage() method.
- Save the image stream to an image file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Shapes.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Iterate through all the shapes in the worksheet
for i, shape in enumerate(sheet.PrstGeomShapes):
xls_shape = XlsShape(shape)
# Save the shape to an image stream
image_stream = shape.SaveToImage()
# Save the image stream to a PNG image file
image_stream.Save(f"Output/shape_{i}.png")
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Create and Execute Conditional Mail Merges in Word Documents
2024-08-09 00:54:29 Written by KoohjiConditional mail merge in Word documents is a powerful method for personalized communication at scale. Unlike other mail merges that apply the same template to all recipients, conditional mail merge allows users to customize content based on specific criteria or conditions, ensuring that each recipient receives information that is directly relevant to them. By leveraging Python, users can automate the creation and execution of conditional mail merges.
This article will show how to create and execute conditional mail merges in Word documents through Python code using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Create Conditional Mail Merge in a Word Document with Python
- Execute Conditional Mail Merge in a Word Document with Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Create Conditional Mail Merge in a Word Document with Python
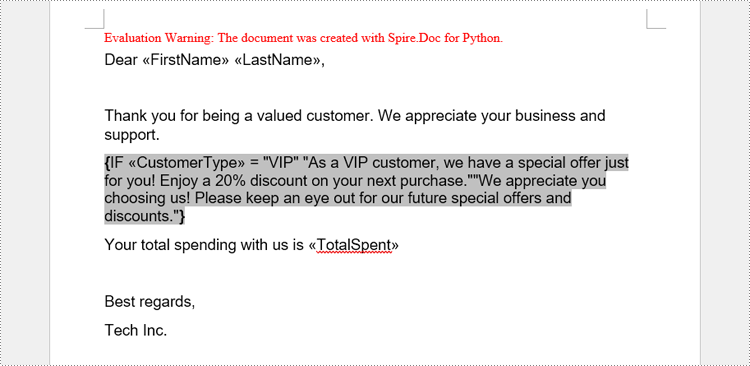
A conditional mail merge uses an If field containing a mail merge field, which alters the merge results based on the data. To add a conditional mail merge to a Word document, insert an If field, then include a mail merge field within the If field’s code, and finish by adding the field end mark to complete the setup. The condition is controlled by the code within the If field.
The detailed steps for adding a conditional mail merge to a Word document are as follows:
- Create an instance of the Document class to generate a Word document.
- Add a section to the document and configure the page setup.
- Create paragraph styles, add paragraphs, and set their formats.
- Create an IfField object, set its starting code through the IfField.Code property, and insert it into a paragraph using the Paragraph.Items.Add() method.
- Append a mail merge field to the paragraph using the Paragraph.AppendField() method.
- Append the remaining code to the paragraph using the Paragraph.AppendText() method.
- Append a field end mark to end the If field using the Paragraph.AppendFieldMark() method.
- Set the end mark as the end mark of the If field through the IfField.End property.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
# Create an instance of Document
doc = Document()
# Add a section to the document
section = doc.AddSection()
# Set the page size and margins
section.PageSetup.PageSize = PageSize.A4()
section.PageSetup.Margins.All = 50
# Create a paragraph style
style = ParagraphStyle(doc)
style.Name = "Style1"
style.CharacterFormat.FontName = "Arial"
style.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 14
style.ParagraphFormat.BeforeSpacing = 5
style.ParagraphFormat.AfterSpacing = 10
doc.Styles.Add(style)
# Add paragraphs and set the style
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Dear ")
paragraph.AppendField("FirstName", FieldType.FieldMergeField)
paragraph.AppendText(" ")
paragraph.AppendField("LastName", FieldType.FieldMergeField)
paragraph.AppendText(",")
paragraph.ApplyStyle(style.Name)
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("\r\nThank you for being a valued customer. We appreciate your business and support.")
paragraph.ApplyStyle(style.Name)
# Add an If field to a paragraph
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
ifField = IfField(doc)
ifField.Type = FieldType.FieldIf
ifField.Code = "IF "
paragraph.Items.Add(ifField)
# Add a mail merge field in the code of the If field
paragraph.AppendField("CustomerType", FieldType.FieldMergeField)
paragraph.AppendText(" = ")
paragraph.AppendText("\"VIP\"")
paragraph.AppendText(" \"As a VIP customer, we have a special offer just for you! Enjoy a 20% discount on your next "
"purchase.\"")
paragraph.AppendText("\"We appreciate you choosing us! Please keep an eye out for our future special offers and "
"discounts.\"")
# Add a field end mark at the end to end the If field
endIf = paragraph.AppendFieldMark(FieldMarkType.FieldEnd)
ifField.End = endIf
paragraph.ApplyStyle(style.Name)
# Add paragraphs and set the style
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Your total spending with us is ")
paragraph.AppendField("TotalSpent", FieldType.FieldMergeField)
paragraph.ApplyStyle(style.Name)
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("\r\nBest regards,\r\nTech Inc.")
paragraph.ApplyStyle(style.Name)
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("output/ConditionalMailMerge.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
Execute Conditional Mail Merge in a Word Document with Python
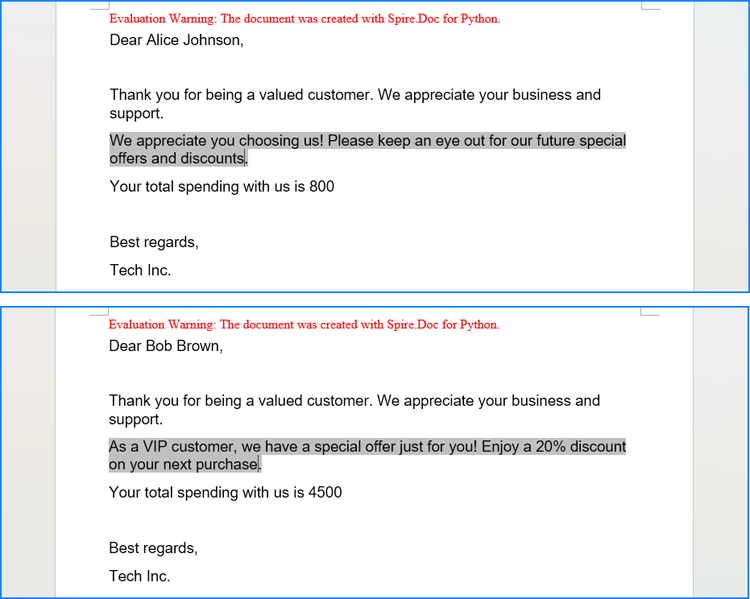
The Document.MailMerge.Execute(fieldNames: list[str], fieldValues: list[str]) method provided by Spire.Doc for Python allows for mail merge operations within Word documents. After the merge, you can update the results of conditional mail merges by setting the Document.IsUpdateFields property to True. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Read the data in the table used for the merge as a two-dimensional list.
- Iterate through the data rows, skipping the header:
- Create an instance of the Document class and load the Word document to be merged.
- Get the names of the mail merge fields as a list using the Document.MailMerge.GetMergeFieldNames() method.
- Execute the mail merge with the data using the Document.MailMerge.Execute() method.
- Update the If field by setting the Document.IsUpdateFields property to True.
- Save the document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
import csv
# Read the data from a CSV file
data = []
with open("Customers.csv", "r") as csvfile:
read = csv.reader(csvfile)
for row in read:
data.append(row)
# Iterate through the data rows by skipping the header
for i in range(1, len(data)):
# Create an instance of Document and load a Word document
doc = Document("output/ConditionalMailMerge.docx")
# Get the field names from the document
fieldNames = doc.MailMerge.GetMergeFieldNames()
# Execute the mail merge
doc.MailMerge.Execute(fieldNames, data[i])
# Update the If field
doc.IsUpdateFields = True
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile(f"output/Customers/{data[i][0]} {data[i][1]}.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Managing PDF documents often involves removing annotations. Whether you're preparing documents for a presentation, sharing the final files with clients when questions are settled down, or archiving important records, deleting annotations can be essential.
Spire.PDF for Python allows users to delete annotations from PDFs in Python efficiently. Follow the instructions below to clean up your PDF files seamlessly.
- Delete Specified Annotations
- Delete All Annotations from a Page
- Delete All Annotations from the PDF Document
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install it, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows.
Delete Specified Annotations from PDF in Python
To delete a specified annotation from PDF documents, you need to target the annotation to be removed at first. Then you can remove it by calling the Page.AnnotationsWidget.RemoveAt() method offered by Spire.PDF for Python. This section will guide you through the whole process step by step.
Steps to remove an annotation from a page:
- Create a new PdfDocument object.
- Load a PDF document from files using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the specific page of the PDF with PdfDocument.Pages.get_Item() method.
- Delete the annotation from the page by calling Page.AnnotationsWidget.RemoveAt() method.
- Save the resulting document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
Here's the code example for you to refer to:
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a new PDF document
doc = PdfDocument()
# Open the PDF document to be modified from the disk
doc.LoadFromFile("sample1.pdf")
# Get the first page of the document
page = doc.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Remove the 2nd annotation from the page
page.AnnotationsWidget.RemoveAt(1)
# Save the PDF document
doc.SaveToFile("output/delete_2nd_annotation.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
doc.Close()
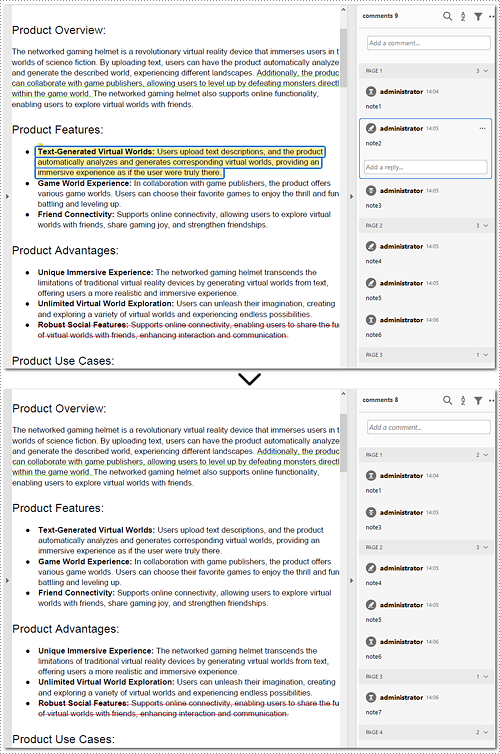
Delete All Annotations from a PDF Page in Python
The Pages.AnnotationsWidget.Clear() method provided by Spire.PDF for Python helps you to complete the task of removing each annotation from a page. This part will demonstrate how to delete all annotations from a page in Python with a detailed guide and a code example.
Steps to delete all annotations from a page:
- Create an instance of the PdfDocument class.
- Read the PDF document from the disk by PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove annotations on the page using Pages.AnnotationsWidget.Clear() method.
- Write the document to disk with PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
Below is the code example of deleting annotations from the first page:
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a new PDF document
document = PdfDocument()
# Load the file from the disk
document.LoadFromFile("sample1.pdf")
# Remove all annotations from the first page
document.Pages[0].AnnotationsWidget.Clear()
# Save the document
document.SaveToFile("output/delete_annotations_page.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
document.Close()
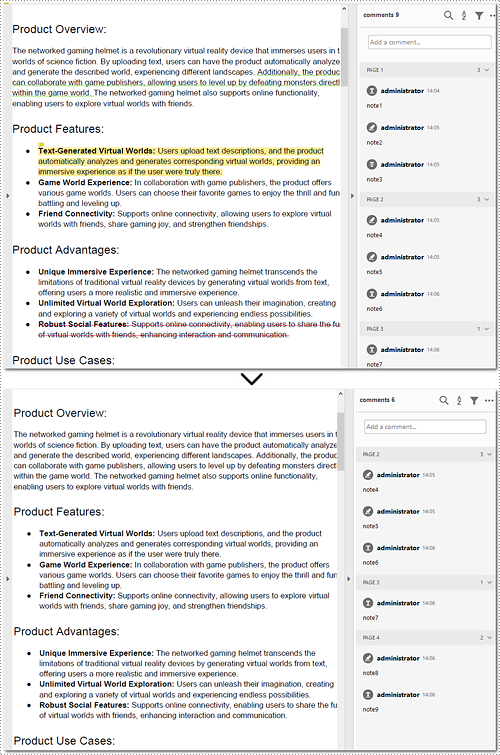
Delete All Annotations of PDF Documents in Python
Removing all annotations from a PDF document involves retrieving the annotations first, which means you need to loop through each page to ensure that every annotation is deleted. The section will introduce how to accomplish the task in Python, providing detailed steps and an example to assist in cleaning up PDF documents.
Steps to remove all annotations of the whole PDF document:
- Instantiate a PdfDocument object.
- Open the document from files using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Loop through pages of the PDF document.
- Get each page of the PDF document with PdfDocument.Pages.get_Item() method.
- Remove all annotations from each page using Page.AnnotationsWidget.Clear() method.
- Save the document to your local file with PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
Here is the example for reference:
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create an object of PDF class
document = PdfDocument()
# Load the file to be operated from the disk
document.LoadFromFile("sample1.pdf")
# Loop through all pages in the PDF document
for i in range(document.Pages.Count):
# Get a specific page
page = document.Pages.get_Item(i)
# Remove all annotations from the page
page.AnnotationsWidget.Clear()
# Save the resulting document
document.SaveToFile("output/delete_all_annotations.pdf", FileFormat.PDF)
document.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Page setup in Excel refers to the various settings that control how an Excel worksheet will be printed or displayed in a print preview. These settings determine the appearance and layout of the printed document, ensuring that it meets the desired formatting and readability standards. Page setup options include page margins, orientation, paper size, print area, headers, footers, scaling, and other print-related settings. In this article, we will explain how to set page setup options in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Set Page Margins in Excel in Python
- Set Page Orientation in Excel in Python
- Set Paper Size in Excel in Python
- Set Print Area in Excel in Python
- Set Scaling Factor in Excel in Python
- Set FitToPages Options in Excel in Python
- Set Headers and Footers in Excel in Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
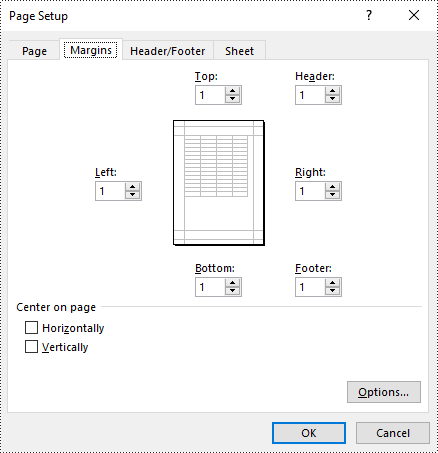
Set Page Margins in Excel in Python
In Spire.XLS for Python, the PageSetup class is used to configure page setup options for Excel worksheets. You can access the PageSetup object of a worksheet through the Worksheet.PageSetup property. Then, you can use properties like PageSetup.TopMargin, PageSetup.BottomMargin, PageSetup.LeftMargin, PageSetup.RightMargin, PageSetup.HeaderMarginInch, and PageSetup.FooterMarginInch to set the respective margins for the worksheet. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using Worksheet.PageSetup property.
- Set the top, bottom, left, right, header, and footer margins using PageSetup.TopMargin, PageSetup.BottomMargin, PageSetup.LeftMargin, PageSetup.RightMargin, PageSetup.HeaderMarginInch, and PageSetup.FooterMarginInch properties.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
pageSetup = sheet.PageSetup
# Set top, bottom, left, and right page margins for the worksheet
# The measure of the unit is Inch (1 inch = 2.54 cm)
pageSetup.TopMargin = 1
pageSetup.BottomMargin = 1
pageSetup.LeftMargin = 1
pageSetup.RightMargin = 1
pageSetup.HeaderMarginInch= 1
pageSetup.FooterMarginInch= 1
# Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("SetPageMargins.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
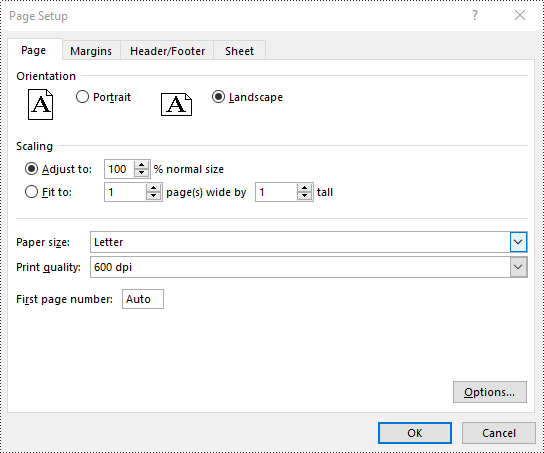
Set Page Orientation in Excel in Python
To set the page orientation for an Excel worksheet, you can use the PageSetup.Orientation property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using Worksheet.PageSetup property.
- Set the page orientation using PageSetup.Orientation property.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
pageSetup = sheet.PageSetup
# Set the page orientation for printing the worksheet to landscape mode
pageSetup.Orientation = PageOrientationType.Landscape
# Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("SetPageOrientation.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Set Paper Size in Excel in Python
You can set a wide range of paper sizes, such as A3, A4, A5, B4, B5, Letter, Legal, and Tabloid for printing an Excel worksheet using the PageSetup.PaperSize property. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using Worksheet.PageSetup property.
- Set the paper size using PageSetup.PaperSize property.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
pageSetup = sheet.PageSetup
# Set the paper size to A4
pageSetup.PaperSize = PaperSizeType.PaperA4
# Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("SetPaperSize.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
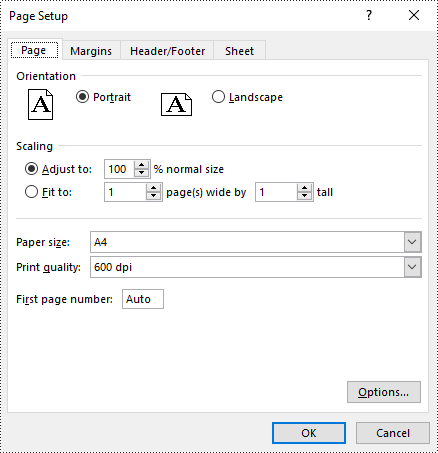
Set Print Area in Excel in Python
The print area of an Excel worksheet can be customized using the PageSetup.PringArea property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using Worksheet.PageSetup property.
- Set the print area using PageSetup.PringArea property.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
pageSetup = sheet.PageSetup
# Set the print area of the worksheet to "A1:E5"
pageSetup.PrintArea = "A1:E5"
# Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("SetPrintArea.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
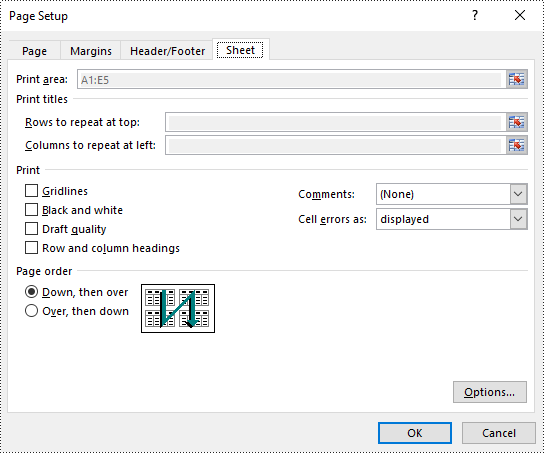
Set Scaling Factor in Excel in Python
You can scale the content of a worksheet to a specific percentage of its original size with the PageSetup.Zoom property. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using Worksheet.PageSetup property.
- Set the scaling factor using PageSetup.Zoom property.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
pageSetup = sheet.PageSetup
# Set the scaling factor of the worksheet to 90%
pageSetup.Zoom = 90
# Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("SetScalingFactor.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
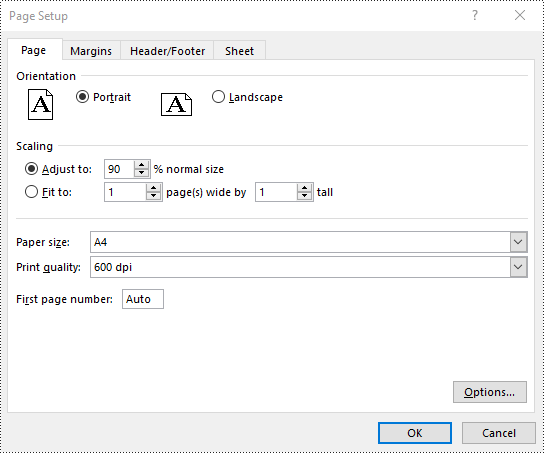
Set FitToPages Options in Excel in Python
In addition to scaling the content of a worksheet to a specific percentage of its original size, you can also fit the content of a worksheet to a specific number of pages using PageSetup.FitToPagesTall and PageSetup.FitToPagesWide properties. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Access the PageSetup object of the worksheet using Worksheet.PageSetup property.
- Fit the content of the worksheet to one page using PageSetup.FitToPagesTall and PageSetup.FitToPagesWide properties.
- Save the modified workbook to a new file using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the PageSetup object of the worksheet
pageSetup = sheet.PageSetup
# Fit the content of the worksheet within one page vertically (i.e., all rows will fit on a single page)
pageSetup.FitToPagesTall = 1
# Fit the content of the worksheet within one page horizontally (i.e., all columns will fit on a single page)
pageSetup.FitToPagesWide = 1
# Save the modified workbook to a new file
workbook.SaveToFile("FitToPages.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Set Headers and Footers in Excel in Python
For setting headers and footers in Excel, please check this article: Python: Add Headers and Footers to Excel.
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Remove Images from Slides and Slide Masters in PowerPoint
2024-07-31 00:55:55 Written by KoohjiRemoving images from slides and slide masters can be essential for many reasons, such as decluttering slides, maintaining uniformity, preparing templates, or modifying a template. Using Python, you can easily handle this task in seconds.
This guide will demonstrate removing images from slides and slide masters in PowerPoint documents in Python with Spire.Presentation for Python. Check this page and make a clean presentation.
- Remove Images from Slides
- Remove Images from Slide Masters
- Remove Specified Images from Slides
- Remove Specified Images from Slide Masters
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install it, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire. Presentation for Python on Windows.
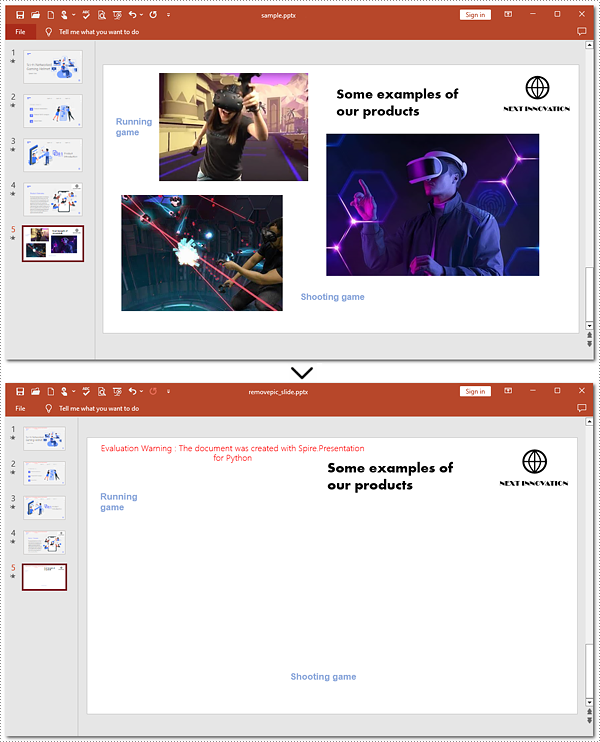
Remove Images from Slides of PowerPoint in Python
Removing images from PowerPoint slides can be efficiently managed using Python. The Presentation.Shapes.RemoveAt() method published by Spire. Presentation for Python allows users to delete pictures from a PowerPoint presentation without effort. The following instructions will guide you through the whole process.
Steps to remove images from a slide:
- Create an object for the Presentation class.
- Load the target PowerPoint document to be operated with the Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the slide that you want to modify using the Presentation.Slides[] property.
- Loop through shapes on the slide.
- Determine if these shapes are images.
- Remove images from the slide using the Presentation.Shapes.RemoveAt() method.
- Save the resulting PowerPoint document with the Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
Here's the code example for reference:
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
ppt = Presentation()
# Load the PowerPoint document to be modified from the disk
ppt.LoadFromFile("sample.pptx")
# Get the fifth slide
slide = ppt.Slides[4]
# Loop through shapes on the slide
for i in range(slide.Shapes.Count - 1, -1, -1):
# Check if those shapes are images
if isinstance(slide.Shapes[i], SlidePicture):
# Remove pictures on the fifth slide
slide.Shapes.RemoveAt(i)
# Save to file
ppt.SaveToFile("removepic_slide.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
# Release the resources
ppt.Dispose()
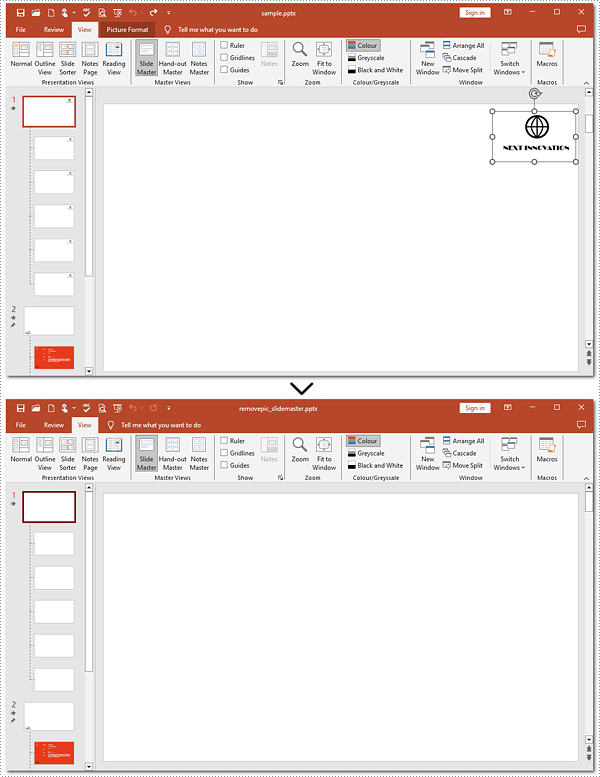
Remove Images from Slide Masters of PowerPoint Using Python
Removing images from slide masters is basically the same as doing that from a slide. To apply this action, you can use Presentation.Shapes.RemoveAt() method provided by Spire.Presentation for Python. Check out the steps below and make a nice and clean presentation.
Steps to remove images from Slide Masters:
- Instantiate a Presentation object.
- Read the PowerPoint document from disk using the Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the second Slide Master with the Presentation.Masters[] property.
- Iterate through images on the second Slide Master.
- Confirm whether these shapes are images.
- Remove images from the second Slide Master using the Shapes.RemoveAt() method.
- Save the modified document with the Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
Here's the code example:
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an instance of the Presentation class
pre = Presentation()
# Open the sample PowerPoint document from the disk
pre.LoadFromFile("sample.pptx")
# Retrieve the first Slide Master
master = pre.Masters[0]
# Loop through shapes on the slide master
for i in range(master.Shapes.Count - 1, -1, -1):
# Check whether these shapes are images
if isinstance(master.Shapes[i], SlidePicture):
# Remove images on the first slide master
master.Shapes.RemoveAt(i)
# Save the generated file
pre.SaveToFile("removepic_slidemaster.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
# Release the resources
pre.Dispose()
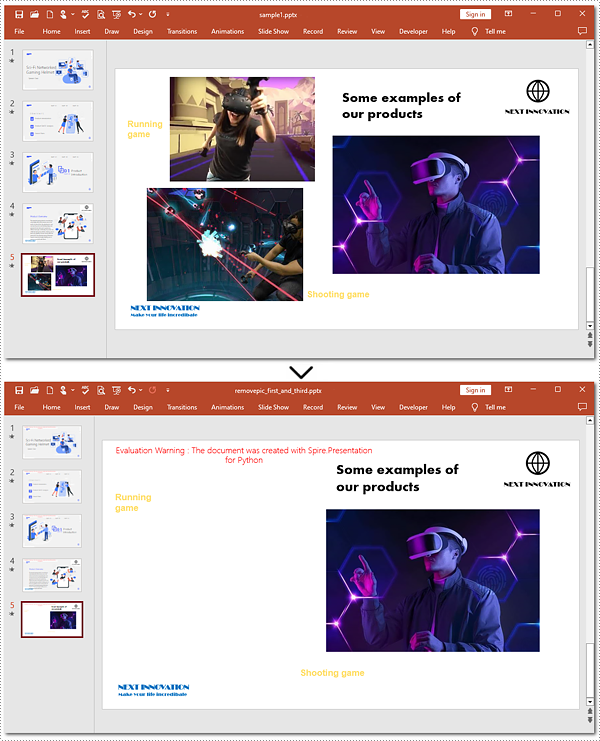
Delete Specified Images from Slides with Python
When working with PowerPoint presentations, you may need to remove specific images from your slides to refine your content. The guide below will walk you through targeting and removing specified images from a slide.
Steps to delete specified images:
- Instantiate an object of the Presentation class.
- Load the target file from the disk with the Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a list to store image indexes.
- Get the 5th slide using the Presentation.Slides[] property.
- Loop through shapes on the slide.
- Verify whether these shapes are images.
- Find the 1st and 3rd pictures.
- Delete these two pictures by the Shapes.RemoveAt() method.
- Save the generated presentation using the Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
Below is the code example to refer to:
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
ppt = Presentation()
# Load the PowerPoint document from the disk
ppt.LoadFromFile("sample1.pptx")
# Create a list to keep track of image indexes to delete
indexes = []
# Get the fifth slide
slide = ppt.Slides[4]
# Iterate through shapes on the slide
image_index = 0
for i in range(slide.Shapes.Count - 1, -1, -1):
# Check if shapes are pictures
if isinstance(slide.Shapes[i], SlidePicture):
image_index += 1
# Record indexes of the first and third images
if image_index in (1, 3):
indexes.append(i)
# Remove the first and third images
for index in indexes:
slide.Shapes.RemoveAt(index)
# Save to file
ppt.SaveToFile("removepic_first_and_third.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
# Release the resources
ppt.Dispose()
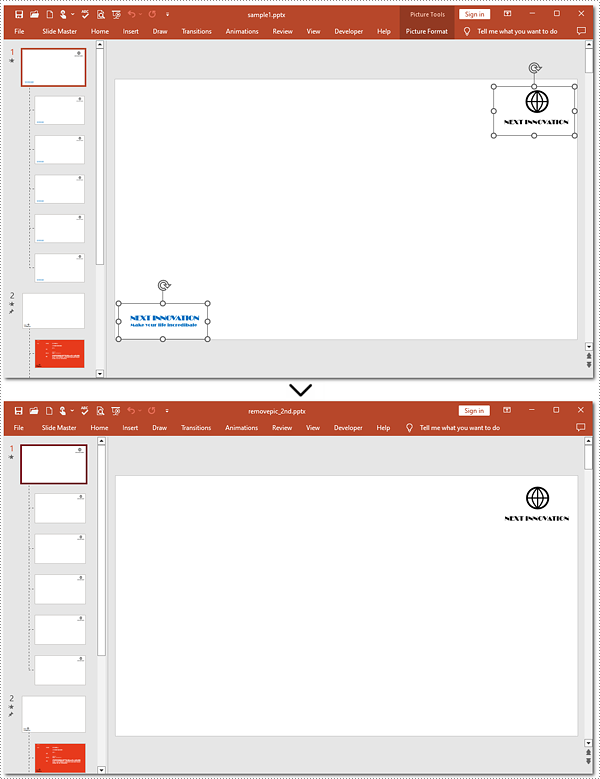
Delete Specified Images from Slide Masters in Python
Shapes.RemoveAt() method also supports removing a specified image from a slide master. To complete the task, you need to target the picture to be deleted. Refer to the detailed steps and a code example to finish the process.
Steps to remove a specified picture from a slide master:
- Create a new object for the Presentation class.
- Read the document from the disk using the Presentation.LoadFromFlie() method.
- Retrieve the 1st slide master by the Presentation.Masters[] property.
- Iterate through shapes on the slide master.
- Check if these shapes are images.
- Remove the 2nd picture with the Shapes.RemoveAt() method.
- Save the resulting presentation to the disk using the Presentation.SaveToFile() method.
Here is the code example:
- Python
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an instance of the Presentation class
pre = Presentation()
# Open the sample PowerPoint document from the disk
pre.LoadFromFile("sample1.pptx")
# Retrieve the first Slide Master
master = pre.Masters[0]
# Loop through the shapes in reverse order
for i in range(master.Shapes.Count - 1, -1, -1):
# Check whether shapes are images
if isinstance(master.Shapes[i], SlidePicture):
# Remove the second image from the slide master
if i == 1:
master.Shapes.RemoveAt(i)
break
# Save the generated file
pre.SaveToFile("removepic_2nd.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
# Release the resources
pre.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
