How to Insert Formulas into Excel: Six Easy Methods
Table of Contents
- Why Learning Multiple Ways Matters
- Method 1. Type Formulas Directly in a Cell
- Method 2. Insert Formulas Using the Formula Bar
- Method 3. Use the Insert Function (fx) Button
- Method 4. Use AutoSum and Quick Functions
- Method 5. Insert Formulas Using the Fill Handle
- Method 6. Insert Formulas Programmatically
- Comparison: Which Method Should You Choose?
- Summary
- FAQs About Inserting Formulas to Excel
Formulas are one of Excel’s most powerful features. They let you run calculations, analyze trends, automate repetitive work, and build dynamic reports. Whether you’re doing a quick sum, building nested conditional logic, or automating bulk spreadsheet generation, Excel gives you multiple ways to insert formulas — each suited to different skill levels and tasks.
In this article, we will walk through several easy and efficient ways to insert formulas into Excel , ranging from built-in UI methods to automation using Python (Spire.XLS). We will also include example use cases, step-by-step instructions, and a comparison table to help you decide which method works best for your workflow.
Method overview:
- Method 1: Type Formulas Directly in a Cell (Fastest for Simple Use)
- Method 2: Insert Formulas Using the Formula Bar (Best for Long or Complex Formulas)
- Method 3: Use the Insert Function (fx) Button (Most Beginner-Friendly)
- Method 4: Use AutoSum and Quick Functions (Extremely Efficient)
- Method 5: Insert Formulas Using the Fill Handle (Best for Repetition)
- Method 6: Insert Formulas Programmatically (Python – Spire.XLS)
Why Learning Multiple Ways Matters
Many Excel users only know how to type equations directly into a cell. While that works for simple calculations, it’s not always the fastest or most reliable method, especially when dealing with large datasets or complex formulas. Excel provides a variety of tools and shortcuts designed to speed up formula creation, improve accuracy, and avoid manual errors.
In addition, developers and data analysts often need automation solutions for generating or updating Excel files in bulk—something that scripting with Python can handle more efficiently than manual entry.
By learning multiple ways to insert formulas, you can:
- Work more efficiently with day-to-day spreadsheets
- Reduce errors caused by manual typing
- Take advantage of Excel’s built-in intelligence
- Automate repetitive tasks or large-scale Excel processing
Below are the six most efficient methods for inserting formulas into Excel, with practical guidance so you can apply them immediately.
Method 1. Type Formulas Directly in a Cell (Fastest for Simple Use)
Typing directly into a cell is the most common and straightforward way of inserting formulas. It’s fast, intuitive, and works perfectly for quick calculations.
Steps:
- Click the cell where you want the formula result to appear.
- Type an equal sign = to start the formula.
- Enter the formula—for example:
- =A1+B1
- =SUM(A1:A10)
- =A1*B1
- Press Enter to apply the formula.
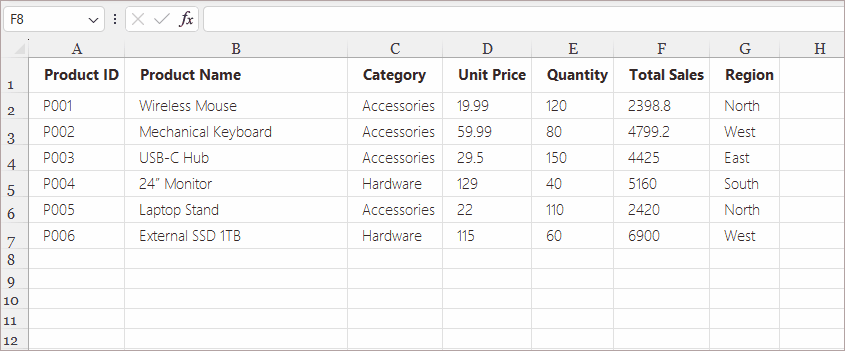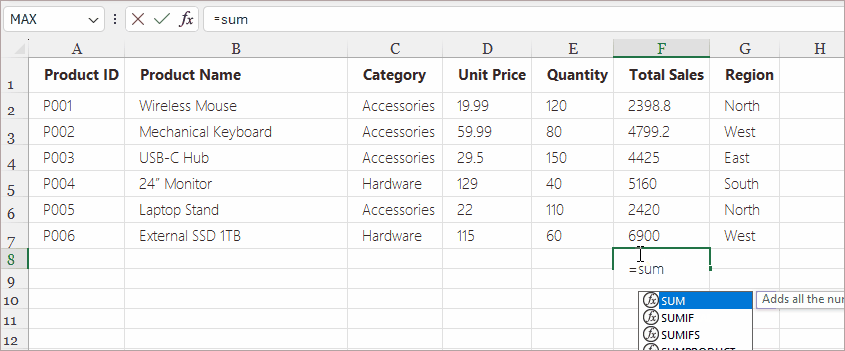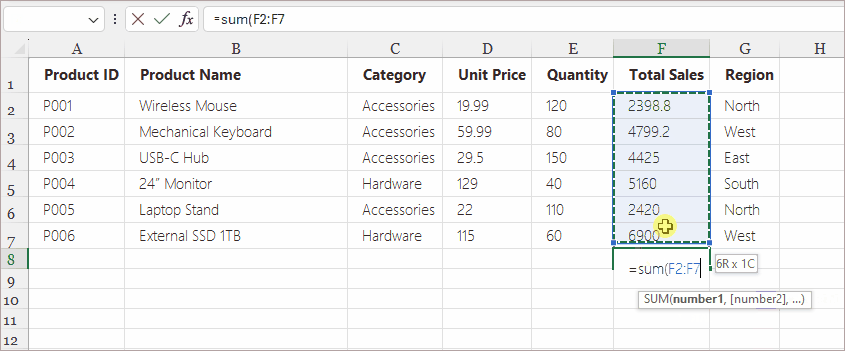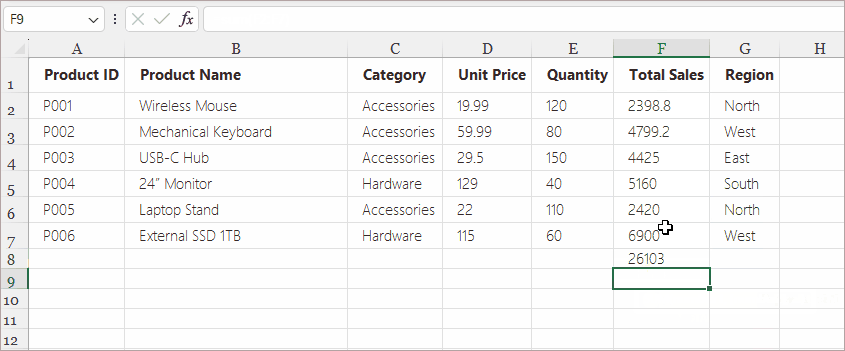
Example Use Cases:
- Adding or subtracting values
- Calculating totals
- Performing basic math operations
- Using simple functions (SUM, AVERAGE, MAX, MIN)
Why this method is useful:
- Extremely fast for simple tasks
- Great for small spreadsheets
- No additional tools or dialogs needed
However, this method becomes inefficient when you need to insert long or complex formulas that require more careful editing.
Method 2. Insert Formulas Using the Formula Bar (Best for Long or Complex Formulas)
The Formula Bar provides more space and clarity, making it ideal for editing long or complicated formulas without accidentally modifying the cell content itself.
Steps:
- Select the cell where your formula belongs.
- Click the Formula Bar at the top of Excel.
- Type or edit your formula.
- Press Enter .
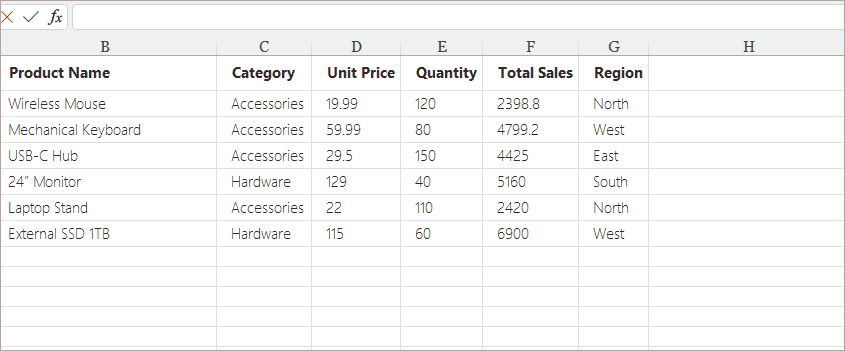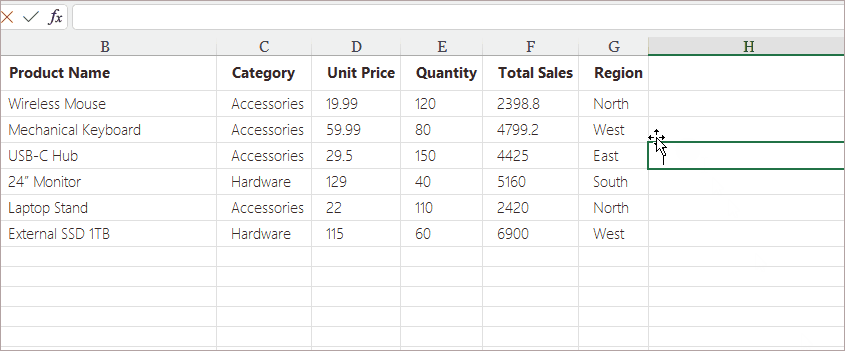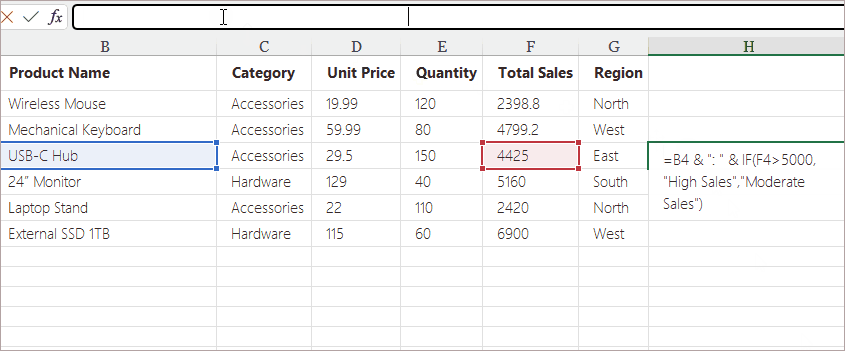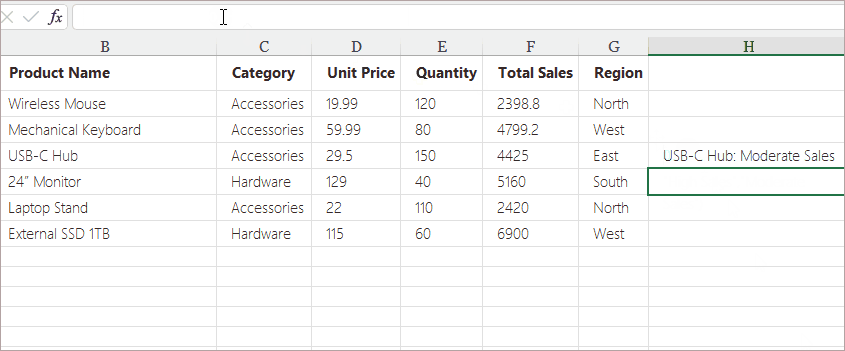
Example Use Cases:
- Nested IF statements
- VLOOKUP , INDEX + MATCH, XLOOKUP
- Concatenation formulas with multiple text segments
- Multi-condition logical formulas
Why this method is useful:
- Allows comfortable editing of long or multi-line formulas
- Reduces accidental cell changes
- Helps maintain a clean view of the worksheet
The Formula Bar also displays formula error warnings, making debugging easier.
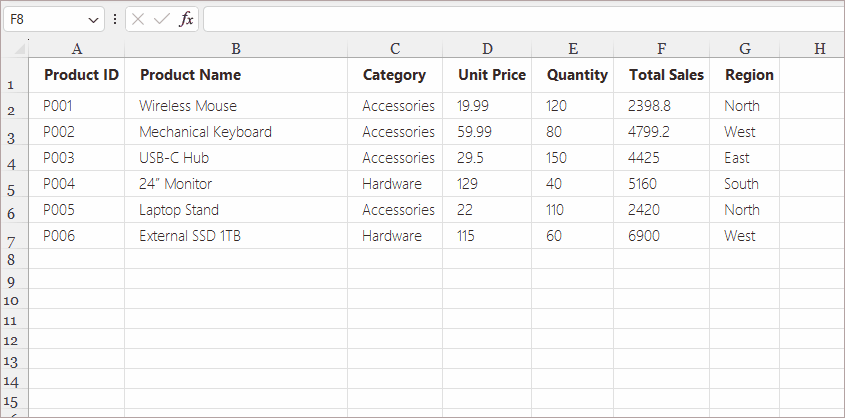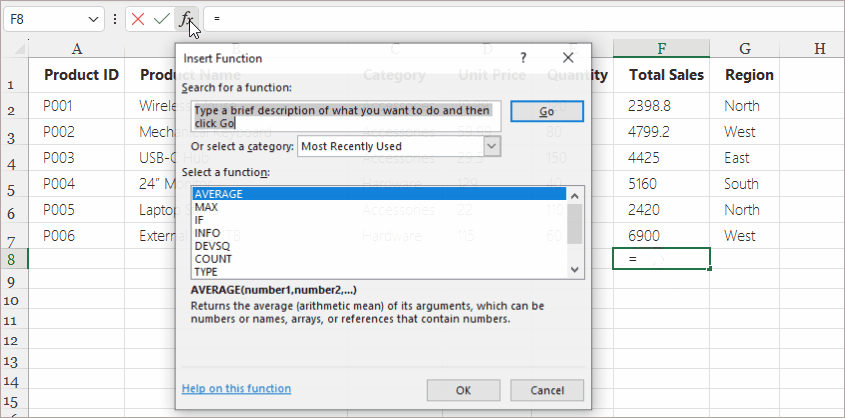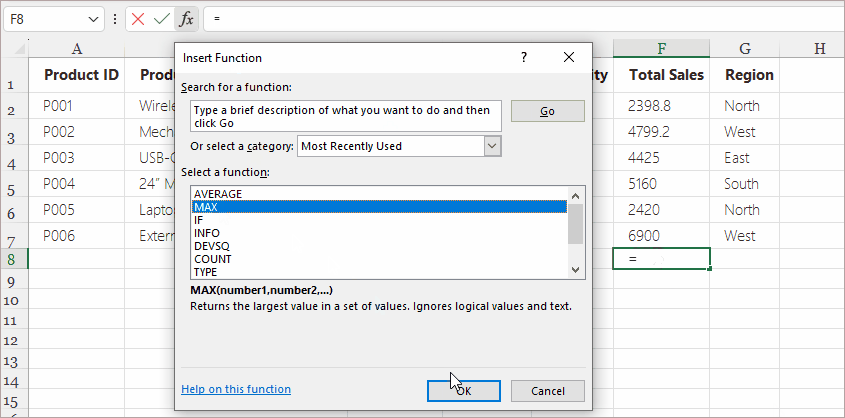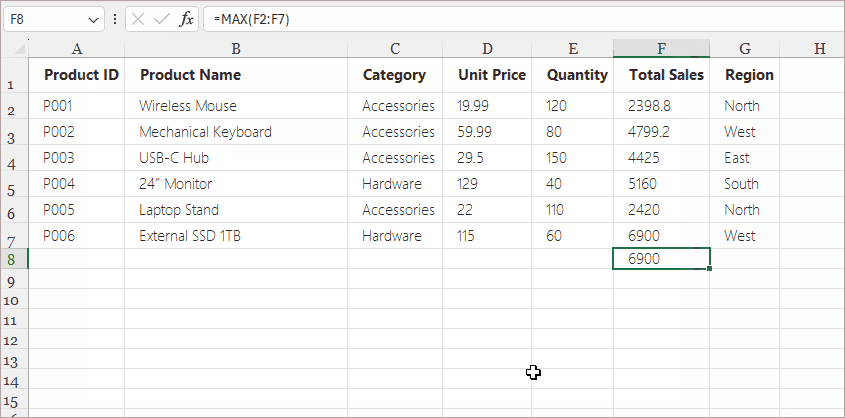
Method 3. Use the Insert Function (fx) Button (Most Beginner-Friendly)
Excel’s Insert Function (fx) tool is specifically designed for users who are still learning formulas or prefer guided steps when building more complex functions.
Steps:
- Click the cell where you want the formula result.
- Click the fx button to the left of the Formula Bar.
- Choose a function category (Math, Text, Date & Time, Logical, Lookup, etc.).
- Select the desired function (e.g., SUMIFS , IF , LEFT , VLOOKUP ).
- Fill in the argument fields in the pop-up dialog.
- Click OK .
Example Use Cases:
- Learning how Excel functions work
- Formulas with multiple arguments
- Financial, date, and statistical calculations
- Anything where you want Excel to help guide the formula setup
Why this method is useful:
- Helps beginners avoid syntax errors
- Shows a description of each function and example usage
- Provides structured fields for entering arguments
This method is slower than direct entry but much more accurate when working with unfamiliar formulas.
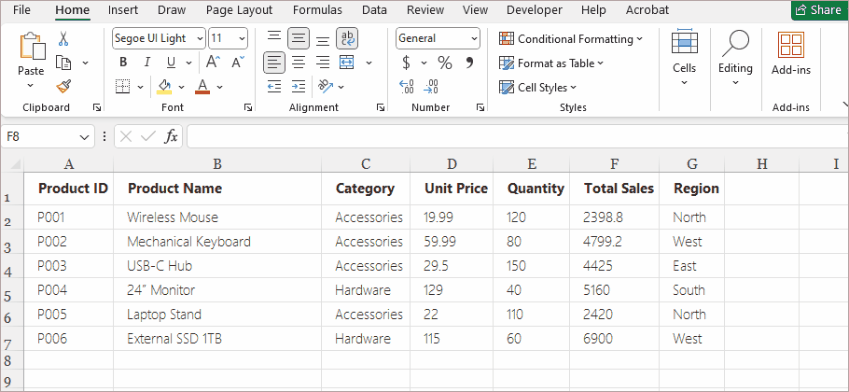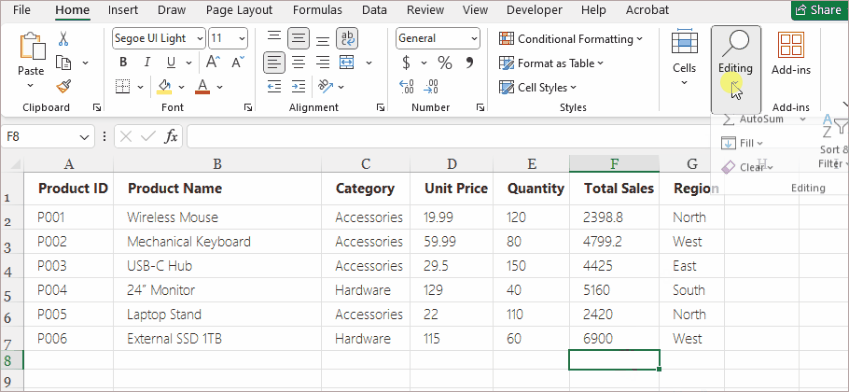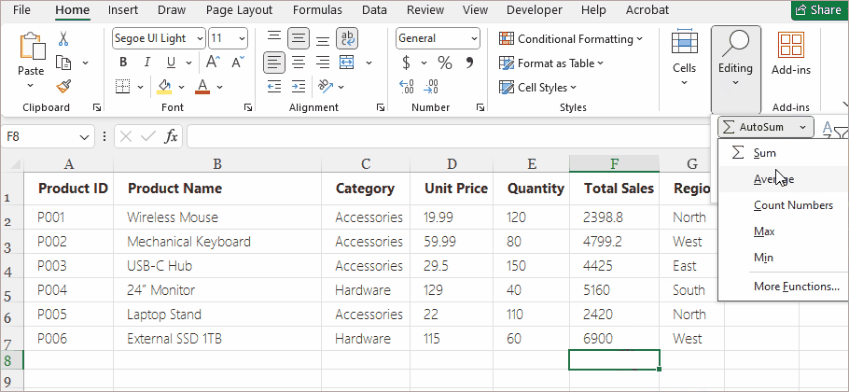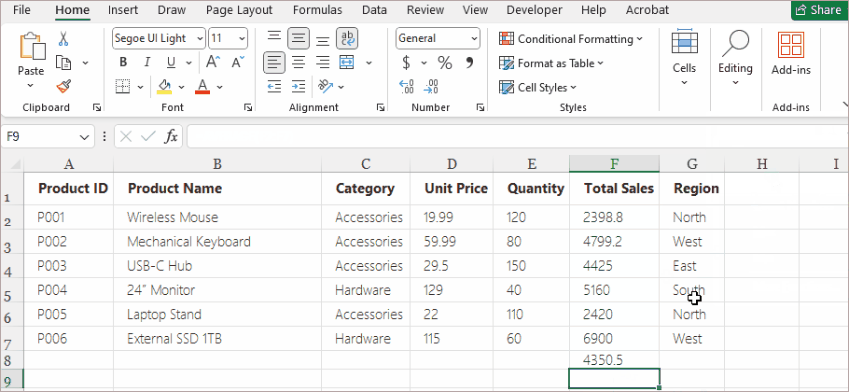
Method 4. Use AutoSum and Quick Functions (Extremely Efficient)
The AutoSum tool provides one-click shortcuts for commonly used functions such as:
- SUM
- AVERAGE
- COUNT
- MAX
- MIN
Steps:
- Select a cell below or beside your numeric data.
- Go to Home > Editing > AutoSum (or choose another function from the dropdown).
- Excel highlights a suggested range automatically.
- Press Enter to accept.
Example Use Cases:
- Summing a column of sales data
- Finding the highest or lowest value in a range
- Calculating an average score
- Counting how many numeric values appear in a dataset
Why this method is useful:
- Saves time—no typing needed
- Perfect for summary reports
- Excel auto-detects relevant cell ranges
- Reduces errors in range selection
If you frequently work with numeric reports, summary tables, or accounting files, AutoSum can speed up your workflow dramatically.
Method 5. Insert Formulas Using the Fill Handle (Best for Repetition)
Once a formula is entered, Excel’s Fill Handle can copy that formula across multiple rows or columns, automatically adjusting cell references.
Steps:
- Enter a formula in the first cell (e.g., =D2*E2).
- Hover over the bottom-right corner until the cursor turns into a small black cross.
- Drag down or across to fill adjacent cells.
- Release the mouse button.
Excel updates the references automatically:
- D2 becomes D3
- E2 becomes E3
- And so on
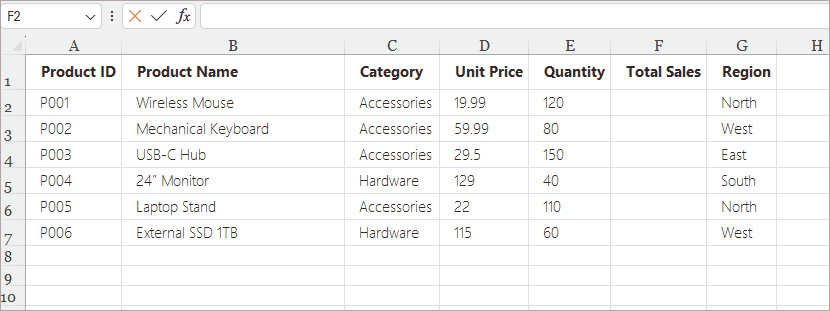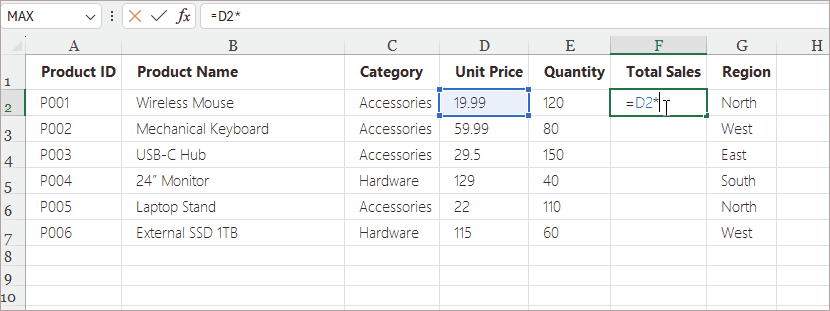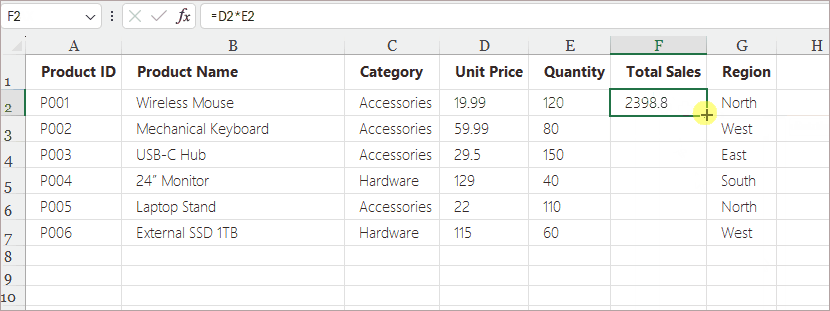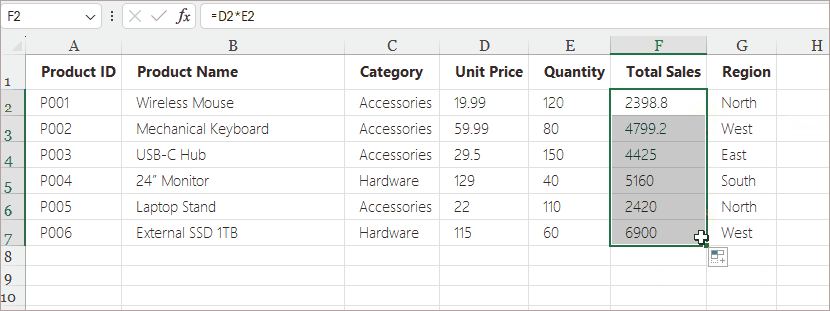
Example Use Cases:
- Calculating totals for hundreds of rows
- Applying the same logic to an entire dataset
- Generating sequences (e.g., =ROW(), =A1+10)
- Copying time or date calculations across cells
Why this method is useful:
- Extremely fast for repetitive calculations
- Automatically adjusts formulas based on position
- Reduces the need to manually type formulas in each row
This method is essential for data entry, financial modeling, budgeting, and any spreadsheet involving large datasets.
Method 6. Insert Formulas Programmatically (Python – Spire.XLS)
For automation, batch processing, or generating Excel files dynamically, inserting formulas programmatically is the most scalable approach. Using Python with Spire.XLS , you can create Excel files, insert formulas, and perform calculations automatically—without opening Excel.
Steps:
-
Install Spire.XLS for Python using pip.
pip install spire.xls -
Import the required module into your script.
-
Load an existing Excel file into a Workbook object.
-
Access the worksheet where you want to insert the formula.
-
Write the formula to the target cell using the Formula property.
-
Save the updated file to a new Excel workbook.
Example:
from spire.xls import *
# Create workbook and load an Excel file
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.LoadFromFile("input.xlsx")
# Get the first worksheet
sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Insert a formula
sheet.Range["F8"].Formula = "=SUM(F2:F7)"
# Save the Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Read further: Add or Read Formulas in Excel Using Python
Example Use Cases:
- Automated reporting
- Data transformation workflows
- Generating financial or sales reports for apps
- Batch processing thousands of Excel files
Why this method is useful:
- Eliminates manual work
- Ensures consistency across generated files
- Integrates Excel logic into larger software systems
This is the most powerful option for developers and analysts, as Spire.XLS for Python not only inserts formulas programmatically but also creates and edits workbooks, applies formatting, generates charts, converts Excel to PDF, and automates complex data tasks.
Comparison: Which Method Should You Choose?
| Method | Best For | Ease of Use | Speed | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Typing in Cell | Quick/basic formulas | Easy | Very fast | Ideal for small tasks |
| Formula Bar | Long or complex formulas | Easy | Medium | Offers more editing space |
| Insert Function (fx) | Beginners/complex functions | Very easy | Medium | Guided formula creation |
| AutoSum | Summaries & common functions | Very easy | Very fast | One-click totals |
| Fill Handle | Repeated formulas | Easy | Extremely fast | Auto-adjusts cell references |
| Python (Spire.XLS) | Automation & batch tasks | Medium | Fastest at scale | Best for developers |
Summary
Inserting formulas in Excel can be done in multiple simple and efficient ways, depending on your workflow. This article covered six practical methods — including using AutoSum, entering formulas through the Formula Bar, selecting functions from the Function Library, using the Fill Handle to copy formulas, typing manual formulas, and automating formula insertion with Spire.XLS for Python . Each method offers unique advantages, from quick calculations to scalable automation. By choosing the approach that best fits your needs, you can improve accuracy, streamline data processing, and make your Excel tasks more efficient.
FAQs About Inserting Formulas to Excel
Q1. My formula is not calculating and displays as text. Why?
The cell is formatted as Text. Change it to General and re-enter the formula.
Q2. What’s the fastest way to apply a formula to hundreds of rows?
Use the Fill Handle or automation via Python (Spire.XLS) .
Q3. Can Excel formulas reference other worksheets?
Yes. Example: =Sheet2!A1 + Sheet3!B5
Q4. Can formulas be generated automatically?
Yes. Tools like Spire.XLS for Python can insert formulas programmatically.
You May Also Be Interested In
5 Efficient Ways to Convert PDF to Black and White
Table of Contents
Converting a PDF to black and white (grayscale) is a quick way to reduce file size, improve print efficiency, and create a clean and consistent style for documents. Whether you’re preparing files for professional printing, archiving scanned documents, or optimizing content for the web, there are several tools—both built-in and third-party—that can convert your PDF into monochrome in just a few clicks.
This article introduces five efficient methods using desktop software, built-in system tools, online converters, and even a Python programming approach.
Method Overview:
- Method 1. Using Adobe Acrobat Pro
- Method 2. Using Microsoft Print to PDF (Windows)
- Method 3. Using Preview on macOS
- Method 4. Using PDF Candy (Online Tool)
- Method 5. Using Spire.PDF for Python
Method 1. Using Adobe Acrobat Pro
Adobe Acrobat Pro is a professional-grade PDF editor widely used for document creation, editing, and print preparation. Its built-in color management ensures accurate and consistent grayscale conversion across all pages. This makes it a reliable choice for users who need high-quality, print-ready black-and-white PDFs.
Steps
-
Open the PDF in Adobe Acrobat Pro.
-
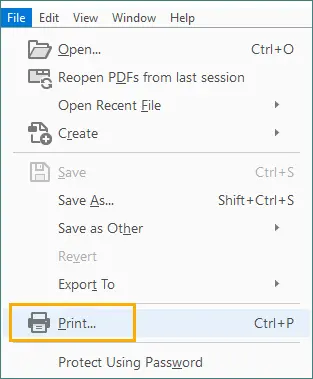
Go to File > Print.
-
Select Adobe PDF as the printer.

-
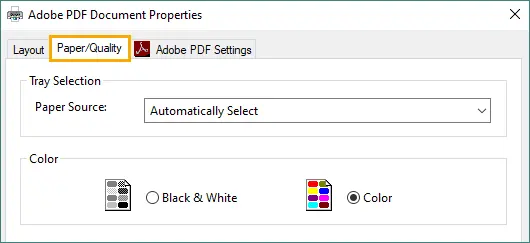
Click Properties and navigate to the Paper/Quality tab.
-
Select Black & White in the Color section, then click OK to apply.
-
Click Print and save the newly generated grayscale PDF.
Why Choose This Method
- High-quality conversion
- Consistent grayscale output
Method 2. Using Microsoft Print to PDF (Windows)
Microsoft Print to PDF is a built-in Windows feature that lets you convert documents into PDF format from any printable application. With its simple print dialog and grayscale option, it provides an easy way to generate black-and-white PDFs without installing extra software. It’s ideal for quick conversions and everyday document tasks.
Steps
-
Open your PDF using Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, or any viewer.
-
Press Ctrl + P to open the Print dialog.
-
Choose Microsoft Print to PDF as the printer.
-
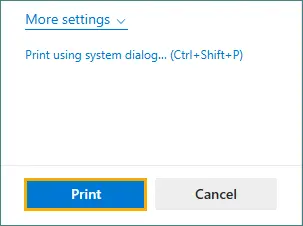
Look for Color and select Black and White option.
-
Click Print, then save the generated grayscale PDF.
Why Choose This Method
- No extra software needed
- Fast and simple
- Works for nearly all PDFs
Method 3. Using Preview on macOS
Preview is the default PDF and image viewer on macOS that includes powerful built-in export and color filtering features. Its Quartz Filters allow you to instantly convert any PDF to black and white with smooth shading and clear text. This makes it one of the fastest and most convenient options for Mac users.
Steps
-
Open the PDF in Preview.
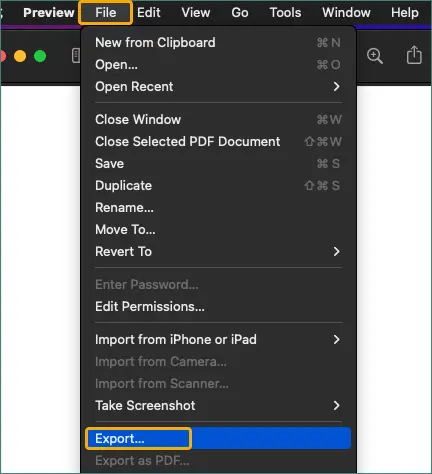
-
Click File > Export.
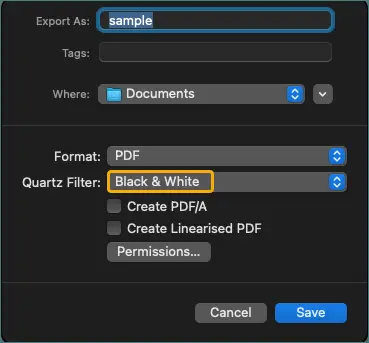
-
Under Quartz Filter, choose Black & White or Gray Tone.
-
Save the exported PDF to apply the filter.
Why Choose This Method
- Built into every Mac
- Easy and fast
- Produces clean monochrome output
Method 4. Using PDF Candy (Online Tool)
PDF Candy is a popular web-based PDF processing toolkit that offers a dedicated grayscale conversion feature accessible from any browser. The tool requires no installation and automatically handles the entire conversion process, making it perfect for quick, one-off tasks. Thanks to its clean interface and fast performance, it’s a great option for casual users on any device.
Steps
-
Visit the PDF Candy's Grayscale PDF Converter.
-
Upload your PDF file by dragging and dropping it into the designated area or selecting it from your device.

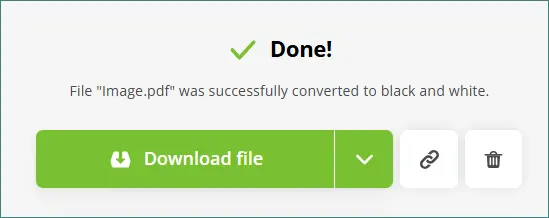
-
Click on the GRAYSCALE 1 File(s) button.

-
Download the newly converted black and white PDF.
Why Choose This Method
- Convenient and accessible anywhere
- No installation required
- Works on all platforms (Windows, macOS, mobile)
Note: Avoid uploading sensitive or confidential files to online tools.
Method 5. Using Spire.PDF for Python
Spire.PDF for Python is a professional PDF library that enables developers to programmatically process and convert PDF documents. Its grayscale conversion API ensures consistent output across all pages, making it suitable for automated or large-scale document workflows. This method is ideal for applications that require repeatable, accurate, and fully scripted PDF processing.
Steps
-
Install Spire.PDF for Python.
pip install spire.pdf -
Import the library and specify the input and output PDF file paths.
-
Use the PdfGrayConverter class to load the original PDF.
-
Call the ToGrayPdf method to generate the black-and-white PDF.
Code Example
from spire.pdf.common import *
from spire.pdf import *
# Specify the input and output PDF file paths
inputFile = "input.pdf"
outputFile = "output.pdf"
# Load the input document using the PdfGrayConverter class
converter = PdfGrayConverter(inputFile)
# Convert it to a black and white PDF
converter.ToGrayPdf(outputFile)
Read Further: Convert PDF to Grayscale or Linearized in Python
Why Choose This Method
- Ideal for automated or bulk conversion
- Highly customizable
- Produces consistent grayscale output across all pages
In addition to converting PDFs to black and white, Spire.PDF also supports advanced features such as converting PDF to PDF/A, exporting PDF to Word, extracting text and images, merging or splitting PDFs, and more.
Comparison: Which Method Should You Choose?
| Method | Best For | Ease of Use | Installation | Automation | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adobe Acrobat Pro | Professional printing, high quality | ★★★★★ | Required (Paid) | No | Most accurate grayscale results |
| Microsoft Print to PDF | Quick Windows conversions | ★★★★★ | Built-in | No | Quality depends on printer options |
| macOS Preview | Mac users | ★★★★★ | Built-in | No | Clean grayscale filters |
| PDF Candy (Online) | Occasional users | ★★★★★ | None | No | Avoid for confidential files |
| Spire.PDF + Python | Developers, batch automation | ★★★☆☆ | Python + Library | Yes | Fully automated, customizable |
Summary
Converting PDFs to black and white can be done easily using built-in tools, online services, or professional software.
- Choose Adobe Acrobat Pro for the highest quality.
- Use Microsoft Print to PDF or Preview for quick platform-built solutions.
- Select PDF Candy for instant online conversions.
- Pick Spire.PDF for Python if you need a programmable, scalable workflow.
No matter your environment, there’s a method that fits your needs.
FAQs
Q1. Will converting a PDF to black and white reduce file size?
Yes. Grayscale files are usually smaller because color data is removed.
Q2. Does grayscale reduce image quality?
Not the page clarity, but it removes color information. Text remains sharp.
Q3. Is it safe to use online tools?
For non-sensitive files, yes. Avoid uploading confidential documents.
Q4. Can I batch convert multiple PDFs?
Yes. PDF Candy and Spire.PDF for Python support batch processing.
You May Also Be Interested In
Find and Replace Text in Word Documents: 5 Easy Methods
Table of Contents
- Method 1: Use Word’s Built-in Find and Replace Tool
- Method 2: Use Word’s Advanced Find & Replace
- Method 3: Find and Replace Formatting in Word
- Method 4: Batch Find and Replace Using Word Macros
- Method 5: Automate Find & Replace with Python
- Comparison: Which Method Should You Use?
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)

Finding and replacing text is one of the most common tasks when working with Word documents. Whether you’re fixing typos, updating names, changing formatting, or processing documents in bulk, Word—and modern tools—offer several reliable ways to get the job done quickly and accurately.
This guide covers the five most practical ways to find and replace text in Word documents, from simple built-in features to full automation with Python.
Method Overview:
- Method 1: Use Word’s Built-in Find and Replace Tool
- Method 2: Use Word’s Advanced Find & Replace
- Method 3: Find and Replace Formatting in Word
- Method 4: Batch Find and Replace Using Word Macros
- Method 5: Automate Find & Replace with Python
Method 1: Use Word’s Built-in Find and Replace Tool
This is the fastest way to update words or phrases in a single document. It highlights each match and lets you replace items individually or all at once, making it ideal for simple, quick edits with no technical steps required.
How to do it
-
Open the Word document.
-
Press Ctrl + H (Windows) or Command + H (Mac).
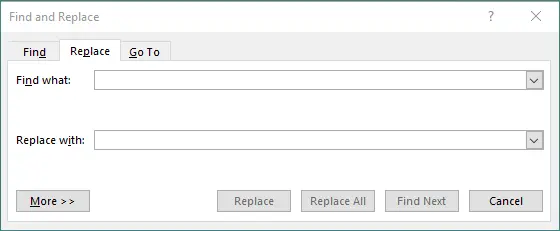
-
In the dialog box:
- Enter the text you want to find.
- Enter the text you want to replace it with.
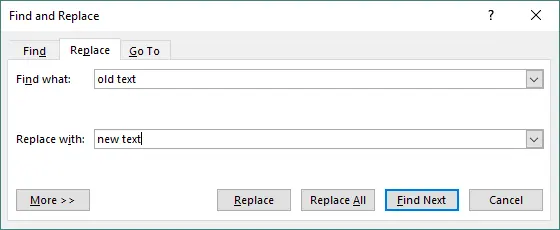
-
Click Find Next, Replace, or Replace All.
Example use cases
- Fixing spelling errors.
- Replacing outdated product names.
- Updating placeholders like [Name] or [Date].
- Changing repeated phrases throughout the document.
Method 2: Use Word’s Advanced Find & Replace (Patterns, Options, and Special Characters)
Advanced Find & Replace offers precise control with wildcards, case sensitivity, whole-word matching, and special character search. It’s great for refining complex documents, fixing layout inconsistencies, or applying structured changes.
How to do it
-
Open Find and Replace → click More >>.
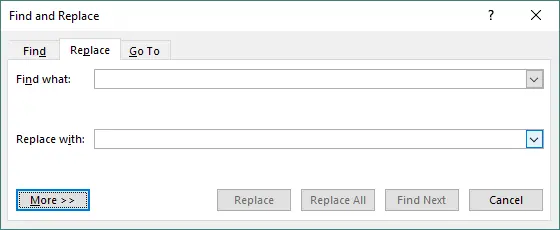
-
Use options such as:
- Match case
- Find whole words only
- Use wildcards
- Special (tabs, line breaks, paragraph marks)
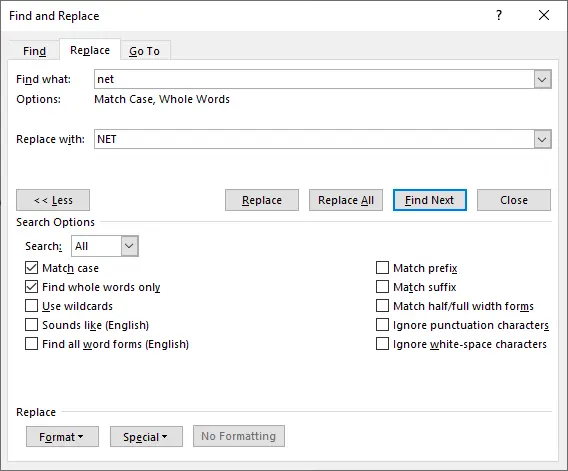
-
Click Find Next, Replace, or Replace All.
Example use cases
- Finding email addresses or dates using wildcard patterns.
- Replacing double spaces with single spaces.
- Removing extra paragraph breaks.
- Changing only capitalized or lowercase text.
Method 3: Find and Replace Formatting in Word
This method focuses on visual consistency. You can change font styles, colors, highlights, or even switch text from one style to another. It’s perfect for refreshing document formatting or aligning content with branding guidelines.
How to do it
-
Open Find and Replace → click More >>.

-
Click Format under the Find or Replace box.
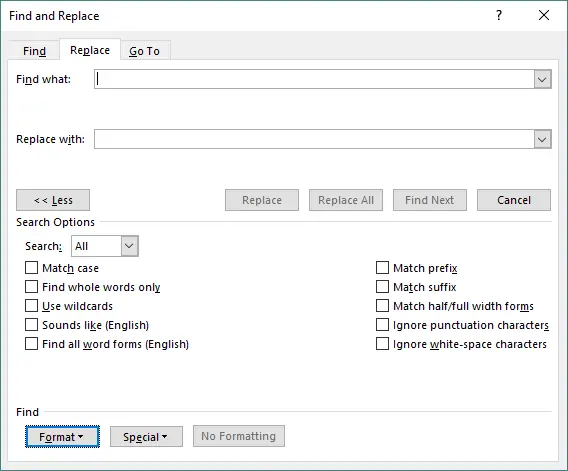
-
Select the formatting to find (e.g., bold, size, color).
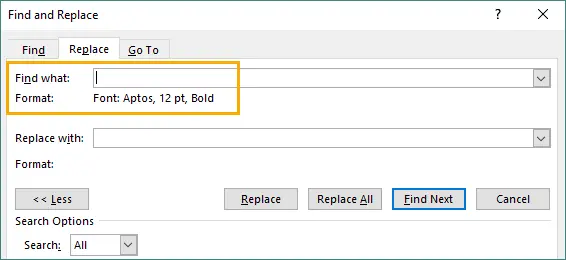
-
Choose formatting to apply OR leave Replace text blank to keep the same words.
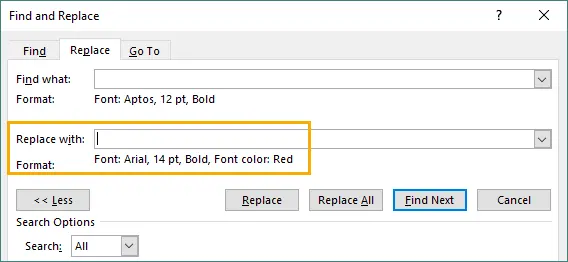
-
Click Replace All.
Example use cases
- Change all bold text to normal.
- Update all 11pt text to 12pt.
- Remove unwanted highlight colors.
- Switch old styles to a new branding style.
Method 4: Batch Find and Replace Using Word Macros (VBA)
VBA Macros allow you to automate repeated find-and-replace tasks across one or many documents. It’s efficient for recurring edits, template updates, or version migrations where manual work would be too slow.
How to do it
-
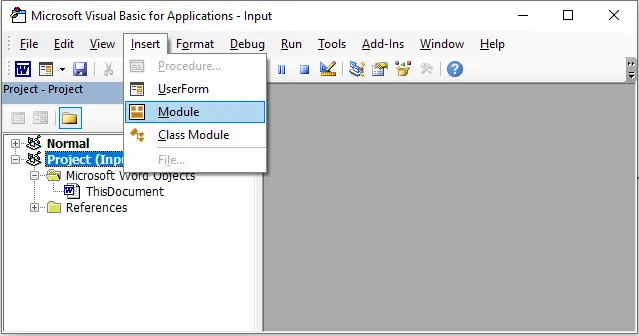
Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor.
-
Go to Insert → Module.
-
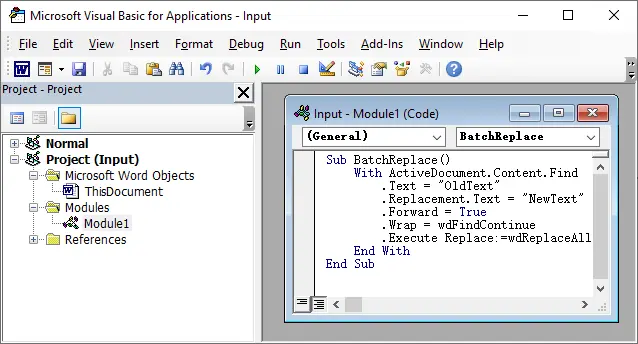
Paste your macro code.
-
Run the macro (Alt+F8) to perform replacements automatically.

Example VBA
Sub BatchReplace()
With ActiveDocument.Content.Find
.Text = "OldText"
.Replacement.Text = "NewText"
.Forward = True
.Wrap = wdFindContinue
.Execute Replace:=wdReplaceAll
End With
End Sub
Example use cases
- Updating monthly report terminology.
- Replacing company names across templates.
- Fixing formatting issues in multiple files.
- Automating repeated editorial tasks.
Method 5: Automate Find & Replace with Python (Using Spire.Doc)
For large-scale or backend workflows, using Python provides high-speed, automated text replacement without opening Word. It’s ideal for processing hundreds of documents, generating reports, or integrating document edits into software systems. Among the many available libraries, Spire.Doc for Python is a powerful, full-featured API that works without Microsoft Word installed.
How to do it
-
Install Spire.Doc for Python.
pip install spire.doc -
Load the document in Python.
-
Call the Replace() method for text substitutions.
-
Save the updated document.
Python example
from spire.doc import *
# Load the Word file
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("input.docx")
# Replace simple text
doc.Replace("OldText", "NewText", True, True) # The two True parameters enable case-insensitive and whole-word matching.
# Save the updated file
doc.SaveToFile("output.docx", FileFormat.Docx)
doc.Close()
Advanced replacement examples
-
Replace text using regex
regex = Regex("""\\#\\w+\\b""") document.Replace(regex, "NewText") -
Replace multiple keywords dynamically
replacements = { "CompanyName": "TechNova", "Year": "2025", "Product": "VisionX" } for key, value in replacements.items(): doc.Replace(key, value, True, True)
Read further: Find and Replace Text in Word Using Python
Why choose the Python/automation method?
- Extremely fast for large batches.
- No user interaction needed.
- Works on servers, CI/CD pipelines, and cloud environments.
- Supports advanced formatting and pattern-based replacement.
- Ideal for enterprise-scale document workflows.
Comparison: Which Method Should You Use?
| Method | Best For | Ease of Use | Automation | Flexibility | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Word’s Built-in Find & Replace | Quick edits; simple replacements | Very easy | None | Medium — supports wildcards & formatting | Not ideal for batch processing or complex logic |
| Advanced Find & Replace | Locating many occurrences visually | Easy | None | Low — mostly visual | Not suitable for mass replacements |
| Replace Formatting-Specific Content | Updating styles, fonts, formatting attributes | Medium | None | Medium — works well for style-driven changes | Still manual; limited logic |
| VBA Macro (Automated Find & Replace) | Repetitive replacements; batch changes; rule-based logic | Medium | Semi/full automation | High — supports loops, conditions, custom rules | Requires scripting; not beginner-friendly |
| Automate with Python (Spire.Doc) | Bulk processing; repetitive tasks; large-scale automation | Medium | Full automation | Very high — control over content, formatting, loops, logs | Requires Python; library installation needed |
Conclusion
Finding and replacing text in Word documents is a fundamental task, yet the method you choose greatly affects your speed and efficiency. For small, everyday edits, Word’s built-in tools are more than enough. For complex formatting adjustments, the advanced features give you fine control. And for enterprise or large-scale needs, automation with VBA or Python provides unmatched power and scalability.
By understanding the strengths of each approach, you can choose the method that best fits your workflow—whether you're editing a single page or generating thousands of documents automatically.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1. Can Word find and replace text inside headers, footers, or text boxes?
Yes, but text boxes are sometimes skipped. For full coverage, use VBA or Python automation.
Q2. How do I find and replace text with formatting in Word?
Use More > Format in Find & Replace to match or apply formatting such as bold, font, and color.
Q3. What’s the best way to replace text in multiple Word files at once?
Use VBA or Python automation, since Word’s built-in tool cannot process multiple files automatically.
Q4. Is Python or VBA better for automating find-and-replace?
VBA is faster for simple desktop tasks. Python is better for large-scale, batch, or server-side operations.
You May Also Be Interested In
How to Convert Numbers to Text in Excel (5 Easy Ways)
Table of Contents

Whether you’re preparing reports, cleaning datasets, or automating invoices, sometimes you need numbers to behave like text in Excel. For example, you may want to preserve leading zeros in ZIP codes, display IDs as text, or format numeric values with specific symbols and patterns.
Converting numbers to text ensures that Excel stops treating those values as numeric data—preventing automatic rounding, unwanted calculations, or scientific notation formatting. Fortunately, Excel provides several built-in and programmatic ways to handle this.
In this article, we’ll explore five effective methods to convert numbers to text in Excel—from simple formatting tricks to automated solutions using VBA and Python (Spire.XLS). Each method serves a different need, so you can choose the one that fits your workflow best.
Method overview:
- Method 1. Using Excel Cell Formatting Tools
- Method 2. Using Text-to-Columns Tool
- Method 3. Using Excel Functions that Return Text
- Method 4. Using VBA Macro
- Method 5. Using Python Automation
Why Convert Numbers to Text?
Numbers in Excel are typically stored in numeric form, which allows for calculations, formulas, and charting. However, in many real-world cases, you need them as text strings instead. Here are a few reasons why:
- Preserve data integrity: Keep phone numbers, employee IDs, or postal codes exactly as entered (e.g., “00123” instead of “123”).
- Avoid calculation errors: When merging datasets, numeric values can accidentally sum or round; converting them to text prevents this.
- Improve formatting flexibility: Text-formatted numbers allow for custom prefixes, suffixes, and display styles (e.g., “USD 123.00”).
- Ensure consistency for exports: When exporting data to other systems (databases, CSVs, or APIs), text format ensures values remain intact.
- Enable automation and scripting: Some automated processes require string inputs instead of numeric ones.
Method 1. Using Excel Cell Formatting Tools
One of the easiest ways to convert numbers to text is through Excel’s Format Cells feature. This method doesn’t require formulas or code, and it’s suitable for small to medium datasets.
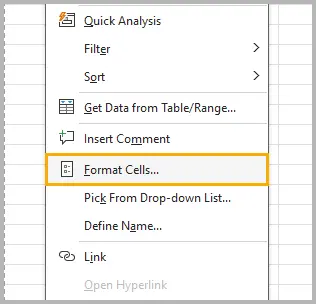
Steps:
- Select the cells containing numbers.
- Right-click and choose Format Cells .
- In the Number tab, select Text .
- Click OK .
- Re-enter the numbers (or press F2 → Enter to refresh existing values).

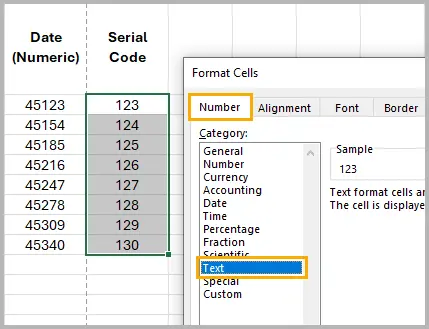
Excel will now treat those values as text instead of numbers. You can confirm this by checking that the cell content is left-aligned and that a small green triangle (text indicator) appears in the upper-left corner.
Alternative:
If you prefer a manual approach, you can add an apostrophe (') before the number. Excel interprets this as text but hides the apostrophe when displayed.
Pros:
- Quick and intuitive.
- No formulas or coding required.
Cons:
- Not ideal for very large datasets.
- Must be repeated if new data is added.
Method 2. Using Text-to-Columns Tool
If you want to convert numbers to text without using formulas or coding, Excel’s Text-to-Columns feature is a quick and practical method. It allows you to reformat numeric values into plain text within their original cells.
Steps:
- Select the range that contains the numbers you want to convert.
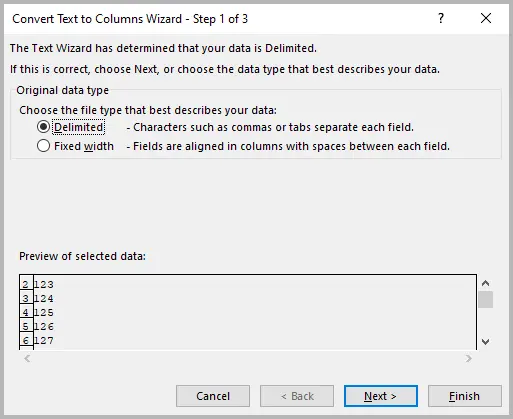
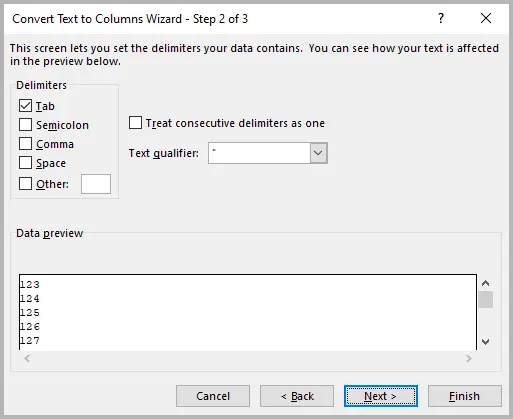
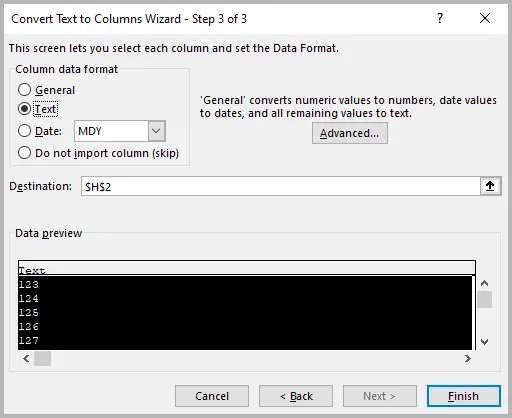
- Go to the Data tab → click Text to Columns .
- In the Convert Text to Columns Wizard , choose Delimited → click Next .
- Skip delimiter options → click Next again.
- In Column Data Format , select Text .
- Click Finish .
After applying Text-to-Columns, the numbers are stored as text values directly in their original cells (indicated by a small green triangle in the corner).
Pros:
- Converts numbers to text in place.
- No need for helper columns or formulas.
- Works in all Excel versions.
Cons:
- Manual process (not dynamic).
- Must be repeated when new data is added.
Method 3. Using Excel Functions that Return Text
Excel offers several functions that can convert numbers to text directly in formulas. Two of the most useful are TEXT() and VALUETOTEXT() .
Option 1: TEXT Function
The TEXT() function converts a numeric value into text while allowing you to specify a custom format.
Syntax:
=TEXT(value, format_text)
Examples:
| A (Original) | B (Formula) |
|---|---|
| 1234.5 | =TEXT(A1, "0.00") → “1234.50” |
| 5678 | =TEXT(A2, "$#,##0") → “$5,678” |
The TEXT() function is especially powerful when you want your text output to follow a specific numeric, date, or currency pattern.
Tip: Combine TEXT() with other text functions like CONCAT(), TEXTJOIN(), or the ampersand (&) operator to create descriptive strings:
="Total amount: " & TEXT(A1, "$#,##0.00")
Option 2: VALUETOTEXT Function (Excel 365 / Excel 2021 and Later)
If you’re using a modern Excel version, the VALUETOTEXT() function provides a more direct and flexible conversion.
Syntax:
=VALUETOTEXT(value, [format])Parameters:
- value — The number you want to convert.
- [format] — Optional; use 0 for simple text or 1 for JSON-compatible output.
Examples:
| A (Original) | B (Formula) |
|---|---|
| 9876 | =VALUETOTEXT(A1) → “9876” |
| 543.21 | =VALUETOTEXT(A2,1) → “543.21” |
This function is particularly useful when you’re working with dynamic arrays, automation scripts, or exporting data that needs to remain textual.
Pros:
- Formula-based and flexible.
- Works dynamically with changing data.
- Supports formatting customization.
Cons:
- VALUETOTEXT() requires newer Excel versions.
- Results depend on correct format strings.
Tip: Replace the Original Numbers with Text Values
When you use formulas such as TEXT() or VALUETOTEXT(), Excel only displays the converted text in the formula cells — it doesn’t overwrite your original numbers.
To permanently replace numbers with text equivalents:
- Enter the formula in a blank column (e.g., column B).
- Verify the results look correct.
- Select the formula cells and copy them.
- Right-click the original numeric column → choose Paste Special → Values .
- Delete the helper column if you no longer need it.
Method 4. Using VBA Macro
For users who frequently need to convert numbers to text, creating a VBA macro offers automation and flexibility. With just a few lines of code, you can convert an entire range in one click.
Steps:
- Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor.
- Click Insert → Module .
- Paste the following code:
- Close the editor and return to Excel.
- Select the range of numbers you want to convert.
- Press Alt + F8 , choose ConvertNumbersToText , and click Run .
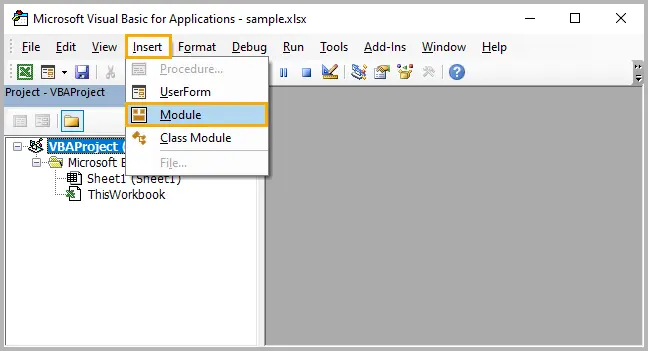
Sub ConvertNumbersToText()
Dim cell As Range
For Each cell In Selection
If IsNumeric(cell.Value) Then
cell.Value = CStr(cell.Value)
End If
Next cell
End Sub
Excel will loop through your selection and convert all numeric values into text strings using VBA’s CStr() function.
Pros:
- Fully automated.
- Works on large data ranges.
- Can be reused anytime.
Cons:
- Requires enabling macros.
- May be restricted by some organizational policies.
Tip: If you want to preserve the original numeric formatting, you can enhance the macro with additional logic using Format() instead of CStr().
Method 5. Using Python Automation (with Spire.XLS for Python)
If you’re working with Excel files programmatically, Spire.XLS for Python provides a straightforward and reliable way to convert numbers to text directly in your scripts. This approach is especially valuable for large-scale automation, batch processing, or web-based systems.
Example Code:
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create a Workbook object
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel document
workbook.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Employee.xlsx")
# Get a specific worksheet
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]
# Get a cell range
cellRange = worksheet.Range["F2:F9"]
# Convert numbers in the cell range to text
cellRange.NumberFormat = "@"
# Save the workbook to a different Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("output/NumbersToText.xlsx", ExcelVersion.Version2013)
# Dispose resources
workbook.Dispose()
How It Works
- Workbook Management: The Workbook object allows you to load and work with existing Excel files using the
LoadFromFilemethod. - Worksheet Access: Each workbook can contain multiple worksheets, which you can access by index.
- Cell Range Selection: The
Rangemethod identifies specific rows and columns for data manipulation. - Formatting Cells: Setting the
NumberFormatproperty to"@"converts the cell format from numeric to text. - Saving Changes: The
SaveToFilemethod saves the modified workbook to a new or existing file.
For more detailed instructions, check out the full tutorial: Convert Text to Numbers and Numbers to Text in Excel in Python
Pros:
- Ideal for bulk and automated conversions.
- Works without launching Excel.
- Easily integrated into data pipelines or web applications.
Cons:
- Requires installing and using Spire.XLS.
- Best suited for users comfortable with Python scripting.
As a comprehensive Python Excel library, Spire.XLS enables programmers to easily manage and customize Excel formatting through code. Want to learn more? Check out this tutorial: Format Excel with Python
Comparison Table: Which Method Should You Choose?
| Method | Type | Works In-Place? | Automation Level | Difficulty | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Formatting | Manual | Yes | None | ★☆☆☆☆ | Simple formatting only |
| Text-to-Columns | Manual | Yes | None | ★★☆☆☆ | One-time conversion |
| TEXT / VALUETOTEXT | Formula | No | Low | ★★☆☆☆ | Dynamic conversion |
| VBA Macro | Code | Yes | High | ★★★☆☆ | Frequent conversions |
| Python (Spire.XLS) | Code | Yes | Very High | ★★★★☆ | Automated batch processing |
Summary
Converting numbers to text in Excel can be as simple—or as advanced—as you need it to be. For most users, Excel’s cell formatting tools and the Text-to-Columns feature provide quick, built-in ways to change numeric data into text without using any formulas.
If you want more control or need formatted text outputs, Excel’s TEXT and VALUETOTEXT functions are flexible options that let you customize display styles or combine numbers with descriptive text. For larger or recurring conversion tasks, automation through VBA macros or Spire.XLS for Python offers speed, accuracy, and scalability—perfect for enterprise-level workflows.
When selecting a method, consider how often you’ll perform the task, whether you need dynamic updates, and if automation is a priority. With these five methods, you can convert numbers to text in Excel efficiently, no matter your skill level or data size.
FAQs
Q1: Will converting numbers to text affect calculations?
Yes. Once a value is text, Excel will no longer treat it as numeric in formulas like SUM or AVERAGE.
Q2: Does changing the cell format to “Text” convert existing numbers automatically?
No. You’ll need to re-enter or refresh values (press F2 → Enter) after changing the format.
Q3: Can I convert numbers to text without losing formatting?
Yes. Use the TEXT() function and specify your desired format string (e.g., "0.00" or "$#,##0.00").
Q4: Can I reverse the process and turn text back into numbers?
Absolutely. Use the VALUE() function or convert the column format back to “Number.”
Q5: Is Spire.XLS free to use?
Spire.XLS offers both a free and a commercial version. The free version supports most common features for small to medium tasks.
You May Also Be Interested In
5 Effective Ways to Password Protect PowerPoint Files
Table of Contents
- Why Protect PowerPoint with a Password
- Method 1. Encrypt the Presentation with a Password
- Method 2. Add an Open or Modify Password via Save Options
- Method 3. Protect PowerPoint with a ZIP Password
- Method 4. Convert to PDF with Password
- Method 5. Automate Password Protection via Code
- Comparison Table: Choose the Right Way to Protect Your Presentation
- Summary
- FAQs

PowerPoint presentations often contain sensitive or confidential information — business reports, marketing plans, or academic research that you don’t want others to access or modify freely. Fortunately, PowerPoint provides several ways to secure your presentations with passwords or encryption.
In this guide, you’ll learn five effective ways to password protect PowerPoint files, from built-in encryption to automated protection using C#. We’ll also compare the methods so you can choose the right level of security for your needs.
Method Overview:
- Method 1. Encrypt the Presentation with a Password
- Method 2. Add an Open or Modify Password via Save Options
- Method 3. Protect PowerPoint with a ZIP Password
- Method 4. Convert to PDF with Password
- Method 5. Automate Password Protection via Code
Why Protect PowerPoint with a Password
While PowerPoint is widely used for creating and sharing presentations, few users realize how easy it is for unauthorized people to open, edit, or copy content if the file isn’t protected. Password protection helps you control who can view, edit, or reuse your work.
Reasons to secure your PowerPoint files with a password:
- Confidentiality: Prevent unauthorized users from viewing sensitive data such as internal financial reports or strategic plans.
- Integrity: Stop others from modifying your slides or altering content without permission.
- Professionalism: Ensure that only finalized versions of presentations are distributed.
- Compliance: Some organizations or clients require password protection to meet data security policies.
PowerPoint protection levels:
- Open protection: Requires a password to open the file.
- Modify protection: Allows viewing but prevents editing without a password.
Now let’s explore five practical ways to apply these protections.
Method 1. Encrypt the Presentation with a Password
The simplest and most secure way to protect your PowerPoint file is by encrypting it with a password using PowerPoint’s built-in Encrypt with Password feature. This method ensures that no one can open the file without entering the correct password.
How to do it:
Step 1: Open your PowerPoint file.
Step 2: Click File → Info → Protect Presentation → Encrypt with Password .
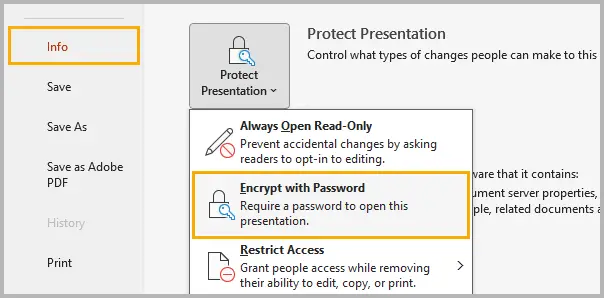
Step 3: Enter a strong password combining uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
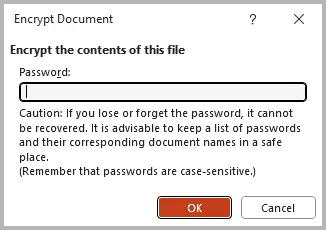
Step 4: Click OK , then save your presentation to apply the password protection.
Next time anyone tries to open the presentation, PowerPoint will prompt for the password before loading any content.
Tips:
- Use a password that’s at least 8–12 characters long.
- Avoid saving the password in the same folder as your presentation.
- If you lose the password, Microsoft cannot recover it.
Method 2. Add an Open or Modify Password via Save Options
PowerPoint’s Save Options feature allows you to apply both open and modify passwords directly while saving your presentation. This built-in protection lets you decide whether others can view the file, edit it, or both.
Step-by-step instructions:
Step 1: Click File → Save As and select your desired location.
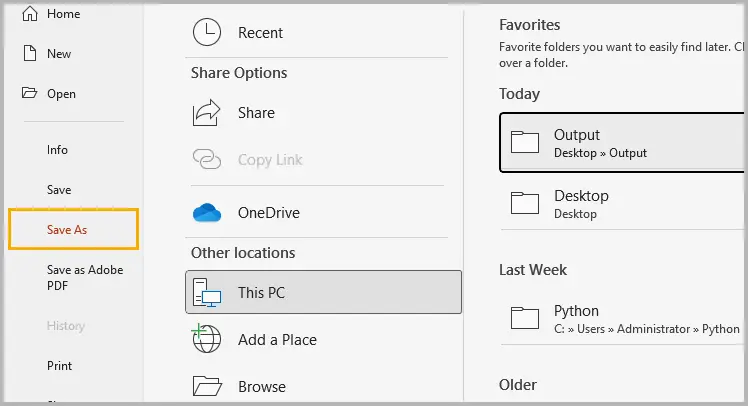
Step 2: In the Save As dialog, click Tools → General Options (Windows) or Options (Mac) .
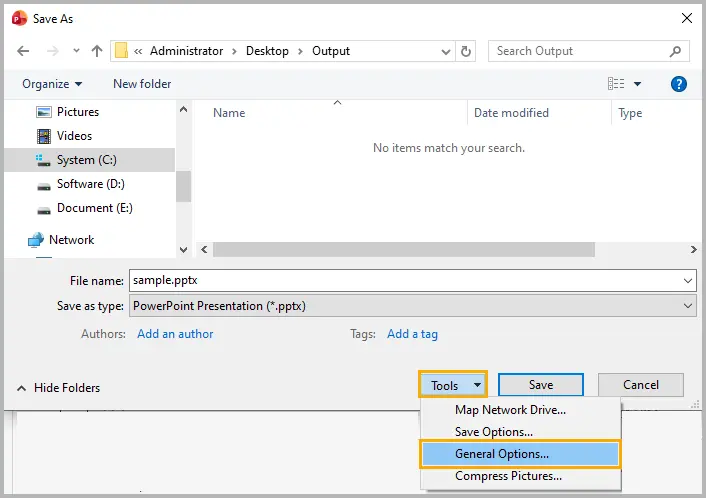
Step 3: Enter a password in the Password to open field to restrict access entirely, or in Password to modify to allow viewing but prevent editing.
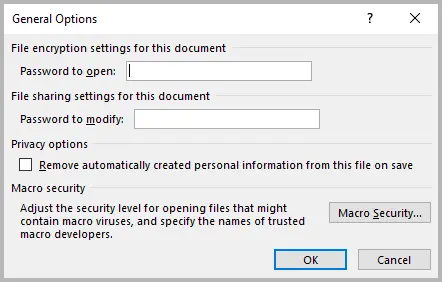
Step 4: Click OK , then save the file to apply the protection.
Tips:
- Use a strong, unique password for each presentation.
- Clearly differentiate between open and modify passwords to avoid confusion.
Method 3. Protect PowerPoint with a ZIP Password
If you frequently share presentations via email or cloud storage, compressing and encrypting them in a ZIP file adds an extra layer of protection. This method secures the file even before it’s opened in PowerPoint.
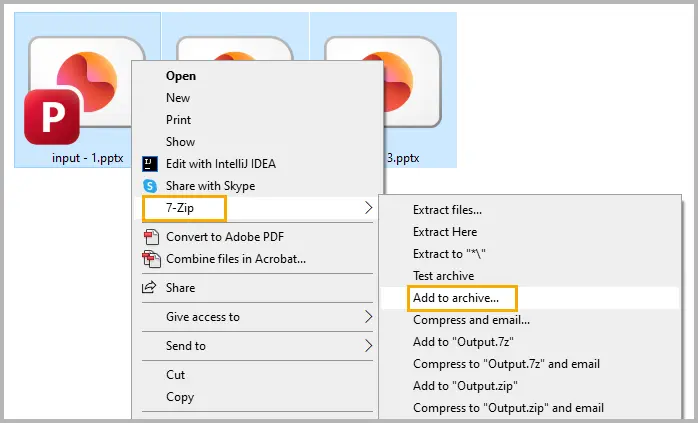
Steps (using 7-Zip or WinRAR):
Step 1: Select one or more PowerPoint files on your computer.
Step 2: Right-click on the selected files and select 7-Zip → Add to archive (or Compress on macOS).
Step 3: Choose the ZIP or RAR format.
Step 4: Enter a strong password, and enable AES-256 encryption if available.
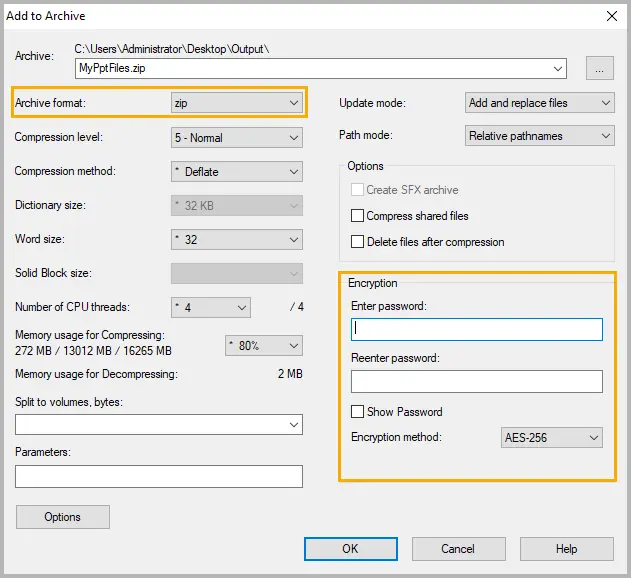
Step 5: Save the archive and share it instead of the original file.
Tips:
- Keep the password separate from the file to prevent unauthorized access.
- For shared projects, create unique passwords per archive to minimize risk.
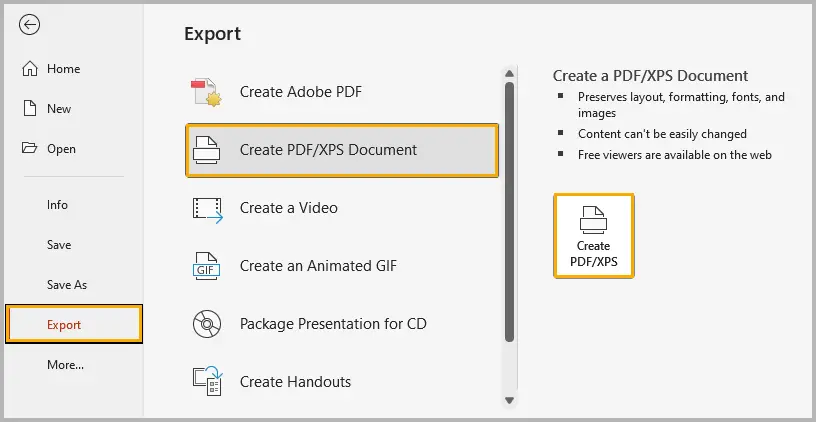
Method 4. Convert to PDF with Password
If you only need to share your PowerPoint slides in read-only form, converting them to a PDF with password protection is a practical choice. Recipients can view the slides but cannot edit or copy them without permission.
Follow these steps:
Step 1: Open your PowerPoint file and go to File → Export → Create PDF/XPS Document → Create PDF/XPS .
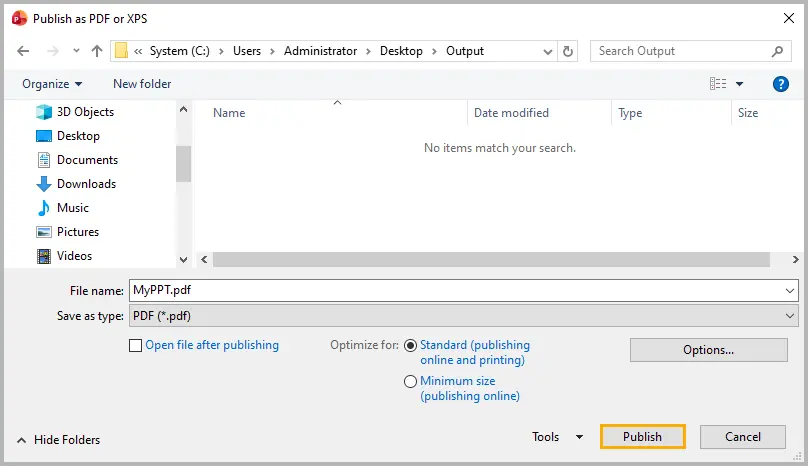
Step 2: Select export options and click Publish to generate the PDF.
Step 3: Open the PDF in Adobe Acrobat or another PDF editor.
Step 4: Select Tools , then click Protect .
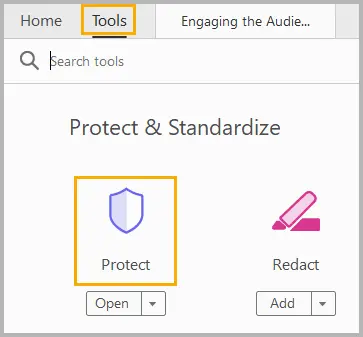
Step 5: Click Protect Using Password to set a password to view or edit the PDF, and then click Apply .
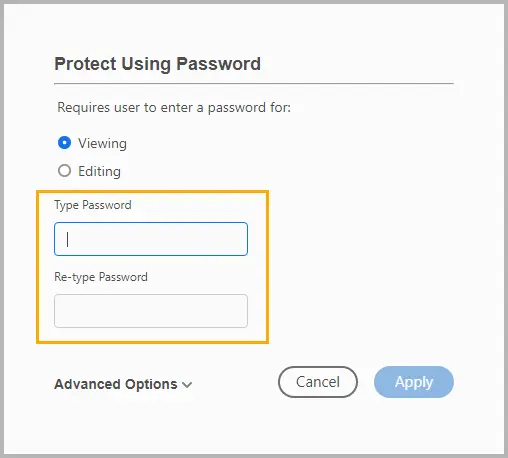
Tips:
- Set both user (open) and owner (edit) passwords for stronger protection.
- If sharing widely, consider applying print and copy restrictions in your PDF tool.
If you frequently export presentations as encrypted PDFs, you can automate this process with code. Check out our tutorial: Convert PowerPoint to Password-Protected PDF in C#
Method 5. Automate Password Protection via Code
For organizations that generate presentations automatically — such as reports, dashboards, or client proposals — manual password setting isn’t scalable. Instead, you can automate PowerPoint encryption using C# .
With the Spire.Presentation for .NET library, you can apply password protection to one or multiple files programmatically.
Step-by-step instructions:
Step 1: Install Spire.Presentation via NuGet.
PM> Install-Package Spire.Presentation
Step 2: Load your PowerPoint file in C#.
Step 3: Apply password protection using the Encrypt() method.
Step 4: Save the encrypted presentation.
Full code example:
using Spire.Presentation;
namespace ProtectPPTWithPassword
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new Presentation instance
Presentation presentation = new Presentation();
// Load the PowerPoint document from file
presentation.LoadFromFile("sample.pptx");
// Encrypt the presentation using a specified password
presentation.Encrypt("your password");
// Save the encrypted presentation to a new file in PPTX format
presentation.SaveToFile("Encrypted.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013);
presentation.Dispose();
}
}
}
Benefits:
Automating password protection with C# ensures consistency and accuracy, reduces the risk of human error, and allows batch encryption of multiple presentations. It also integrates easily with other automated tasks, streamlining your workflow and saving time.
Read further: Protect or Unprotect PowerPoint Presentations Using C#
Comparison Table: Choose the Right Way to Protect Your Presentation
| Method | Protection Type | Encryption Strength | Difficulty | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Encrypt with Password | Full encryption | AES 128-bit or higher | Easy | Confidential or sensitive presentations | Built-in strong security | Password recovery impossible |
| Save Options | File-level password | Moderate (legacy RC4 or partial) | Easy | Shared editable files | Flexible open/modify options | Weaker encryption for older formats |
| Third-Party Encryption Tools | Archive-level protection | AES 256-bit (depends on tool) | Medium | File sharing and storage | Works for multiple files | Requires extraction software |
| PDF with Password | Read-only protection | AES 128-bit (Adobe standard) | Medium | Sharing finalized content | Locks content, prevents edits | Original PPT remains unprotected |
| Automation via C# | Programmatic full encryption | AES 128-bit (Spire.Presentation) | Advanced | Batch protection or enterprise use | Scalable and efficient | Requires coding knowledge |
Summary
Password protection is one of the most effective ways to safeguard PowerPoint presentations against unauthorized access or modification. Whether you need to encrypt confidential slides, control editing permissions, or distribute a secure read-only version, PowerPoint provides flexible options for every situation.
The built-in encryption feature offers strong, immediate protection; the Save As password options let you decide who can open or edit the file; third-party encryption tools add an extra layer of security for shared archives; PDF conversion ensures your audience can only view the content; and automation with C# simplifies protection for large-scale or repetitive tasks.
By choosing the right password protection method for your workflow, you can keep your presentations private, professional, and secure at every stage of use.
FAQs
Q1. Can I remove a password from a PowerPoint file?
Yes. Open the presentation using the correct password, go to File → Info → Protect Presentation → Encrypt with Password , and clear the password field, then save the file.
Q2. What happens if I forget my PowerPoint password?
Microsoft doesn’t offer a recovery method for encrypted presentations. You must re-create the file or restore a backup. Always store passwords securely in a password manager.
Q3. Is PowerPoint password protection secure?
Yes. Modern PowerPoint versions (2010 and later) use AES 128-bit encryption, which provides strong security when a complex password is used.
Q4. Can I use VBA or macros to set a PowerPoint password?
Yes, you can use VBA to set or remove passwords automatically, but C# libraries like Spire.Presentation offer more flexible and modern options.
Q5. What’s the difference between open and modify passwords?
An open password prevents anyone from opening the file without it, while a modify password allows opening but restricts editing.
See Also
How to Change PowerPoint Slide Backgrounds — 5 Methods
Table of Contents
- Method 1. Change Background Using “Format Background”
- Method 2. Use a Custom Background Image
- Method 3. Apply Background to All Slides via Slide Master
- Method 4. Change Background with VBA Macro
- Method 5. Change Background Programmatically with Python
- Comparison Table: Which Method Should You Choose?
- Summary
- FAQs About Changing Background of Slides

PowerPoint is widely used for delivering ideas, reports, and marketing content. A slide’s background does more than decorate — it sets the tone, improves readability, and reinforces branding. Choosing the right background can make any presentation more professional and visually appealing.
Slide backgrounds can be customized manually using built-in tools like solid colors, gradients, patterns, or images. For advanced users, automation with VBA or Python (Spire.Presentation) helps save time on multiple slides or presentations. This article covers five practical methods for changing slide backgrounds, from manual edits to programmatic solutions.
Method Overview
- Method 1. Change Background Using “Format Background”
- Method 2. Use a Custom Background Image
- Method 3. Apply Background to All Slides via Slide Master
- Method 4. Change Background with VBA Macro
- Method 5. Change Background Programmatically with Python
Method 1. Change Background Using “Format Background”
One of the easiest ways to change a slide’s background is through PowerPoint’s Format Background feature. It offers several fill options — Solid, Gradient, Picture or Texture, and Pattern — all accessible from a single pane.
How to do it:
- Open your PowerPoint presentation.
- Select the slide you want to modify.
- Go to the Design tab in the ribbon.
- Click Format Background on the far right.
- Choose your preferred fill type:
- Solid Fill: Pick a single color for a clean and professional look.
- Gradient Fill: Blend two or more colors smoothly for a dynamic effect.
- Picture or Texture Fill: Apply an image or one of PowerPoint’s built-in textures.
- Pattern Fill: Use repeating designs like stripes or dots for subtle backgrounds.
- Click Apply to All to use the same background on every slide, or leave it unchecked to apply only to the current slide.

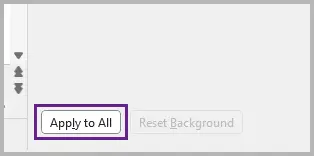
Tips:
- Choose colors that contrast well with your text and visuals. For readability, use light backgrounds with dark text or vice versa.
- Use the Format Painter to copy a background style from one slide to another quickly.
When to use it:
This method is ideal for most users who want a consistent, professional background without any effort. It’s quick, intuitive, and integrates seamlessly with PowerPoint’s built-in themes.
Method 2. Use a Custom Background Image
While Format Background supports picture fills, manually inserting an image gives you extra creative control. Use this approach when you need to position, crop, layer, or partially cover the slide with visuals — for example, placing a hero image, offsetting a photo behind text, or composing multiple images and shapes.
Quick guide:
- Go to Insert → Pictures → This Device (or online source).
- Choose and insert your image.
- Resize or crop it to fit your design.
- Right-click the image → Send to Back so that text and objects appear on top.
- Adjust transparency if needed to prevent the background from overwhelming the slide content.
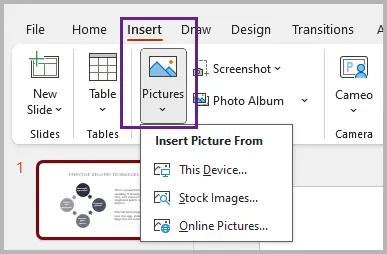
Tips:
- Use this method for standout slides, such as cover pages or transitions, where you want a distinct image separate from the rest of the deck.
- Keep file sizes small — compress large images to prevent slow presentation loading.
When to use it:
Choose this approach when you need precise placement, a unique composition, or layered visual effects beyond what Format Background provides.
Method 3. Apply Background to All Slides via Slide Master
If you want to apply a background consistently across every slide — including future ones you’ll add — the Slide Master is the best solution. This method ensures your presentation maintains uniform branding and saves time when editing large decks.
Step-by-step:
- Go to View → Slide Master .
- Select the topmost master slide in the left panel.
- Click Background Styles → Format Background and choose your desired background (color, gradient, picture, or pattern).
- Close the Slide Master view to return to the normal slide editor.

Tips:
- Create multiple Slide Master layouts, each with a different background, to visually separate presentation sections.
- Lock key elements (logos, background shapes) in the master to prevent accidental edits.
When to use it:
Use the Slide Master when creating templates, corporate presentations, or educational decks that require a consistent background across all slides and layouts.
Method 4. Change Background with VBA Macro
For power users comfortable with scripting, VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) provides a way to automate background changes directly within PowerPoint. It’s useful when you need to update multiple slides or presentations quickly with the same settings.
Example VBA script:
Sub SetSlideBackgroundColor()
Dim sld As Slide
For Each sld In ActivePresentation.Slides
sld.FollowMasterBackground = False
sld.Background.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(100, 149, 237) 'Sky blue
Next sld
End Sub
Here's how to do it:
- Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor in PowerPoint.
- Right-click on the project name, and select Insert → Module .
- Copy and paste the provided VBA code into the module.
- Press F5 to execute the macro, which will change the background of all slides.
When to use it:
VBA is best for users who already work inside PowerPoint and need fast, repeatable automation — for example, corporate template updates or bulk formatting tasks.
Method 5. Change Background Programmatically with Python
For developers or analysts who want to generate presentations dynamically, Spire.Presentation for Python provides a powerful way to manipulate PowerPoint files, including changing slide backgrounds, without opening PowerPoint.
Installation:
pip install spire.presentation
Here is an example of how to apply a solid background color to all slides, using Spire.Presentation for Python:
from spire.presentation import *
# Create a Presentation object
presentation = Presentation()
# Load the PowerPoint file
presentation.LoadFromFile("Input.pptx")
# Loop through all slides
for slide in presentation.Slides:
# Access and customize background
background = slide.SlideBackground
background.Type = BackgroundType.Custom
background.Fill.FillType = FillFormatType.Solid
background.Fill.SolidColor.Color = Color.get_LightYellow()
# Save the modified presentation
presentation.SaveToFile("AllSlidesBackground.pptx", FileFormat.Pptx2013)
presentation.Dispose()
Core steps explained:
- Loads an existing PowerPoint file.
- Iterates through all slides.
- Sets a custom solid color as the background.
- Saves the modified presentation.
Read Further: Set Background Color or Picture for PowerPoint Slides in Python
Output:

Why use Spire.Presentation:
- Works across platforms (Windows, macOS, Linux).
- Allows bulk automation (apply backgrounds to hundreds of slides).
- Can integrate with data sources (Excel, XML, databases) for dynamic slide creation.
Comparison Table: Which Method Should You Choose?
| Method | Skill Level | Best For | Scope | Flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Format Background | Beginner | Quick, per-slide edits | Single or all slides | Moderate – offers multiple fill options |
| Custom Background Image | Beginner–Intermediate | Creative designs and unique layouts | Per-slide | High – allows cropping, layering, and effects |
| Slide Master | Intermediate | Consistent design for entire decks or templates | All slides (current & future) | High – controls layout and theme together |
| VBA Macro | Intermediate–Advanced | Bulk updates within PowerPoint | All slides or multiple presentations | Medium – limited by PowerPoint’s VBA environment |
| Python (Spire.Presentation) | Advanced | Automation, batch generation, or integration with data pipelines | Multiple slides or files | Very High – full programmatic control |
Summary
Changing the background of a PowerPoint slide can be simple or highly automated, depending on your needs. For everyday users , PowerPoint’s Format Background , custom images , and Slide Master provide flexible options for both single slides and entire presentations. For advanced users or developers , automation via VBA or Python (Spire.Presentation) makes it easy to apply backgrounds programmatically, saving time and ensuring consistency across large or multiple presentations.
By understanding these methods, you can choose the right approach for your workflow — whether it’s a quick manual tweak for one slide, a branded corporate template, or fully automated background updates for hundreds of slides.
FAQs About Changing Background of Slides
Q1. How can I reset the background of a slide?
Use Format Background → Reset Background to revert the slide to the theme’s default style.
Q2. Can I apply different backgrounds to different slides?
Yes, either manually via Format Background or by creating multiple layouts in the Slide Master.
Q3. What image resolution is best for slide backgrounds?
Use at least 1920×1080 pixels for full HD slides. Higher resolution is recommended for large screens or projectors.
Q4. Can I use Python to apply gradient or picture backgrounds?
Yes, Spire.Presentation for Python supports solid colors, gradients, and picture fills programmatically.
Q5. Is VBA safer than Python for automation?
VBA runs inside PowerPoint and is easier for non-developers but only works on Windows. Python is cross-platform and more flexible for large-scale automation.
See Also
How to Attach Files to a Word Document (5 Effective Ways)
Table of Contents

In many business or academic settings, a Word document is more than just text — it often serves as a hub for related materials like reports, spreadsheets, charts, or reference PDFs. Instead of sending multiple files separately, attach them directly to your Word document to keep everything organized in one place.
This is particularly useful when preparing project reports, proposals, or technical documentation that requires supporting data. In this guide, you’ll learn five practical ways to attach a file to a Word document, ranging from simple manual approaches to automated methods using Python.
Method Overview:
- Method 1: Insert a File as an Embedded Object
- Method 2: Insert a File as a Linked Object
- Method 3: Add a File as a Hyperlink
- Method 4: Drag and Drop to Attach a File Quickly
- Method 5: Attach Files Programmatically with Python
Method 1: Insert a File as an Embedded Object
If you want the attached file to become a permanent and self-contained part of your Word document, embedding it as an object is the most reliable approach. This method stores the entire file inside the Word document itself, allowing you to share one single file that includes all related materials. It’s ideal when you need the document to remain fully functional even without access to external resources.
Steps:
- Open your Word document.
- Go to the Insert tab.
- Click Object in the Text group.
- Select Create from File .
- Click Browse , select the file, and confirm.
- (Optional) Check Display as icon for a tidy layout.
- Click OK.
Your chosen file (e.g., PDF, Excel, or image) now becomes part of the document. You can double-click the inserted icon to open it at any time.
Pros:
- The attached file travels with the document.
- Works completely offline.
Cons:
- Increases file size.
- Doesn’t update automatically if the source changes.
Best for: finalized reports, archives, and official submissions.
Method 2: Insert a File as a Linked Object
When you want your Word document to stay lightweight while reflecting updates from an external source, inserting the file as a linked object is the smarter choice. Instead of embedding a copy, Word maintains a live link to the original file — so any changes made to the source are automatically reflected in your document. This is perfect for dynamic data, such as financial sheets or charts that evolve over time.
Steps:
- Follow the same steps as in Method 1.
- Before confirming, check Link to file .
- Click OK .
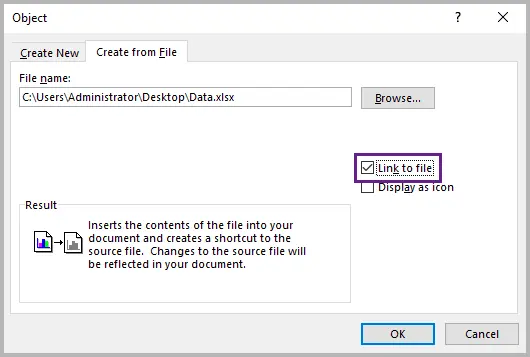
You’ll see a file icon or preview in your Word document, but the content is stored externally.
Pros:
- Keeps your Word document lightweight.
- Automatically updates when the original file changes.
- Works offline if the linked file is stored locally.
Cons:
- The link breaks if the source file is moved, renamed, or deleted.
- Requires access to the linked file’s path or drive (e.g., local or network).
Best for: collaborative projects or documents that rely on frequently updated data.
Method 3: Add a File as a Hyperlink
If you only need to reference a file rather than include its contents, adding a hyperlink offers a clean and efficient solution. This method simply points readers to the file’s location — whether on your local drive, a shared server, or a cloud service like OneDrive or SharePoint — without embedding or linking the actual file. It’s lightweight, quick, and ideal for distributed teams.
Steps:
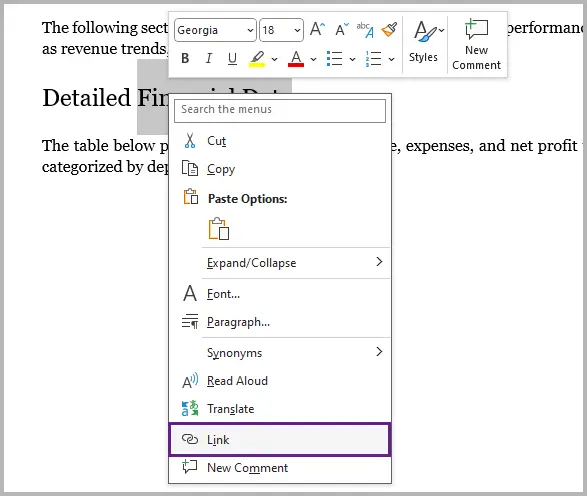
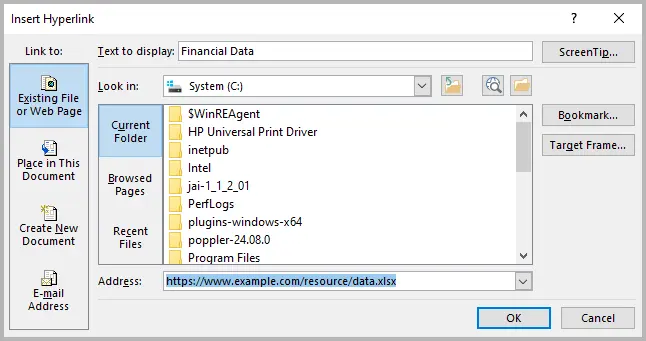
- Highlight the text or image where you want to add the link.
- Right-click on the selected text or image, and choose Link from the prompted menu.
- Select your file or paste the full path/URL.
- Click OK .
When clicked, the link opens the file directly in its associated program.
Pros:
- Doesn’t increase document size.
- Easy to edit or update the link target.
- Works offline if linked to a local file path.
Cons:
- Requires access to the file or network location.
- Cloud-based links (e.g., OneDrive or SharePoint) need an internet connection.
Best for: online collaboration, shared drives, or linking to local resources.
Method 4: Drag and Drop to Attach a File Quickly
When you need to attach a file on the fly without going through menus, the drag-and-drop method is the fastest and most intuitive approach. Simply drag a file from your desktop or file explorer directly into your open Word window — and Word will handle the rest.
Depending on the file type:
- Images are inserted inline automatically.
- Other file types (e.g., PDFs, Excel sheets) are displayed as icons that open with a double-click.
This method works best for quick edits or informal documents where convenience is key.
Pros:
- Incredibly fast and easy.
- Works for most common file formats.
Cons:
- Larger resulting file size.
- Less control over how the attachment appears or behaves.
Best for: quick one-time inserts or when you need to drop in a few files during editing.
Method 5: Attach Files Programmatically with Python
For advanced users and developers, automating file attachments using Python can save time and ensure consistency — especially when generating large numbers of documents or assembling reports programmatically. By using Spire.Doc for Python, you can embed external files as OLE objects directly into Word without manual steps.
This is ideal for automated workflows, such as generating weekly reports, attaching PDFs or charts, or bundling supporting documents dynamically.
Here’s an example of how to embed a PDF file into a Word document:
from spire.doc import *
from spire.doc.common import *
# Create a Document object
doc = Document()
# Load a Word document
doc.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\input.docx")
# Get the first section
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(0)
# Add a paragraph to the section
para = section.AddParagraph()
# Load an image which will be used as the icon of the OLE object
picture = DocPicture(doc)
picture.LoadImage("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\PDF-Icon.png")
picture.Width = 60
picture.Height = 60
# Append an OLE object (a PDF file) to the paragraph
object = para.AppendOleObject("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\report.pdf", picture, OleObjectType.AdobeAcrobatDocument)
# Display the object as icon
object.DisplayAsIcon = True
# Add a caption under the icon
object.OlePicture.AddCaption("Attachment", CaptionNumberingFormat.Number, CaptionPosition.BelowItem)
doc.IsUpdateFields = True
# Save the document
doc.SaveToFile("AttachFile.docx", FileFormat.Docx2013)
doc.Close()
You can replace the file path and OLE object type for other formats such as Excel sheets, images, or Word documents. Refer to this guide for detailed instructions on inserting or extracting OLE objects in Word using Python.
Output:

In addition to embedding files in a Word document, Spire.Doc allows you to attach files as linked objects using the AppendOleObject(String, DocPicture, OleLinkType) method, or create hyperlinks from text or images that redirect to external files.
Why use automation?
- Perfect for batch processing or report generation.
- Integrates smoothly with data-driven systems.
- Ensures repeatable, error-free results.
Best for: professionals or teams that manage document generation at scale.
Comparison Table: Which Method Should You Use?
| Method | Embedded | Linked | File Size | Works Offline | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Object (Embed) | √ | x | Large | √ | Archiving, sharing full copies |
| Object (Link) | x | √ | Small | √ (if file is local) / x (if file is online) | Dynamic or updatable references |
| Hyperlink | x | √ | Small | √ (local path) / x (online path) | Linking to shared or cloud files |
| Drag & Drop | √ | x | Large | √ | Quick one-off inserts |
| Python Automation | √ | √ | Flexible | √ | Automated workflows and batch processing |
Conclusion
Attaching files to a Word document is a simple yet powerful way to keep related materials organized and accessible. The method you choose depends on your needs: embedding a file in Word ensures everything stays in one document, linking files in Word keeps documents lightweight and automatically updated, and adding hyperlinks makes sharing online resources effortless.
For quick edits, drag-and-drop attachments offer speed and convenience, while automating file attachments with Python provides efficiency at scale. Whether you’re compiling a single report or managing automated document generation, selecting the right way to attach files to Word helps you balance portability, accessibility, and performance for a more streamlined workflow.
FAQs
Q1. What types of files can I attach to a Word document?
You can attach almost any file type, including PDFs, Excel spreadsheets, images, and even other Word files. Some file types may require specific software to open.
Q2. Can I attach multiple files at once?
Yes. You can embed or link multiple files in one document. For bulk operations, using automation (like Python) is more efficient.
Q3. Why can’t I open the attached file in Word?
If the attachment was linked rather than embedded, Word needs access to the original file’s location. Check if it has been moved or renamed.
Q4. How to attach a PDF file inside a Word document?
Go to Insert → Object → Create from File → Browse , select your PDF, and click OK . Check Display as icon if you want it shown as an icon instead of inline content.
Q5. How to attach Excel file in Word document?
In Word, choose Insert → Object → Create from File → Browse , select the Excel file, and click OK . To keep it updated automatically, check Link to file before inserting.
See Also
How to Split Excel Sheets into Multiple Files (3 Ways)
Table of Contents

Excel is one of the most powerful tools for organizing and analyzing structured data — from financial models to department reports. However, as a workbook grows to include multiple worksheets for different teams or purposes, it can become difficult to manage, share, or extract specific information. In such cases, it’s often more practical to split a workbook by worksheets , turning each sheet into its own file for easier distribution and collaboration.
For example, you might want to send the Sales worksheet to the sales team, the HR worksheet to the HR department, and the Finance worksheet to your accountant. The simplest way to achieve this is to split Excel sheets into separate files , so each recipient receives only the data relevant to them. In this article, we’ll explore three effective methods: a quick manual process, a VBA solution for Excel users, and a Python-based approach ideal for automation.
Methods Overview:
- Quick Manual Trick: Copy Sheets into New Workbooks
- Automate in Excel: VBA Macro to Split Sheets
- Automate with Python: Save Each Worksheet as a File
Why Split Excel Sheets into Separate Files?
There are several practical reasons why splitting a workbook into multiple files is helpful:
- Selective Sharing : Not every stakeholder needs access to all the data. Splitting sheets lets you distribute relevant files only.
- Improved Performance : Large workbooks with many sheets can become slow to open and process. Splitting them into smaller files improves performance.
- Better Organization : Separate files can make project management and reporting more structured.
- Automation and Reporting : Splitting is often part of automated workflows where different reports are generated for different departments.
- Version Control : Smaller files are easier to track and maintain in version control systems compared to one giant workbook.
Whether you’re an everyday Excel user or a developer building automated reporting pipelines, splitting sheets is a task worth mastering.
Quick Manual Trick: Copy Sheets into New Workbooks
If you only need to split a few sheets and don’t mind a bit of clicking, Excel’s built-in interface provides a straightforward way to do this.
How it works:
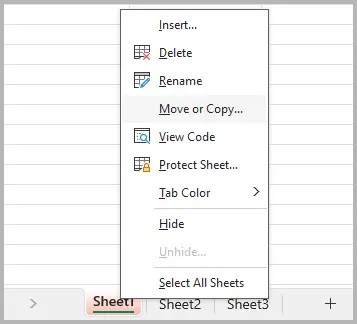
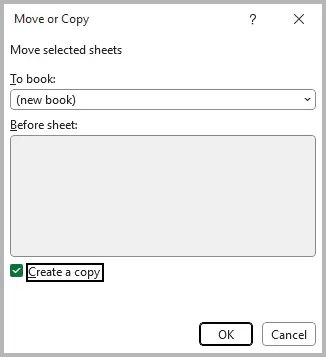
- Open your workbook using MS Excel.
- Right-click on the sheet tab you want to separate and select Move or Copy... .
- In the To book: dropdown, select (new book) . Check the Create a copy box, then click OK .
- Repeat this process for every sheet you want to split into an individual file.
Pros:
- Requires no coding skills.
- Built directly into Excel — no installation needed.
- Simple and reliable for one-time tasks.
Cons:
- Time-consuming if you need to split many sheets.
- Prone to errors (forgetting to save or rename files properly).
- No automation — you must repeat the steps manually every time.
Best for:
- Users who rarely need to split sheets.
- Quick, one-off tasks where only a couple of sheets need separation.
Automate in Excel: VBA Macro to Split Sheets
For more frequent use, Excel’s built-in VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) editor provides a way to automate splitting. With a small macro, Excel can loop through every worksheet and save it as a new workbook — saving hours of manual work.
How it works:
- Open Excel and press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor.
- Go to Insert > Module .
- Paste the following code into the module window:
- Press F5 (or go to Run > Run Sub/UserForm) to execute the macro.
- Excel will create separate files for each worksheet in the same folder as your original workbook.
Sub SplitSheetsIntoWorkbooks()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim newWorkbook As Workbook
Dim originalWorkbook As Workbook
Set originalWorkbook = ThisWorkbook
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
For Each ws In originalWorkbook.Worksheets
ws.Copy
Set newWorkbook = ActiveWorkbook
newWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=originalWorkbook.Path & "\" & ws.Name & ".xlsx"
newWorkbook.Close SaveChanges:=False
Next ws
MsgBox "All sheets have been saved as separate files!"
End Sub
Pros:
- Fully automated— one click and every sheet is exported.
- Built into Excel — no extra software needed.
- Saves significant time compared to the manual approach.
Cons:
- Requires enabling macros, which some organizations restrict for security reasons.
- VBA is somewhat outdated, and debugging errors can be frustrating for beginners.
- Limited flexibility (e.g., handling very large workbooks or custom export rules requires editing the macro).
Best for:
- Intermediate to advanced Excel users.
- Scenarios where you frequently need to split sheets in workbooks.
Automate with Python: Save Each Worksheet as a File
If you’re a developer or need maximum flexibility, Python provides a modern approach. Using libraries like Spire.XLS for Python, you can process Excel files programmatically and split sheets in bulk. This is ideal for workflows involving large files, multiple workbooks, or integration with other systems.
How it works:
- Install Python (if you don’t already have it).
- Install the Spire.XLS for Python library:
- Use a script like the following:
pip install spire.xls
from spire.xls import *
from spire.xls.common import *
# Create an object of the Workbook class
workbook = Workbook()
# Load an Excel file
workbook.LoadFromFile("Sample.xlsx")
# Specify the folder path for the generated Excel files
folderPath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Output\\"
# Iterate through all worksheets in the Excel file
for worksheet in workbook.Worksheets:
# For each worksheet, create a new Workbook object
newWorkbook = Workbook()
# Remove the worksheets from the new workbook
newWorkbook.Worksheets.Clear()
# Copy the worksheet from the Excel file to the new workbook
newWorkbook.Worksheets.AddCopy(worksheet)
# Save the new workbook to the specified folder
newWorkbook.SaveToFile(folderPath + worksheet.Name + ".xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()
Here is the full guide on how to split Excel by sheets, rows, and columns in Python.
Output:
Pros:
- Highly flexible — you can extend the script to filter sheets, split by row/column, or export to CSV/PDF.
- Perfect for batch processing and large-scale automation.
- Integrates with other systems and workflows.
Cons:
- Requires some coding knowledge.- Initial setup (Python + libraries) takes longer than VBA.
Best for:
- Developers automating data pipelines.
- Businesses with large, repetitive splitting tasks.
- Advanced users who need more control than VBA offers.
Summary: Which Method Should You Choose?
Splitting Excel sheets into individual files is a common challenge, but the right method depends on your context:
- Quick Manual Trick : Perfect if you only need to separate a couple of sheets once in a while. It’s easy and doesn’t require any coding.
- VBA Macro : The go-to method for power Excel users. Once set up, it can save hours of manual work, especially if you frequently split workbooks.
- Python Script : The best option for developers or anyone building automated workflows. It provides full control, scalability, and the ability to extend the solution to fit complex business needs.
At the end of the day, the method you choose comes down to how often you need to split sheets and how comfortable you are with automation . Occasional users can rely on Excel’s interface, while professionals benefit more from VBA or Python automation.
See Also
C# для чтения файлов Excel и экспорта данных в DataTable и базу данных
Содержание
Установить через Nuget
Install-Package Spire.XLS
Похожие ссылки
Чтение файлов Excel на C# — это обычное требование для многих приложений, будь то для анализа данных, создания отчетов или интеграции с базами данных. Хотя можно использовать библиотеки Microsoft Interop, у них есть ограничения (например, требование установленного Excel). Вместо этого мы рассмотрим более эффективный подход с использованием Spire.XLS, библиотеки .NET, которая позволяет читать и записывать файлы Excel без Interop. В этой статье рассматриваются:
- Библиотека C# .NET для чтения Excel без Interop
- Как прочитать файл Excel на C#
- Чтение данных Excel в DataTable
- Чтение данных Excel в базу данных
- Заключение
- Часто задаваемые вопросы
Библиотека C# .NET для чтения Excel без Interop
Excel Interop от Microsoft требует, чтобы Excel был установлен на компьютере, что делает его непригодным для серверных приложений. Вместо этого библиотеки, такие как Spire.XLS, предлагают легкое, высокопроизводительное решение без зависимостей от Excel.
Зачем использовать Spire.XLS?
- Не требуется установка Excel – работает независимо.
- Поддерживает .NET Core и .NET Framework – кроссплатформенная совместимость.
- Чтение/запись файлов Excel – поддерживает .xls, .xlsx и .xlsm.
- Импорт в DataTable и базы данных – бесшовная интеграция с ADO.NET.
Установка Spire.XLS
Для начала установите библиотеку через менеджер пакетов NuGet:
Install-Package Spire.XLS
Кроме того, вы можете скачать Spire.XLS для .NET с нашего официального сайта и вручную сослаться на DLL-файл.
Как прочитать файл Excel на C#
В этом разделе показано, как прочитать файл Excel на C# с помощью библиотеки Spire.XLS. Процесс включает загрузку файла, доступ к рабочим листам и программное получение значений ячеек. Это полезно для автоматизации извлечения данных, обработки отчетов Excel или интеграции данных электронных таблиц в приложения.
Шаг 1. Импортируйте необходимое пространство имен
Чтобы использовать функциональность Spire.XLS, вам необходимо импортировать его пространство имен. Это дает доступ к таким классам, как Workbook и Worksheet, которые необходимы для операций с файлами Excel.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;Шаг 2. Загрузите файл Excel
Чтобы загрузить файл Excel, создайте объект Workbook и вызовите метод LoadFromFile. Это считывает файл в память, позволяя дальнейшие манипуляции.
- C#
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
wb.LoadFromFile("input.xlsx");Шаг 3. Получите определенный рабочий лист
Файлы Excel могут содержать несколько рабочих листов. Вы можете получить доступ к определенному листу, индексируя коллекцию Worksheets (начиная с нуля). Первый лист находится по индексу 0, второй — по индексу 1 и так далее.
- C#
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0]; //Первый листШаг 4. Получение значения определенной ячейки
Чтобы получить значение ячейки, используйте свойство CellRange.Value. Укажите индексы строки и столбца (начиная с 1), чтобы найти ячейку. Это полезно для извлечения структурированных данных, таких как заголовки или отдельные записи.
- C#
CellRange cell = sheet.Range[1, 1]; // Строка1, Столбец 1 (A1)
string value = cell.Value;Ниже приведен полный пример чтения данных со всего рабочего листа и вывода их в консоль:
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
namespace ReadExcelData
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
// Load an existing Excel file
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
// Get the cell range containing data
CellRange locatedRange = sheet.AllocatedRange;
// Iterate through the rows
for (int i = 0; i < locatedRange.Rows.Length; i++)
{
// Iterate through the columns
for (int j = 0; j < locatedRange.Rows[i].ColumnCount; j++)
{
// Get data of a specific cell
string cellValue = locatedRange[i + 1, j + 1].Value?.ToString() ?? "N/A";
// Align output with a width of 22
Console.Write($"{cellValue,-22}");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}Результат:
Чтение данных Excel в DataTable
Экспорт данных Excel в DataTable обеспечивает бесшовную интеграцию с элементами управления пользовательского интерфейса, такими как DataGridView, или обработку данных на стороне сервера. Spire.XLS упрощает этот процесс с помощью встроенного метода ExportDataTable(), который автоматически преобразует данные рабочего листа в структурированный DataTable, сохраняя заголовки столбцов и типы данных.
Шаг 1. Импортируйте необходимое пространство имен
Включите пространство имен Spire.XLS для доступа к основным классам.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;Шаг 2. Создайте форму и событие нажатия кнопки
Создайте форму (например, Form1) и добавьте кнопку с обработчиком событий для чтения файла Excel.
- C#
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Код будет здесь
}
}Шаг 3. Загрузите рабочую книгу
В обработчике события нажатия кнопки создайте объект Workbook и загрузите файл Excel.
- C#
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");Шаг 4. Экспорт данных в DataTable
Получите доступ к определенному рабочему листу по его индексу и экспортируйте его данные в DataTable с помощью метода ExportDataTable.
- C#
DataTable dataTable = wb.Worksheets[0].ExportDataTable();Шаг 5. Привязка данных к DataGridView
Предполагая, что у вас есть элемент управления DataGridView на вашей форме, привяжите DataTable к DataGridView для отображения данных.
- C#
dataGridView1.DataSource = dataTable;Ниже приведен полный код для чтения данных из файла Excel в DataTable и отображения их в элементе управления DataGridView в Windows Forms:
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Data;
namespace ReadExcelIntoDataTable
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
// Load an existing Excel file
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
// Export data from worksheet into a DataTable
DataTable dataTable = sheet.ExportDataTable();
// Bind DataTable to DataGridView
dataGridView1.DataSource = dataTable;
// Dispose resources
wb.Dispose();
}
}
}Результат:
Чтение данных Excel в базу данных
Интеграция данных Excel с базой данных может упростить управление данными. Ниже мы рассмотрим процесс чтения файла Excel и импорта его содержимого в базу данных MySQL. Этот метод идеально подходит для автоматизации миграции данных, создания отчетов или синхронизации данных Excel со структурированной базой данных.
Шаг 1. Установите библиотеку данных MySQL
Для взаимодействия с базами данных MySQL в ваших .NET-приложениях вам необходимо установить библиотеку MySql.Data. Этот пакет NuGet предоставляет необходимые классы и методы для подключения к базам данных MySQL и управления ими.
- C#
Install-Package MySql.DataШаг 2. Импортируйте необходимые пространства имен
Перед работой с файлами Excel и MySQL необходимо включить требуемые пространства имен. Spire.XLS используется для операций с Excel, а MySql.Data.MySqlClient обеспечивает подключение к базе данных MySQL.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using MySql.Data.MySqlClient;Шаг 3. Извлечение заголовков и данных из Excel
Следующий фрагмент кода демонстрирует, как извлечь заголовки и данные из файла Excel. Заголовки очищаются, чтобы избежать конфликтов имен столбцов MySQL, а данные сохраняются в структурированном формате для последующей вставки.
- C#
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel document
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get a specific sheet
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
// Retrieve headers
List<string> headers = new List<string>();
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
string header = sheet.Range[1, col].Value?.ToString();
// Removing spaces to avoid conflicts with MySQL column names
string cleanHeader = header?.Replace(" ", "");
headers.Add($"`{cleanHeader}`");
}
// Retrieve data
List<List<string>> data = new List<List<string>>();
for (int row = 2; row <= sheet.LastRow; row++) {
List<string> record = new List<string>();
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
record.Add(sheet.Range[row, col].Value?.ToString() ?? string.Empty);
}
data.Add(record);
}Шаг 4. Подключение к базе данных MySQL
Соединение с базой данных MySQL устанавливается с помощью строки подключения, которая включает сведения о сервере, учетные данные и имя целевой базы данных. Оператор using обеспечивает надлежащее освобождение ресурсов.
- C#
string connectionString = "server=localhost;user=root;password=yourpassword;database=yourdatabase;";
using (MySqlConnection connection = new MySqlConnection(connectionString))
{
connection.Open();
// Connection is established; perform database operations here
}Шаг 5. Динамическое создание таблицы в MySQL
На этом шаге динамически создается таблица MySQL со столбцами, соответствующими заголовкам Excel. для простоты все столбцы установлены как VARCHAR(255), но типы данных можно настроить в соответствии с требованиями.
- C#
// Create a table with dynamic columns based on headers
List<string> columns = new List<string>();
foreach (string header in headers)
{
// Assuming all header values are VARCHAR for simplicity; adjust types as needed
columns.Add($"{header} VARCHAR(255)");
}
// Create a table in database
string columnsSql = string.Join(", ", columns);
string createTableQuery = $ @"
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS my_table (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
{columnsSql}
)";
// Execute the create table query
using (MySqlCommand createCommand = new MySqlCommand(createTableQuery, connection))
{
createCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}Шаг 6. Заполнение таблицы данными
Извлеченные данные Excel вставляются в таблицу MySQL с использованием параметризованных запросов для предотвращения SQL-инъекций. Каждая строка из файла Excel сопоставляется с соответствующей записью в базе данных.
- C#
// Prepare the SQL INSERT statement
string placeholders = string.Join(", ", new string[headers.Count].Select(h => "?"));
string insertQuery = $"INSERT INTO my_table ({string.Join(", ", headers.Select(h => h.Trim('`')))}) VALUES ({placeholders})";
// Insert data into the table
foreach (List<string> record in data)
{
using (MySqlCommand insertCommand = new MySqlCommand(insertQuery, connection))
{
for (int i = 0; i < record.Count; i++)
{
insertCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue($" @2024\本地文件打包__20180302\Spire.Web\trunk\src\website\components\com_virtuemart\themes\default\templates\browse\includes\browse_searchparameter_form.tpl.php{i}", record[i]);
}
insertCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}Вот полный код для импорта данных из файла Excel в таблицу MySQL:
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using MySql.Data.MySqlClient;
namespace ExcelToMySQL
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel document
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get a specific sheet
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
// Retrieve headers
List<string> headers = new List<string>();
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
string header = sheet.Range[1, col].Value?.ToString();
// Removing spaces to avoid conflicts with MySQL column names
string cleanHeader = header?.Replace(" ", "");
headers.Add($"`{cleanHeader}`");
}
// Retrieve data
List<List<string>> data = new List<List<string>>();
for (int row = 2; row <= sheet.LastRow; row++)
{
List<string> record = new List<string>();
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
record.Add(sheet.Range[row, col].Value?.ToString() ?? string.Empty);
}
data.Add(record);
}
// Establish a connection to the MySQL database
string connectionString = "server=localhost;user=root;password=admin;database=excel_db;";
using (MySqlConnection connection = new MySqlConnection(connectionString))
{
connection.Open();
// Create a table with dynamic columns based on headers
List<string> columns = new List<string>();
foreach (string header in headers)
{
// Assuming all header values are VARCHAR for simplicity; adjust types as needed
columns.Add($"{header} VARCHAR(255)");
}
// Create a table in database
string columnsSql = string.Join(", ", columns);
string createTableQuery = $ @"
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS my_table (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
{columnsSql}
)";
// Execute the create table query
using (MySqlCommand createCommand = new MySqlCommand(createTableQuery, connection))
{
createCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
// Prepare the SQL INSERT statement
string placeholders = string.Join(", ", new string[headers.Count].Select(h => "?"));
string insertQuery = $"INSERT INTO my_table ({string.Join(", ", headers.Select(h => h.Trim('`')))}) VALUES ({placeholders})";
// Insert data into the table
foreach (List<string> record in data)
{
using (MySqlCommand insertCommand = new MySqlCommand(insertQuery, connection))
{
for (int i = 0; i < record.Count; i++)
{
insertCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue($" @2024\本地文件打包__20180302\Spire.Web\trunk\src\website\components\com_virtuemart\themes\default\templates\browse\includes\browse_searchparameter_form.tpl.php{i}", record[i]);
}
insertCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Данные успешно экспортированы!");
}
}
}Результат:
Заключение
Чтение файлов Excel на C# никогда не было таким простым благодаря таким библиотекам, как Spire.XLS. В этом руководстве вы ознакомились с процессом загрузки файлов Excel, чтения их содержимого и даже импорта данных в базу данных MySQL. С помощью этих методов вы можете значительно расширить возможности обработки данных в своих приложениях.
Часто задаваемые вопросы
В1: Могу ли я читать защищенные паролем файлы Excel?
О: Да, Spire.XLS поддерживает чтение зашифрованных файлов Excel с помощью:
- C#
wb.OpenPassword = "psd";
wb.LoadFromFile("file.xlsx");В2: Как мне прочитать результаты формулы вместо самой формулы?
О: У вас есть два варианта получения результатов формулы:
Для отдельных ячеек:
Проверьте, содержит ли ячейка формулу, с помощью CellRange.HasFormula, и получите значение с помощью CellRange.FormulaValue:
- C#
CellRange cell = sheet.Range[1, 1];
if (cell.HasFormula)
{
string result = cell.FormulaValue.ToString();
}Для массового экспорта в DataTable:
Используйте Worksheet.ExportDataTable() с computedFormulaValue: true для экспорта вычисленных значений:
- C#
DataTable data = sheet.ExportDataTable(range, exportColumnNames: true, computedFormulaValue: true);В3: Как я могу прочитать данные Excel в DataTable?
О: Используйте метод Worksheet.ExportDataTable(), предоставляемый Spire.XLS.
В4: Как я могу прочитать файл Excel построчно?
О: Обратитесь к следующему коду:
- C#
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("input.xlsx");
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
for (int row = 1; row <= sheet.LastRow; row++)
{
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
string cellValue = sheet.Range[row, col].Value?.ToString() ?? string.Empty;
Console.WriteLine(cellValue);
}
}Получить бесплатную лицензию
Чтобы в полной мере ощутить возможности Spire.XLS для .NET без каких-либо оценочных ограничений, вы можете запросить бесплатную 30-дневную пробную лицензию.
Смотрите также
Excel 파일을 읽고 DataTable 및 데이터베이스로 데이터를 내보내는 C#
목차
Nuget으로 설치
Install-Package Spire.XLS
관련 링크
C#에서 Excel 파일을 읽는 것은 데이터 분석, 보고 또는 데이터베이스 통합 등 많은 애플리케이션의 일반적인 요구 사항입니다. Microsoft의 Interop 라이브러리를 사용할 수 있지만, Excel 설치가 필요하다는 등의 제한이 있습니다. 대신, Interop 없이 Excel 파일을 읽고 쓸 수 있는 .NET 라이브러리인 Spire.XLS를 사용하는 더 효율적인 접근 방식을 살펴보겠습니다. 이 문서에서는 다음 내용을 다룹니다.
- Interop 없이 Excel을 읽기 위한 C# .NET 라이브러리
- C#에서 Excel 파일을 읽는 방법
- Excel 데이터를 DataTable로 읽기
- Excel 데이터를 데이터베이스로 읽기
- 결론
- 자주 묻는 질문
Interop 없이 Excel을 읽기 위한 C# .NET 라이브러리
Microsoft의 Excel Interop은 컴퓨터에 Excel이 설치되어 있어야 하므로 서버 측 애플리케이션에는 적합하지 않습니다. 대신 Spire.XLS와 같은 라이브러리는 Excel에 대한 종속성 없이 가볍고 고성능의 솔루션을 제공합니다.
Spire.XLS를 사용하는 이유
- Excel 설치 필요 없음 – 독립적으로 작동합니다.
- .NET Core 및 .NET Framework 지원 – 플랫폼 간 호환성.
- Excel 파일 읽기/쓰기 – .xls, .xlsx 및 .xlsm을 지원합니다.
- DataTable 및 데이터베이스로 가져오기 – ADO.NET과의 원활한 통합.
Spire.XLS 설치
시작하려면 NuGet 패키지 관리자를 통해 라이브러리를 설치하십시오.
Install-Package Spire.XLS
또는 공식 웹사이트에서 .NET용 Spire.XLS를 다운로드하고 DLL 파일을 수동으로 참조할 수 있습니다.
C#에서 Excel 파일을 읽는 방법
이 섹션에서는 Spire.XLS 라이브러리를 사용하여 C#에서 Excel 파일을 읽는 방법을 보여줍니다. 이 프로세스에는 파일 로드, 워크시트 액세스 및 프로그래밍 방식으로 셀 값 검색이 포함됩니다. 이는 데이터 추출 자동화, Excel 보고서 처리 또는 스프레드시트 데이터를 애플리케이션에 통합하는 데 유용합니다.
1단계. 필요한 네임스페이스 가져오기
Spire.XLS 기능을 활용하려면 해당 네임스페이스를 가져와야 합니다. 이를 통해 Excel 파일 작업에 필수적인 Workbook 및 Worksheet와 같은 클래스에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;2단계. Excel 파일 로드
Excel 파일을 로드하려면 Workbook 개체를 만들고 LoadFromFile 메서드를 호출합니다. 이렇게 하면 파일이 메모리로 읽혀 추가 조작이 가능합니다.
- C#
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
wb.LoadFromFile("input.xlsx");3단계. 특정 워크시트 가져오기
Excel 파일에는 여러 워크시트가 포함될 수 있습니다. Worksheets 컬렉션(0부터 시작)을 인덱싱하여 특정 시트에 액세스할 수 있습니다. 첫 번째 시트는 인덱스 0, 두 번째 시트는 1에 있는 식입니다.
- C#
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0]; //First sheet4단계. 특정 셀의 값 검색
셀 값을 검색하려면 CellRange.Value 속성을 사용합니다. 행 및 열 인덱스(1부터 시작)를 지정하여 셀을 찾습니다. 이는 헤더나 개별 레코드와 같은 구조화된 데이터를 추출하는 데 유용합니다.
- C#
CellRange cell = sheet.Range[1, 1]; // Row1, Column 1 (A1)
string value = cell.Value;다음은 전체 워크시트에서 데이터를 읽어 콘솔에 인쇄하는 전체 예제입니다.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
namespace ReadExcelData
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
// Load an existing Excel file
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
// Get the cell range containing data
CellRange locatedRange = sheet.AllocatedRange;
// Iterate through the rows
for (int i = 0; i < locatedRange.Rows.Length; i++)
{
// Iterate through the columns
for (int j = 0; j < locatedRange.Rows[i].ColumnCount; j++)
{
// Get data of a specific cell
string cellValue = locatedRange[i + 1, j + 1].Value?.ToString() ?? "N/A";
// Align output with a width of 22
Console.Write($"{cellValue,-22}");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}결과:

Excel 데이터를 DataTable로 읽기
Excel 데이터를 DataTable로 내보내면 DataGridView와 같은 UI 컨트롤 또는 백엔드 데이터 처리와 원활하게 통합할 수 있습니다. Spire.XLS는 워크시트 데이터를 열 헤더와 데이터 유형을 유지하면서 구조화된 DataTable로 자동 변환하는 내장 ExportDataTable() 메서드를 사용하여 이 프로세스를 단순화합니다.
1단계. 필요한 네임스페이스 가져오기
필수 클래스에 액세스하려면 Spire.XLS 네임스페이스를 포함하십시오.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;2단계. 양식 및 버튼 클릭 이벤트 만들기
양식(예: Form1)을 만들고 Excel 파일을 읽기 위한 이벤트 처리기가 있는 버튼을 추가합니다.
- C#
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Code will go here
}
}3단계. 통합 문서 로드
버튼 클릭 이벤트 내에서 Workbook 개체를 만들고 Excel 파일을 로드합니다.
- C#
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");4단계. 데이터를 DataTable로 내보내기
인덱스로 특정 워크시트에 액세스하고 ExportDataTable 메서드를 사용하여 해당 데이터를 DataTable로 내보냅니다.
- C#
DataTable dataTable = wb.Worksheets[0].ExportDataTable();5단계. 데이터를 DataGridView에 바인딩
양식에 DataGridView 컨트롤이 있다고 가정하고 DataTable을 DataGridView에 바인딩하여 데이터를 표시합니다.
- C#
dataGridView1.DataSource = dataTable;다음은 Excel 파일에서 데이터를 읽어 DataTable에 넣고 Windows Forms DataGridView 컨트롤에 표시하는 전체 코드입니다.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using System.Data;
namespace ReadExcelIntoDataTable
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
// Load an existing Excel file
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get the first worksheet
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
// Export data from worksheet into a DataTable
DataTable dataTable = sheet.ExportDataTable();
// Bind DataTable to DataGridView
dataGridView1.DataSource = dataTable;
// Dispose resources
wb.Dispose();
}
}
}결과:

Excel 데이터를 데이터베이스로 읽기
Excel 데이터를 데이터베이스와 통합하면 데이터 관리를 간소화할 수 있습니다. 아래에서는 Excel 파일을 읽고 그 내용을 MySQL 데이터베이스로 가져오는 과정을 안내합니다. 이 방법은 데이터 마이그레이션, 보고 또는 Excel 데이터를 구조화된 데이터베이스와 동기화하는 작업을 자동화하는 데 이상적입니다.
1단계. MySQL 데이터 라이브러리 설치
.NET 애플리케이션에서 MySQL 데이터베이스와 상호 작용하려면 MySql.Data 라이브러리를 설치해야 합니다. 이 NuGet 패키지는 MySQL 데이터베이스에 연결하고 조작하는 데 필요한 클래스와 메서드를 제공합니다.
- C#
Install-Package MySql.Data2단계. 필요한 네임스페이스 가져오기
Excel 파일 및 MySQL로 작업하기 전에 필요한 네임스페이스를 포함해야 합니다. Spire.XLS는 Excel 작업에 사용되고 MySql.Data.MySqlClient는 MySQL 데이터베이스 연결을 활성화합니다.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using MySql.Data.MySqlClient;3단계. Excel에서 헤더 및 데이터 추출
다음 코드 조각은 Excel 파일에서 헤더와 데이터를 추출하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 헤더는 MySQL 열 이름 충돌을 피하기 위해 정리되고 데이터는 나중에 삽입할 수 있도록 구조화된 형식으로 저장됩니다.
- C#
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel document
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get a specific sheet
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
// Retrieve headers
List<string> headers = new List<string>();
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
string header = sheet.Range[1, col].Value?.ToString();
// Removing spaces to avoid conflicts with MySQL column names
string cleanHeader = header?.Replace(" ", "");
headers.Add($"`{cleanHeader}`");
}
// Retrieve data
List<List<string>> data = new List<List<string>>();
for (int row = 2; row <= sheet.LastRow; row++) {
List<string> record = new List<string>();
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
record.Add(sheet.Range[row, col].Value?.ToString() ?? string.Empty);
}
data.Add(record);
}4단계. MySQL 데이터베이스에 연결
연결 문자열을 사용하여 MySQL 데이터베이스에 대한 연결이 설정됩니다. 여기에는 서버 세부 정보, 자격 증명 및 대상 데이터베이스 이름이 포함됩니다. using 문은 적절한 리소스 폐기를 보장합니다.
- C#
string connectionString = "server=localhost;user=root;password=yourpassword;database=yourdatabase;";
using (MySqlConnection connection = new MySqlConnection(connectionString))
{
connection.Open();
// Connection is established; perform database operations here
}5단계. MySQL에서 동적으로 테이블 만들기
이 단계에서는 Excel 헤더와 일치하는 열이 있는 MySQL 테이블을 동적으로 생성합니다. 단순화를 위해 모든 열은 VARCHAR(255)로 설정되지만 요구 사항에 따라 데이터 유형을 조정할 수 있습니다.
- C#
// Create a table with dynamic columns based on headers
List<string> columns = new List<string>();
foreach (string header in headers)
{
// Assuming all header values are VARCHAR for simplicity; adjust types as needed
columns.Add($"{header} VARCHAR(255)");
}
// Create a table in database
string columnsSql = string.Join(", ", columns);
string createTableQuery = $ @"
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS my_table (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
{columnsSql}
)";
// Execute the create table query
using (MySqlCommand createCommand = new MySqlCommand(createTableQuery, connection))
{
createCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}6단계. 데이터로 테이블 채우기
추출된 Excel 데이터는 SQL 삽입을 방지하기 위해 매개변수화된 쿼리를 사용하여 MySQL 테이블에 삽입됩니다. Excel 파일의 각 행은 해당 데이터베이스 레코드에 매핑됩니다.
- C#
// Prepare the SQL INSERT statement
string placeholders = string.Join(", ", new string[headers.Count].Select(h => "?"));
string insertQuery = $"INSERT INTO my_table ({string.Join(", ", headers.Select(h => h.Trim('`')))}) VALUES ({placeholders})";
// Insert data into the table
foreach (List<string> record in data)
{
using (MySqlCommand insertCommand = new MySqlCommand(insertQuery, connection))
{
for (int i = 0; i < record.Count; i++)
{
insertCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue($" @2024\本地文件打包__20180302\Spire.Web\trunk\src\website\components\com_virtuemart\themes\default\templates\browse\includes\browse_searchparameter_form.tpl.php{i}", record[i]);
}
insertCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}다음은 Excel 파일에서 MySQL 테이블로 데이터를 가져오는 전체 코드입니다.
- C#
using Spire.Xls;
using MySql.Data.MySqlClient;
namespace ExcelToMySQL
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a Workbook object
Workbook wb = new Workbook();
// Load an Excel document
wb.LoadFromFile("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\Input.xlsx");
// Get a specific sheet
Worksheet sheet = wb.Worksheets[0];
// Retrieve headers
List<string> headers = new List<string>();
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
string header = sheet.Range[1, col].Value?.ToString();
// Removing spaces to avoid conflicts with MySQL column names
string cleanHeader = header?.Replace(" ", "");
headers.Add($"`{cleanHeader}`");
}
// Retrieve data
List<List<string>> data = new List<List<string>>();
for (int row = 2; row <= sheet.LastRow; row++)
{
List<string> record = new List<string>();
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
record.Add(sheet.Range[row, col].Value?.ToString() ?? string.Empty);
}
data.Add(record);
}
// Establish a connection to the MySQL database
string connectionString = "server=localhost;user=root;password=admin;database=excel_db;";
using (MySqlConnection connection = new MySqlConnection(connectionString))
{
connection.Open();
// Create a table with dynamic columns based on headers
List<string> columns = new List<string>();
foreach (string header in headers)
{
// Assuming all header values are VARCHAR for simplicity; adjust types as needed
columns.Add($"{header} VARCHAR(255)");
}
// Create a table in database
string columnsSql = string.Join(", ", columns);
string createTableQuery = $ @"
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS my_table (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
{columnsSql}
)";
// Execute the create table query
using (MySqlCommand createCommand = new MySqlCommand(createTableQuery, connection))
{
createCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
// Prepare the SQL INSERT statement
string placeholders = string.Join(", ", new string[headers.Count].Select(h => "?"));
string insertQuery = $"INSERT INTO my_table ({string.Join(", ", headers.Select(h => h.Trim('`')))}) VALUES ({placeholders})";
// Insert data into the table
foreach (List<string> record in data)
{
using (MySqlCommand insertCommand = new MySqlCommand(insertQuery, connection))
{
for (int i = 0; i < record.Count; i++)
{
insertCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue($" @2024\本地文件打包__20180302\Spire.Web\trunk\src\website\components\com_virtuemart\themes\default\templates\browse\includes\browse_searchparameter_form.tpl.php{i}", record[i]);
}
insertCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine("데이터를 성공적으로 내보냈습니다!");
}
}
}결과:

결론
Spire.XLS와 같은 라이브러리 덕분에 C#에서 Excel 파일을 읽는 것이 그 어느 때보다 쉬워졌습니다. 이 가이드에서는 Excel 파일을 로드하고, 내용을 읽고, 데이터를 MySQL 데이터베이스로 가져오는 과정을 안내했습니다. 이러한 기술을 사용하면 애플리케이션의 데이터 처리 기능을 크게 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
자주 묻는 질문
Q1: 비밀번호로 보호된 Excel 파일을 읽을 수 있나요?
A: 예, Spire.XLS는 다음을 사용하여 암호화된 Excel 파일을 읽는 것을 지원합니다.
- C#
wb.OpenPassword = "psd";
wb.LoadFromFile("file.xlsx");Q2: 수식 자체가 아닌 수식 결과를 읽으려면 어떻게 해야 하나요?
A: 수식 결과를 검색하는 두 가지 옵션이 있습니다.
개별 셀의 경우:
CellRange.HasFormula를 사용하여 셀에 수식이 포함되어 있는지 확인하고 CellRange.FormulaValue로 값을 가져옵니다.
- C#
CellRange cell = sheet.Range[1, 1];
if (cell.HasFormula)
{
string result = cell.FormulaValue.ToString();
}DataTable로 대량 내보내기의 경우:
계산된 값을 내보내려면 computedFormulaValue: true와 함께 Worksheet.ExportDataTable()을 사용하십시오.
- C#
DataTable data = sheet.ExportDataTable(range, exportColumnNames: true, computedFormulaValue: true);Q3: Excel 데이터를 DataTable로 어떻게 읽을 수 있나요?
A: Spire.XLS에서 제공하는 Worksheet.ExportDataTable() 메서드를 사용하십시오.
Q4: Excel 파일을 한 줄씩 어떻게 읽을 수 있나요?
A: 다음 코드를 참조하십시오.
- C#
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.LoadFromFile("input.xlsx");
Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
for (int row = 1; row <= sheet.LastRow; row++)
{
for (int col = 1; col <= sheet.LastColumn; col++)
{
string cellValue = sheet.Range[row, col].Value?.ToString() ?? string.Empty;
Console.WriteLine(cellValue);
}
}무료 라이선스 받기
평가 제한 없이 .NET용 Spire.XLS의 모든 기능을 경험하려면 30일 무료 평가판 라이선스를 요청할 수 있습니다.