
Python (355)
Setting the number format for cells in Excel worksheets is crucial for data management and presentation, which enhances readability, ensures consistency, and facilitates accurate data analysis. Proper number formatting allows users to distinguish between different types of numerical data, such as currency, percentages, dates, and scientific notations, making complex datasets more comprehensible at a glance. In this article, we will explore how to automate the process of setting the number format for cells in Excel worksheets with Spire.XLS for Python in Python programs.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Set the Number Format for Cells in Excel Worksheets
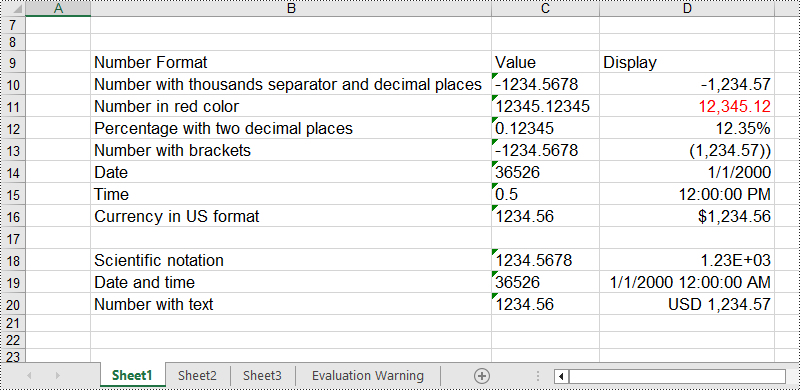
In an Excel workbook, the number format of a cell is determined by its format code. Developers can utilize various symbols in format code to define how numerical data, date and time, currency, etc. are displayed. Below are some commonly used symbols in number format codes:
- #: Represents a digit placeholder that displays only non-zero digits.
- 0: Represents a digit placeholder and always occupies at least one position.
- ; (semicolon): Separates formats for positive numbers, negative numbers, and zero.
- / (slash): In date formats, separates year, month, and day.
- $: Currency symbol, used for representing monetary values, adaptable to system regional settings.
- () (parentheses): Formats negative numbers by enclosing them in parentheses.
- [ ] (square brackets): Utilized in conditional formatting, such as color settings [Red] or conditions like [<=100]"Low";[>100]"High".
Spire.XLS for Python provides the CellRange.NumberValue property to set the number value of a cell and the CellRange.NumberFormat property to set the number format with format code. Below are the steps for setting the number format for cells in Excel worksheets with Python:
- Create an instance of Workbook class to create an Excel workbook.
- Get the first default worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Add text to header row through Worksheet.Range[].Text property.
- Add number value to cells through Worksheet.Range[].NumberValue property and set the number format for the cells with format code through Worksheet.Range[].NumberFormat property.
- Save the Excel workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an instance of Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Set the header row
sheet.Range["B9"].Text = "Number Format"
sheet.Range["C9"].Text = "Value"
sheet.Range["D9"].Text = "Display"
# Number with thousands separator and decimal places
sheet.Range["B10"].Text = "Number with thousands separator and decimal places"
sheet.Range["C10"].Text = "-1234.5678"
sheet.Range["D10"].NumberValue = -1234.5678
sheet.Range["D10"].NumberFormat = "#,##0.00"
# Number in red color
sheet.Range["B11"].Text = "Number in red color"
sheet.Range["C11"].Text = "12345.12345"
sheet.Range["D11"].NumberValue = 12345.12345
sheet.Range["D11"].NumberFormat = "[Red]#,##0.00"
# Percentage with two decimal places
sheet.Range["B12"].Text = "Percentage with two decimal places"
sheet.Range["C12"].Text = "0.12345"
sheet.Range["D12"].NumberValue = 0.12345
sheet.Range["D12"].NumberFormat = "0.00%"
# Number with brackets
sheet.Range["B13"].Text = "Number with brackets"
sheet.Range["C13"].Text = "-1234.5678"
sheet.Range["D13"].NumberValue = -1234.5678
sheet.Range["D13"].NumberFormat = "(#,##0.00;(#,##0.00))"
# Date
sheet.Range["B14"].Text = "Date"
sheet.Range["C14"].Text = "36526"
sheet.Range["D14"].NumberValue = 36526
sheet.Range["D14"].NumberFormat = "m/d/yyyy"
# Time
sheet.Range["B15"].Text = "Time"
sheet.Range["C15"].Text = "0.5"
sheet.Range["D15"].NumberValue = 0.5
sheet.Range["D15"].NumberFormat = "h:mm:ss AM/PM"
# Currency in US format
sheet.Range["B16"].Text = "Currency in US format"
sheet.Range["C16"].Text = "1234.56"
sheet.Range["D16"].NumberValue = 1234.56
sheet.Range["D16"].NumberFormat = "$#,##0.00"
# Scientific notation
sheet.Range["B18"].Text = "Scientific notation"
sheet.Range["C18"].Text = "1234.5678"
sheet.Range["D18"].NumberValue = 1234.5678
sheet.Range["D18"].NumberFormat = "0.00E+00"
# Date and time
sheet.Range["B19"].Text = "Date and time"
sheet.Range["C19"].Text = "36526"
sheet.Range["D19"].NumberValue = 36526
sheet.Range["D19"].NumberFormat = "m/d/yyyy h:mm:ss AM/PM"
# Number with text
sheet.Range["B20"].Text = "Number with text"
sheet.Range["C20"].Text = "1234.56"
sheet.Range["D20"].NumberValue = 1234.5678
sheet.Range["D20"].NumberFormat = "\"USD \"#,##0.00"
# Set the font size and autofit rows and columns
sheet.AllocatedRange.Style.Font.Size = 13
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitRows()
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns()
# Save the file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/SetNumberFormatExcel.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Copying data in Excel is a fundamental feature that allows you to quickly and efficiently reproduce data. It can be especially valuable when building spreadsheets with similar structures, or needing to propagate the same information across multiple areas of your workbook. By mastering the art of copying in Excel, you can boost your productivity and reduce the risk of manual data entry errors. In this article, we will explain how to copy rows, columns and cells in Excel in Python using Spire.XLS for Python.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Copy Rows in Excel in Python
You can use the Worksheet.CopyRow(sourceRow, destSheet, destRowIndex, copyOptions) method provided by Spire.XLS for Python to easily copy a row in the same or between different worksheets in Excel. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the source worksheet and the destination worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get the desired row that you want to copy using the Worksheet.Rows[index] property.
- Copy the row and its format from the source worksheet to the destination worksheet using the Worksheet.CopyRow(sourceRow, destSheet, destRowIndex, copyOptions) method.
- Copy the column widths of cells in the source row to the corresponding cells in the destination row.
- Save the workbook to a file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("ContactList.xlsx")
# Get the source worksheet
sheet1 = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the destination worksheet
sheet2 = workbook.Worksheets[1]
# Get the desired row that you want to copy
row = sheet1.Rows[0]
# Copy the row from the source worksheet to the first row of the destination worksheet
sheet1.CopyRow(row, sheet2, 1, CopyRangeOptions.All)
columns = sheet1.Columns.Length
# Copy the column widths of the cells in the source row to the corresponding cells in the destination row
for i in range(columns):
column_width = row.Columns[i].ColumnWidth
sheet2.Rows[0].Columns[i].ColumnWidth = column_width
# Save the workbook to a file
workbook.SaveToFile("CopyRow.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Copy Columns in Excel in Python
To copy a column in an Excel worksheet, you can use the Worksheet.CopyColumn(sourceColumn, destSheet, destColIndex, copyOptions) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the source worksheet and the destination worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get the desired column that you want to copy using the Worksheet.Columns[index] property.
- Copy the column and its format from the source worksheet to the destination worksheet using the Worksheet.CopyColumn(sourceColumn, destSheet, destColIndex, copyOptions) method.
- Copy the row heights of cells in the source column to the corresponding cells in the destination column.
- Save the workbook to a file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("ContactList.xlsx")
# Get the source worksheet
sheet1 = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the destination worksheet
sheet2 = workbook.Worksheets[1]
# Get the desired column that you want to copy
column = sheet1.Columns[0]
# Copy the column from the source worksheet to the first column of the destination worksheet
sheet1.CopyColumn(column, sheet2, 1, CopyRangeOptions.All)
rows = column.Rows.Length
# Copy the row heights of cells in the source column to the corresponding cells in the destination column
for i in range(rows):
row_height = column.Rows[i].RowHeight
sheet2.Columns[0].Rows[i].RowHeight = row_height
# Save the workbook to a file
workbook.SaveToFile("CopyColumn.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Copy Cells in Excel in Python
In addition to copying entire rows and columns, you are also able to copy an individual cell or a range of cells using the CellRange.Copy(destRange, copyOptions) method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using the Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the source worksheet and the destination worksheet using the Workbook.Worksheets[index] property.
- Get the source cell range and the destination cell range using the Worksheet.Range[] property.
- Copy the source cell range and its format from the source worksheet to the destination cell range in the destination worksheet using the CellRange.Copy(destRange, copyOptions) method.
- Copy the row heights and column widths of the source cell range to the destination cell range.
- Save the workbook to a file using the Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("ContactList.xlsx")
# Get the source worksheet
sheet1 = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get the destination worksheet
sheet2 = workbook.Worksheets[1]
# Get the source cell range
range1 = sheet1.Range["A1:E7"]
# Get the destination cell range
range2 = sheet2.Range["A1:E7"]
# Copy the source cell range from the source worksheet to the destination cell range in the destination worksheet
range1.Copy(range2, CopyRangeOptions.All)
# Copy the row heights and column widths of the source cell range to the destination cell range
for i, row in enumerate(range1.Rows):
for j, column in enumerate(row.Columns):
range2.Rows[i].Columns[j].ColumnWidth = column.ColumnWidth
range2.Rows[i].RowHeight = row.RowHeight
# Save the workbook to a file
workbook.SaveToFile("CopyCells.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Tables are a powerful formatting tool in Word, allowing you to organize and present data effectively. However, the default table borders may not always align with your document's style and purpose. By selectively changing or removing the borders, you can achieve a variety of visual effects to suit your requirements. In this article, we will explore how to change and remove borders for tables in Word documents in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python. It can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Change Borders for a Table in Word in Python
Spire.Doc for Python empowers you to retrieve the borders collection of a table by using the Table.TableFormat.Borders property. Once retrieved, you can access individual borders (like top border, bottom border, left border, right border, horizontal border, and vertical border) from the collection and then modify them by adjusting their line style, width, and color. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific section using Document.Sections[index] property.
- Get a specific table using Section.Tables[index] property.
- Get the borders collection of the table using Table.TableFormat.Borders property.
- Get an individual border, such as the top border from the borders collection using Borders.Top property, and then change its line style, width and color.
- Refer to the above step to get other individual borders from the borders collection, and then change their line style, width and color.
- Save the resulting document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of the Document class
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Table.docx")
# Add a section to the document
section = document.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get the first table in the section
table = section.Tables.get_Item(0) if isinstance(section.Tables.get_Item(0), Table) else None
# Get the collection of the borders
borders = table.TableFormat.Borders
# Get the top border and change border style, line width, and color
topBorder = borders.Top
topBorder.BorderType = BorderStyle.Single
topBorder.LineWidth = 1.0
topBorder.Color = Color.get_YellowGreen()
# Get the left border and change border style, line width, and color
leftBorder = borders.Left
leftBorder.BorderType = BorderStyle.Single
leftBorder.LineWidth = 1.0
leftBorder.Color = Color.get_YellowGreen()
# Get the right border and change border style, line width, and color
rightBorder = borders.Right
rightBorder.BorderType = BorderStyle.Single
rightBorder.LineWidth = 1.0
rightBorder.Color = Color.get_YellowGreen()
# Get the bottom border and change border style, line width, and color
bottomBorder = borders.Bottom
bottomBorder.BorderType = BorderStyle.Single
bottomBorder.LineWidth = 1.0
bottomBorder.Color = Color.get_YellowGreen()
# Get the horizontal border and change border style, line width, and color
horizontalBorder = borders.Horizontal
horizontalBorder.BorderType = BorderStyle.Dot
horizontalBorder.LineWidth = 1.0
horizontalBorder.Color = Color.get_Orange()
# Get the vertical border and change border style, line width, and color
verticalBorder = borders.Vertical
verticalBorder.BorderType = BorderStyle.Dot
verticalBorder.LineWidth = 1.0
verticalBorder.Color = Color.get_CornflowerBlue()
# Save the resulting document
document.SaveToFile("ChangeBorders.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
document.Close()
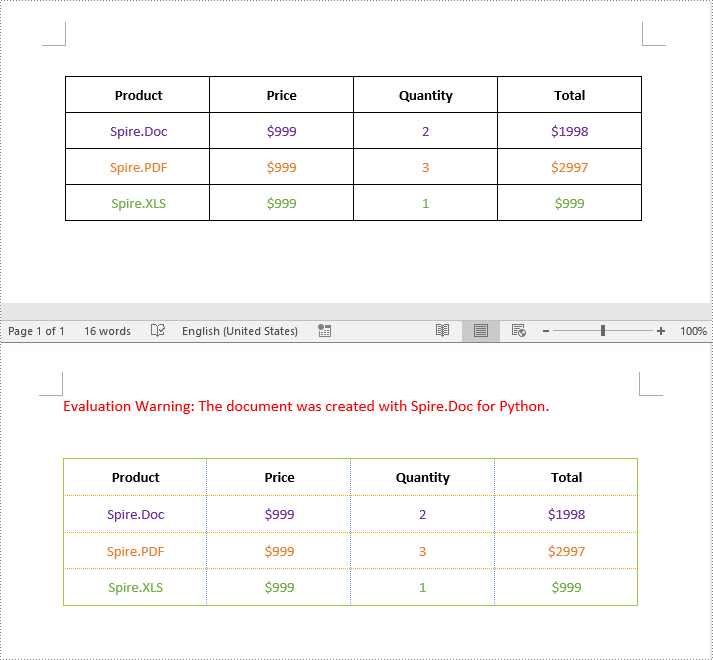
Remove Borders from a Table in Word in Python
To remove borders from a table, you need to set the BorderType property of the borders to BorderStyle.none. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific section using Document.Sections[index] property.
- Get a specific table using Section.Tables[index] property.
- Get the borders collection of the table using Table.TableFormat.Borders property.
- Get an individual border, such as the top border from the borders collection using Borders.Top property. Then set the BorderType property of the top border to BorderStyle.none.
- Refer to the above step to get other individual borders from the borders collection and then set the BorderType property of the borders to BorderStyle.none.
- Save the resulting document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Initialize an instance of the Document class
document = Document()
document.LoadFromFile("ChangeBorders.docx")
# Add a section to the document
section = document.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Get the first table in the section
table = section.Tables.get_Item(0) if isinstance(section.Tables.get_Item(0), Table) else None
# Get the borders collection of the table
borders = table.TableFormat.Borders
# Remove top border
topBorder = borders.Top
topBorder.BorderType = BorderStyle.none
# Remove left border
leftBorder = borders.Left
leftBorder.BorderType = BorderStyle.none
# Remove right border
rightBorder = borders.Right
rightBorder.BorderType = BorderStyle.none
# Remove bottom border
bottomBorder = borders.Bottom
bottomBorder.BorderType = BorderStyle.none
# remove inside horizontal border
horizontalBorder = borders.Horizontal
horizontalBorder.BorderType = BorderStyle.none
# Remove inside vertical border
verticalBorder = borders.Vertical
verticalBorder.BorderType = BorderStyle.none
# Save the resulting document
document.SaveToFile("RemoveBorders.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
document.Close()
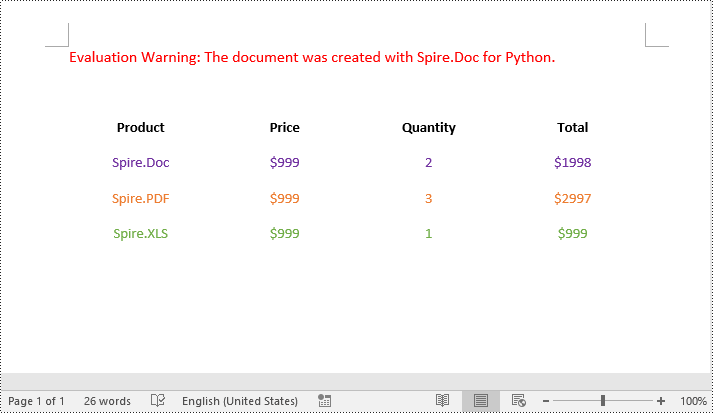
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
PowerPoint presentations often serve as repositories of essential data and information shared during meetings, lectures, and conferences. They frequently include tables for data presentation and basic analysis. However, to further analyze the data or integrate it into reports and spreadsheets, it becomes necessary to extract these tables and save them in other formats. By leveraging Python, users can efficiently extract tables from PowerPoint presentations, transforming static slides into dynamic data sets ready for processing.
This article aims to demonstrate how to extract tables from PowerPoint presentations and write them to text and Excel worksheets using Spire.Presentation for Python, thereby enhancing the utilization of data in presentations and streamlining the data extraction process.
- Extract Table Data from PowerPoint Presentations to Text Files
- Extract Table Data from PowerPoint Presentations to Excel Worksheets
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
Extract Table Data from PowerPoint Presentations to Text Files
Spire.Presentation for Python provides the ITable class which represents a table in a presentation slide. By iterating through the shapes in each slide to check if it’s an instance of ITable class, developers can retrieve all the tables in the presentation file and get the data in the tables.
The detailed steps for extracting tables from PowerPoint presentations and writing them to text files are as follows:
- Create an instance of Presentation class and load a PowerPoint file using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Iterate through all the slides in the file and then all the shapes in the slides.
- Check if a shape is an instance of ITable class. If it is, iterate through the rows and then the cells in each row. Get the cell values using TableRow[].TextFrame.Text property and append them to strings.
- Write the table data to text files.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
from spire.presentation.common import *
# Create an instance of Presentation
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint file
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
tables = []
# Iterate through all the slides
for slide in presentation.Slides:
# Iterate through all the shapes
for shape in slide.Shapes:
# Check whether the shape is a table
if isinstance(shape, ITable):
tableData = ""
# Iterate through all the rows
for row in shape.TableRows:
rowData = ""
# Iterate through all the cells in the row
for i in range(0, row.Count):
# Get the cell value
cellValue = row[i].TextFrame.Text
rowData += (cellValue + "\t" if i < row.Count - 1 else cellValue)
tableData += (rowData + "\n")
tables.append(tableData)
# Write the tables to text files
for idx, table in enumerate(tables, start=1):
fileName = f"output/Tables/Table-{idx}.txt"
with open(fileName, "w") as f:
f.write(table)
presentation.Dispose()
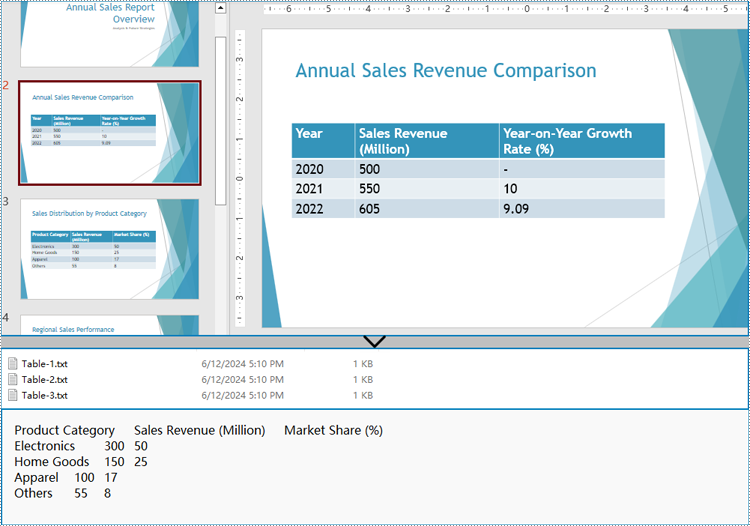
Extract Table Data from PowerPoint Presentations to Excel Worksheets
After extracting table data from presentations using Spire.Presentation for Python, developers can further utilize Spire.XLS for Python to write this data into Excel worksheets, facilitating further analysis, referencing, and format conversion.
Install Spire.XLS for Python via PyPI:
pip install Spire.XLS
The detailed steps for extracting tables from PowerPoint presentations and writing them to Excel worksheets are as follows:
- Create an instance of Presentation class and load a PowerPoint file using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create an instance of Workbook class and clear the default worksheets.
- Iterate through the slides in the presentation and then the shapes in the slides to check if the shapes are instances of ITable class. Append all the ITable instances to a list.
- Iterate through the tables in the list and add a worksheet to the workbook for each table using Workbook.Worksheets.Add() method.
- Iterate through the rows of each table and then the cells in the rows to get the cell values through TableRow.TextFrame.Text property. Write the values to the corresponding cells in the worksheet through Worksheet.Range[].Value property.
- Save the workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
from spire.presentation.common import *
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an instance of Presentation
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint file
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Create an Excel file and clear the default worksheets
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.Worksheets.Clear()
tables = []
# Iterate through all the slides
for slide in presentation.Slides:
# Iterate through all the shapes
for shape in slide.Shapes:
# Check whether the shape is a table
if isinstance(shape, ITable):
tables.append(shape)
# Iterate through all the tables
for t in range(len(tables)):
table = tables[t]
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add(f"Sheet-{t+1}")
for i in range(0, table.TableRows.Count):
row = table.TableRows[i]
for j in range(0, row.Count):
sheet.Range[i + 1, j + 1].Value = row[j].TextFrame.Text
# Autofit rows and columns
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns()
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitRows()
# Save the Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/PresentationTables.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
presentation.Dispose()
workbook.Dispose()
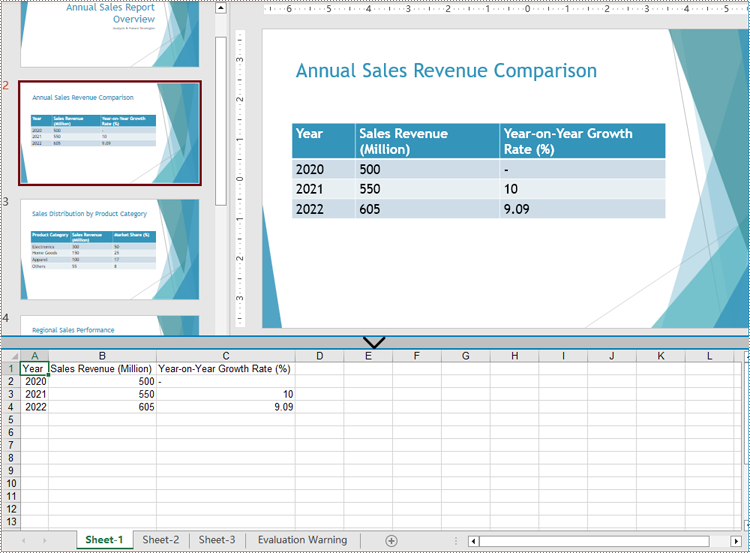
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Python: Count Words, Pages, Characters, Paragraphs and Lines in Word
2024-06-17 01:10:38 Written by AdministratorVarious written documents, such as academic papers, reports, and legal materials, often have specific formatting guidelines that encompass word count, page count, and other essential metrics. Accurately measuring these elements is crucial as it ensures that your document adheres to the required standards and meets the expected quality benchmarks. In this article, we will explain how to count words, pages, characters, paragraphs, and lines in a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Count Words, Pages, Characters, Paragraphs, and Lines in a Word Document in Python
- Count Words and Characters in a Specific Paragraph of a Word Document in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python. It can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Count Words, Pages, Characters, Paragraphs, and Lines in a Word Document in Python
Spire.Doc for Python offers the BuiltinDocumentProperties class that empowers you to retrieve crucial information from your Word document. By utilizing this class, you can access a wealth of details, including the built-in document properties, as well as the number of words, pages, characters, paragraphs, and lines contained within the document.
The steps below explain how to get the number of words, pages, characters, paragraphs, and lines in a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python:
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the BuiltinDocumentProperties object using the Document.BuiltinDocumentProperties property.
- Get the number of words, characters, paragraphs, lines, and pages in the document using the WordCount, CharCount, ParagraphCount, LinesCount, PageCount properties of the BuiltinDocumentProperties class, and append the result to a list.
- Write the content of the list into a text file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of the Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc = Document("Input.docx")
# Create a list
sb = []
# Get the built-in properties of the document
properties = doc.BuiltinDocumentProperties
# Get the number of words, characters, paragraphs, lines, and pages and append the result to the list
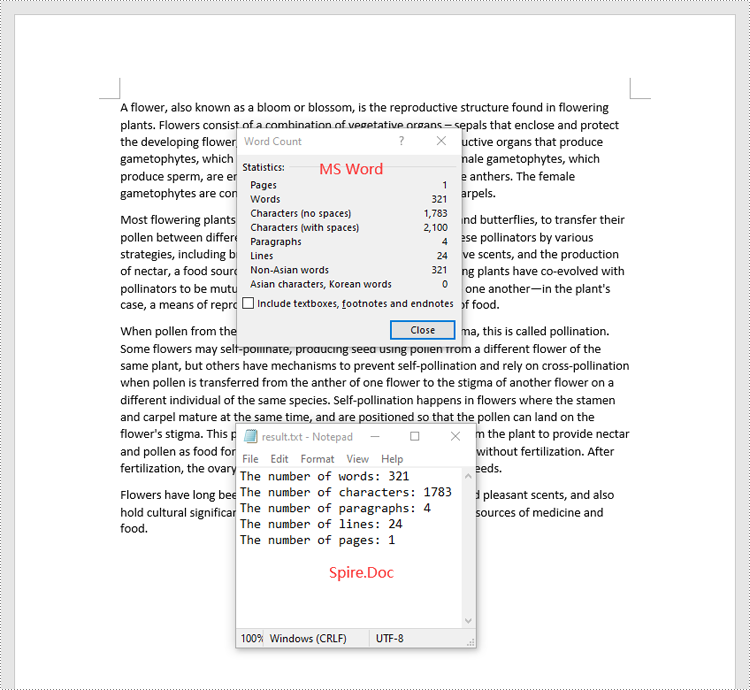
sb.append("The number of words: " + str(properties.WordCount))
sb.append("The number of characters: " + str(properties.CharCount))
sb.append("The number of paragraphs: " + str(properties.ParagraphCount))
sb.append("The number of lines: " + str(properties.LinesCount))
sb.append("The number of pages: " + str(properties.PageCount))
# Save the data in the list to a text file
with open("result.txt", "w") as file:
file.write("\n".join(sb))
doc.Close()
Count Words and Characters in a Specific Paragraph of a Word Document in Python
In addition to retrieving the overall word count, page count, and other metrics for an entire Word document, you are also able to get the word count and character count for a specific paragraph by using the Paragraph.WordCount and Paragraph.CharCount properties.
The steps below explain how to get the number of words and characters of a paragraph in a Word document in Python using Spire.Doc for Python:
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific paragraph using the Document.Sections[sectionIndex].Paragraphs[paragraphIndex] property.
- Get the number of words and characters in the paragraph using the Paragraph.WordCount and Paragraph.CharCount properties, and append the result to a list.
- Write the content of the list into a text file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of the Document class
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc = Document("Input.docx")
# Get a specific paragraph
paragraph = doc.Sections.get_Item(0).Paragraphs.get_Item(0)
# Create a list
sb = []
# Get the number of words and characters in the paragraph and append the result to the list
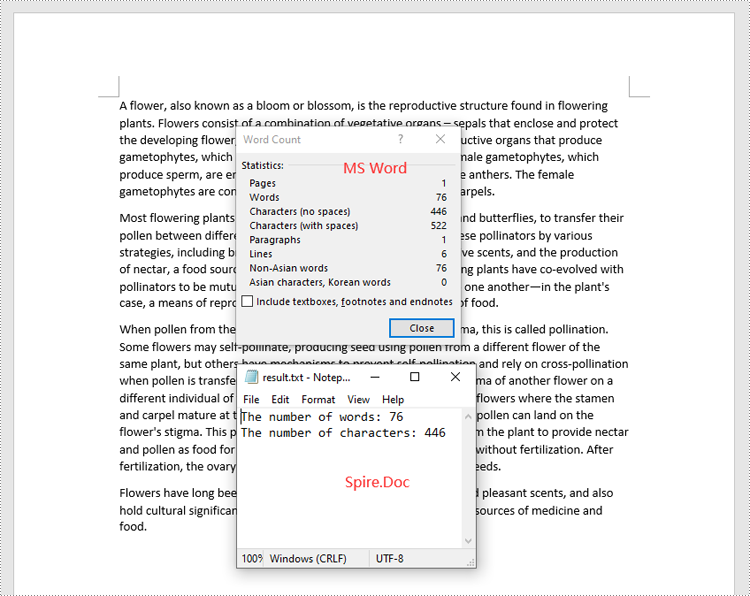
sb.append("The number of words: " + str(paragraph.WordCount))
sb.append("The number of characters: " + str(paragraph.CharCount))
# Save the data in the list to a text file
with open("result.txt", "w") as file:
file.write("\n".join(sb))
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
When dealing with a large volume of customized documents such as contracts, reports, or personal letters, the variable feature in Word documents becomes crucial. Variables allow you to store and reuse information like dates, names, or product details, making the documents more personalized and dynamic. This article will delve into how to use Spire.Doc for Python to insert, count, retrieve, and delete variables in Word documents, enhancing the efficiency and flexibility of document management.
- Add Variables into Word Documents
- Count the Number of Variables in a Word Document
- Retrieve Variables from a Word Document
- Delete Variables from a Word Document
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Window through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Window
Add Variables into Word Documents with Python
The way Word variables work is based on the concept of "fields". When you insert a variable into a Word document, what you're actually doing is inserting a field, which points to a value stored either in the document properties or an external data source. Upon updating the fields, Word recalculates them to display the most current information.
Spire.Doc for Python offers the VariableCollection.Add(name, value) method to insert variables into Word documents. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Call the Document.AddSection() method to create a new section.
- Call the Section.AddParagraph() method to create a new paragraph.
- Call the Paragraph.AppendField(fieldName, fieldType) method to add a variable field (FieldDocVariable) within the paragraph.
- Set Document.IsUpdateFields to True to update the fields.
- Save the document by Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Add a new section to the document
section = document.AddSection()
# Add a new paragraph within the newly created section
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
# Append a FieldDocVariable type field named "CompanyName" to the paragraph
paragraph.AppendField("CompanyName", FieldType.FieldDocVariable)
# Add the variable to the document's variable collection
document.Variables.Add("CompanyName", "E-ICEBLUE")
# Update fields
document.IsUpdateFields = True
# Save the document to a specified path
document.SaveToFile("AddVariable.docx", FileFormat.Docx2016)
# Dispose the document
document.Dispose()

Count the Number of Variables in a Word Document with Python
Here are the detailed steps to use the Document.Variables.Count property to get the number of variables:
- Create a Document object.
- Call the Document.LoadFromFile() method to load the document that contains the variables.
- Use the Document.Variables.Count property to obtain the number of variables.
- Print the count in console.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load an existing document
document.LoadFromFile("AddVariable.docx")
# Get the count of variables in the document
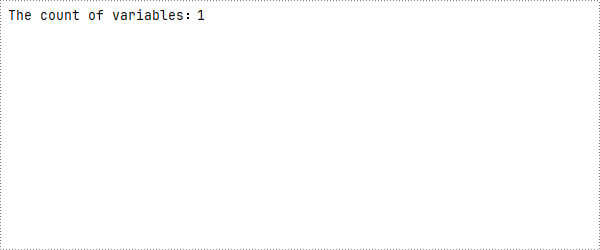
count=document.Variables.Count
# Print to console
print(f"The count of variables:{count}")
Retrieve Variables from a Word Document with Python
Spire.Doc for Python provides the GetNameByIndex(int index) and GetValueByIndex(int index) methods to retrieve variable names and values by their indices. Below are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document object.
- Call the Document.LoadFromFile() method to load the document that contains the variables.
- Call the Document.Variables.GetNameByIndex(index) method to obtain the variable name.
- Call the Document.Variables.GetValueByIndex(index) method to obtain the variable value.
- Call the Document.Variables.get_Item(name) to obtain variable value through the variable name.
- Print the count in console.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load an existing document
document.LoadFromFile("AddVariable.docx")
# Obtain variable name based on index 0
name=document.Variables.GetNameByIndex(0)
# Obtain variable value based on index 0
value=document.Variables.GetValueByIndex(0)
# Obtain variable value through the variable name
value1=document.Variables.get_Item("CompanyName")
# Print to console
print("Variable Name:", name)
print("Variable Value:", value)

Delete Variables from a Word Document with Python
The VariableCollection.Remove(name) method can be used to delete a specified variable from the document, with the parameter being the name of the variable.
- Create a Document object.
- Call the Document.LoadFromFile() method to load the document that contains the variables.
- Call the Document.Variables.Remove(name) method to remove the variable.
- Set Document.IsUpdateFields to True to update the fields.
- Save the document by Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load an existing document
document.LoadFromFile("AddVariable.docx")
# Remove the variable named "CompanyName"
document.Variables.Remove("CompanyName")
# Update fields
document.IsUpdateFields=True
# Save the document
document.SaveToFile("RemoveVariable.docx",FileFormat.Docx2016)
# Dispose the document
document.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Spire.Doc for Python is a robust library that enables you to read and write Microsoft Word documents using Python. With Spire.Doc, you can create, read, edit, and convert both DOC and DOCX file formats without requiring Microsoft Word to be installed on your system.
This article demonstrates how to install Spire.Doc for Python on Mac.
Step 1
Download the most recent version of Python for macOS and install it on your Mac. If you have already completed this step, proceed directly to step 2.
Step 2
Open VS Code and search for 'Python' in the Extensions panel. Click 'Install' to add support for Python in your VS Code.
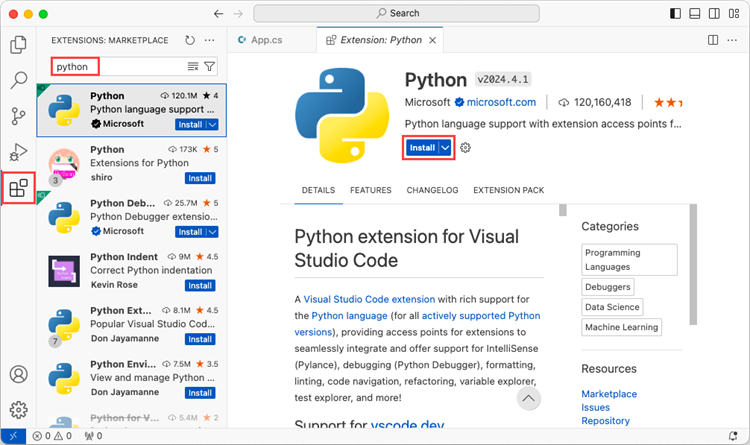
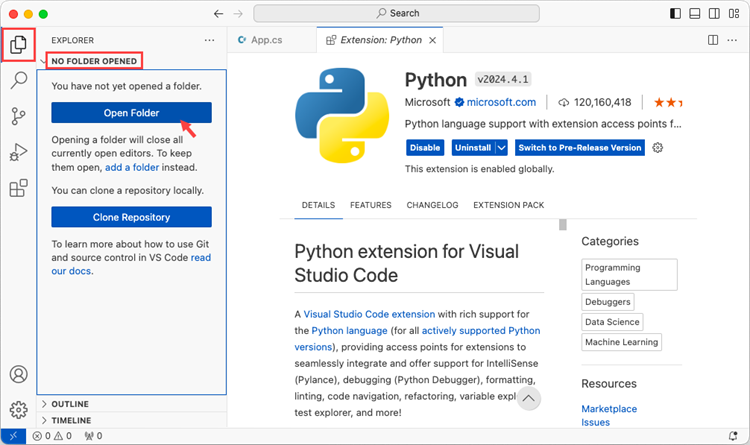
Step 3
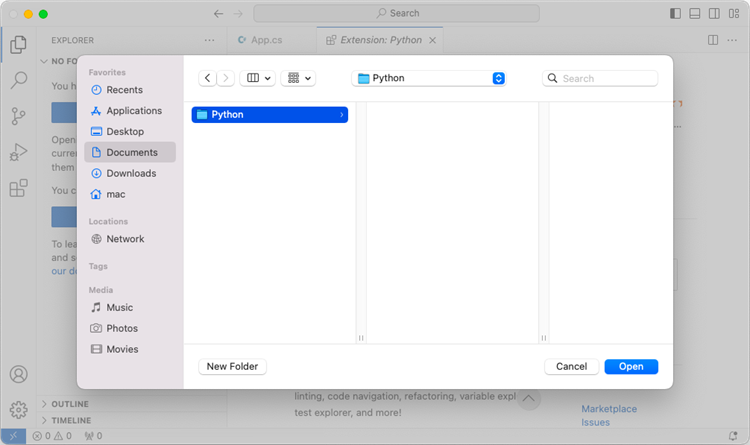
Click 'Explorer' > 'NO FOLRDER OPENED' > 'Open Folder'.
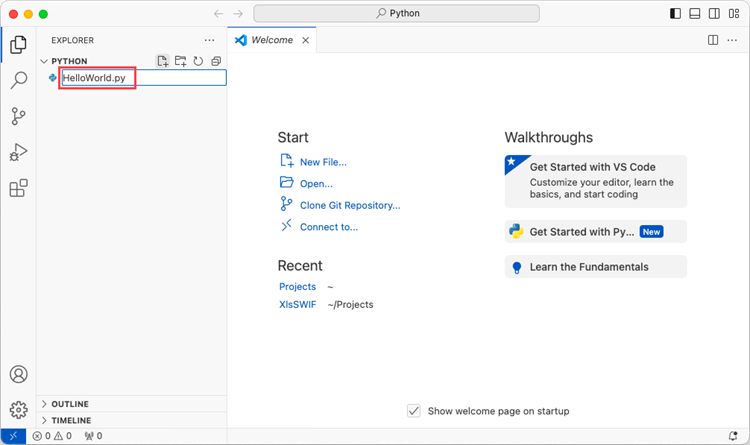
Choose an existing folder as the workspace, or you can create a new folder and then open it.
Add a .py file to the folder you just opened and name it whatever you want (in this case, HelloWorld.py).
Step 4
Use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + ' to open the Terminal. Then, install Spire.Doc for Python by entering the following command line in the terminal.
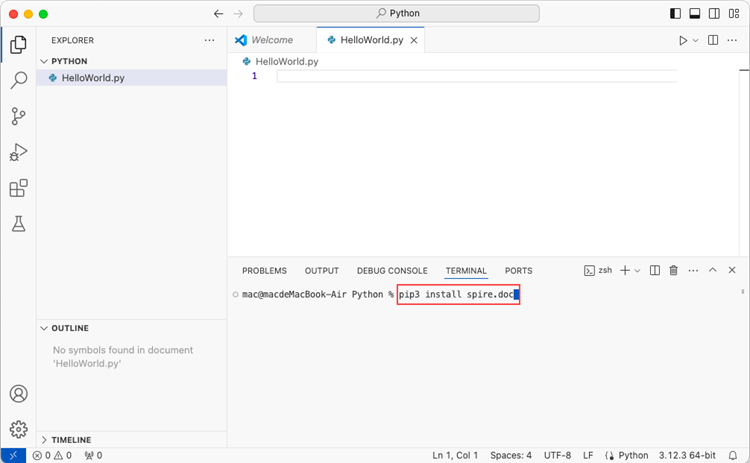
pip3 install spire.doc
Note that pip3 is a package installer specifically designed for Python 3.x versions, while pip is a package installer for Python 2.x versions. If you are working with Python 2.x, you can use the pip command.
Step 5
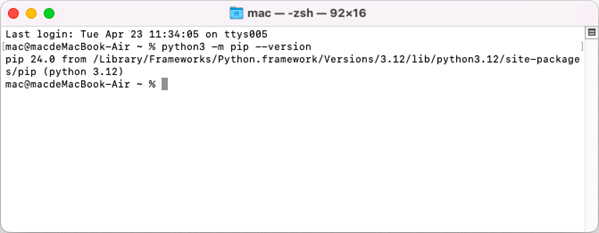
Open a Terminal window on your Mac, and type the following command to obtain the installation path of Python on your system.
python3 -m pip --version
Step 6
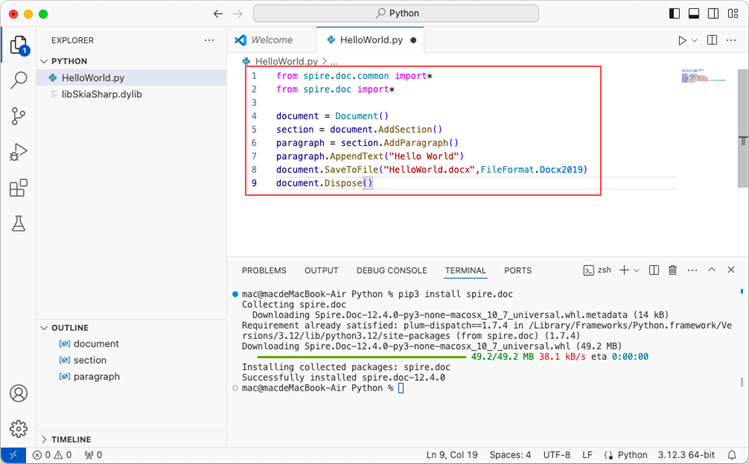
Add the following code snippet to the 'HelloWorld.py' file.
- Python
from spire.doc.common import *
from spire.doc import *
document = Document()
section = document.AddSection()
paragraph = section.AddParagraph()
paragraph.AppendText("Hello World")
document.SaveToFile("HelloWorld.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019)
document.Dispose()
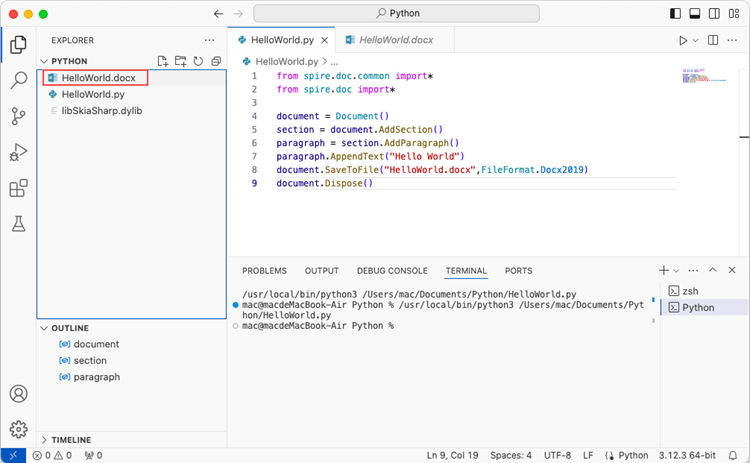
After executing the Python file, you will find the resulting Word document in the 'EXPLORER' panel.
Section breaks in Word allow users to divide a document into sections, each with unique formatting options. This is especially useful when working with long documents where you want to apply different layouts, headers, footers, margins or page orientations within the same document. In this article, you will learn how to insert or remove section breaks in Word in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Insert Section Breaks in Word in Python
Spire.Doc for Python provides the Paragraph.InsertSectionBreak(breakType: SectionBreakType) method to insert a specified type of section break to a paragraph. The following table provides an overview of the supported section break types, along with their corresponding Enums and descriptions:
| Section Break | Enum | Description |
| New page | SectionBreakType.New_Page | Start the new section on a new page. |
| Continuous | SectionBreakType.No_Break | Start the new section on the same page, allowing for continuous content flow. |
| Odd page | SectionBreakType.Odd_Page | Start the new section on the next odd-numbered page. |
| Even page | SectionBreakType.Even_Page | Start the new section on the next even-numbered page. |
| New column | SectionBreakType.New_Column | Start the new section in the next column if columns are enabled. |
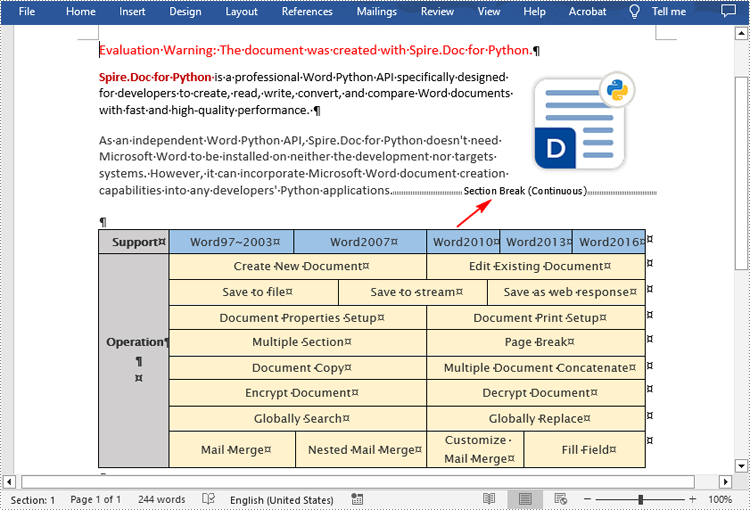
The following are the detailed steps to insert a continuous section break:
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section using Document.Sections[] property.
- Get a specified paragraph of the section using Section.Paragraphs[] property.
- Add a section break to the end of the paragraph using Paragraph.InsertSectionBreak() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import * from spire.doc.common import * inputFile = "sample.docx" outputFile = "InsertSectionBreak.docx" # Create a Document instance document = Document() # Load a Word document document.LoadFromFile(inputFile) # Get a specific section section = document.Sections.get_Item(0) # Get a specific paragraph paragraph = section.Paragraphs.get_Item(0) # Insert a continuous section break paragraph.InsertSectionBreak(SectionBreakType.NoBreak) # Save the result document document.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx2016) document.Close()
Remove Section Breaks in Word in Python
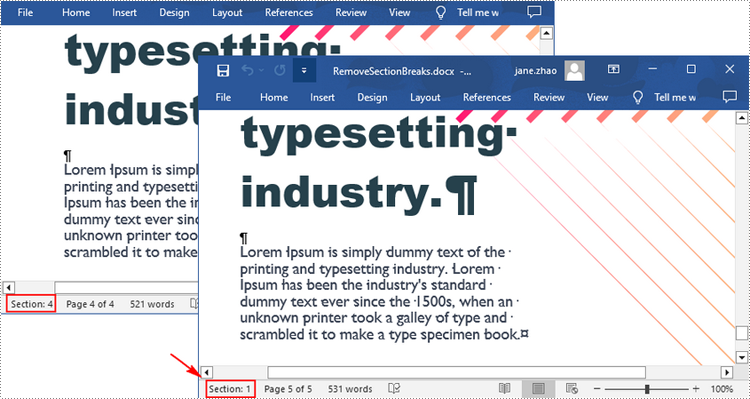
To delete all sections breaks in a Word document, we need to access the first section in the document, then copy the contents of the other sections to the first section and delete them. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the first section using Document.Sections[] property.
- Iterate through other sections in the document.
- Get the second section, and then iterate through to get its child objects.
- Clone the child objects of the second section and add them to the first section using Section.Body.ChildObjects.Add() method.
- Delete the second section using Document.Sections.Remove() method.
- Repeat the process to copy and delete the remaining sections.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
inputFile = "Report.docx"
outputFile = "RemoveSectionBreaks.docx"
# Create a Document instance
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get a specific section
section = document.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Iterate through other sections in the document
for i in range(document.Sections.Count - 1):
# Get the second section in the document
section = document.Sections[1]
# Iterate through all child objects of the second section
for j in range(section.Body.ChildObjects.Count):
# Get the child objects
obj = section.Body.ChildObjects.get_Item(j)
# Clone the child objects to the first section
sec.Body.ChildObjects.Add(obj.Clone())
# Remove the second section
document.Sections.Remove(section)
# Save the result document
document.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx2016)
document.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Knowing how to remove headers or footers in Word is an essential skill as there may be times you need to change the formatting of your document or collaborate with others who do not need the headers or footers. In this article, you will learn how to remove headers or footers in Word in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
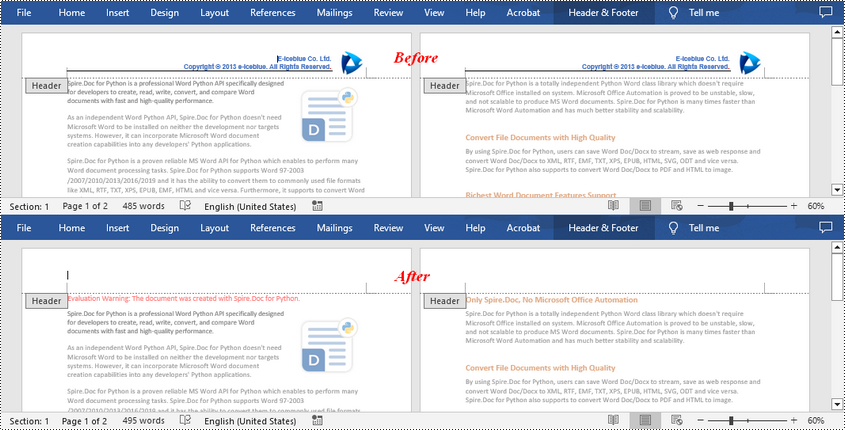
Remove Headers in a Word Document in Python
Spire.Doc for Python supports getting different headers in the first pages, odd pages, and even pages, and then delete all of them through the HeaderFooter.ChildObjects.Clear() method. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section using Document.Sections[] property.
- Iterate through all paragraphs in the section, and then all child objects in each paragraph.
- Get the headers for the first, odd, and even pages using Section.HeadersFooters[hfType: HeaderFooterType] property, and then delete them using HeaderFooter.ChildObjects.Clear() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
inputFile = "HeaderFooter.docx"
outputFile = "RemoveHeaders.docx"
# Create a Document instance
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get the first section
section = doc.Sections[0]
# Iterate through all paragraphs in the section
for i in range(section.Paragraphs.Count):
para = section.Paragraphs.get_Item(i)
# Iterate through all child objects in each paragraph
for j in range(para.ChildObjects.Count):
obj = para.ChildObjects.get_Item(j)
# Delete header in the first page
header = None
header = section.HeadersFooters[HeaderFooterType.HeaderFirstPage]
if header is not None:
header.ChildObjects.Clear()
# Delete headers in the odd pages
header = section.HeadersFooters[HeaderFooterType.HeaderOdd]
if header is not None:
header.ChildObjects.Clear()
# Delete headers in the even pages
header = section.HeadersFooters[HeaderFooterType.HeaderEven]
if header is not None:
header.ChildObjects.Clear()
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
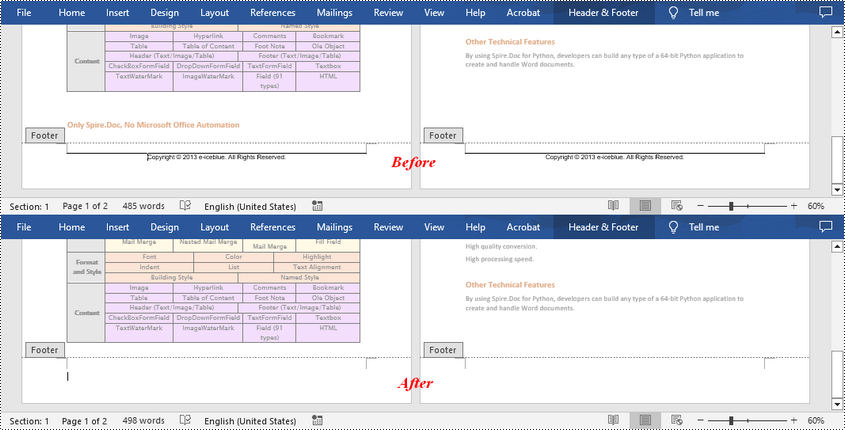
Remove Footers in a Word Document in Python
Deleting footers is similar to that of deleting headers, you can also get the footers on different pages first and then delete them at once. The following are the detailed steps:
- Create a Document instance.
- Load a Word document using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified section using Document.Sections[] property.
- Iterate through all paragraphs in the section, and then all child objects in each paragraph.
- Get the footers for the first, odd, and even pages using Section.HeadersFooters[hfType: HeaderFooterType] property, and then delete them using HeaderFooter.ChildObjects.Clear() method.
- Save the result document using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
inputFile = "HeaderFooter.docx"
outputFile = "RemoveFooters.docx"
# Create a Document instance
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile(inputFile)
# Get the first section
section = doc.Sections[0]
# Iterate through all paragraphs in the section
for i in range(section.Paragraphs.Count):
para = section.Paragraphs.get_Item(i)
# Iterate through all child objects in each paragraph
for j in range(para.ChildObjects.Count):
obj = para.ChildObjects.get_Item(j)
# Delete footer in the first page
footer = None
footer = section.HeadersFooters[HeaderFooterType.FooterFirstPage]
if footer is not None:
footer.ChildObjects.Clear()
# Delete footers in the odd pages
footer = section.HeadersFooters[HeaderFooterType.FooterOdd]
if footer is not None:
footer.ChildObjects.Clear()
# Delete footers in the even pages
footer = section.HeadersFooters[HeaderFooterType.FooterEven]
if footer is not None:
footer.ChildObjects.Clear()
# Save the result document
doc.SaveToFile(outputFile, FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Comments in Word documents are often used for collaborative review and feedback purposes. They may contain text and images that provide valuable information to guide document improvements. Extracting the text and images from comments allows you to analyze and evaluate the feedback provided by reviewers, helping you gain a comprehensive understanding of the strengths, weaknesses, and suggestions related to the document. In this article, we will demonstrate how to extract text and images from Word comments in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Extract Text from Word Comments in Python
You can easily retrieve the author and text of a Word comment using the Comment.Format.Author and Comment.Body.Paragraphs[index].Text properties provided by Spire.Doc for Python. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a list to store the extracted comment data.
- Iterate through the comments in the document.
- For each comment, iterate through the paragraphs of the comment body.
- For each paragraph, get the text using the Comment.Body.Paragraphs[index].Text property.
- Get the author of the comment using the Comment.Format.Author property.
- Add the text and author of the comment to the list.
- Save the content of the list to a text file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of the Document class
document = Document()
# Load a Word document containing comments
document.LoadFromFile("Comments.docx")
# Create a list to store the extracted comment data
comments = []
# Iterate through the comments in the document
for i in range(document.Comments.Count):
comment = document.Comments[i]
comment_text = ""
# Iterate through the paragraphs in the comment body
for j in range(comment.Body.Paragraphs.Count):
paragraph = comment.Body.Paragraphs[j]
comment_text += paragraph.Text + "\n"
# Get the comment author
comment_author = comment.Format.Author
# Append the comment data to the list
comments.append({
"author": comment_author,
"text": comment_text
})
# Write the comment data to a file
with open("comment_data.txt", "w", encoding="utf-8") as file:
for comment in comments:
file.write(f"Author: {comment['author']}\nText: {comment['text']}\n\n")
Extract Images from Word Comments in Python
To extract images from Word comments, you need to iterate through the child objects in the paragraphs of the comments to find the DocPicture objects, then get the image data using DocPicture.ImageBytes property, finally save the image data to image files.
- Create an object of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Create a list to store the extracted image data.
- Iterate through the comments in the document.
- For each comment, iterate through the paragraphs of the comment body.
- For each paragraph, iterate through the child objects of the paragraph.
- Check if the object is a DocPicture object.
- If the object is a DocPicture, get the image data using the DocPicture.ImageBytes property and add it to the list.
- Save the image data in the list to individual image files.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create an object of the Document class
document = Document()
# Load a Word document containing comments
document.LoadFromFile("Comments.docx")
# Create a list to store the extracted image data
images = []
# Iterate through the comments in the document
for i in range(document.Comments.Count):
comment = document.Comments.get_Item(i)
# Iterate through the paragraphs in the comment body
for j in range(comment.Body.Paragraphs.Count):
paragraph = comment.Body.Paragraphs.get_Item(j)
# Iterate through the child objects in the paragraph
for o in range(paragraph.ChildObjects.Count):
obj = paragraph.ChildObjects.get_Item(o)
# Find the images
if isinstance(obj, DocPicture):
picture = obj
# Get the image data and add it to the list
data_bytes = picture.ImageBytes
images.append(data_bytes)
# Save the image data to image files
for i, image_data in enumerate(images):
file_name = f"CommentImage-{i}.png"
with open(os.path.join("CommentImages/", file_name), 'wb') as image_file:
image_file.write(image_data)
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
