
Python (355)
The Excel workbook, as a widely used data management tool, can be combined with Python to enable the automation of large-scale data processing. Using Python to set, update, and read cell values in Excel can significantly improve work efficiency, reduce repetitive tasks, and enhance the flexibility and scalability of data processing workflows, thus creating added value. This approach is applicable across a range of fields, from automating financial reports to generating data analysis reports, and can greatly boost productivity in various work contexts.
This article will demonstrate how to set, update, and retrieve cell values in Excel files using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Set cell values in Excel Files with Python
- Update cell values in Excel Files with Python
- Retrieve cell values in Excel Files with Python
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Set cell values in Excel Files with Python
We can use the Worksheet.Range.get_Item() method from Spire.XLS for Python to obtain a specified cell in an Excel worksheet as a CellRange object, such as Range.get_Item(2, 1) or Range.get_Item("A2") (row 2, column 1). Then, we can use the CellRange.Value property to set the cell value, or other properties within this class to set text, numbers, boolean values, and other types of data. The following is an example of the procedure:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Get the first default worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Obtain the specified cell as a CellRange object using Worksheet.Range.get_Item() method.
- Use properties within the CellRange class, such as Text, Value, DateTimeValue, Formula, and NumberValue, to set cell values.
- Format the cells.
- Save the workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile().
- Python
from spire.xls import Workbook, FileFormat, DateTime, HorizontalAlignType
import datetime
# Create an instance of Workbook to create an Excel workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first default worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Get cell and set text
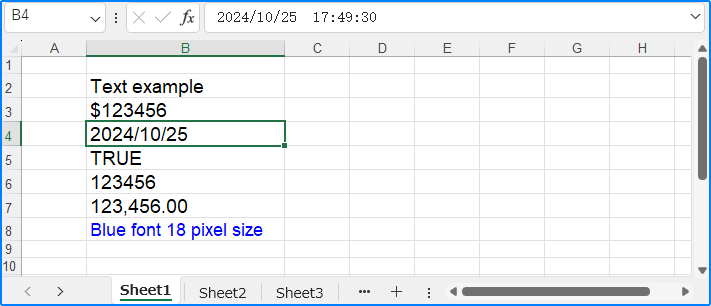
cell = sheet.Range.get_Item(2, 2)
cell.Text = "Text example"
# Get cell and set a regular value
cell1 = sheet.Range.get_Item(3, 2)
cell1.Value = "$123456"
# Get cell and set a date value
cell2 = sheet.Range.get_Item(4, 2)
cell2.DateTimeValue = DateTime.get_Now()
# Get cell and set a boolean value
cell3 = sheet.Range.get_Item(5, 2)
cell3.BooleanValue = True
# Get cell and set a formula
cell4 = sheet.Range.get_Item(6, 2)
cell4.Formula = "=SUM(B7)"
# Get cell, set a number value, and set number format
cell5 = sheet.Range.get_Item(7, 2)
cell5.NumberValue = 123456
cell5.NumberFormat = "#,##0.00"
# Get cell and set a formula array
cell6 = sheet.Range.get_Item(8, 2)
cell6.HtmlString = "<p><span style='color: blue; font-size: 18px;'>Blue font 18 pixel size</span></p>"
# Set formatting
cellRange = sheet.Range.get_Item(2, 2, 7, 2)
cellRange.Style.Font.FontName = "Arial"
cellRange.Style.Font.Size = 14
cellRange.Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Left
# Auto-fit the column width
sheet.AutoFitColumn(2)
# Save the file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/SetExcelCellValue.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Update cell values in Excel Files with Python
To update a cell value in Excel, we can retrieve the cell to update and use the same approach as above to reset its value, thus updating the cell value. Below is an example of the procedure:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load the Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Obtain the cell to update using Worksheet.Range.get_Item() method.
- Use properties under the CellRange class to reset the cell value.
- Save the workbook with Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import Workbook
# Create an instance of Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("output/SetExcelCellValue.xlsx")
# Get the worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Get the cell
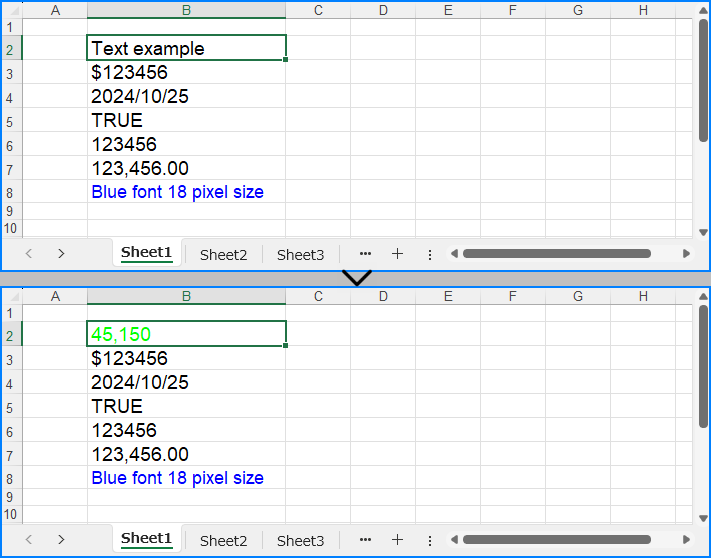
cell = sheet.Range.get_Item(2, 2)
# Change the cell value to a number
cell.NumberValue = 45150
# Set the cell number format
cell.NumberFormat = "[Green]#,##0;[RED]-#,##0"
# Save the workbook
workbook.SaveToFile("output/UpdateExcelCellValue.xlsx")
workbook.Dispose()
Retrieve cell values in Excel Files with Python
The CellRange.Value property can also be used to directly read cell values. Below is an example of the procedure to read cell values in Excel files:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load the Excel file with Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Loop through the specified cell range and use the CellRange.Value property to get the cell value.
- Print the results.
- Python
from spire.xls import Workbook
# Create an instance of Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Load the Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("output/SetExcelCellValue.xlsx")
# Get the worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
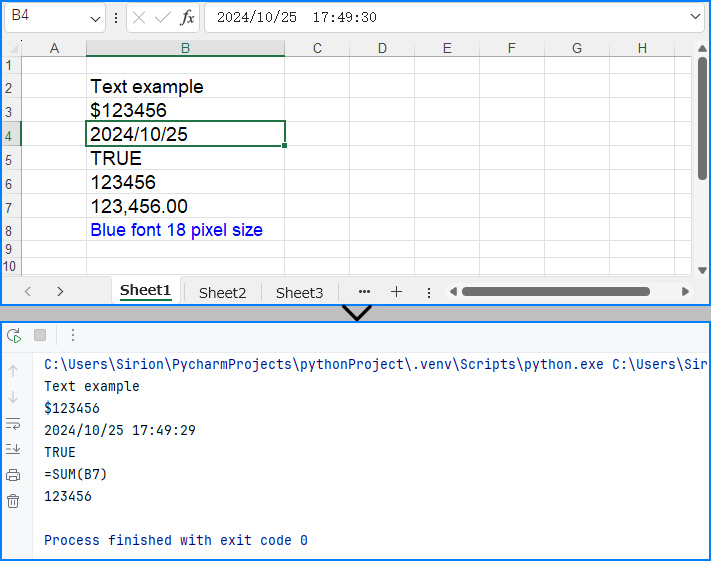
# Loop through cells from row 2 to 8 in column 2
for i in range(2, 8):
# Get the cell
cell = sheet.Range.get_Item(i, 2)
# Get the cell value
value = cell.Value
# Output the value
print(value)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
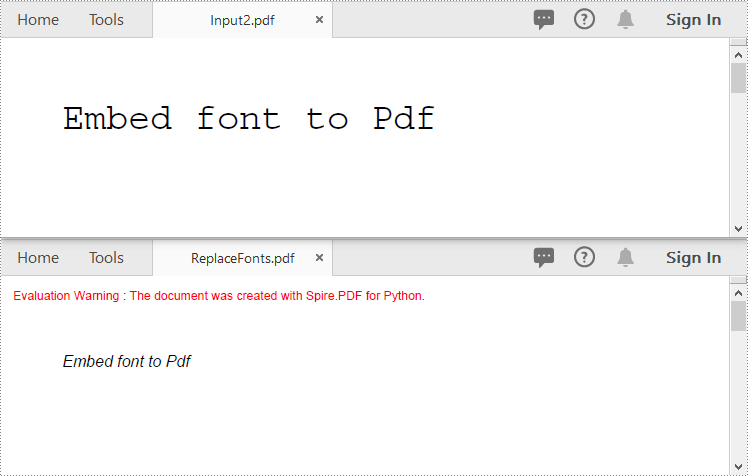
PDFs often use a variety of fonts and there are situations where you may need to get or replace these fonts. For instance, getting fonts allows you to inspect details such as font name, size, type, and style, which is especially useful for maintaining design consistency or adhering to specific standards. On the other hand, replacing fonts can help address compatibility issues, particularly when the original fonts are not supported on certain devices or software. In this article, we will explain how to get and replace the used fonts in PDF in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Get Used Fonts in PDF in Python
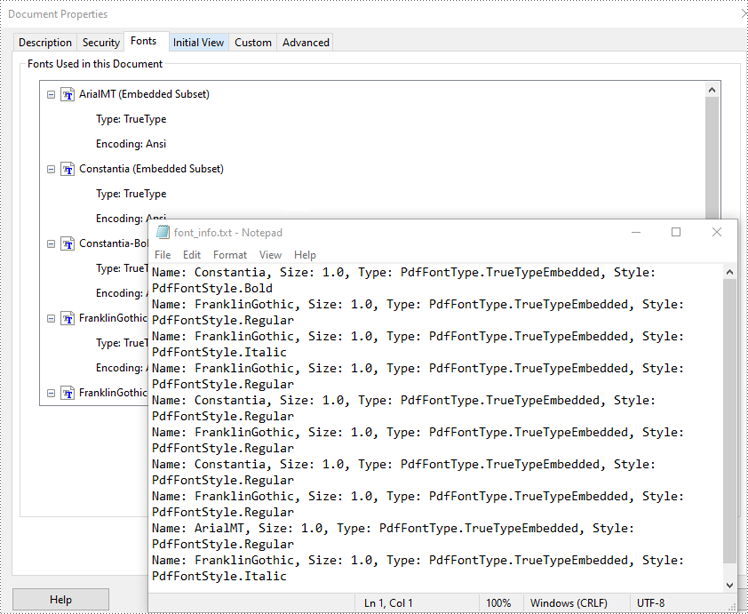
Spire.PDF for Python provides the PdfDocument.UsedFonts property to retrieve a list of all fonts used in a PDF. By iterating through this list, you can easily access detailed font information such as the font name, size, type and style using the PdfUsedFont.Name, PdfUsedFont.Size, PdfUsedFont.Type and PdfUsedFont.Style properties. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the PdfDocument class.
- Load a PDF document using the PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the list of fonts used in this document using the PdfDocument.UsedFonts property.
- Create a text file to save the extracted font information.
- Iterate through the font list.
- Get the information of each font, such as font name, size, type and style using the PdfUsedFont.Name, PdfUsedFont.Size, PdfUsedFont.Type and PdfUsedFont.Style properties, and save it to the text file.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create an object of the PdfDocument class
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("Input1.pdf")
# Get the list of fonts used in this document
usedFonts = pdf.UsedFonts
# Create a text file to save the extracted font information
with open("font_info.txt", "w") as file:
# Iterate through the font list
for font in usedFonts:
# Get the information of each font, such as font name, size, type and style
font_info = f"Name: {font.Name}, Size: {font.Size}, Type: {font.Type}, Style: {font.Style}\n"
file.write(font_info)
pdf.Close()
Replace Used Fonts in PDF in Python
You can replace the fonts used in a PDF with the desired font using the PdfUsedFont.Replace() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create an object of the PdfDocument class.
- Load a PDF document using the PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get the list of fonts used in this document using the PdfDocument.UsedFonts property.
- Create a new font using the PdfTrueTypeFont class.
- Iterate through the font list.
- Replace each used font with the new font using the PdfUsedFont.Replace() method.
- Save the resulting document to a new PDF using the PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create an object of the PdfDocument class
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF document
pdf.LoadFromFile("Input2.pdf")
# Get the list of fonts used in this document
usedFonts = pdf.UsedFonts
# Create a new font
newFont = PdfTrueTypeFont("Arial", 13.0, PdfFontStyle.Italic ,True)
# Iterate through the font list
for font in usedFonts:
# Replace each font with the new font
font.Replace(newFont)
# Save the resulting document to a new PDF
pdf.SaveToFile("ReplaceFonts.pdf")
pdf.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
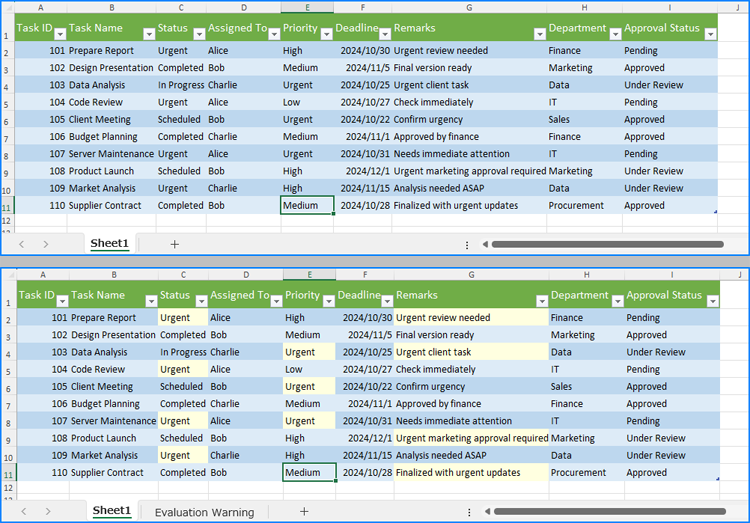
Efficiently emphasizing critical data within Excel workbooks is essential for swift analysis. This process not only draws immediate attention to the most relevant information but also aids in identifying trends, anomalies, and key metrics. By using Python to handle Excel workbooks, users can automate the search and highlight functions, enhancing productivity and ensuring precision. This article explores how to leverage Python for finding and highlighting data in Excel worksheets using Spire.XLS for Python library.
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Find and Highlight Data in Excel Worksheets
Using Spire.XLS for Python, we can find all cells containing a specific string and return them as a list by using the Worksheet.FindAllString(stringValue: str, formula: bool, formulaValue: bool) method. After that, we can iterate through the found cells and apply a highlight color by setting it via the CellRange.Style.Color property.
The detailed steps for finding and highlighting data in an Excel worksheet are as follows:
- Create an instance of Workbook class and load an Excel workbook using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Find all the cells containing the string to be highlighted using Worksheet.FindAllString() method.
- Iterate through the results to highlight the cells by setting a fill color through CellRange.Style.Color property.
- Save the workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
Python
from spire.xls import *
# Create an instance of Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Find the data to be highlighted
cellRanges = sheet.FindAllString("Urgent", False, True)
# Iterate through the found ranges
for cellRange in cellRanges:
# Highlight the data
cellRange.Style.Color = Color.get_LightYellow()
# Save the workbook
workbook.SaveToFile("output/FindHighlightDataExcel.xlsx")
workbook.Dispose()
Find and Highlight Data in a Specific Cell Range
In addition to searching for data across the entire worksheet, we can use the CellRange.FindAllString(stringValue: str, formula: bool, formulaValue: bool) method to find and highlight data within a specified cell range. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a worksheet using Workbook.Worksheets.get_Item() method.
- Get a cell range through Worksheet.Range[] property.
- Find all the cells containing the string to be highlighted using CellRange.FindAllString() method.
- Iterate through the results to highlight the cells by setting a fill color through CellRange.Style.Color property.
- Save the workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
# Create an instance of Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.get_Item(0)
# Get the cell range
findRange = sheet.Range["C1:C11"]
# Find the data to be highlighted
cellRanges = findRange.FindAllString("Urgent", False, True)
# Iterate the found ranges
for cellRange in cellRanges:
# Highlight the data
cellRange.Style.Color = Color.get_LightYellow()
# Save the workbook
workbook.SaveToFile("output/FindHighlightRange.xlsx")
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Macros in Word documents are small programs created using the Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) language. They are designed to automate repetitive tasks or add advanced functionality. While these macros can be powerful tools for improving productivity, they also pose security risks if used maliciously. Therefore, it is essential to detect and remove potentially harmful macros from Word documents, especially when handling files from untrusted sources. In this article, we will explain how to detect and remove VBA macros in Word documents in Python using Spire.Doc for Python.
- Detect Whether a Word Document Contains VBA Macros in Python
- Remove VBA Macros from a Word Document in Python
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
Detect Whether a Word Document Contains VBA Macros in Python
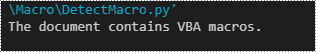
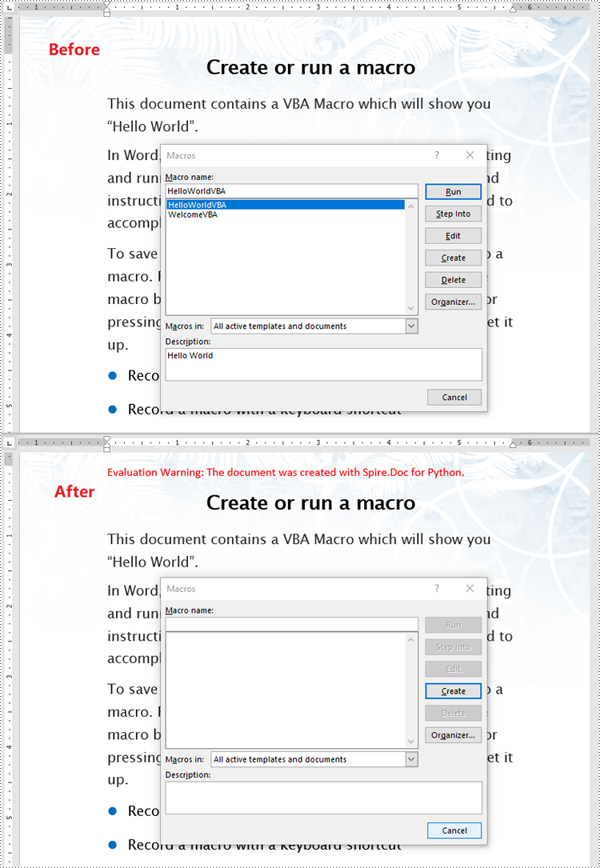
Spire.Doc for Python provides the Document.IsContainMacro property, enabling developers to check whether a Word document contains VBA macros easily. This property returns a boolean value: True indicates that the document includes one or more VBA macros, while False indicates that no macros are present in the document.
The following steps explain how to detect whether a Word document contains VBA macros using Spire.Doc for Python:
- Initialize an instance of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Detect whether the document includes VBA macros using the Document.IsContainMacro property.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Initialize an instance of the Document class
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Test.docm")
# Detect if the document contains VBA macros
if document.IsContainMacro:
print("The document contains VBA macros.")
else:
print("The document does not contain any VBA macros.")
document.Close()
Remove VBA Macros from a Word Document in Python
Developers can remove all macros from a Word document at once by using the Document.ClearMacros() method. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Initialize an instance of the Document class.
- Load a Word document using the Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove all macros from the document using the Document.ClearMacros() method.
- Save the result document using the Document.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Initialize an instance of the Document class
document = Document()
# Load a Word document
document.LoadFromFile("Test.docm")
# Remove all VBA macros from the document
document.ClearMacros()
# Save the modified document to a docm file
document.SaveToFile("RemoveMacros.docm", FileFormat.Docm2016)
document.Close()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Textboxes in a Word document serve as versatile containers for text, enabling users to enhance layout and design. They allow for the separation of content from the main body, making documents more visually appealing and organized. Extracting or updating textboxes can be essential for improving document efficiency, ensuring information is current, and facilitating data analysis.
In this article, you will learn how to extract or update textboxes in a Word document using Python and Spire.Doc for Python.
Install Spire.Doc for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Doc for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Doc
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.Doc for Python on Windows
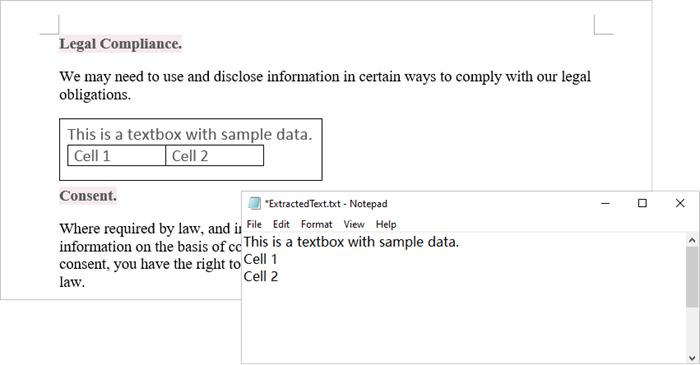
Extract Text from a Textbox in Word
Using Spire.Doc for Python, you can access a specific text box in a document by utilizing the Document.TextBoxes[index] property. After retrieving the text box, you can iterate through its child objects to identify whether each one is a paragraph or a table. If the object is a paragraph, you can retrieve its text using the Paragraph.Text property. In cases where the object is a table, you will need to loop through each cell to extract text from every individual cell within that table.
The steps to extract text from a text box in a Word document are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- load a Word file by using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Access a specific text box using Document.TextBoxes[index] property.
- Iterate through the child objects within the text box.
- Determine if a child object is a paragraph. If it is, retrieve the text from the paragraph using Paragraph.Text property.
- Check if a child object is a table. If so, iterate through the cells in the table to extract text from each cell.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word file
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx")
# Get a specific textbox
textBox = document.TextBoxes.get_Item(0)
with open('ExtractedText.txt','w') as sw:
# Iterate through the child objects in the textbox
for i in range(textBox.ChildObjects.Count):
# Get a specific child object
object = textBox.ChildObjects.get_Item(i)
# Determine if the child object is paragraph
if object.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Paragraph:
# Write paragraph text to txt file
sw.write((object if isinstance(object, Paragraph) else None).Text + "\n")
# Determine if the child object is table
if object.DocumentObjectType == DocumentObjectType.Table:
table = object if isinstance(object, Table) else None
for i in range(table.Rows.Count):
row = table.Rows[i]
for j in range(row.Cells.Count):
cell = row.Cells[j]
for k in range(cell.Paragraphs.Count):
paragraph = cell.Paragraphs.get_Item(k)
# Write paragrah text of a specific cell to txt file
sw.write(paragraph.Text + "\n")
# Dispose resources
document.Dispose()
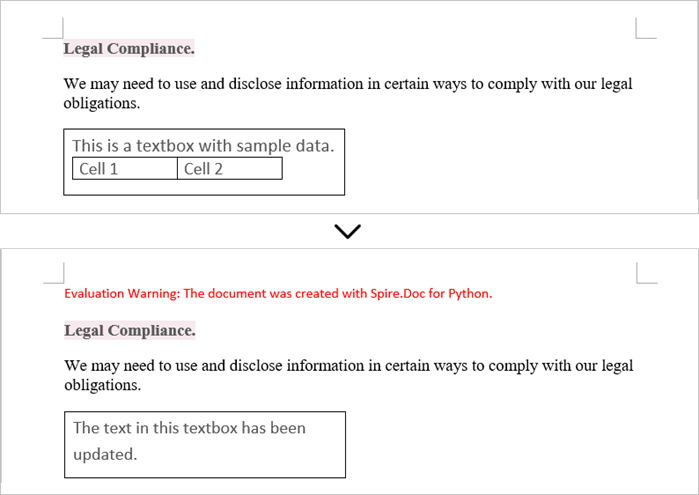
Update Text in a Textbox in Word
To update a textbox in a Word document, start by clearing its existing content with the TextBox.ChildObjects.Clear() method. This action removes all child objects, including any paragraphs or tables currently contained within the textbox. After clearing the content, you can add a new paragraph to the text box. Once the paragraph is created, set its text to the desired value.
The steps to update a textbox in a Word document are as follows:
- Create a Document object.
- Load a Word file using Document.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specific textbox using Document.TextBoxes[index] property
- Remove existing content of the textbox using TextBox.ChildObjects.Clear() method.
- Add a paragraph to the textbox using TextBox.Body.AddParagraph() method.
- Add text to the paragraph using Paragraph.AppendText() method.
- Save the document to a different Word file.
- Python
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
document = Document()
# Load a Word file
document.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.docx")
# Get a specific textbox
textBox = document.TextBoxes.get_Item(0)
# Remove child objects of the textbox
textBox.ChildObjects.Clear()
# Add a new paragraph to the textbox
paragraph = textBox.Body.AddParagraph()
# Set line spacing
paragraph.Format.LineSpacing = 15.0
# Add text to the paragraph
textRange = paragraph.AppendText("The text in this textbox has been updated.")
# Set font size
textRange.CharacterFormat.FontSize = 15.0
# Save the document to a different Word file
document.SaveToFile("UpdateTextbox.docx", FileFormat.Docx2019);
# Dispose resources
document.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
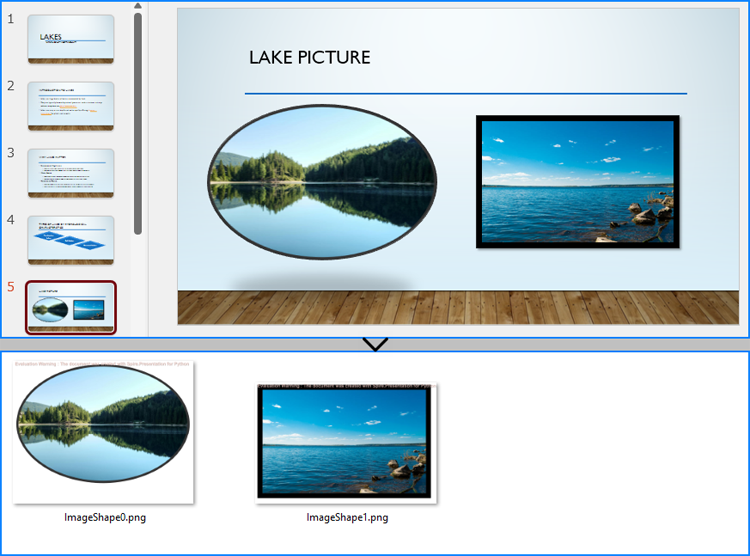
Python: Save Shapes as Image Files in PowerPoint Presentations
2024-10-21 01:03:20 Written by KoohjiExtracting and repurposing elements from PowerPoint presentations is a valuable skill for cross-platform content sharing. By converting shapes from slides into standalone image files, users can seamlessly integrate them into documents, web pages, or design projects without losing their original formatting and visual effects. With Python, this process becomes straightforward. In this article, we'll explore how to use Spire.Presentation for Python to save shapes from presentation slides as image files with simple Python code.
- Save Shapes from Slides as Image Files with Python
- Save Images from Slides with Formatting as Images Files
Install Spire.Presentation for Python
This scenario requires Spire.Presentation for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.Presentation
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.Presentation for Python on Windows
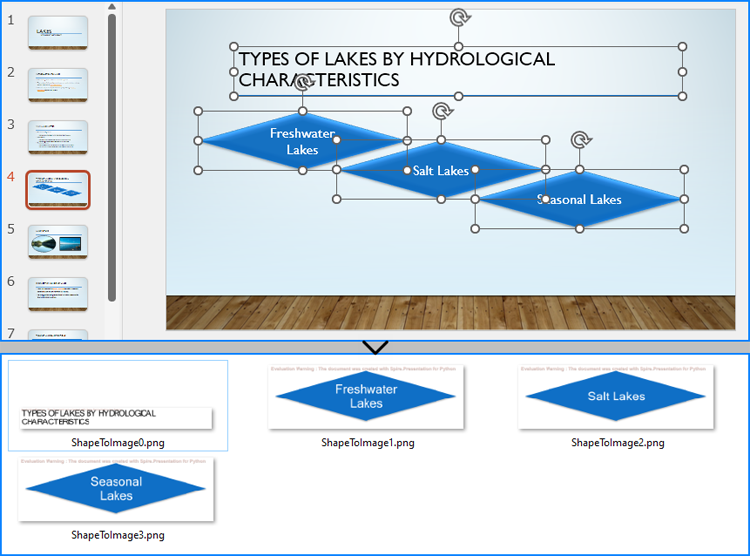
Save Shapes from Slides as Image Files with Python
Spire.Presentation for Python provides the Slide.Shapes.SaveAsImage(shapIndex: int, dpiX: int, dpiY: int) method to save shapes in presentation slides as images with the specified DPI(optional). With this method, developers can save either a specific shape or all shapes in a PowerPoint presentation. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an instance of Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a slide using Presentation.Slides.get_Item() method.
- Iterate through the shapes in the slide:
- Save each shape as an image stream using Slide.Shapes.SaveAsImage() method.
- Save the image stream as an image file using Stream.Save() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an instance of Presentation
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint file
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Get the first slide
slide = presentation.Slides.get_Item(3)
# Save the shape as an image stream
for i in range(slide.Shapes.Count):
imageStream = slide.Shapes.SaveAsImage(i, 256, 256)
# Save the image
imageStream.Save(f"output/Shapes/ShapeToImage{i}.png")
# Release resources
presentation.Dispose()
Save Images from Slides with Formatting as Images Files
By using the methods provided by Spire.Presentation for Python, developers can also save images from slides as image files while preserving the edits and formatting applied to them. This requires first checking if the shape is an object of SlidePicture class, and if so, the shape can be saved as an image file. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an instance of Presentation class.
- Load a PowerPoint presentation using Presentation.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a slide using Presentation.Slides.get_Item() method.
- Iterate through the shapes in the slide:
- Check if each shape is an object of SlidePicture class.
- If it is, save the shape as an image stream using Slide.Shapes.SaveAsImage() method.
- Save the image stream to a file using Stream.Save() method.
- Python
from spire.presentation import *
# Create an instance of Presentation
presentation = Presentation()
# Load a PowerPoint file
presentation.LoadFromFile("Sample.pptx")
# Get a slide
slide = presentation.Slides.get_Item(4)
# Iterate through all shapes in the slide
i = 0
for shape in slide.Shapes:
# Check if the shape is an object of SlidePicture
if isinstance(shape, SlidePicture):
# Save the shape as an image
shape = shape if isinstance(shape, SlidePicture) else None
image = slide.Shapes.SaveAsImage(slide.Shapes.IndexOf(shape), 256, 256)
image.Save(f"output/Images/ImageShape{i}.png")
i += 1
# Release resources
presentation.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Using Python to manipulate text formatting in PDFs provides a powerful way to automate and customize documents. With the Spire.PDF for Python library, developers can efficiently find text with advanced search options to retrieve and modify text properties like font, size, color, and style, enabling users to find and update text formatting across large document sets, saving time and reducing manual work. This article will demonstrate how to use Spire.PDF for Python to retrieve and modify text formatting in PDF documents with Python code.
- Find Text and Retrieve the Font Information in PDFs
- Find and Modify Text Formatting in PDF Documents
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Find Text and Retrieve Formatting Information in PDFs
Developers can use the PdfTextFinder and PdfTextFindOptions classes provided by Spire.PDF for Python to precisely search for specific text in a PDF document and obtain a collection of PdfTextFragment objects representing the search results. Then, developers can access the format information of the specified search result text through properties such as FontName, FontSize, and FontFamily, under PdfTextFragment.TextStates[] property.
The detailed steps for finding text in PDF and retrieving its font information are as follows:
- Create an instance of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a page using PdfDocument.Pages.get_Item() method.
- Create a PdfTextFinder object using the page.
- Create a PdfTextFindOptions object, set the search options, and apply the search options through PdfTextFinder.Options property.
- Find specific text on the page using PdfTextFinder.Find() method and get a collection of PdfTextFragment objects.
- Get the formatting of the first finding result through PdfTextFragment.TextStates property.
- Get the font name, font size, and font family of the result through PdfTextStates[0].FontName, PdfTextStates[0].FontSize, and PdfTextStates[0].FontFamily properties.
- Print the result.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Create a PdfTextFinder instance
finder = PdfTextFinder(page)
# Create a PdfTextFindOptions instance and set the search options
options = PdfTextFindOptions()
options.CaseSensitive = True
options.WholeWords = True
# Apply the options
finder.Options = options
# Find the specified text
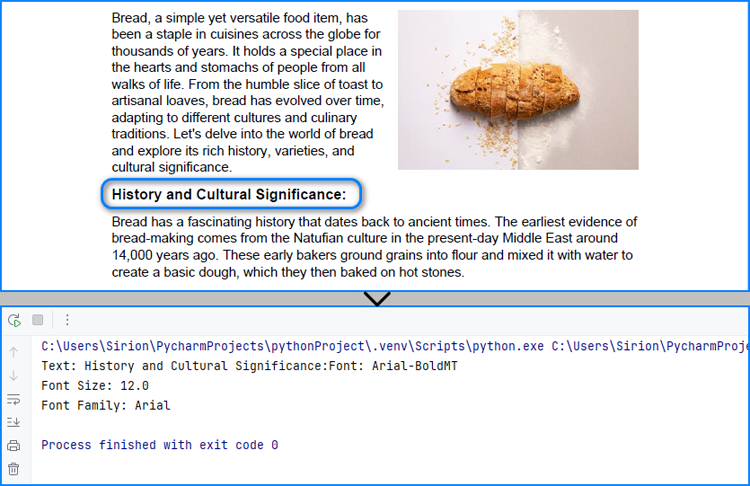
fragments = finder.Find("History and Cultural Significance:")
# Get the formatting of the first fragment
formatting = fragments[0].TextStates
# Get the formatting information
fontInfo = ""
fontInfo += "Text: " + fragments[0].Text
fontInfo += "Font: " + formatting[0].FontName
fontInfo += "\nFont Size: " + str(formatting[0].FontSize)
fontInfo += "\nFont Family: " + formatting[0].FontFamily
# Output font information
print(fontInfo)
# Release resources
pdf.Dispose()
Find and Modify Text Formatting in PDF Documents
After finding specific text, developers can overlay it with a rectangle in the same color as the background and then redraw the text in a new format at the same position, thus achieving text format modification of simple PDF text fragments on solid color pages. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an instance of PdfDocument class and load a PDF document using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a page using PdfDocument.Pages.get_Item() method.
- Create a PdfTextFinder object using the page.
- Create a PdfTextFindOptions object, set the search options, and apply the search options through PdfTextFinder.Options property.
- Find specific text on the page using PdfTextFinder.Find() method and get the first result.
- Get the color of the page background through PdfPageBase.BackgroundColor property and change the color to white if the background is empty.
- Draw rectangles with the obtained color in the position of the found text using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawRectangle() method.
- Create a new font, brush, and string format and calculate the text frame.
- Draw the text in the new format in the same position using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawString() method.
- Save the document using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument instance
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file
pdf.LoadFromFile("Sample.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages.get_Item(0)
# Create a PdfTextFinder instance
finder = PdfTextFinder(page)
# Create a PdfTextFindOptions instance and set the search options
options = PdfTextFindOptions()
options.CaseSensitive = True
options.WholeWords = True
finder.Options = options
# Find the specified text
fragments = finder.Find("History and Cultural Significance:")
# Get the first result
fragment = fragments[0]
# Get the background color and change it to white if its empty
backColor = page.BackgroundColor
if backColor.ToArgb() == 0:
backColor = Color.get_White()
# Draw a rectangle with the background color to cover the text
for i in range(len(fragment.Bounds)):
page.Canvas.DrawRectangle(PdfSolidBrush(PdfRGBColor(backColor)), fragment.Bounds[i])
# Create a new font and a new brush
font = PdfTrueTypeFont("Times New Roman", 16.0, 3, True)
brush = PdfBrushes.get_Brown()
# Create a PdfStringFormat instance
stringFormat = PdfStringFormat()
stringFormat.Alignment = PdfTextAlignment.Left
# Calculate the rectangle that contains the text
point = fragment.Bounds[0].Location
size = SizeF(fragment.Bounds[-1].Right, fragment.Bounds[-1].Bottom)
rect = RectangleF(point, size)
# Draw the text with the specified format in the same rectangle
page.Canvas.DrawString("History and Cultural Significance", font, brush, rect, stringFormat)
# Save the document
pdf.SaveToFile("output/FindModifyTextFormat.pdf")
# Release resources
pdf.Close()

Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Digital signatures serve as a critical layer of security, ensuring that an Excel file has not been altered since it was signed and verifying the identity of its originator. However, there are scenarios where the detection and removal of these digital signatures become necessary, such as when consolidating multiple documents, updating content, or preparing files for systems that do not support digitally signed documents. This article shows how to detect and remove digital signatures in Excel files with Python code using Spire.XLS for Python, providing a simple way to batch process Excel file digital signatures.
- Detecting the Presence of Digital Signatures in Excel Files
- Removing Digital Signatures from Excel Files
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip commands.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Detecting the Presence of Digital Signatures in Excel Files
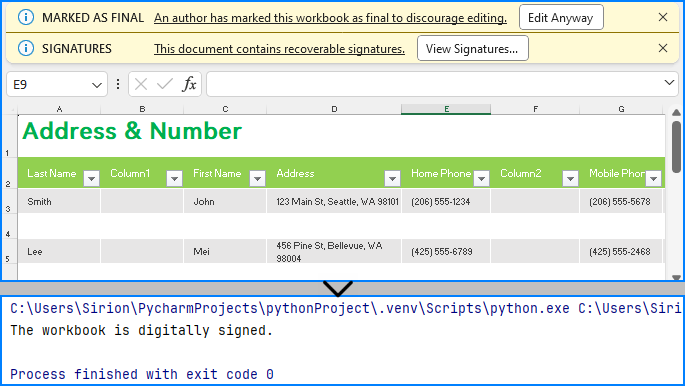
Spire.XLS for Python provides the Workbook class to deal with Excel files and the Workbook.IsDigitallySigned property to check if an Excel file has digital signatures. Developers can use the Boolean value returned by this property to determine whether the Excel file contains a digital signature.
The detailed steps for detecting if an Excel file has digital signatures are as follows:
- Create an instance of Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Check whether the workbook is digitally signed by the value of the Workbook.IsDigitallySigned property.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
# Create an instance of Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Check whether the workbook is digitally signed
if workbook.IsDigitallySigned is False:
print("The workbook is not digitally signed.")
else:
print("The workbook is digitally signed.")
Removing Digital Signatures from Excel Files
Developers can use the Workbook.RemoveAllDigitalSignatures() method to effortlessly delete all digital signatures in an Excel workbook. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Create an instance of Workbook class.
- Load an Excel file using Workbook.LoadFromFile() method.
- Remove all digital signatures from the workbook using Workbook.RemoveAllDigitalSignatures() method.
- Save the workbook using Workbook.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
# Create an instance of Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Remove digital signatures
workbook.RemoveAllDigitalSignatures()
# Save the document
workbook.SaveToFile("output/RemoveExcelDigitalSignature.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
PDF format has now become a standard for sharing and preserving documents. When working with PDF files, you may sometimes need to copy specific pages in the PDF to extract valuable content, create summaries, or simply share relevant sections without distributing the entire document. In this article, you will learn how to copy pages in PDF in Python using Spire.PDF for Python.
Install Spire.PDF for Python
This scenario requires Spire.PDF for Python. It can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.PDF
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.PDF for Python on Windows
Copy Pages within the Same PDF in Python
To duplicate PDF pages, you can first create template based on a specified page in PDF, and then draw the template on a newly added page through the PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawTemplate() method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load a PDF file using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified page using PdfDocument.Pages[] property.
- Get the size of the page using PdfPageBase.Size property.
- Create a template based on the page using PdfPageBase.CreateTemplate() method.
- Add a new page of the same size at the end using PdfDocument.Pages.Add(size: SizeF, margins: PdfMargins) method. Or you can insert a new page of the same size at a specified location using PdfDocument.Pages.Insert(index: int, size: SizeF, margins: PdfMargins) method.
- Draw template on the newly added page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawTemplate(template: PdfTemplate, location: PointF) method.
- Save the result file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Create a PdfDocument object
pdf = PdfDocument()
# Load a PDF file from disk
pdf.LoadFromFile("Butterflies.pdf")
# Get the first page
page = pdf.Pages[0]
# Get the size of the page
size = page.Size
# Create a template based on the page
template = page.CreateTemplate()
# Add a new page of the same size at the end
page = pdf.Pages.Add(size, PdfMargins(0.0))
# Insert a new page at the specified location
# page = pdf.Pages.Insert(1, size, PdfMargins(0.0))
# Draw the template on the newly added page
page.Canvas.DrawTemplate(template, PointF(0.0, 0.0))
# Save the PDF file
pdf.SaveToFile("CopyPDFPages.pdf");
pdf.Close()
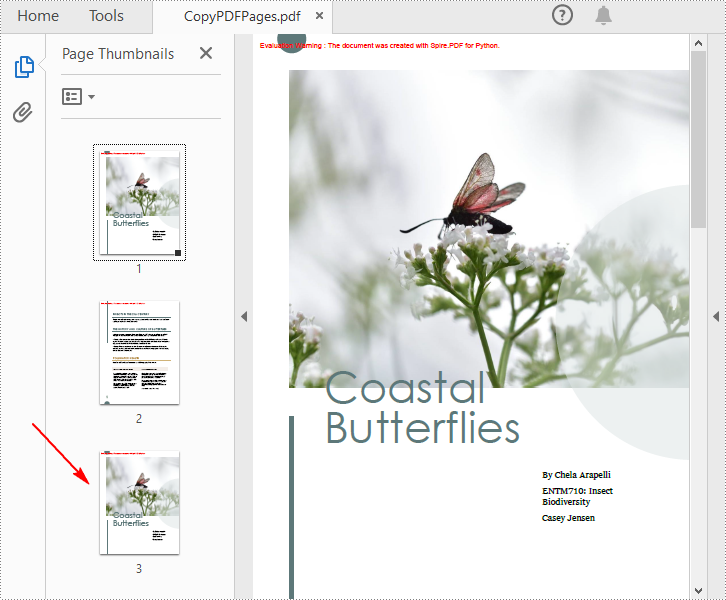
Copy Pages from One PDF to Another in Python
Spire.PDF for Python also allows you to load two PDF files, create templates based on the pages in one PDF file, and then draw them onto the pages in another PDF file. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a PdfDocument instance.
- Load two PDF files using PdfDocument.LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified page in the first PDF using PdfDocument.Pages[] property.
- Get the size of the page using PdfPageBase.Size property.
- Create a template based on the page using PdfPageBase.CreateTemplate() method.
- Insert a new page of the same size at a specified location in the second PDF using PdfDocument.Pages.Insert(index: int, size: SizeF, margins: PdfMargins) method. Or you can add a new page of the same size at the end of the second PDF using PdfDocument.Pages.Add(size: SizeF, margins: PdfMargins) method.
- Draw template on the newly added page using PdfPageBase.Canvas.DrawTemplate(template: PdfTemplate, location: PointF) method.
- Save the result file using PdfDocument.SaveToFile() method.
- Python
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Load the first PDF file
pdf1 = PdfDocument()
pdf1.LoadFromFile("Butterflies.pdf")
# Load the second PDF file
pdf2 = PdfDocument()
pdf2.LoadFromFile("SamplePDF.pdf")
# Get the first page in the first PDF file
page = pdf1.Pages[0]
# Get the size of the page
size = page.Size
# Create a template based on the page
template = page.CreateTemplate()
# Insert a new page at a specified location in the second PDF file
newPage = pdf2.Pages.Insert(0, size, PdfMargins(0.0))
# Add a new page at the end of the second PDF file
# newPage = pdf2.Pages.Add(size, PdfMargins(0.0))
# Draw the template on the newly added page
newPage.Canvas.DrawTemplate(template, PointF(0.0, 0.0))
# Save the result file
pdf2.SaveToFile("CopyPagesToAnotherPDF.pdf")
pdf2.Close()
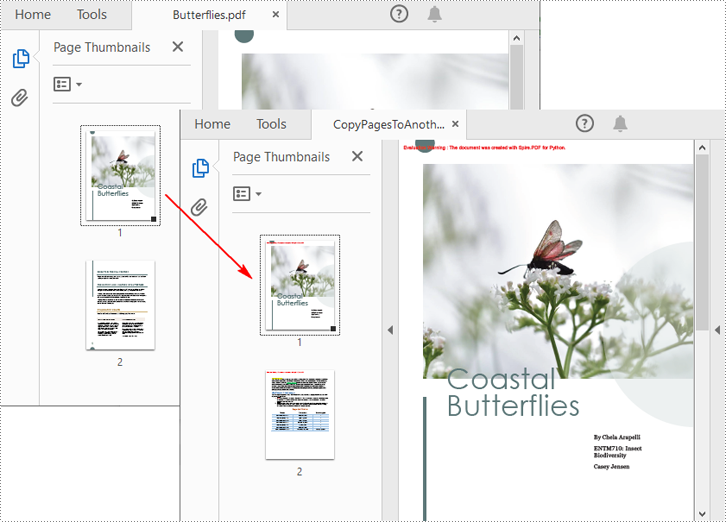
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
A pie chart is a circular statistical graphic that is divided into slices to illustrate numerical proportions. Each slice represents a category's contribution to the whole, making it an effective way to visualize relative sizes. In this article, you will learn how to create a standard pip chart, an exploded pip chart, and a pie of pie chart in Excel using Spire.XLS for Python.
- Create a Pie Chart in Excel
- Create an Exploded Pie Chart in Excel
- Create a Pie of Pie Chart in Excel
Install Spire.XLS for Python
This scenario requires Spire.XLS for Python and plum-dispatch v1.7.4. They can be easily installed in your Windows through the following pip command.
pip install Spire.XLS
If you are unsure how to install, please refer to this tutorial: How to Install Spire.XLS for Python on Windows
Create a Pie Chart in Excel in Python
To add a pie chart to a worksheet, use the Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Pie) method, which returns a Chart object. You can then set various properties, such as DataRange, ChartTitle, LeftColumn, TopRow, and Series to define the chart's data, title, position, and series formatting.
Here are the steps to create a pie chart in Excel:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Retrieve a specific worksheet from the workbook.
- Insert values into the worksheet cells that will be used as chart data.
- Add a pie chart to the worksheet using Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Pie) method.
- Set the chart data using Chart.DataRange property.
- Define the chart's position and size using Chart.LeftColumn, Chart.TopRow, Chart.RightColumn, and Chart.BottomRow properties.
- Set the chart title using Chart.ChartTitle property.
- Access and format the series through Chart.Series property.
- Save the workbook as an Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first sheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set values of the specified cells
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Year"
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "2002"
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "2003"
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "2004"
sheet.Range["A5"].Value = "2005"
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Sales"
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 4000
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 6000
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 7000
sheet.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 8500
# Format the cells
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].RowHeight = 15
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.Color = Color.get_DarkGray()
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["B2:B5"].Style.NumberFormat = "\"$\"#,##0"
# Add a pie chart
chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.Pie)
# Set region of chart data
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["B2:B5"]
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = False
# Set position of chart
chart.LeftColumn = 4
chart.TopRow = 2
chart.RightColumn = 12
chart.BottomRow = 20
# Set chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Sales by year"
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 12
# Get the first series
cs = chart.Series[0]
# Set category labels for the series
cs.CategoryLabels = sheet.Range["A2:A5"]
# Set values for the series
cs.Values = sheet.Range["B2:B5"]
# Show vales in data labels
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = True
# Save the workbook to an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/PieChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
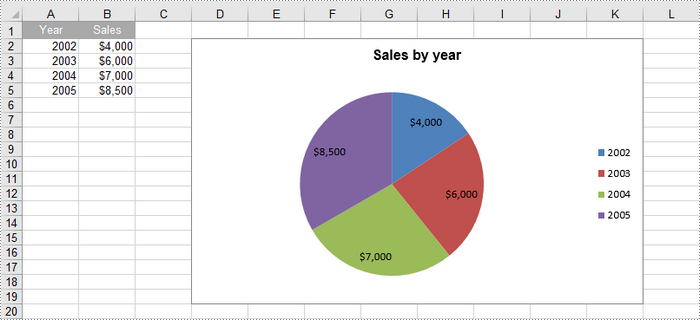
Create an Exploded Pie Chart in Excel in Python
An exploded pie chart is a variation of the standard pie chart where one or more slices are separated or "exploded" from the main chart. To create an exploded pie chart, you can use the Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.PieExploded) method.
The steps to create an exploded pip chart in Excel are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Retrieve a specific worksheet from the workbook.
- Insert values into the worksheet cells that will be used as chart data.
- Add an exploded pie chart to the worksheet using Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType. PieExploded) method.
- Set the chart data using Chart.DataRange property.
- Define the chart's position and size using Chart.LeftColumn, Chart.TopRow, Chart.RightColumn, and Chart.BottomRow properties.
- Set the chart title using Chart.ChartTitle property.
- Access and format the series through Chart.Series property.
- Save the workbook as an Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first sheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set values of the specified cells
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Year"
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "2002"
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "2003"
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "2004"
sheet.Range["A5"].Value = "2005"
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Sales"
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 4000
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 6000
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 7000
sheet.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 8500
# Format the cells
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].RowHeight = 15
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.Color = Color.get_DarkGray()
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["B2:B5"].Style.NumberFormat = "\"$\"#,##0"
# Add an exploded pie chart
chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.PieExploded)
# Set region of chart data
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["B2:B5"]
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = False
# Set position of chart
chart.LeftColumn = 4
chart.TopRow = 2
chart.RightColumn = 12
chart.BottomRow = 20
# Set chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Sales by year"
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 12
# Get the first series
cs = chart.Series[0]
# Set category labels for the series
cs.CategoryLabels = sheet.Range["A2:A5"]
# Set values for the series
cs.Values = sheet.Range["B2:B5"]
# Show vales in data labels
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = True
# Save the workbook to an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/ExplodedPieChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
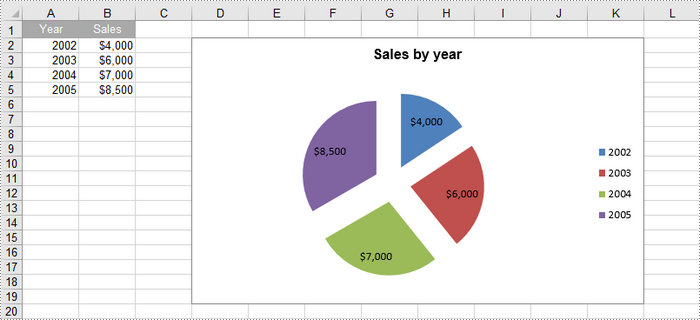
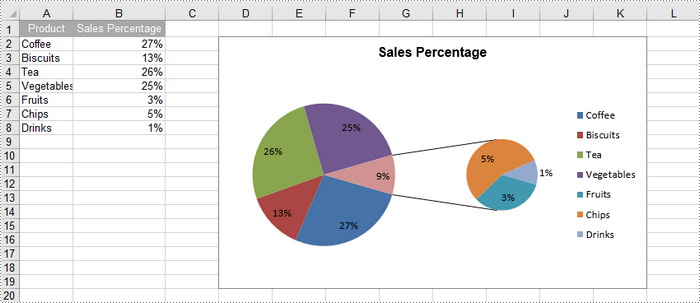
Create a Pie of Pie Chart in Excel in Python
A pie of pie chart is a specialized type of pie chart that allows for more detailed representation of data by providing a secondary pie chart for specific categories. To add a pip of pie chart to a worksheet, use the Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.PieOfPie) method.
The detailed steps to create a pie of pie chart in Excel are as follows:
- Create a Workbook object.
- Retrieve a specific worksheet from the workbook.
- Insert values into the worksheet cells that will be used as chart data.
- Add a pie of pie chart to the worksheet using Worksheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.PieOfPie) method.
- Set the chart data, position, size, title using the properties under the Chart object.
- Access the first series using Chart.Series[0] property.
- Set the split value that determines what displays in the secondary pie using Series.Format.Options.SplitValue property.
- Save the workbook as an Excel file.
- Python
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a workbook
workbook = Workbook()
# Get the first sheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Set values of the specified cells
sheet.Range["A1"].Value = "Product"
sheet.Range["A2"].Value = "Coffee"
sheet.Range["A3"].Value = "Biscuits"
sheet.Range["A4"].Value = "Tea"
sheet.Range["A5"].Value = "Vegetables"
sheet.Range["A6"].Value = "Fruits"
sheet.Range["A7"].Value = "Chips"
sheet.Range["A8"].Value = "Drinks"
sheet.Range["B1"].Value = "Sales Percentage"
sheet.Range["B2"].NumberValue = 0.27
sheet.Range["B3"].NumberValue = 0.13
sheet.Range["B4"].NumberValue = 0.26
sheet.Range["B5"].NumberValue = 0.25
sheet.Range["B6"].NumberValue = 0.03
sheet.Range["B7"].NumberValue = 0.05
sheet.Range["B8"].NumberValue = 0.01
# Autofit column width
sheet.AutoFitColumn(2)
# Format the cells
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].RowHeight = 15
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.Color = Color.get_DarkGray()
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.Font.Color = Color.get_White()
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["A1:B1"].Style.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignType.Center
sheet.Range["B2:B8"].Style.NumberFormat = "0%"
# Add a pie of pie chart
chart = sheet.Charts.Add(ExcelChartType.PieOfPie)
# Set region of chart data
chart.DataRange = sheet.Range["B2:B58"]
chart.SeriesDataFromRange = False
# Set position of chart
chart.LeftColumn = 4
chart.TopRow = 2
chart.RightColumn = 12
chart.BottomRow = 20
# Chart title
chart.ChartTitle = "Sales Percentage"
chart.ChartTitleArea.IsBold = True
chart.ChartTitleArea.Size = 12
# Get the first series
cs = chart.Series[0]
# Set category labels for the series
cs.CategoryLabels = sheet.Range["A2:A8"]
# Set values for the series
cs.Values = sheet.Range["B2:B8"]
# Show vales in data labels
cs.DataPoints.DefaultDataPoint.DataLabels.HasValue = True
# Set the size of the secondary pie
cs.Format.Options.PieSecondSize = 50
# Set the split value, which determines what displays in the secondary pie
cs.Format.Options.SplitType = SplitType.Percent
cs.Format.Options.SplitValue = 10
# Save the workbook to an Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/PieOfPieChart.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
