
Knowledgebase (2311)
Children categories
Copying worksheets is very useful when you need to create similar worksheets or want to make changes to worksheets without affecting the original. This feature can save you a significant amount of time and effort, as it allows you to quickly reuse information such as data, formulas, formatting, and layouts from existing worksheets without having to create new worksheets from scratch. This article will explain how to copy worksheets in Excel in C++ using Spire.XLS for C++.
- Copy a Worksheet in the Same Workbook
- Copy a Worksheet to Another Workbook
- Copy Visible Worksheets to a New Workbook
Install Spire.XLS for C++
There are two ways to integrate Spire.XLS for C++ into your application. One way is to install it through NuGet, and the other way is to download the package from our website and copy the libraries into your program. Installation via NuGet is simpler and more recommended. You can find more details by visiting the following link.
Integrate Spire.XLS for C++ in a C++ Application
Copy a Worksheet in the Same Workbook in C++
You can copy a worksheet within the same workbook by adding a new worksheet to the workbook and then copying the worksheet to the new worksheet.
The following steps demonstrate how to copy a worksheet within the same workbook:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load an Excel workbook using the Workbook->LoadFromFile(LPCWSTR_S name) method.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(int index) method.
- Add a new worksheet to the workbook using the Workbook->GetWorksheets()->Add(LPCWSTR_S name) method.
- Copy the specific worksheet to the new worksheet using the Worksheet->CopyFrom(Worksheet* worksheet) method.
- Save the result workbook to another file using the Workbook->SaveToFile(LPCWSTR_S fileName, ExcelVersion version) method.
- C++
#include "Spire.Xls.o.h";
using namespace Spire::Xls;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
Workbook* workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel workbook
workbook->LoadFromFile(L"Input.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet* sourceSheet = workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(0);
//Get the name of the first worksheet
wstring sheetName = sourceSheet->GetName();
//Add a new worksheet with a specific name to the workbook
Worksheet* destSheet = workbook->GetWorksheets()->Add((sheetName + L"_Copy").c_str());
//Copy the first worksheet to the new worksheet
destSheet->CopyFrom(sourceSheet);
//Save the result workbook to another file
workbook->SaveToFile(L"CopyInSameWorkbook.xlsx", ExcelVersion::Version2016);
workbook->Dispose();
delete workbook;
}
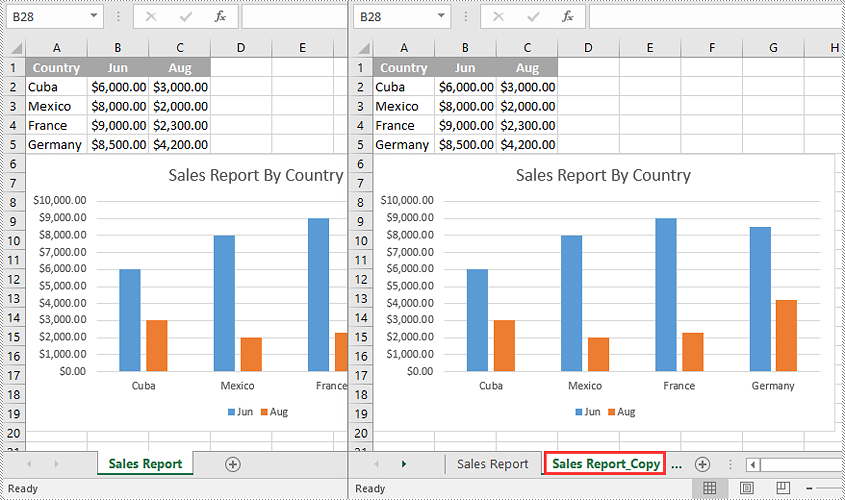
Copy a Worksheet to Another Workbook in C++
To copy a worksheet from one workbook to another, you need to add a new worksheet to the destination workbook and then copy the worksheet from the source workbook to the new worksheet of the destination workbook. It’s worth noting that if you want to keep the source formatting of the source worksheet, you need to copy the theme of the source workbook to the destination workbook.
The following steps demonstrate how to copy a worksheet from one workbook to another and keep its source formatting:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load the source workbook using the Workbook->LoadFromFile(LPCWSTR_S name) method.
- Get a specific worksheet using the Workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(int index) method.
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load the destination workbook using the Workbook->LoadFromFile(LPCWSTR_S name) method.
- Add a new worksheet to the destination workbook using the Workbook->GetWorksheets()->Add(LPCWSTR_S name) method.
- Copy the specific worksheet of the source workbook to the new worksheet of the destination workbook using the Worksheet->CopyFrom(Worksheet* worksheet) method.
- Copy the theme from the source workbook to the destination workbook using the Workbook->CopyTheme (Workbook* srcWorkbook) method.
- Save the result workbook to another file using the Workbook->SaveToFile(LPCWSTR_S fileName, ExcelVersion version) method.
- C++
#include "Spire.Xls.o.h";
using namespace Spire::Xls;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
Workbook* sourceWorkbook = new Workbook();
//Load the source Excel workbook
sourceWorkbook->LoadFromFile(L"Input.xlsx");
//Get the first worksheet of the source workbook
Worksheet* sourceSheet = sourceWorkbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(0);
//Get the name of the first worksheet
wstring sheetName = sourceSheet->GetName();
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
Workbook* destWorkbook = new Workbook();
//Load the destination Excel workbook
destWorkbook->LoadFromFile(L"Sample.xlsx");
//Add a new worksheet with a specific name to the destination workbook
Worksheet* destSheet = destWorkbook->GetWorksheets()->Add((sheetName + L"_Copy").c_str());
//Copy the first worksheet of the source workbook to the new worksheet of the destination workbook
destSheet->CopyFrom(sourceSheet);
//Copy the theme from the source workbook to the destination workbook
destWorkbook->CopyTheme(sourceWorkbook);
//Save the destination workbook to another file
destWorkbook->SaveToFile(L"CopyToAnotherWorkbook.xlsx", ExcelVersion::Version2016);
sourceWorkbook->Dispose();
delete sourceWorkbook;
destWorkbook->Dispose();
delete destWorkbook;
}
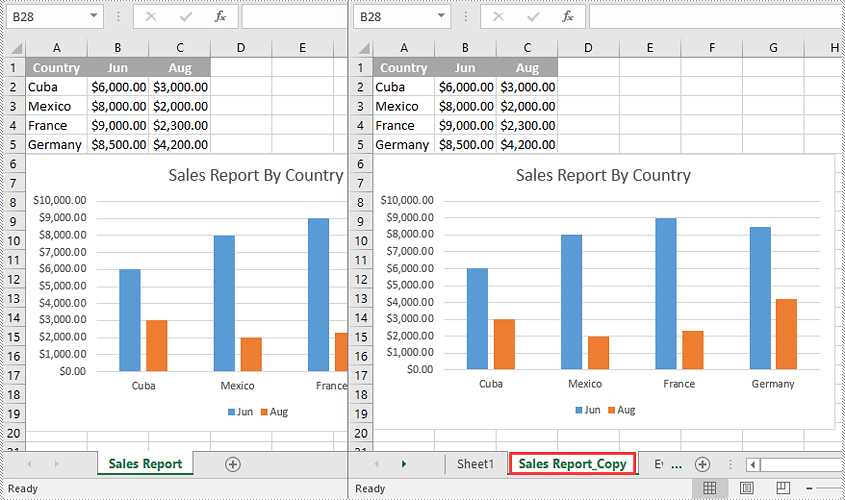
Copy Visible Worksheets to a New Workbook in C++
If you only want to share visible worksheets rather than the entire workbook with others, you can copy the visible worksheets to a new workbook.
The following steps demonstrate how to copy visible worksheets from a workbook to a new workbook:
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class.
- Load the source workbook using the Workbook->LoadFromFile(LPCWSTR_S name) method.
- Initialize an instance of the Workbook class to create a new workbook, then clear the default worksheets in the new workbook using the Workbook->GetWorksheets()->Clear() method.
- Iterate through all the worksheets in the source workbook.
- Check if the current worksheet is visible using the XlsWorksheetBase->GetVisibility() method.
- If the result is true, add a new worksheet to the new workbook using the Workbook->GetWorksheets()->Add(LPCWSTR_S name) method.
- Copy the worksheet from the source workbook to the new worksheet of the new workbook using the Worksheet->CopyFrom(Worksheet* worksheet) method.
- Copy the theme from the source workbook to the new workbook using the Workbook->CopyTheme (Workbook* srcWorkbook) method.
- Save the new workbook to another file using the Workbook->SaveToFile(LPCWSTR_S fileName, ExcelVersion version) method.
- C++
#include "Spire.Xls.o.h";
using namespace Spire::Xls;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class
Workbook* sourceWorkbook = new Workbook();
//Load the source Excel workbook
sourceWorkbook->LoadFromFile(L"Input.xlsx");
//Initialize an instance of the Workbook class to create a new workbook
Workbook* newWorkbook = new Workbook();
//Clear the default worksheets in the new workbook
newWorkbook->GetWorksheets()->Clear();
//Iterate through all the worksheets in the source workbook
for (int i = 0; i < sourceWorkbook->GetWorksheets()->GetCount(); i++)
{
Worksheet* sourceSheet = sourceWorkbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(i);
//Check if the current worksheet is visible
if (sourceSheet->GetVisibility() == WorksheetVisibility::Visible)
{
//Get the name of the worksheet
wstring sheetName = sourceSheet->GetName();
//Add a new worksheet with a specific name to the new workbook
Worksheet* destSheet = newWorkbook->GetWorksheets()->Add((sheetName + L"_Copy").c_str());
//Copy the worksheet from the source workbook to the new worksheet of the new workbook
destSheet->CopyFrom(sourceSheet);
}
}
//Copy the theme from the source workbook to the new workbook
newWorkbook->CopyTheme(sourceWorkbook);
//Save the new workbook to another file
newWorkbook->SaveToFile(L"CopyVisibleSheetsToNewWorkbook.xlsx", ExcelVersion::Version2016);
sourceWorkbook->Dispose();
delete sourceWorkbook;
newWorkbook->Dispose();
delete newWorkbook;
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Lists are used in Word documents to outline, arrange, and emphasize text, making it easy for users to scan and understand a series of items. There are three different types of lists in Word, namely numbered lists, bulleted lists and multi-level lists. Numbered lists are used for items that have a sequence or priority, such as a series of instructions. Bulleted lists are used for items that have no particular priority, such as a list of functions or facts. Multi-level lists are used where there is a sequence and you want each paragraph numbered separately.
In this article, you will learn how to insert these types of lists into a Word document in C# and VB.NET using Spire.Doc for .NET.
- Insert a Numbered List in Word
- Insert a Bulleted List in Word
- Insert a Multi-Level Numbered List in Word
- Insert a Multi-Level Mixed-Type List in Word
Install Spire.Doc for .NET
To begin with, you need to add the DLL files included in the Spire.Doc for.NET package as references in your .NET project. The DLL files can be either downloaded from this link or installed via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.Doc
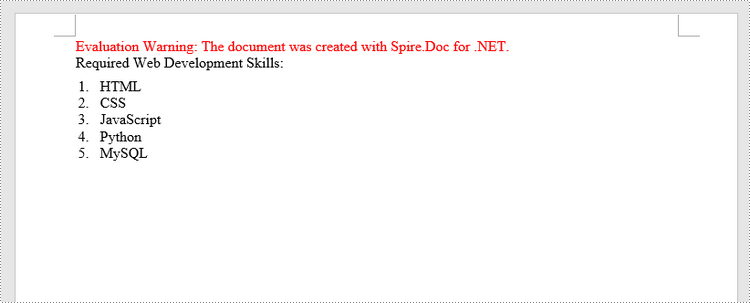
Insert a Numbered List in Word in C#, VB.NET
Spire.Doc for .NET offers the ListStyle class that you can use to create a numbered list style or a bulleted style. Then, the list style can be applied to a paragraph using Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method. The steps to create a numbered list are as follows.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create an instance of ListStyle class, specifying the list type to Numbered.
- Get a specific level of the list through ListStyle.Levels[index] property, and set the numbering type through ListLevel.PatternType property.
- Add the list style to the document using Document.ListStyles.Add() method.
- Add several paragraphs to the document using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Apply the list style to a specific paragraph using Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method.
- Specify the list level through Paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber property.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
namespace CreateOrderedList
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Document object
Document document = new Document();
//Add a section
Section section = document.AddSection();
//Create a numbered list style
ListStyle listStyle = document.Styles.Add(ListType.Numbered, "numberedList");
listStyle.Name = "numberedList";
listStyle.ListRef.Levels[0].PatternType = ListPatternType.DecimalEnclosedParen;
listStyle.ListRef.Levels[0].TextPosition = 20;
//Add a paragraph
Paragraph paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("Required Web Development Skills:");
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 5f;
//Add a paragraph and apply the numbered list style to it
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("HTML");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
//Add another four paragraphs and apply the numbered list style to them
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("CSS");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("JavaScript");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("Python");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("MySQL");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedList");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
//Save the document to file
document.SaveToFile("NumberedList.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
}
}
}
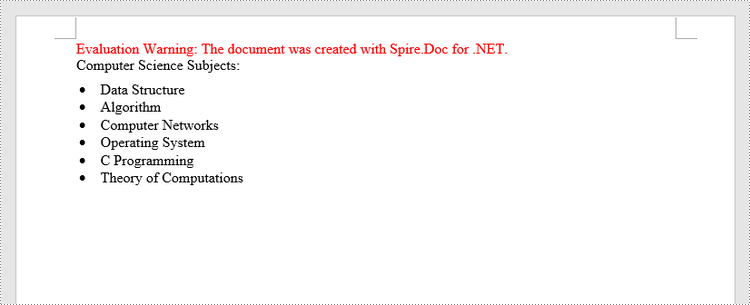
Insert a Bulleted List in Word in C#, VB.NET
The process of creating a bulleted list is similar to that of creating a numbered list. The difference is that when creating a list style, you must specify the list type as Bulleted and set a bullet symbol for it. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create an instance of ListStyle class, specifying the list type to Bulleted.
- Get a specific level of the list through ListStyle.Levels[index] property, and set the bullet symbol through ListLevel.BulletCharacter property.
- Add the list style to the document using Document.ListStyles.Add() method.
- Add several paragraphs to the document using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Apply the list style to a specific paragraph using Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method.
- Specify the list level through Paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber property.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
namespace CreateUnorderedList
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Document object
Document document = new Document();
//Add a section
Section section = document.AddSection();
//Create a bulleted list style
ListStyle listStyle = document.Styles.Add( ListType.Bulleted, "bulletedList");
listStyle.Name = "bulletedList";
listStyle.ListRef.Levels[0].BulletCharacter = "\x00B7";
listStyle.ListRef.Levels[0].CharacterFormat.FontName = "Symbol";
listStyle.ListRef.Levels[0].TextPosition = 20;
//Add a paragraph
Paragraph paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("Computer Science Subjects:");
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 5f;
//Add a paragraph and apply the bulleted list style to it
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("Data Structure");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
//Add another five paragraphs and apply the bulleted list style to them
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("Algorithm");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("Computer Networks");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("Operating System");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("C Programming");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("Theory of Computations");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulletedList");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
//Save the document to file
document.SaveToFile("BulletedList.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
}
}
}
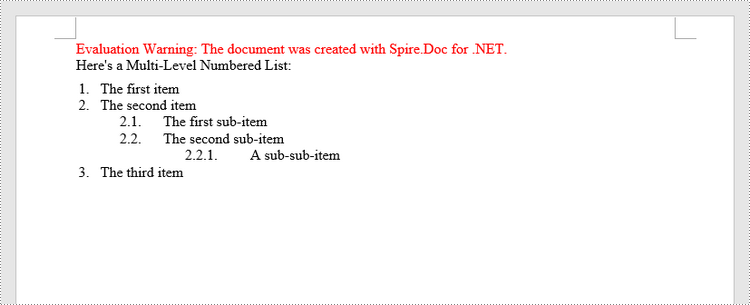
Insert a Multi-Level Numbered List in Word in C#, VB.NET
A multi-level list consists of at least two different levels. Each level of a nested list is represented by the ListStyle.Levels[index] property, through which you can set the numbering type and prefix for a certain level. The following are the steps to create a multi-level numbered list in Word.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create an instance of ListStyle class, specifying the list type to Numbered.
- Get a specific level of the list through ListStyle.Levels[index] property, and set the numbering type and prefix.
- Add the list style to the document using Document.ListStyles.Add() method.
- Add several paragraphs to the document using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Apply the list style to a specific paragraph using Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method.
- Specify the list level through Paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber property.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
namespace CreateMultiLevelList
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Document object
Document document = new Document();
//Add a section
Section section = document.AddSection();
//Create a numbered list style, specifying number prefix and pattern type of each level
ListStyle listStyle = document.Styles.Add(ListType.Numbered, "levelstyle");
listStyle.Name = "levelstyle";
listStyle.ListRef.Levels[0].PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic;
listStyle.ListRef.Levels[0].TextPosition = 20;
listStyle.ListRef.Levels[1].NumberPrefix = "\x0000.";
listStyle.ListRef.Levels[1].PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic;
listStyle.ListRef.Levels[2].NumberPrefix = "\x0000.\x0001.";
listStyle.ListRef.Levels[2].PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic;
//Add a paragraph
Paragraph paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("Here's a Multi-Level Numbered List:");
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 5f;
//Add a paragraph and apply the numbered list style to it
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("The first item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
//Add another five paragraphs and apply the numbered list stype to them
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("The second item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("The first sub-item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 1;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("The second sub-item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ContinueListNumbering();
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle");
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("A sub-sub-item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 2;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("The third item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("levelstyle");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
//Save the document to file
document.SaveToFile("MultilevelNumberedList.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
}
}
}
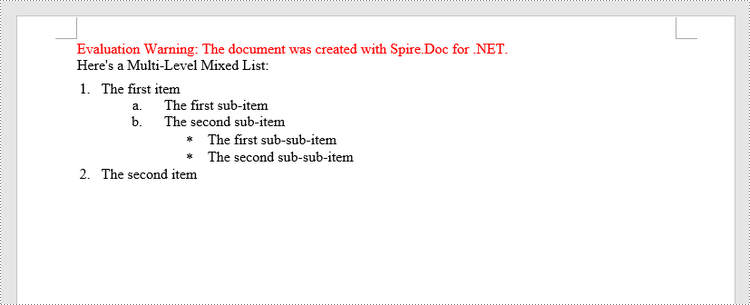
Insert a Multi-Level Mixed-Type List in Word in C#, VB.NET
In some cases, you may want to mix number and symbol bullet points in a multi-level list. To create a mixed-type list, you just need to create a numbered list style and a bulleted list style and apply them to different paragraphs. The detailed steps are as follows.
- Create a Document object.
- Add a section using Document.AddSection() method.
- Create a numbered list style and a bulleted list style.
- Add several paragraphs to the document using Section.AddParagraph() method.
- Apply different list style to different paragraphs using Paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle() method.
- Save the document to a Word file using Document.SaveToFile() method.
- C#
- VB.NET
using Spire.Doc;
using Spire.Doc.Documents;
namespace CreateMultilevelMixedList
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a Document object
Document document = new Document();
//Add a section
Section section = document.AddSection();
//Create a numbered list style
ListStyle numberedListStyle = document.Styles.Add(ListType.Numbered, "numberedStyle");
numberedListStyle.ListRef.Levels[0].PatternType = ListPatternType.Arabic;
numberedListStyle.ListRef.Levels[0].TextPosition = 20;
numberedListStyle.ListRef.Levels[1].PatternType = ListPatternType.LowLetter;
//Create a bulleted list style
ListStyle bulletedListStyle = document.Styles.Add(ListType.Bulleted, "bulltedStyle");
bulletedListStyle.Name = "bulltedStyle";
bulletedListStyle.ListRef.Levels[2].BulletCharacter = "\x002A";
bulletedListStyle.ListRef.Levels[2].CharacterFormat.FontName = "Symbol";
//Add a paragraph
Paragraph paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("Here's a Multi-Level Mixed List:");
paragraph.Format.AfterSpacing = 5f;
//Add a paragraph and apply the numbered list style to it
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("The first item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedStyle");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
//Add another five paragraphs and apply different list stype to them
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("The first sub-item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedStyle");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 1;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("The second sub-item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 1;
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedStyle");
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("The first sub-sub-item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulltedStyle");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 2;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("The second sub-sub-item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("bulltedStyle");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 2;
paragraph = section.AddParagraph();
paragraph.AppendText("The second item");
paragraph.ListFormat.ApplyStyle("numberedStyle");
paragraph.ListFormat.ListLevelNumber = 0;
//Save the document to file
document.SaveToFile("MultilevelMixedList.docx", FileFormat.Docx);
}
}
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
Excel is a popular spreadsheet software widely used for data analysis, financial management, budgeting, etc. However, when you need to embed Excel files into other files or share them with others, Excel format may have compatibility issues, and in such a case converting Excel to image is an alternative option. In this article, you will learn how to convert an Excel worksheet or a specific cell range to an image in C++ using Spire.XLS for C++.
- Convert an Entire Excel Worksheet to an Image in C++
- Convert a Specific Cell Range to an Image in C++
- Convert a Worksheet to an Image Without White Spaces in C++
Install Spire.XLS for C++
There are two ways to integrate Spire.XLS for C++ into your application. One way is to install it through NuGet, and the other way is to download the package from our website and copy the libraries into your program. Installation via NuGet is simpler and more recommended. You can find more details by visiting the following link.
Integrate Spire.XLS for C++ in a C++ Application
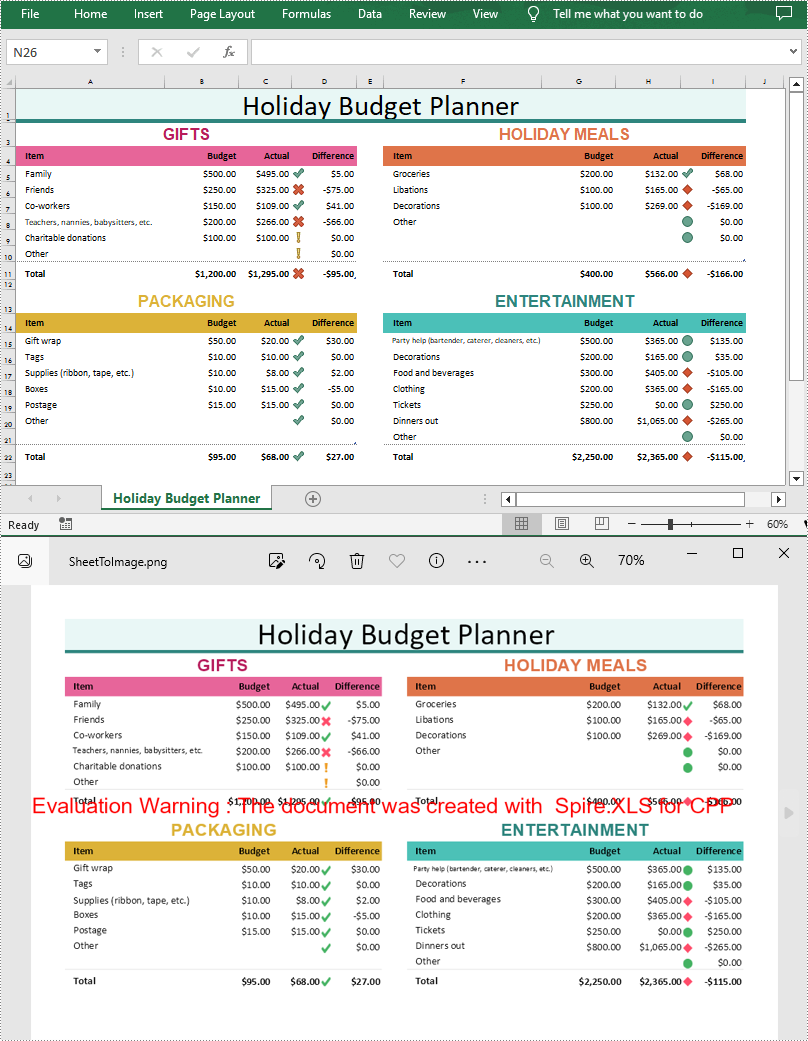
Convert an Entire Excel Worksheet to an Image in C++
Spire.XLS for C++ offers the Worksheet->ToImage() method to convert a specific worksheet to an image, and then you can save the image in PNG, JPG or BMP format using Image->Save() method. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load a sample Excel document using Workbook->LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get() method.
- Convert the worksheet to an image using Worksheet->ToImage() method.
- Save the image as a PNG file using Image->Save() method.
- C++
#include "Spire.Xls.o.h";
using namespace Spire::Xls;
using namespace std;
int main() {
//Specify the input and output file paths
wstring inputFile = L"Data\\Planner.xlsx";
wstring outputFile = L"Output\\SheetToImage";
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook* workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel document from disk
workbook->LoadFromFile(inputFile.c_str());
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet* sheet = workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(0);
//Convert the worksheet to an image
Image* image = sheet->ToImage(sheet->GetFirstRow(), sheet->GetFirstColumn(), sheet->GetLastRow(), sheet->GetLastColumn());
//Save the image as a PNG file
wstring fileName = outputFile + L".png";
image->Save(fileName.c_str());
workbook->Dispose();
}
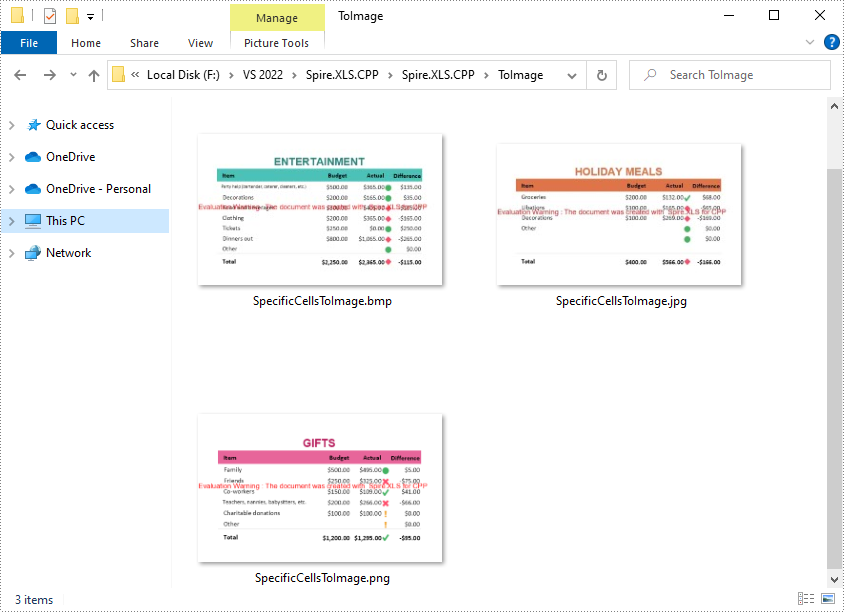
Convert a Specific Cell Range to an Image in C++
Spire.XLS for C++ also allows you to use the Worksheet->ToImage(int firstRow, int firstColumn, int lastRow, int lastColumn) method to convert a specified cell range to an image. The following are the steps convert several cell ranges to different image formats.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load a sample Excel document using Workbook->LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get() method.
- Specify a cell range and save it to a specified image format using Worksheet->ToImage()->Save(LPCWSTR_S filename, ImageFormat* format) method.
- C++
#include "Spire.Xls.o.h";
using namespace Spire::Xls;
using namespace std;
int main() {
//Specify input file path and name
wstring inputFile = L"Data\\Planner.xlsx";
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook* workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel document from disk
workbook->LoadFromFile(inputFile.c_str());
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet* sheet = workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(0);
//Specify cell ranges and save them to certain image formats
sheet->ToImage(3, 1, 11, 4)->Save(L"ToImage\\SpecificCellsToImage.png", ImageFormat::GetPng());
sheet->ToImage(3, 6, 11, 9)->Save(L"ToImage\\SpecificCellsToImage.jpg", ImageFormat::GetJpeg());
sheet->ToImage(13, 6, 22, 9)->Save(L"ToImage\\SpecificCellsToImage.bmp", ImageFormat::GetBmp());
workbook->Dispose();
}
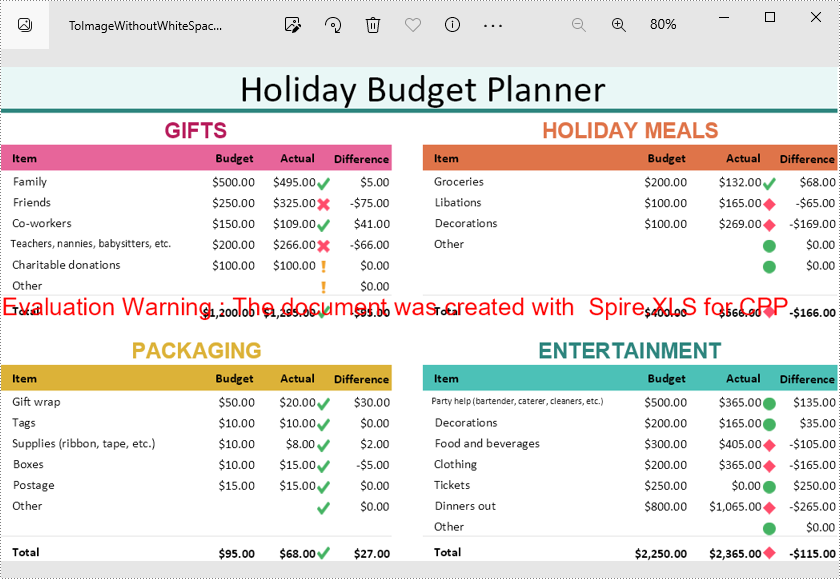
Convert a Worksheet to an Image Without White Spaces in C++
When converting a worksheet directly to an image, there are white spaces around the converted image. If you want to remove these white spaces, you can set the left, right, top and bottom margins of the worksheet to zero while conversion. The following are the detailed steps.
- Create a Workbook object.
- Load a sample Excel document using Workbook->LoadFromFile() method.
- Get a specified worksheet using Workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get() method.
- Return a page setup object using Worksheet->GetPageSetup() method, and then set the left, right, top and bottom margins of the worksheet using the methods of PageSetup class.
- Save the worksheet as an image using Worksheet->ToImage()->Save() method.
- C++
#include "Spire.Xls.o.h";
using namespace Spire::Xls;
using namespace std;
int main() {
//Specify output file path and name
wstring inputFile = L"Data\\Planner.xlsx";
wstring outputFile = L"Output\\ToImageWithoutWhiteSpace.png";
//Create a Workbook object
Workbook* workbook = new Workbook();
//Load an Excel document from disk
workbook->LoadFromFile(inputFile.c_str());
//Get the first worksheet
Worksheet* sheet = workbook->GetWorksheets()->Get(0);
//Set the margin as 0 to remove the white space around the image
sheet->GetPageSetup()->SetLeftMargin(0);
sheet->GetPageSetup()->SetBottomMargin(0);
sheet->GetPageSetup()->SetTopMargin(0);
sheet->GetPageSetup()->SetRightMargin(0);
//Save the worksheet as an image
Image* image = sheet->ToImage(sheet->GetFirstRow(), sheet->GetFirstColumn(), sheet->GetLastRow(), sheet->GetLastColumn());
image->Save(outputFile.c_str());
workbook->Dispose();
}
Apply for a Temporary License
If you'd like to remove the evaluation message from the generated documents, or to get rid of the function limitations, please request a 30-day trial license for yourself.
