DOCX를 XLSX로 변환하는 방법: Word를 Excel로 쉽게 변환

Word 문서(DOCX)를 Excel 스프레드시트(XLSX)로 변환하는 것은 사무 자동화, 데이터 처리 및 보고 워크플로에서 일반적인 요구 사항입니다. 많은 사용자가 Word 파일에 저장된 표를 재사용하기를 원하며, 다른 사용자는 최소한의 노력으로 직접적인 문서 대 스프레드시트 변환을 기대합니다.
그러나 Word와 Excel은 매우 다른 목적으로 설계되었습니다. Word는 자유 형식의 문서 레이아웃에 중점을 두는 반면, Excel은 구조화된 표 형식 데이터를 중심으로 구축되었습니다. 이 차이점을 이해하는 것이 올바른 DOCX를 XLSX로 변환하는 방법을 선택하는 데 중요합니다.
이 가이드에서는 온라인 도구, 데스크톱 솔루션 및 Python 자동화를 사용하여 DOCX를 XLSX로 변환하는 방법과 각 접근 방식의 장점과 한계에 대해 알아봅니다.
빠른 탐색
- Word(DOCX) 파일을 Excel(XLSX)로 정말 변환할 수 있나요?
- 방법 1: 온라인에서 DOCX를 XLSX로 변환
- 방법 2: 데스크톱 소프트웨어를 사용하여 Word 콘텐츠를 Excel로 변환
- 방법 3: Python으로 DOCX를 XLSX로 변환(자동화된 워크플로에 이상적)
- DOCX를 XLSX로 변환하는 방법 비교
- 자주 묻는 질문
Word(DOCX) 파일을 Excel(XLSX)로 정말 변환할 수 있나요?
변환 방법을 선택하기 전에 "DOCX-to-XLSX 변환"이 실제로 무엇을 의미하는지 명확히 하는 것이 중요합니다.
- Word 문서에는 단락, 이미지, 제목 및 표가 포함될 수 있습니다.
- Excel 파일은 행, 열 및 구조화된 데이터에 최적화되어 있습니다.
실제로 DOCX를 XLSX로 변환하는 것은 Word 문서에 표가 포함된 경우 가장 잘 작동합니다. 일반 텍스트 단락과 복잡한 레이아웃은 스프레드시트 셀로 깔끔하게 변환되지 않을 수 있습니다.
목표가 Word에서 표 형식 데이터를 추출하여 Excel에서 재사용하는 것이라면 변환은 일반적으로 신뢰할 수 있습니다. 전체 Word 문서가 Excel에 완벽하게 나타날 것으로 기대한다면 일부 서식 손실이 예상되어야 합니다. 그러나 여전히 Word 텍스트 및 이미지 단락을 Excel에 삽입할 수 있습니다.
방법 1: 온라인에서 DOCX를 XLSX로 변환
온라인 도구는 빠르고 일회성 변환이 필요한 사용자에게 종종 첫 번째 선택입니다. 예를 들어 Online2PDF DOCX to XLSX 변환기를 사용하여 추가 소프트웨어를 설치하지 않고도 브라우저에서 직접 문서를 변환할 수 있습니다.
일반적인 워크플로는 다음과 같습니다.
-
온라인 DOCX to XLSX 변환기를 엽니다.
-
Word(DOCX) 파일을 업로드합니다.
-
변환 프로세스를 시작합니다.
-
변환된 Excel(XLSX) 파일을 다운로드합니다.
많은 온라인 변환기가 DOCX-to-XLSX 변환을 지원하므로 Word 문서를 몇 초 만에 편집 가능한 스프레드시트로 쉽게 변환할 수 있습니다.
온라인 DOCX to XLSX 변환기의 장단점
장점
- 소프트웨어 설치 필요 없음
- 초보자도 사용하기 쉬움
- 작은 파일 및 가끔씩의 작업에 적합
한계
- 파일 크기 및 사용량 제한
- 잠재적인 개인 정보 및 데이터 보안 문제
- 서식에 대한 제한된 제어
- 일괄 또는 자동화된 처리에 적합하지 않음
온라인 변환기는 편리하지만 간단하고 민감하지 않은 파일에 가장 적합합니다.
많은 온라인 도구는 Word 파일을 여러 형식으로 변환하는 것을 지원합니다. 예를 들어 프레젠테이션 자료를 준비할 때 Word를 PowerPoint로 변환하는 방법을 탐색할 수도 있습니다.
방법 2: 데스크톱 소프트웨어를 사용하여 Word 콘텐츠를 Excel로 변환
구조화되거나 반구조화된 데이터가 포함된 문서의 경우 데스크톱 오피스 소프트웨어는 높은 수준의 시각적 제어로 Word에서 Excel로 콘텐츠를 이동하는 실용적인 방법을 제공합니다. 일반적인 도구로는 Microsoft Office 및 LibreOffice가 있으며, 사용자는 Word 콘텐츠를 복사하여 Excel 스프레드시트에 직접 붙여넣을 수 있습니다.
이러한 데스크톱 소프트웨어는 기본 "DOCX to XLSX 내보내기" 기능을 제공하지 않지만, 특히 Word 문서에 표가 포함된 경우 신뢰할 수 있는 결과를 생성할 수 있습니다.
표가 더 정확하게 변환되는 이유
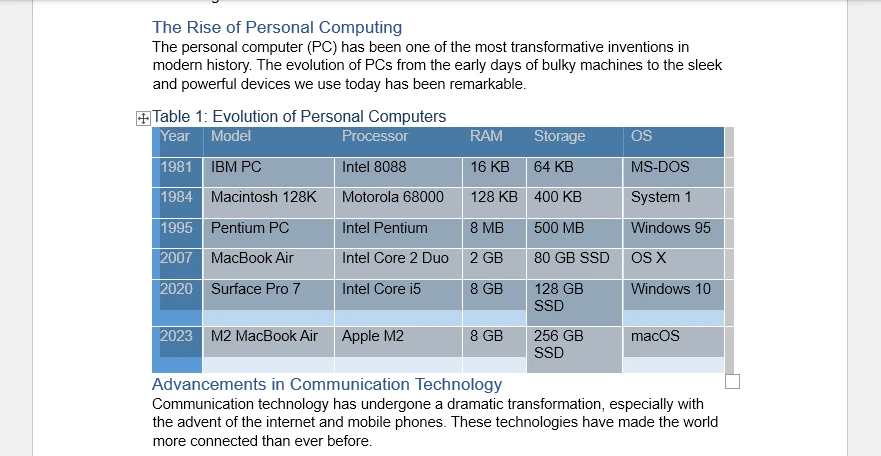
가장 성공적인 DOCX to XLSX 변환은 표 기반 콘텐츠에 의존합니다. Word의 표는 이미 행과 열을 정의하며, 이는 Excel의 그리드 기반 데이터 모델과 밀접하게 일치합니다. Excel에 붙여넣을 때 Word 표는 일반적으로 최소한의 조정으로 구조, 정렬 및 셀 경계를 유지합니다.
비표 형식 콘텐츠도 전송할 수 있습니다. 단락, 제목 및 목록을 Excel 셀에 붙여넣을 수 있으며, 각 줄은 개별 행에 배치됩니다. 추가 서식이 필요할 수 있지만 이 접근 방식은 종종 문서 콘텐츠를 스프레드시트 형식으로 구성하는 데 충분합니다.
예: Microsoft Office를 사용하여 Word 콘텐츠를 Excel에 복사
다음은 Microsoft Office를 사용한 일반적인 워크플로입니다.
-
Microsoft Word에서 DOCX 파일을 엽니다.
-
전송할 콘텐츠를 선택합니다.
- 최상의 구조적 정확도를 위해 표만
- 또는 필요한 경우 전체 문서
-
선택 항목을 복사합니다(Ctrl + C).
-
Microsoft Excel을 열고 대상 워크시트를 선택합니다.
-
콘텐츠를 Excel에 붙여넣습니다(Ctrl + V).
-
필요에 따라 열 너비, 셀 정렬 또는 텍스트 줄 바꿈을 조정합니다.
이 방법은 주로 표, 양식 또는 구조화된 레이아웃을 포함하는 Word 문서에 특히 효과적입니다. 문서에 복잡한 표가 포함된 경우 더 높은 정확도와 제어를 위해 프로그래밍 방식으로 Word에서 표를 추출하는 방법을 배우는 것이 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
데스크톱 기반 변환의 한계
데스크톱 도구는 유연성과 시각적 제어를 제공하지만 몇 가지 한계가 있습니다.
- 진정한 DOCX to XLSX 내보내기 또는 일괄 변환 없음
- 각 문서에 대해 수동 단계 필요
- 파일 간 서식 일관성 유지 어려움
여러 문서를 처리하거나 반복적인 변환 작업을 수행할 때 수동 데스크톱 워크플로는 금방 시간이 많이 소요될 수 있습니다. 이러한 경우 자동화되거나 프로그래밍 방식의 솔루션이 일반적으로 더 효율적입니다.
방법 3: Python으로 DOCX를 XLSX로 변환(자동화된 워크플로에 이상적)
수동 방법이 비효율적이 될 때 Python은 Word 문서를 Excel 파일로 변환하는 확장 가능한 방법을 제공합니다. 이 접근 방식은 데스크톱 응용 프로그램에 의존하지 않고 일관되고 반복 가능한 결과가 필요한 개발자에게 특히 유용합니다.
Python 기반 변환은 다음에 적합합니다.
- 많은 수의 DOCX 파일 일괄 처리
- 자동화된 데이터 파이프라인
- 서버 측 문서 워크플로
- Microsoft Office를 사용할 수 없는 환경
수동 내보내기와 비교할 때 스크립팅은 더 큰 유연성을 제공하고 반복적인 작업을 크게 줄입니다.
Python이 Word 데이터를 Excel로 변환하는 방법
실용적인 전략은 Word에서 구조화된 데이터(특히 표)를 추출하여 Excel 통합 문서에 직접 쓰는 것입니다. 표는 이미 콘텐츠를 행과 열로 구성하므로 논리적 구조를 유지하면서 스프레드시트 형식으로 자연스럽게 변환됩니다.
이 예에서는:
- Spire.Doc for Python은 DOCX 파일을 로드하고 표 데이터를 검색합니다.
- Spire.XLS for Python은 Excel 통합 문서를 만들고 추출된 콘텐츠를 워크시트에 씁니다.
이러한 라이브러리를 결합하면 프로덕션 환경에 적합한 제어된 프로그래밍 방식의 변환 프로세스가 가능합니다.
프로젝트에서 라이브러리를 사용하기 전에 필요한 패키지를 설치했는지 확인하십시오. pip를 통해 설치할 수 있습니다.
단계별: Python으로 Word 표를 Excel로 변환
다음은 Python을 사용하여 DOCX 표를 XLSX로 변환하는 일반적인 워크플로입니다.
-
DOCX 파일 로드 Spire.Doc for Python을 사용하여 Word 문서를 엽니다.
-
문서에서 표 추출 문서 구조를 반복하고 표 데이터를 검색합니다.
-
Excel 통합 문서 만들기 Spire.XLS for Python을 사용하여 새 통합 문서를 초기화합니다.
-
워크시트에 표 데이터 쓰기 Word 표의 행과 셀을 Excel 행과 열에 매핑합니다.
-
파일을 XLSX로 저장 최종 결과를 Excel 스프레드시트로 내보냅니다.
Python 코드: DOCX 표를 XLSX로 변환
다음 예는 Word 문서에서 표를 추출하여 Excel 워크시트로 내보내는 방법을 보여줍니다.
from spire.doc import Document
from spire.xls import Workbook, Color
# Load the Word document
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Create a new Excel workbook
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.Worksheets.Clear()
# Iterate through all sections in the Word document
for sec_index in range(len(doc.Sections)):
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(sec_index)
# Iterate through all tables in the current section
for table_index in range(len(section.Tables)):
table = section.Tables.get_Item(table_index)
# Create a worksheet for each Word table
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add(f"Table-{table_index + 1}")
# Iterate through rows in the Word table
for row_index in range(len(table.Rows)):
row = table.Rows.get_Item(row_index)
# Iterate through cells in the current row
for cell_index in range(len(row.Cells)):
table_cell = row.Cells.get_Item(cell_index)
# Collect all paragraph text inside the Word table cell
cell_data = ""
for para_index in range(len(table_cell.Paragraphs)):
para = table_cell.Paragraphs.get_Item(para_index)
cell_data += para.Text + "\n"
# Write text to the corresponding Excel cell
cell = sheet.Range.get_Item(row_index + 1, cell_index + 1)
cell.Value = cell_data
# Copy the Word table cell background color to Excel
# Note: Color must be assigned directly to the Style to take effect
table_cell_color = table_cell.CellFormat.BackColor
cell.Style.Color = Color.FromRgb(
table_cell_color.R,
table_cell_color.G,
table_cell_color.B
)
# Auto-fit columns after writing the table
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns()
# Save the Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("WordTableToExcel.xlsx")
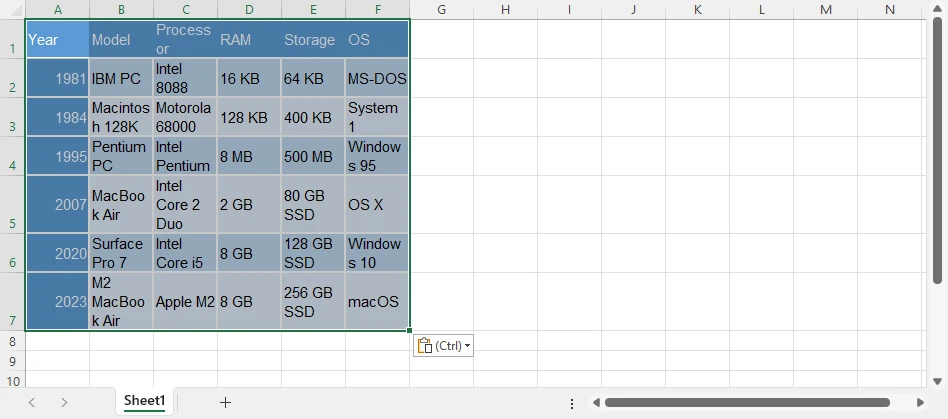
다음은 Word 문서에서 변환된 XLSX 파일의 미리보기입니다.
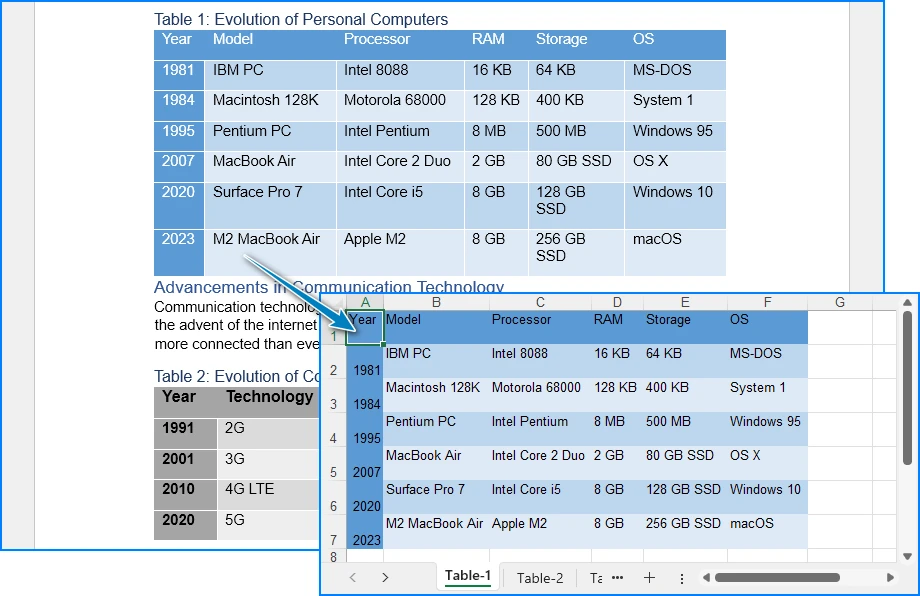
이 접근 방식은 표가 핵심 데이터를 나타내는 구조화된 문서, 보고서 및 양식 기반 Word 파일에 특히 유용합니다.
Word에서 Excel로 변환하는 동안 표 서식 및 스타일을 유지하는 것을 포함하여 더 고급 Python 기술에 대해서는 Python으로 Word 표를 Excel로 변환에 대한 자세한 가이드를 확인하십시오.
DOCX를 XLSX로 변환하는 방법 비교
올바른 방법을 선택하는 것은 문서 볼륨, 자동화 요구 사항 및 데이터 민감도와 같은 요소에 따라 다릅니다. 아래 표는 각 옵션을 평가하는 데 도움이 되는 빠른 개요를 제공합니다.
| 방법 | 최적 대상 | 자동화 수준 | 장점 | 한계 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 온라인 변환기 | 일회성 작업 | 없음 | 빠르고 쉬움 | 개인 정보 위험, 제한된 정확도 |
| 데스크톱 소프트웨어 | 소규모 작업량 | 낮음 | 시각적 제어 | 시간 소모적, 확장성 없음 |
| Python 자동화 | 대규모 워크플로 | 높음 | 유연하고 반복 가능 | 프로그래밍 필요 |
올바른 방법 선택 방법
- 속도가 중요하고 파일이 민감하지 않은 경우 온라인 변환기를 사용하십시오.
- 소수의 문서에 대해 수동 제어를 선호하는 경우 데스크톱 소프트웨어를 선택하십시오.
- 대규모 데이터 세트를 처리하거나 반복 가능한 워크플로를 구축할 때 Python 자동화를 선택하십시오.
진행 중이거나 비즈니스에 중요한 프로세스의 경우 자동화된 솔루션은 일반적으로 장기적으로 더 큰 효율성과 일관성을 제공합니다.
FAQ: DOCX to XLSX 변환
모든 Word 문서를 Excel로 변환할 수 있나요?
대부분의 Word 파일은 변환할 수 있지만 표나 구조화된 데이터가 있는 문서가 가장 잘 작동합니다. 자유 형식 텍스트와 복잡한 레이아웃은 변환 후 조정이 필요할 수 있습니다.
변환 후 서식이 동일하게 유지되나요?
항상 그런 것은 아닙니다. Word와 Excel은 레이아웃을 다르게 처리하므로 일부 간격, 병합된 셀 또는 텍스트 흐름이 변경될 수 있습니다. 일반적으로 Excel에서 약간의 조정이 필요합니다.
Word에서 표만 Excel로 변환할 수 있나요?
예. Word 문서에 표가 포함된 경우 더 정확하고 신뢰할 수 있는 변환을 위해 표만 추출할 수 있습니다.
여러 DOCX 파일을 변환하는 가장 쉬운 방법은 무엇인가요?
여러 파일의 경우 Python 라이브러리와 같은 자동화된 솔루션이나 일괄 처리 도구를 사용하면 시간을 절약하고 특히 대용량 문서에 대해 일관된 결과를 보장할 수 있습니다.
결론
DOCX를 XLSX로 변환하는 것은 모든 경우에 적용되는 단일한 작업이 아닙니다. 온라인 및 데스크톱 도구는 간단한 시나리오에 유용하지만 정확성, 확장성 또는 자동화가 필요한 경우에는 종종 부족합니다.
Word 문서의 구조를 이해하고 올바른 변환 접근 방식을 선택하면 신뢰할 수 있는 결과를 얻을 수 있습니다. 개발자와 고급 사용자의 경우 Python은 Word 표를 Excel 스프레드시트로 효율적으로 변환하는 강력하고 유연한 방법을 제공합니다.
참고 항목
Come convertire DOCX in XLSX: Trasforma facilmente Word in Excel
Indice
- È davvero possibile convertire un file Word (DOCX) in Excel (XLSX)?
- Metodo 1: Convertire DOCX in XLSX online
- Metodo 2: Convertire il contenuto di Word in Excel utilizzando software desktop
- Metodo 3: Convertire DOCX in XLSX con Python
- Confronto dei metodi di conversione da DOCX a XLSX
- Domande frequenti

La conversione di un documento Word (DOCX) in un foglio di calcolo Excel (XLSX) è un requisito comune nell'automazione dell'ufficio, nell'elaborazione dei dati e nei flussi di lavoro di reporting. Molti utenti desiderano riutilizzare le tabelle archiviate nei file Word, mentre altri si aspettano una conversione diretta da documento a foglio di calcolo con il minimo sforzo.
Tuttavia, Word ed Excel sono progettati per scopi molto diversi. Word si concentra sul layout di documenti in formato libero, mentre Excel è costruito attorno a dati strutturati e tabulari. Comprendere questa differenza è fondamentale per scegliere il metodo di conversione da DOCX a XLSX corretto.
In questa guida imparerai come convertire DOCX in XLSX utilizzando strumenti online, soluzioni desktop e automazione Python, insieme ai vantaggi e ai limiti di ciascun approccio.
Navigazione rapida
- È davvero possibile convertire un file Word (DOCX) in Excel (XLSX)?
- Metodo 1: Convertire DOCX in XLSX online
- Metodo 2: Convertire il contenuto di Word in Excel utilizzando software desktop
- Metodo 3: Convertire DOCX in XLSX con Python
- Confronto dei metodi di conversione da DOCX a XLSX
- Domande frequenti
È davvero possibile convertire un file Word (DOCX) in Excel (XLSX)?
Prima di scegliere un metodo di conversione, è importante chiarire cosa significhi effettivamente “conversione da DOCX a XLSX”.
- I documenti Word possono contenere paragrafi, immagini, intestazioni e tabelle.
- I file Excel sono ottimizzati per righe, colonne e dati strutturati.
In pratica, la conversione da DOCX a XLSX funziona meglio quando il documento Word contiene tabelle. I paragrafi di testo semplice e i layout complessi non sempre si traducono in modo pulito nelle celle del foglio di calcolo.
Se il tuo obiettivo è estrarre dati tabulari da Word e riutilizzarli in Excel, la conversione è solitamente affidabile. Se ti aspetti che un intero documento Word appaia perfettamente in Excel, dovresti aspettarti una certa perdita di formattazione. Tuttavia, puoi comunque inserire paragrafi di testo e immagini di Word in Excel.
Metodo 1: Convertire DOCX in XLSX online
Gli strumenti online sono spesso la prima scelta per gli utenti che necessitano di una conversione rapida e una tantum. Ad esempio, è possibile utilizzare il convertitore da DOCX a XLSX di Online2PDF per convertire i documenti direttamente nel browser senza installare software aggiuntivo.
Un flusso di lavoro tipico è simile a questo:
-
Apri il convertitore online da DOCX a XLSX.

-
Carica il tuo file Word (DOCX).
-
Avvia il processo di conversione.
-
Scarica il file Excel (XLSX) convertito.

Molti convertitori online supportano la conversione da DOCX a XLSX, rendendo facile trasformare i documenti Word in fogli di calcolo modificabili in pochi secondi.
Pro e contro dei convertitori online da DOCX a XLSX
Vantaggi
- Nessuna installazione di software richiesta
- Facile da usare per i principianti
- Adatto per file di piccole dimensioni e attività occasionali
Limitazioni
- Limiti di dimensione e utilizzo dei file
- Potenziali problemi di privacy e sicurezza dei dati
- Controllo limitato sulla formattazione
- Non adatto per l'elaborazione batch o automatizzata
I convertitori online sono convenienti, ma sono più adatti per file semplici e non sensibili.
Molti strumenti online supportano la conversione di file Word in più formati. Ad esempio, puoi anche esplorare come convertire Word in PowerPoint durante la preparazione dei materiali per la presentazione.
Metodo 2: Convertire il contenuto di Word in Excel utilizzando software desktop
Per i documenti che contengono dati strutturati o semistrutturati, il software per ufficio desktop offre un modo pratico per spostare il contenuto da Word a Excel con un alto livello di controllo visivo. Gli strumenti comuni includono Microsoft Office e LibreOffice, che consentono agli utenti di copiare il contenuto di Word e incollarlo direttamente nei fogli di calcolo di Excel.
Sebbene questo software desktop non fornisca una funzione nativa di “esportazione da DOCX a XLSX”, può comunque produrre risultati affidabili, specialmente quando i documenti Word contengono tabelle.
Perché le tabelle si convertono in modo più accurato
La maggior parte delle conversioni da DOCX a XLSX riuscite si basa su contenuti basati su tabelle. Le tabelle in Word definiscono già righe e colonne, che si allineano strettamente con il modello di dati basato su griglia di Excel. Quando vengono incollate in Excel, le tabelle di Word di solito mantengono la loro struttura, allineamento e confini delle celle con una regolazione minima.
È possibile trasferire anche contenuti non tabulari. Paragrafi, intestazioni ed elenchi possono essere incollati nelle celle di Excel, dove ogni riga viene inserita in righe individuali. Sebbene possa essere richiesta una formattazione aggiuntiva, questo approccio è spesso sufficiente per organizzare il contenuto del documento in un formato di foglio di calcolo.
Esempio: copiare il contenuto di Word in Excel utilizzando Microsoft Office
Di seguito è riportato un flusso di lavoro tipico utilizzando Microsoft Office:
-
Apri il file DOCX in Microsoft Word.

-
Seleziona il contenuto che desideri trasferire:
- Solo tabelle, per la migliore accuratezza strutturale
- Oppure l'intero documento, se necessario
-
Copia la selezione (Ctrl + C).
-
Apri Microsoft Excel e seleziona il foglio di lavoro di destinazione.
-
Incolla il contenuto (Ctrl + V) in Excel.

-
Regola la larghezza delle colonne, l'allineamento delle celle o il ritorno a capo del testo secondo necessità.
Questo metodo funziona particolarmente bene per i documenti Word che contengono principalmente tabelle, moduli o layout strutturati. Se il tuo documento contiene tabelle complesse, potresti trarre vantaggio dall'imparare come estrarre le tabelle da Word a livello di codice per una maggiore precisione e controllo.
Limitazioni della conversione basata su desktop
Sebbene gli strumenti desktop offrano flessibilità e controllo visivo, presentano diverse limitazioni:
- Nessuna vera esportazione da DOCX a XLSX o conversione batch
- Sono necessari passaggi manuali per ogni documento
- La coerenza della formattazione può essere difficile da mantenere tra i file
Quando si ha a che fare con più documenti o attività di conversione ricorrenti, i flussi di lavoro desktop manuali possono diventare rapidamente dispendiosi in termini di tempo. In tali casi, le soluzioni automatizzate o programmatiche sono solitamente più efficienti.
Metodo 3: Convertire DOCX in XLSX con Python (ideale per flussi di lavoro automatizzati)
Quando i metodi manuali diventano inefficienti, Python offre un modo scalabile per convertire i documenti Word in file Excel. Questo approccio è particolarmente prezioso per gli sviluppatori che necessitano di risultati coerenti e ripetibili senza fare affidamento su applicazioni desktop.
La conversione basata su Python è adatta per:
- Elaborazione batch di un gran numero di file DOCX
- Pipeline di dati automatizzate
- Flussi di lavoro di documenti lato server
- Ambienti in cui Microsoft Office non è disponibile
Rispetto alle esportazioni manuali, lo scripting offre una maggiore flessibilità e riduce significativamente il lavoro ripetitivo.
Come Python converte i dati di Word in Excel
Una strategia pratica consiste nell'estrarre dati strutturati da Word, in particolare le tabelle, e scriverli direttamente in una cartella di lavoro di Excel. Poiché le tabelle organizzano già il contenuto in righe e colonne, si traducono naturalmente in formato foglio di calcolo preservando la struttura logica.
In questo esempio:
- Spire.Doc for Python carica il file DOCX e recupera i dati della tabella.
- Spire.XLS for Python crea la cartella di lavoro di Excel e scrive il contenuto estratto nei fogli di lavoro.
La combinazione di queste librerie consente un processo di conversione controllato e programmatico adatto agli ambienti di produzione.
Prima di utilizzare le librerie nel tuo progetto, assicurati di aver installato i pacchetti necessari. Puoi installarli tramite pip:
Passo dopo passo: convertire le tabelle di Word in Excel con Python
Di seguito è riportato un flusso di lavoro tipico per la conversione di tabelle DOCX in XLSX utilizzando Python:
-
Carica il file DOCX Usa Spire.Doc for Python per aprire il documento Word.
-
Estrai tabelle dal documento Itera attraverso la struttura del documento e recupera i dati della tabella.
-
Crea una cartella di lavoro di Excel Inizializza una nuova cartella di lavoro utilizzando Spire.XLS for Python.
-
Scrivi i dati della tabella nei fogli di lavoro Mappa righe e celle dalle tabelle di Word in righe e colonne di Excel.
-
Salva il file come XLSX Esporta il risultato finale come foglio di calcolo Excel.
Codice Python: convertire tabelle DOCX in XLSX
L'esempio seguente mostra come estrarre le tabelle da un documento Word ed esportarle in un foglio di lavoro di Excel.
from spire.doc import Document
from spire.xls import Workbook, Color
# Load the Word document
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Create a new Excel workbook
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.Worksheets.Clear()
# Iterate through all sections in the Word document
for sec_index in range(len(doc.Sections)):
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(sec_index)
# Iterate through all tables in the current section
for table_index in range(len(section.Tables)):
table = section.Tables.get_Item(table_index)
# Create a worksheet for each Word table
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add(f"Table-{table_index + 1}")
# Iterate through rows in the Word table
for row_index in range(len(table.Rows)):
row = table.Rows.get_Item(row_index)
# Iterate through cells in the current row
for cell_index in range(len(row.Cells)):
table_cell = row.Cells.get_Item(cell_index)
# Collect all paragraph text inside the Word table cell
cell_data = ""
for para_index in range(len(table_cell.Paragraphs)):
para = table_cell.Paragraphs.get_Item(para_index)
cell_data += para.Text + "\n"
# Write text to the corresponding Excel cell
cell = sheet.Range.get_Item(row_index + 1, cell_index + 1)
cell.Value = cell_data
# Copy the Word table cell background color to Excel
# Note: Color must be assigned directly to the Style to take effect
table_cell_color = table_cell.CellFormat.BackColor
cell.Style.Color = Color.FromRgb(
table_cell_color.R,
table_cell_color.G,
table_cell_color.B
)
# Auto-fit columns after writing the table
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns()
# Save the Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("WordTableToExcel.xlsx")
Di seguito è riportata un'anteprima del file XLSX convertito dal documento Word:

Questo approccio è particolarmente utile per documenti strutturati, report e file Word basati su moduli in cui le tabelle rappresentano i dati principali.
Per tecniche Python più avanzate, inclusa la conservazione della formattazione e degli stili delle tabelle durante la conversione da Word a Excel, consulta la nostra guida dettagliata sulla conversione di tabelle Word in Excel con Python.
Confronto dei metodi di conversione da DOCX a XLSX
La scelta del metodo giusto dipende da fattori quali il volume dei documenti, le esigenze di automazione e la sensibilità dei dati. La tabella seguente fornisce una rapida panoramica per aiutarti a valutare ogni opzione.
| Metodo | Ideale per | Livello di automazione | Vantaggi | Limitazioni |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Convertitore online | Attività una tantum | Nessuno | Veloce e facile | Rischi per la privacy, precisione limitata |
| Software desktop | Carichi di lavoro ridotti | Basso | Controllo visivo | Dispendioso in termini di tempo, non scalabile |
| Automazione Python | Grandi flussi di lavoro | Alto | Flessibile, ripetibile | Richiede programmazione |
Come scegliere il metodo giusto
- Usa i convertitori online quando la velocità è importante e i file non sono sensibili.
- Scegli il software desktop se preferisci il controllo manuale per un numero ridotto di documenti.
- Opta per l'automazione Python quando gestisci grandi set di dati o crei flussi di lavoro ripetibili.
Per i processi in corso o critici per l'azienda, le soluzioni automatizzate offrono in genere una maggiore efficienza e coerenza a lungo termine.
FAQ: Conversione da DOCX a XLSX
Posso convertire qualsiasi documento Word in Excel?
La maggior parte dei file Word può essere convertita, ma i documenti con tabelle o dati strutturati funzionano meglio. Il testo in formato libero e i layout complessi potrebbero richiedere un aggiustamento dopo la conversione.
La formattazione rimarrà la stessa dopo la conversione?
Non sempre. Word ed Excel gestiscono i layout in modo diverso, quindi alcuni spazi, celle unite o flusso di testo potrebbero cambiare. Di solito sono necessarie piccole modifiche in Excel.
Posso convertire solo le tabelle da Word a Excel?
Sì. Se il tuo documento Word contiene tabelle, puoi estrarre solo le tabelle per una conversione più accurata e affidabile.
Qual è il modo più semplice per convertire più file DOCX?
Per più file, soluzioni automatizzate o strumenti batch, come le librerie Python, possono far risparmiare tempo e garantire risultati coerenti, specialmente per documenti di grandi dimensioni.
Conclusione
La conversione da DOCX a XLSX non è un'attività valida per tutti. Sebbene gli strumenti online e desktop siano utili per scenari semplici, spesso non sono all'altezza quando sono richieste precisione, scalabilità o automazione.
Comprendendo la struttura dei tuoi documenti Word e scegliendo il giusto approccio di conversione, puoi ottenere risultati affidabili. Per sviluppatori e utenti avanzati, Python offre un modo potente e flessibile per convertire in modo efficiente le tabelle di Word in fogli di calcolo di Excel.
Vedi anche
Comment convertir DOCX en XLSX : Transformez facilement Word en Excel
Table des matières
- Pouvez-vous vraiment convertir un fichier Word (DOCX) en Excel (XLSX) ?
- Méthode 1 : Convertir DOCX en XLSX en ligne
- Méthode 2 : Convertir le contenu de Word en Excel à l'aide d'un logiciel de bureau
- Méthode 3 : Convertir DOCX en XLSX avec Python
- Comparer les méthodes de conversion DOCX en XLSX
- Foire aux questions

La conversion d'un document Word (DOCX) en une feuille de calcul Excel (XLSX) est une exigence courante dans les flux de travail d'automatisation de bureau, de traitement de données et de reporting. De nombreux utilisateurs souhaitent réutiliser des tableaux stockés dans des fichiers Word, tandis que d'autres s'attendent à une conversion directe de document en feuille de calcul avec un minimum d'effort.
Cependant, Word et Excel sont conçus à des fins très différentes. Word se concentre sur la mise en page de documents de forme libre, tandis qu'Excel est construit autour de données structurées et tabulaires. Comprendre cette différence est essentiel pour choisir la bonne méthode de conversion de DOCX en XLSX.
Dans ce guide, vous apprendrez comment convertir DOCX en XLSX à l'aide d'outils en ligne, de solutions de bureau et d'automatisation Python, ainsi que les avantages et les limites de chaque approche.
Navigation rapide
- Pouvez-vous vraiment convertir un fichier Word (DOCX) en Excel (XLSX) ?
- Méthode 1 : Convertir DOCX en XLSX en ligne
- Méthode 2 : Convertir le contenu de Word en Excel à l'aide d'un logiciel de bureau
- Méthode 3 : Convertir DOCX en XLSX avec Python
- Comparer les méthodes de conversion DOCX en XLSX
- Foire aux questions
Pouvez-vous vraiment convertir un fichier Word (DOCX) en Excel (XLSX) ?
Avant de choisir une méthode de conversion, il est important de clarifier ce que signifie réellement la « conversion DOCX en XLSX ».
- Les documents Word peuvent contenir des paragraphes, des images, des titres et des tableaux.
- Les fichiers Excel sont optimisés pour les lignes, les colonnes et les données structurées.
En pratique, la conversion de DOCX en XLSX fonctionne mieux lorsque le document Word contient des tableaux. Les paragraphes de texte brut et les mises en page complexes ne se traduisent pas toujours proprement dans les cellules d'une feuille de calcul.
Si votre objectif est d'extraire des données tabulaires de Word et de les réutiliser dans Excel, la conversion est généralement fiable. Si vous vous attendez à ce qu'un document Word entier apparaisse parfaitement dans Excel, une certaine perte de formatage est à prévoir. Cependant, vous pouvez toujours insérer des paragraphes de texte et d'images Word dans Excel.
Méthode 1 : Convertir DOCX en XLSX en ligne
Les outils en ligne sont souvent le premier choix des utilisateurs qui ont besoin d'une conversion rapide et ponctuelle. Par exemple, vous pouvez utiliser le convertisseur Online2PDF DOCX to XLSX pour convertir des documents directement dans votre navigateur sans installer de logiciel supplémentaire.
Un flux de travail typique ressemble à ceci :
-
Ouvrez le convertisseur DOCX en XLSX en ligne.

-
Téléchargez votre fichier Word (DOCX).
-
Démarrez le processus de conversion.
-
Téléchargez le fichier Excel (XLSX) converti.

De nombreux convertisseurs en ligne prennent en charge la conversion de DOCX en XLSX, ce qui facilite la transformation de documents Word en feuilles de calcul modifiables en quelques secondes.
Avantages et inconvénients des convertisseurs DOCX en XLSX en ligne
Avantages
- Aucune installation de logiciel requise
- Facile à utiliser pour les débutants
- Convient aux petits fichiers et aux tâches occasionnelles
Limites
- Limites de taille de fichier et d'utilisation
- Problèmes potentiels de confidentialité et de sécurité des données
- Contrôle limité sur le formatage
- Ne convient pas au traitement par lots ou automatisé
Les convertisseurs en ligne sont pratiques, mais ils conviennent mieux aux fichiers simples et non sensibles.
De nombreux outils en ligne prennent en charge la conversion de fichiers Word en plusieurs formats. Par exemple, vous pouvez également explorer comment convertir Word en PowerPoint lors de la préparation de supports de présentation.
Méthode 2 : Convertir le contenu de Word en Excel à l'aide d'un logiciel de bureau
Pour les documents contenant des données structurées ou semi-structurées, les logiciels de bureautique de bureau offrent un moyen pratique de déplacer le contenu de Word vers Excel avec un haut niveau de contrôle visuel. Les outils courants incluent Microsoft Office et LibreOffice, qui permettent aux utilisateurs de copier le contenu de Word et de le coller directement dans des feuilles de calcul Excel.
Bien que ces logiciels de bureau ne fournissent pas de fonctionnalité native « d'exportation DOCX vers XLSX », ils peuvent tout de même produire des résultats fiables, en particulier lorsque les documents Word contiennent des tableaux.
Pourquoi les tableaux se convertissent plus précisément
La plupart des conversions DOCX en XLSX réussies reposent sur un contenu basé sur des tableaux. Les tableaux dans Word définissent déjà des lignes et des colonnes, qui s'alignent étroitement sur le modèle de données en grille d'Excel. Lorsqu'ils sont collés dans Excel, les tableaux Word conservent généralement leur structure, leur alignement et les bordures de leurs cellules avec un ajustement minimal.
Le contenu non tabulaire peut également être transféré. Les paragraphes, les titres et les listes peuvent être collés dans des cellules Excel, où chaque ligne est placée dans des lignes individuelles. Bien qu'un formatage supplémentaire puisse être nécessaire, cette approche est souvent suffisante pour organiser le contenu du document dans un format de feuille de calcul.
Exemple : Copier le contenu de Word dans Excel à l'aide de Microsoft Office
Voici un flux de travail typique utilisant Microsoft Office :
-
Ouvrez le fichier DOCX dans Microsoft Word.

-
Sélectionnez le contenu que vous souhaitez transférer :
- Tableaux uniquement, pour une meilleure précision structurelle
- Ou le document entier, si nécessaire
-
Copiez la sélection (Ctrl + C).
-
Ouvrez Microsoft Excel et sélectionnez la feuille de calcul cible.
-
Collez le contenu (Ctrl + V) dans Excel.

-
Ajustez la largeur des colonnes, l'alignement des cellules ou le retour à la ligne automatique selon les besoins.
Cette méthode fonctionne particulièrement bien pour les documents Word qui contiennent principalement des tableaux, des formulaires ou des mises en page structurées. Si votre document contient des tableaux complexes, vous pourriez bénéficier d'apprendre comment extraire des tableaux de Word par programme pour une plus grande précision et un meilleur contrôle.
Limites de la conversion basée sur le bureau
Bien que les outils de bureau offrent flexibilité et contrôle visuel, ils présentent plusieurs limites :
- Pas de véritable exportation DOCX vers XLSX ni de conversion par lots
- Des étapes manuelles sont requises pour chaque document
- La cohérence du formatage peut être difficile à maintenir entre les fichiers
Lorsque vous traitez plusieurs documents ou des tâches de conversion récurrentes, les flux de travail manuels sur ordinateur peuvent rapidement devenir chronophages. Dans de tels cas, les solutions automatisées ou programmatiques sont généralement plus efficaces.
Méthode 3 : Convertir DOCX en XLSX avec Python (Idéal pour les flux de travail automatisés)
Lorsque les méthodes manuelles deviennent inefficaces, Python offre un moyen évolutif de convertir des documents Word en fichiers Excel. Cette approche est particulièrement précieuse pour les développeurs qui ont besoin de résultats cohérents et reproductibles sans dépendre des applications de bureau.
La conversion basée sur Python est bien adaptée pour :
- Traitement par lots d'un grand nombre de fichiers DOCX
- Pipelines de données automatisés
- Flux de travail de documents côté serveur
- Environnements où Microsoft Office n'est pas disponible
Par rapport aux exportations manuelles, les scripts offrent une plus grande flexibilité et réduisent considérablement le travail répétitif.
Comment Python convertit les données Word en Excel
Une stratégie pratique consiste à extraire des données structurées de Word, en particulier des tableaux, et à les écrire directement dans un classeur Excel. Parce que les tableaux organisent déjà le contenu en lignes et en colonnes, ils se traduisent naturellement au format feuille de calcul tout en préservant la structure logique.
Dans cet exemple :
- Spire.Doc for Python charge le fichier DOCX et récupère les données du tableau.
- Spire.XLS for Python crée le classeur Excel et écrit le contenu extrait dans des feuilles de calcul.
La combinaison de ces bibliothèques permet un processus de conversion contrôlé et programmatique adapté aux environnements de production.
Avant d'utiliser les bibliothèques dans votre projet, assurez-vous d'avoir installé les packages nécessaires. Vous pouvez les installer via pip :
Étape par étape : Convertir des tableaux Word en Excel avec Python
Voici un flux de travail typique pour convertir des tableaux DOCX en XLSX à l'aide de Python :
-
Charger le fichier DOCX Utilisez Spire.Doc for Python pour ouvrir le document Word.
-
Extraire les tableaux du document Parcourez la structure du document et récupérez les données du tableau.
-
Créer un classeur Excel Initialisez un nouveau classeur à l'aide de Spire.XLS for Python.
-
Écrire les données du tableau dans les feuilles de calcul Mapper les lignes et les cellules des tableaux Word dans les lignes et les colonnes d'Excel.
-
Enregistrer le fichier au format XLSX Exportez le résultat final sous forme de feuille de calcul Excel.
Code Python : Convertir des tableaux DOCX en XLSX
L'exemple suivant montre comment extraire des tableaux d'un document Word et les exporter vers une feuille de calcul Excel.
from spire.doc import Document
from spire.xls import Workbook, Color
# Load the Word document
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Create a new Excel workbook
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.Worksheets.Clear()
# Iterate through all sections in the Word document
for sec_index in range(len(doc.Sections)):
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(sec_index)
# Iterate through all tables in the current section
for table_index in range(len(section.Tables)):
table = section.Tables.get_Item(table_index)
# Create a worksheet for each Word table
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add(f"Table-{table_index + 1}")
# Iterate through rows in the Word table
for row_index in range(len(table.Rows)):
row = table.Rows.get_Item(row_index)
# Iterate through cells in the current row
for cell_index in range(len(row.Cells)):
table_cell = row.Cells.get_Item(cell_index)
# Collect all paragraph text inside the Word table cell
cell_data = ""
for para_index in range(len(table_cell.Paragraphs)):
para = table_cell.Paragraphs.get_Item(para_index)
cell_data += para.Text + "\n"
# Write text to the corresponding Excel cell
cell = sheet.Range.get_Item(row_index + 1, cell_index + 1)
cell.Value = cell_data
# Copy the Word table cell background color to Excel
# Note: Color must be assigned directly to the Style to take effect
table_cell_color = table_cell.CellFormat.BackColor
cell.Style.Color = Color.FromRgb(
table_cell_color.R,
table_cell_color.G,
table_cell_color.B
)
# Auto-fit columns after writing the table
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns()
# Save the Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("WordTableToExcel.xlsx")
Voici un aperçu du fichier XLSX converti à partir du document Word :

Cette approche est particulièrement utile pour les documents structurés, les rapports et les fichiers Word basés sur des formulaires où les tableaux représentent les données de base.
Pour des techniques Python plus avancées, y compris la préservation du formatage et des styles des tableaux lors de la conversion de Word vers Excel, consultez notre guide détaillé sur la conversion de tableaux Word en Excel avec Python.
Comparer les méthodes de conversion DOCX en XLSX
Le choix de la bonne méthode dépend de facteurs tels que le volume de documents, les besoins d'automatisation et la sensibilité des données. Le tableau ci-dessous fournit un aperçu rapide pour vous aider à évaluer chaque option.
| Méthode | Idéal pour | Niveau d'automatisation | Avantages | Limites |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Convertisseur en ligne | Tâches ponctuelles | Aucun | Rapide et facile | Risques de confidentialité, précision limitée |
| Logiciel de bureau | Petites charges de travail | Faible | Contrôle visuel | Chronophage, non évolutif |
| Automatisation Python | Grands flux de travail | Élevé | Flexible, reproductible | Nécessite une programmation |
Comment choisir la bonne méthode
- Utilisez des convertisseurs en ligne lorsque la vitesse est importante et que les fichiers ne sont pas sensibles.
- Choisissez un logiciel de bureau si vous préférez un contrôle manuel pour un petit nombre de documents.
- Optez pour l'automatisation Python lorsque vous traitez de grands ensembles de données ou que vous créez des flux de travail reproductibles.
Pour les processus continus ou critiques pour l'entreprise, les solutions automatisées offrent généralement une plus grande efficacité et cohérence à long terme.
FAQ : Conversion de DOCX en XLSX
Puis-je convertir n'importe quel document Word en Excel ?
La plupart des fichiers Word peuvent être convertis, mais les documents avec des tableaux ou des données structurées fonctionnent mieux. Le texte de forme libre et les mises en page complexes peuvent nécessiter un ajustement après la conversion.
Le formatage restera-t-il le même après la conversion ?
Pas toujours. Word et Excel gèrent les mises en page différemment, de sorte que certains espacements, cellules fusionnées ou flux de texte peuvent changer. Des ajustements mineurs dans Excel sont généralement nécessaires.
Puis-je convertir uniquement des tableaux de Word vers Excel ?
Oui. Si votre document Word contient des tableaux, vous pouvez extraire uniquement les tableaux pour une conversion plus précise et fiable.
Quelle est la manière la plus simple de convertir plusieurs fichiers DOCX ?
Pour plusieurs fichiers, les solutions automatisées ou les outils par lots, comme les bibliothèques Python, peuvent faire gagner du temps et garantir des résultats cohérents, en particulier pour les documents volumineux.
Conclusion
La conversion de DOCX en XLSX n'est pas une tâche universelle. Bien que les outils en ligne et de bureau soient utiles pour des scénarios simples, ils sont souvent insuffisants lorsque la précision, l'évolutivité ou l'automatisation sont requises.
En comprenant la structure de vos documents Word et en choisissant la bonne approche de conversion, vous pouvez obtenir des résultats fiables. Pour les développeurs et les utilisateurs avancés, Python offre un moyen puissant et flexible de convertir efficacement les tableaux Word en feuilles de calcul Excel.
Voir aussi
Cómo convertir DOCX a XLSX: Convierta fácilmente Word a Excel
Tabla de Contenidos

Convertir un documento de Word (DOCX) a una hoja de cálculo de Excel (XLSX) es un requisito común en la automatización de oficinas, el procesamiento de datos y los flujos de trabajo de informes. Muchos usuarios quieren reutilizar tablas almacenadas en archivos de Word, mientras que otros esperan una conversión directa de documento a hoja de cálculo con un esfuerzo mínimo.
Sin embargo, Word y Excel están diseñados para propósitos muy diferentes. Word se centra en el diseño de documentos de formato libre, mientras que Excel se basa en datos estructurados y tabulares. Comprender esta diferencia es clave para elegir el método de conversión de DOCX a XLSX adecuado.
En esta guía, aprenderá cómo convertir DOCX a XLSX utilizando herramientas en línea, soluciones de escritorio y automatización con Python, junto con las ventajas y limitaciones de cada enfoque.
Navegación Rápida
- ¿Puedes Realmente Convertir un Archivo de Word (DOCX) a Excel (XLSX)?
- Método 1: Convertir DOCX a XLSX en Línea
- Método 2: Convertir Contenido de Word a Excel Usando Software de Escritorio
- Método 3: Convertir DOCX a XLSX con Python
- Comparar Métodos de Conversión de DOCX a XLSX
- Preguntas Frecuentes
¿Puedes Realmente Convertir un Archivo de Word (DOCX) a Excel (XLSX)?
Antes de elegir un método de conversión, es importante aclarar qué significa realmente “conversión de DOCX a XLSX”.
- Los documentos de Word pueden contener párrafos, imágenes, encabezados y tablas.
- Los archivos de Excel están optimizados para filas, columnas y datos estructurados.
En la práctica, la conversión de DOCX a XLSX funciona mejor cuando el documento de Word contiene tablas. Los párrafos de texto sin formato y los diseños complejos no siempre se traducen limpiamente en celdas de hoja de cálculo.
Si su objetivo es extraer datos tabulares de Word y reutilizarlos en Excel, la conversión suele ser fiable. Si espera que un documento de Word completo aparezca perfectamente en Excel, debe esperar alguna pérdida de formato. Sin embargo, aún puede insertar párrafos de texto e imágenes de Word en Excel.
Método 1: Convertir DOCX a XLSX en Línea
Las herramientas en línea suelen ser la primera opción para los usuarios que necesitan una conversión rápida y única. Por ejemplo, puede utilizar el convertidor de DOCX a XLSX de Online2PDF para convertir documentos directamente en su navegador sin instalar software adicional.
Un flujo de trabajo típico se ve así:
-
Abra el convertidor de DOCX a XLSX en línea.

-
Suba su archivo de Word (DOCX).
-
Inicie el proceso de conversión.
-
Descargue el archivo de Excel (XLSX) convertido.

Muchos convertidores en línea admiten la conversión de DOCX a XLSX, lo que facilita la transformación de documentos de Word en hojas de cálculo editables en segundos.
Ventajas y Desventajas de los Convertidores de DOCX a XLSX en Línea
Ventajas
- No se requiere instalación de software
- Fácil de usar para principiantes
- Adecuado para archivos pequeños y tareas ocasionales
Limitaciones
- Límites de tamaño de archivo y uso
- Posibles preocupaciones sobre la privacidad y la seguridad de los datos
- Control limitado sobre el formato
- No apto para procesamiento por lotes o automatizado
Los convertidores en línea son convenientes, pero son más adecuados para archivos simples y no sensibles.
Muchas herramientas en línea admiten la conversión de archivos de Word a múltiples formatos. Por ejemplo, también puede explorar cómo convertir Word a PowerPoint al preparar materiales de presentación.
Método 2: Convertir Contenido de Word a Excel Usando Software de Escritorio
Para documentos que contienen datos estructurados o semiestructurados, el software de ofimática de escritorio ofrece una forma práctica de mover contenido de Word a Excel con un alto nivel de control visual. Las herramientas comunes incluyen Microsoft Office y LibreOffice, que permiten a los usuarios copiar contenido de Word y pegarlo directamente en hojas de cálculo de Excel.
Si bien este software de escritorio no proporciona una función nativa de “exportación de DOCX a XLSX”, aún puede producir resultados fiables, especialmente cuando los documentos de Word contienen tablas.
Por Qué las Tablas se Convierten con Mayor Precisión
La mayoría de las conversiones exitosas de DOCX a XLSX se basan en contenido basado en tablas. Las tablas en Word ya definen filas y columnas, que se alinean estrechamente con el modelo de datos basado en cuadrícula de Excel. Cuando se pegan en Excel, las tablas de Word suelen conservar su estructura, alineación y límites de celda con un ajuste mínimo.
También se puede transferir contenido no tabular. Los párrafos, encabezados y listas se pueden pegar en celdas de Excel, donde cada línea se coloca en filas individuales. Aunque puede ser necesario un formato adicional, este enfoque suele ser suficiente para organizar el contenido del documento en un formato de hoja de cálculo.
Ejemplo: Copiar Contenido de Word a Excel Usando Microsoft Office
A continuación se muestra un flujo de trabajo típico usando Microsoft Office:
-
Abra el archivo DOCX en Microsoft Word.

-
Seleccione el contenido que desea transferir:
- Solo tablas, para una mejor precisión estructural
- O el documento completo, si es necesario
-
Copie la selección (Ctrl + C).
-
Abra Microsoft Excel y seleccione la hoja de trabajo de destino.
-
Pegue el contenido (Ctrl + V) en Excel.

-
Ajuste el ancho de las columnas, la alineación de las celdas o el ajuste del texto según sea necesario.
Este método funciona particularmente bien para documentos de Word que contienen principalmente tablas, formularios o diseños estructurados. Si su documento contiene tablas complejas, puede beneficiarse de aprender cómo extraer tablas de Word mediante programación para una mayor precisión y control.
Limitaciones de la Conversión Basada en Escritorio
Aunque las herramientas de escritorio brindan flexibilidad y control visual, tienen varias limitaciones:
- Sin exportación real de DOCX a XLSX ni conversión por lotes
- Se requieren pasos manuales para cada documento
- La consistencia del formato puede ser difícil de mantener entre archivos
Cuando se trata de múltiples documentos o tareas de conversión recurrentes, los flujos de trabajo manuales de escritorio pueden volverse rápidamente lentos. En tales casos, las soluciones automatizadas o programáticas suelen ser más eficientes.
Método 3: Convertir DOCX a XLSX con Python (Ideal para Flujos de Trabajo Automatizados)
Cuando los métodos manuales se vuelven ineficientes, Python ofrece una forma escalable de convertir documentos de Word en archivos de Excel. Este enfoque es particularmente valioso para los desarrolladores que necesitan resultados consistentes y repetibles sin depender de aplicaciones de escritorio.
La conversión basada en Python es muy adecuada para:
- Procesamiento por lotes de grandes cantidades de archivos DOCX
- Canalizaciones de datos automatizadas
- Flujos de trabajo de documentos del lado del servidor
- Entornos donde Microsoft Office no está disponible
En comparación con las exportaciones manuales, la creación de scripts proporciona una mayor flexibilidad y reduce significativamente el trabajo repetitivo.
Cómo Python Convierte Datos de Word a Excel
Una estrategia práctica es extraer datos estructurados de Word, especialmente tablas, y escribirlos directamente en un libro de trabajo de Excel. Debido a que las tablas ya organizan el contenido en filas y columnas, se traducen naturalmente al formato de hoja de cálculo conservando la estructura lógica.
En este ejemplo:
- Spire.Doc for Python carga el archivo DOCX y recupera los datos de la tabla.
- Spire.XLS for Python crea el libro de trabajo de Excel y escribe el contenido extraído en las hojas de trabajo.
La combinación de estas bibliotecas permite un proceso de conversión controlado y programático adecuado para entornos de producción.
Antes de usar las bibliotecas en su proyecto, asegúrese de haber instalado los paquetes necesarios. Puede instalarlos a través de pip:
Paso a Paso: Convertir Tablas de Word a Excel con Python
A continuación se muestra un flujo de trabajo típico para convertir tablas de DOCX a XLSX usando Python:
-
Cargar el archivo DOCX Use Spire.Doc for Python para abrir el documento de Word.
-
Extraer tablas del documento Iterar a través de la estructura del documento y recuperar los datos de la tabla.
-
Crear un libro de trabajo de Excel Inicialice un nuevo libro de trabajo usando Spire.XLS for Python.
-
Escribir datos de la tabla en hojas de trabajo Asigne filas y celdas de las tablas de Word a filas y columnas de Excel.
-
Guardar el archivo como XLSX Exporte el resultado final como una hoja de cálculo de Excel.
Código Python: Convertir Tablas de DOCX a XLSX
El siguiente ejemplo demuestra cómo extraer tablas de un documento de Word y exportarlas a una hoja de cálculo de Excel.
from spire.doc import Document
from spire.xls import Workbook, Color
# Load the Word document
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Create a new Excel workbook
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.Worksheets.Clear()
# Iterate through all sections in the Word document
for sec_index in range(len(doc.Sections)):
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(sec_index)
# Iterate through all tables in the current section
for table_index in range(len(section.Tables)):
table = section.Tables.get_Item(table_index)
# Create a worksheet for each Word table
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add(f"Table-{table_index + 1}")
# Iterate through rows in the Word table
for row_index in range(len(table.Rows)):
row = table.Rows.get_Item(row_index)
# Iterate through cells in the current row
for cell_index in range(len(row.Cells)):
table_cell = row.Cells.get_Item(cell_index)
# Collect all paragraph text inside the Word table cell
cell_data = ""
for para_index in range(len(table_cell.Paragraphs)):
para = table_cell.Paragraphs.get_Item(para_index)
cell_data += para.Text + "\n"
# Write text to the corresponding Excel cell
cell = sheet.Range.get_Item(row_index + 1, cell_index + 1)
cell.Value = cell_data
# Copy the Word table cell background color to Excel
# Note: Color must be assigned directly to the Style to take effect
table_cell_color = table_cell.CellFormat.BackColor
cell.Style.Color = Color.FromRgb(
table_cell_color.R,
table_cell_color.G,
table_cell_color.B
)
# Auto-fit columns after writing the table
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns()
# Save the Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("WordTableToExcel.xlsx")
A continuación se muestra una vista previa del archivo XLSX convertido desde el documento de Word:

Este enfoque es especialmente útil para documentos estructurados, informes y archivos de Word basados en formularios donde las tablas representan los datos principales.
Para técnicas más avanzadas de Python, incluida la preservación del formato y los estilos de las tablas durante la conversión de Word a Excel, consulte nuestra guía detallada sobre cómo convertir tablas de Word a Excel con Python.
Comparar Métodos de Conversión de DOCX a XLSX
Elegir el método correcto depende de factores como el volumen de documentos, las necesidades de automatización y la sensibilidad de los datos. La siguiente tabla proporciona una descripción general rápida para ayudarlo a evaluar cada opción.
| Método | Mejor Para | Nivel de Automatización | Ventajas | Limitaciones |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Convertidor en Línea | Tareas únicas | Ninguno | Rápido y fácil | Riesgos de privacidad, precisión limitada |
| Software de Escritorio | Cargas de trabajo pequeñas | Bajo | Control visual | Consume mucho tiempo, no es escalable |
| Automatización con Python | Grandes flujos de trabajo | Alto | Flexible, repetible | Requiere programación |
Cómo Elegir el Método Correcto
- Use convertidores en línea cuando la velocidad importa y los archivos no son sensibles.
- Elija software de escritorio si prefiere el control manual para una pequeña cantidad de documentos.
- Opte por la automatización con Python cuando maneje grandes conjuntos de datos o cree flujos de trabajo repetibles.
Para procesos continuos o críticos para el negocio, las soluciones automatizadas suelen proporcionar una mayor eficiencia y consistencia a largo plazo.
Preguntas Frecuentes: Conversión de DOCX a XLSX
¿Puedo convertir cualquier documento de Word a Excel?
La mayoría de los archivos de Word se pueden convertir, pero los documentos con tablas o datos estructurados funcionan mejor. El texto de formato libre y los diseños complejos pueden necesitar ajustes después de la conversión.
¿El formato se mantendrá igual después de la conversión?
No siempre. Word y Excel manejan los diseños de manera diferente, por lo que algunos espaciados, celdas combinadas o flujo de texto pueden cambiar. Generalmente se necesitan ajustes menores en Excel.
¿Puedo convertir solo tablas de Word a Excel?
Sí. Si su documento de Word contiene tablas, puede extraer solo las tablas para una conversión más precisa y fiable.
¿Cuál es la forma más fácil de convertir múltiples archivos DOCX?
Para múltiples archivos, las soluciones automatizadas o las herramientas por lotes, como las bibliotecas de Python, pueden ahorrar tiempo y garantizar resultados consistentes, especialmente para documentos grandes.
Conclusión
Convertir DOCX a XLSX no es una tarea única para todos. Si bien las herramientas en línea y de escritorio son útiles para escenarios simples, a menudo se quedan cortas cuando se requiere precisión, escalabilidad o automatización.
Al comprender la estructura de sus documentos de Word y elegir el enfoque de conversión correcto, puede lograr resultados fiables. Para desarrolladores y usuarios avanzados, Python ofrece una forma potente y flexible de convertir tablas de Word en hojas de cálculo de Excel de manera eficiente.
Ver También
So konvertieren Sie DOCX in XLSX: Verwandeln Sie Word einfach in Excel
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- Können Sie wirklich eine Word (DOCX)-Datei in Excel (XLSX) konvertieren?
- Methode 1: DOCX in XLSX online konvertieren
- Methode 2: Word-Inhalte mit Desktop-Software in Excel konvertieren
- Methode 3: DOCX mit Python in XLSX konvertieren
- Vergleich der DOCX-zu-XLSX-Konvertierungsmethoden
- Häufig gestellte Fragen

Die Konvertierung eines Word-Dokuments (DOCX) in eine Excel-Tabelle (XLSX) ist eine häufige Anforderung in der Büroautomatisierung, Datenverarbeitung und bei Berichtsworkflows. Viele Benutzer möchten in Word-Dateien gespeicherte Tabellen wiederverwenden, während andere eine direkte Konvertierung von Dokument zu Tabelle mit minimalem Aufwand erwarten.
Allerdings sind Word und Excel für sehr unterschiedliche Zwecke konzipiert. Word konzentriert sich auf das freie Dokumentenlayout, während Excel auf strukturierten, tabellarischen Daten basiert. Das Verständnis dieses Unterschieds ist entscheidend für die Wahl der richtigen Konvertierungsmethode von DOCX zu XLSX.
In dieser Anleitung erfahren Sie, wie Sie DOCX mit Online-Tools, Desktop-Lösungen und Python-Automatisierung in XLSX konvertieren, sowie die Vorteile und Einschränkungen jedes Ansatzes.
Schnellnavigation
- Können Sie wirklich eine Word (DOCX)-Datei in Excel (XLSX) konvertieren?
- Methode 1: DOCX in XLSX online konvertieren
- Methode 2: Word-Inhalte mit Desktop-Software in Excel konvertieren
- Methode 3: DOCX mit Python in XLSX konvertieren
- Vergleich der DOCX-zu-XLSX-Konvertierungsmethoden
- Häufig gestellte Fragen
Können Sie wirklich eine Word (DOCX)-Datei in Excel (XLSX) konvertieren?
Bevor Sie eine Konvertierungsmethode wählen, ist es wichtig zu klären, was „DOCX-zu-XLSX-Konvertierung“ eigentlich bedeutet.
- Word-Dokumente können Absätze, Bilder, Überschriften und Tabellen enthalten.
- Excel-Dateien sind für Zeilen, Spalten und strukturierte Daten optimiert.
In der Praxis funktioniert die Konvertierung von DOCX zu XLSX am besten, wenn das Word-Dokument Tabellen enthält. Reine Textabsätze und komplexe Layouts lassen sich nicht immer sauber in Tabellenzellen übertragen.
Wenn Ihr Ziel darin besteht, tabellarische Daten aus Word zu extrahieren und in Excel wiederzuverwenden, ist die Konvertierung in der Regel zuverlässig. Wenn Sie erwarten, dass ein ganzes Word-Dokument perfekt in Excel erscheint, müssen Sie mit einem gewissen Formatierungsverlust rechnen. Sie können jedoch weiterhin Text- und Bildabsätze aus Word in Excel einfügen.
Methode 1: DOCX in XLSX online konvertieren
Online-Tools sind oft die erste Wahl für Benutzer, die eine schnelle, einmalige Konvertierung benötigen. Sie können beispielsweise den Online2PDF DOCX to XLSX Konverter verwenden, um Dokumente direkt in Ihrem Browser zu konvertieren, ohne zusätzliche Software zu installieren.
Ein typischer Arbeitsablauf sieht so aus:
-
Öffnen Sie den Online-Konverter von DOCX zu XLSX.

-
Laden Sie Ihre Word (DOCX)-Datei hoch.
-
Starten Sie den Konvertierungsprozess.
-
Laden Sie die konvertierte Excel (XLSX)-Datei herunter.

Viele Online-Konverter unterstützen die Konvertierung von DOCX zu XLSX, sodass Word-Dokumente in Sekundenschnelle in bearbeitbare Tabellen umgewandelt werden können.
Vor- und Nachteile von Online-DOCX-zu-XLSX-Konvertern
Vorteile
- Keine Softwareinstallation erforderlich
- Einfach für Anfänger zu bedienen
- Geeignet für kleine Dateien und gelegentliche Aufgaben
Einschränkungen
- Dateigrößen- und Nutzungsbeschränkungen
- Mögliche Bedenken hinsichtlich Datenschutz und Datensicherheit
- Begrenzte Kontrolle über die Formatierung
- Nicht für die Stapel- oder automatisierte Verarbeitung geeignet
Online-Konverter sind praktisch, eignen sich aber am besten für einfache, nicht sensible Dateien.
Viele Online-Tools unterstützen die Konvertierung von Word-Dateien in mehrere Formate. Sie können zum Beispiel auch untersuchen, wie man Word in PowerPoint konvertiert, wenn Sie Präsentationsmaterialien vorbereiten.
Methode 2: Word-Inhalte mit Desktop-Software in Excel konvertieren
Für Dokumente, die strukturierte oder halbstrukturierte Daten enthalten, bietet Desktop-Office-Software eine praktische Möglichkeit, Inhalte von Word nach Excel zu verschieben, mit einem hohen Maß an visueller Kontrolle. Gängige Tools sind Microsoft Office und LibreOffice, mit denen Benutzer Word-Inhalte kopieren und direkt in Excel-Tabellen einfügen können.
Obwohl diese Desktop-Software keine native „DOCX-zu-XLSX-Export“-Funktion bietet, kann sie dennoch zuverlässige Ergebnisse liefern – insbesondere wenn Word-Dokumente Tabellen enthalten.
Warum Tabellen genauer konvertiert werden
Die meisten erfolgreichen Konvertierungen von DOCX zu XLSX basieren auf tabellenbasierten Inhalten. Tabellen in Word definieren bereits Zeilen und Spalten, die eng mit dem gitterbasierten Datenmodell von Excel übereinstimmen. Wenn sie in Excel eingefügt werden, behalten Word-Tabellen in der Regel ihre Struktur, Ausrichtung und Zellgrenzen mit minimalen Anpassungen bei.
Auch nicht-tabellarische Inhalte können übertragen werden. Absätze, Überschriften und Listen können in Excel-Zellen eingefügt werden, wobei jede Zeile in einzelne Zeilen platziert wird. Obwohl möglicherweise zusätzliche Formatierungen erforderlich sind, ist dieser Ansatz oft ausreichend, um Dokumenteninhalte in einem Tabellenformat zu organisieren.
Beispiel: Kopieren von Word-Inhalten nach Excel mit Microsoft Office
Unten finden Sie einen typischen Arbeitsablauf mit Microsoft Office:
-
Öffnen Sie die DOCX-Datei in Microsoft Word.

-
Wählen Sie den Inhalt aus, den Sie übertragen möchten:
- Nur Tabellen, für beste strukturelle Genauigkeit
- Oder das gesamte Dokument, falls erforderlich
-
Kopieren Sie die Auswahl (Strg + C).
-
Öffnen Sie Microsoft Excel und wählen Sie das Zielarbeitsblatt aus.
-
Fügen Sie den Inhalt (Strg + V) in Excel ein.

-
Passen Sie bei Bedarf Spaltenbreiten, Zellausrichtung oder Textumbruch an.
Diese Methode eignet sich besonders gut für Word-Dokumente, die hauptsächlich Tabellen, Formulare oder strukturierte Layouts enthalten. Wenn Ihr Dokument komplexe Tabellen enthält, können Sie davon profitieren, zu lernen, wie man Tabellen programmgesteuert aus Word extrahiert, um eine größere Genauigkeit und Kontrolle zu erzielen.
Einschränkungen der Desktop-basierten Konvertierung
Obwohl Desktop-Tools Flexibilität und visuelle Kontrolle bieten, haben sie mehrere Einschränkungen:
- Kein echter DOCX-zu-XLSX-Export oder Stapelkonvertierung
- Für jedes Dokument sind manuelle Schritte erforderlich
- Die Formatierungskonsistenz kann über Dateien hinweg schwer aufrechtzuerhalten sein
Bei der Bearbeitung mehrerer Dokumente oder wiederkehrender Konvertierungsaufgaben können manuelle Desktop-Workflows schnell zeitaufwändig werden. In solchen Fällen sind automatisierte oder programmgesteuerte Lösungen in der Regel effizienter.
Methode 3: DOCX mit Python in XLSX konvertieren (Ideal für automatisierte Arbeitsabläufe)
Wenn manuelle Methoden ineffizient werden, bietet Python eine skalierbare Möglichkeit, Word-Dokumente in Excel-Dateien zu konvertieren. Dieser Ansatz ist besonders wertvoll für Entwickler, die konsistente, wiederholbare Ergebnisse benötigen, ohne auf Desktop-Anwendungen angewiesen zu sein.
Die Python-basierte Konvertierung eignet sich gut für:
- Stapelverarbeitung großer Mengen von DOCX-Dateien
- Automatisierte Datenpipelines
- Serverseitige Dokumenten-Workflows
- Umgebungen, in denen Microsoft Office nicht verfügbar ist
Im Vergleich zu manuellen Exporten bietet das Skripting eine größere Flexibilität und reduziert sich wiederholende Arbeiten erheblich.
Wie Python Word-Daten in Excel konvertiert
Eine praktische Strategie besteht darin, strukturierte Daten aus Word – insbesondere Tabellen – zu extrahieren und direkt in eine Excel-Arbeitsmappe zu schreiben. Da Tabellen Inhalte bereits in Zeilen und Spalten organisieren, lassen sie sich auf natürliche Weise in ein Tabellenformat übersetzen, während die logische Struktur erhalten bleibt.
In diesem Beispiel:
- Spire.Doc for Python lädt die DOCX-Datei und ruft Tabellendaten ab.
- Spire.XLS for Python erstellt die Excel-Arbeitsmappe und schreibt den extrahierten Inhalt in Arbeitsblätter.
Die Kombination dieser Bibliotheken ermöglicht einen kontrollierten, programmgesteuerten Konvertierungsprozess, der für Produktionsumgebungen geeignet ist.
Bevor Sie die Bibliotheken in Ihrem Projekt verwenden, stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie die erforderlichen Pakete installiert haben. Sie können sie über pip installieren:
Schritt-für-Schritt: Word-Tabellen mit Python in Excel konvertieren
Unten finden Sie einen typischen Arbeitsablauf für die Konvertierung von DOCX-Tabellen in XLSX mit Python:
-
Laden Sie die DOCX-Datei Verwenden Sie Spire.Doc for Python, um das Word-Dokument zu öffnen.
-
Extrahieren Sie Tabellen aus dem Dokument Iterieren Sie durch die Dokumentstruktur und rufen Sie Tabellendaten ab.
-
Erstellen Sie eine Excel-Arbeitsmappe Initialisieren Sie eine neue Arbeitsmappe mit Spire.XLS for Python.
-
Schreiben Sie Tabellendaten in Arbeitsblätter Ordnen Sie Zeilen und Zellen aus Word-Tabellen Excel-Zeilen und -Spalten zu.
-
Speichern Sie die Datei als XLSX Exportieren Sie das Endergebnis als Excel-Tabelle.
Python-Code: DOCX-Tabellen in XLSX konvertieren
Das folgende Beispiel zeigt, wie Tabellen aus einem Word-Dokument extrahiert und in ein Excel-Arbeitsblatt exportiert werden.
from spire.doc import Document
from spire.xls import Workbook, Color
# Load the Word document
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Create a new Excel workbook
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.Worksheets.Clear()
# Iterate through all sections in the Word document
for sec_index in range(len(doc.Sections)):
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(sec_index)
# Iterate through all tables in the current section
for table_index in range(len(section.Tables)):
table = section.Tables.get_Item(table_index)
# Create a worksheet for each Word table
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add(f"Table-{table_index + 1}")
# Iterate through rows in the Word table
for row_index in range(len(table.Rows)):
row = table.Rows.get_Item(row_index)
# Iterate through cells in the current row
for cell_index in range(len(row.Cells)):
table_cell = row.Cells.get_Item(cell_index)
# Collect all paragraph text inside the Word table cell
cell_data = ""
for para_index in range(len(table_cell.Paragraphs)):
para = table_cell.Paragraphs.get_Item(para_index)
cell_data += para.Text + "\n"
# Write text to the corresponding Excel cell
cell = sheet.Range.get_Item(row_index + 1, cell_index + 1)
cell.Value = cell_data
# Copy the Word table cell background color to Excel
# Note: Color must be assigned directly to the Style to take effect
table_cell_color = table_cell.CellFormat.BackColor
cell.Style.Color = Color.FromRgb(
table_cell_color.R,
table_cell_color.G,
table_cell_color.B
)
# Auto-fit columns after writing the table
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns()
# Save the Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("WordTableToExcel.xlsx")
Unten sehen Sie eine Vorschau der aus dem Word-Dokument konvertierten XLSX-Datei:

Dieser Ansatz ist besonders nützlich für strukturierte Dokumente, Berichte und formularbasierte Word-Dateien, bei denen Tabellen die Kerndaten darstellen.
Für fortgeschrittenere Python-Techniken, einschließlich der Beibehaltung von Tabellenformatierungen und -stilen während der Konvertierung von Word nach Excel, lesen Sie unsere detaillierte Anleitung zum Konvertieren von Word-Tabellen in Excel mit Python.
Vergleich der DOCX-zu-XLSX-Konvertierungsmethoden
Die Wahl der richtigen Methode hängt von Faktoren wie Dokumentenvolumen, Automatisierungsbedarf und Datensensibilität ab. Die folgende Tabelle bietet einen schnellen Überblick, um Ihnen bei der Bewertung jeder Option zu helfen.
| Methode | Am besten für | Automatisierungsgrad | Vorteile | Einschränkungen |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Online-Konverter | Einmalige Aufgaben | Keine | Schnell und einfach | Datenschutzrisiken, begrenzte Genauigkeit |
| Desktop-Software | Kleine Arbeitslasten | Niedrig | Visuelle Kontrolle | Zeitaufwändig, nicht skalierbar |
| Python-Automatisierung | Große Arbeitsabläufe | Hoch | Flexibel, wiederholbar | Erfordert Programmierung |
So wählen Sie die richtige Methode
- Verwenden Sie Online-Konverter, wenn es auf Geschwindigkeit ankommt und die Dateien nicht sensibel sind.
- Wählen Sie Desktop-Software, wenn Sie die manuelle Kontrolle für eine kleine Anzahl von Dokumenten bevorzugen.
- Entscheiden Sie sich für die Python-Automatisierung, wenn Sie große Datenmengen verarbeiten oder wiederholbare Arbeitsabläufe erstellen.
Für laufende oder geschäftskritische Prozesse bieten automatisierte Lösungen in der Regel eine höhere langfristige Effizienz und Konsistenz.
FAQ: DOCX-zu-XLSX-Konvertierung
Kann ich jedes Word-Dokument in Excel konvertieren?
Die meisten Word-Dateien können konvertiert werden, aber Dokumente mit Tabellen oder strukturierten Daten funktionieren am besten. Freitext und komplexe Layouts müssen nach der Konvertierung möglicherweise angepasst werden.
Bleibt die Formatierung nach der Konvertierung erhalten?
Nicht immer. Word und Excel behandeln Layouts unterschiedlich, sodass sich einige Abstände, verbundene Zellen oder der Textfluss ändern können. Kleinere Anpassungen in Excel sind in der Regel erforderlich.
Kann ich nur Tabellen von Word nach Excel konvertieren?
Ja. Wenn Ihr Word-Dokument Tabellen enthält, können Sie nur die Tabellen für eine genauere und zuverlässigere Konvertierung extrahieren.
Was ist der einfachste Weg, mehrere DOCX-Dateien zu konvertieren?
Für mehrere Dateien können automatisierte Lösungen oder Stapelverarbeitungstools – wie Python-Bibliotheken – Zeit sparen und konsistente Ergebnisse gewährleisten, insbesondere bei großen Dokumenten.
Fazit
Die Konvertierung von DOCX in XLSX ist keine Einheitsaufgabe. Während Online- und Desktop-Tools für einfache Szenarien nützlich sind, reichen sie oft nicht aus, wenn Genauigkeit, Skalierbarkeit oder Automatisierung erforderlich sind.
Indem Sie die Struktur Ihrer Word-Dokumente verstehen und den richtigen Konvertierungsansatz wählen, können Sie zuverlässige Ergebnisse erzielen. Für Entwickler und fortgeschrittene Benutzer bietet Python eine leistungsstarke und flexible Möglichkeit, Word-Tabellen effizient in Excel-Tabellen zu konvertieren.
Siehe auch
Как конвертировать DOCX в XLSX: Легко преобразуйте Word в Excel
Содержание
- Действительно ли можно преобразовать файл Word (DOCX) в Excel (XLSX)?
- Метод 1: Конвертировать DOCX в XLSX онлайн
- Метод 2: Конвертировать содержимое Word в Excel с помощью настольного программного обеспечения
- Метод 3: Конвертировать DOCX в XLSX с помощью Python
- Сравнение методов конвертации DOCX в XLSX
- Часто задаваемые вопросы

Преобразование документа Word (DOCX) в электронную таблицу Excel (XLSX) — это обычное требование в рабочих процессах автоматизации офиса, обработки данных и создания отчетов. Многие пользователи хотят повторно использовать таблицы, хранящиеся в файлах Word, в то время как другие ожидают прямого преобразования документа в электронную таблицу с минимальными усилиями.
Однако Word и Excel предназначены для совершенно разных целей. Word ориентирован на свободный макет документа, в то время как Excel построен на основе структурированных табличных данных. Понимание этой разницы является ключом к выбору правильного метода преобразования DOCX в XLSX.
В этом руководстве вы узнаете, как конвертировать DOCX в XLSX с помощью онлайн-инструментов, настольных решений и автоматизации на Python, а также о преимуществах и ограничениях каждого подхода.
Быстрая навигация
- Действительно ли можно преобразовать файл Word (DOCX) в Excel (XLSX)?
- Метод 1: Конвертировать DOCX в XLSX онлайн
- Метод 2: Конвертировать содержимое Word в Excel с помощью настольного программного обеспечения
- Метод 3: Конвертировать DOCX в XLSX с помощью Python
- Сравнение методов конвертации DOCX в XLSX
- Часто задаваемые вопросы
Действительно ли можно преобразовать файл Word (DOCX) в Excel (XLSX)?
Прежде чем выбрать метод преобразования, важно уточнить, что на самом деле означает «преобразование DOCX в XLSX».
- Документы Word могут содержать абзацы, изображения, заголовки и таблицы.
- Файлы Excel оптимизированы для строк, столбцов и структурированных данных.
На практике преобразование DOCX в XLSX работает лучше всего, когда документ Word содержит таблицы. Простые текстовые абзацы и сложные макеты не всегда чисто преобразуются в ячейки электронной таблицы.
Если ваша цель — извлечь табличные данные из Word и повторно использовать их в Excel, преобразование обычно надежно. Если вы ожидаете, что весь документ Word будет идеально отображаться в Excel, следует ожидать некоторой потери форматирования. Однако вы все равно можете вставлять текстовые и графические абзацы Word в Excel.
Метод 1: Конвертировать DOCX в XLSX онлайн
Онлайн-инструменты часто являются первым выбором для пользователей, которым требуется быстрое одноразовое преобразование. Например, вы можете использовать конвертер Online2PDF DOCX в XLSX для преобразования документов прямо в браузере без установки дополнительного программного обеспечения.
Типичный рабочий процесс выглядит так:
-
Откройте онлайн-конвертер DOCX в XLSX.

-
Загрузите ваш файл Word (DOCX).
-
Начните процесс конвертации.
-
Скачайте сконвертированный файл Excel (XLSX).

Многие онлайн-конвертеры поддерживают преобразование DOCX в XLSX, что позволяет легко превращать документы Word в редактируемые электронные таблицы за считанные секунды.
Плюсы и минусы онлайн-конвертеров DOCX в XLSX
Преимущества
- Не требуется установка программного обеспечения
- Простота в использовании для новичков
- Подходит для небольших файлов и редких задач
Ограничения
- Ограничения на размер файла и использование
- Потенциальные проблемы с конфиденциальностью и безопасностью данных
- Ограниченный контроль над форматированием
- Не подходит для пакетной или автоматизированной обработки
Онлайн-конвертеры удобны, но они лучше всего подходят для простых, неконфиденциальных файлов.
Многие онлайн-инструменты поддерживают преобразование файлов Word в несколько форматов. Например, вы также можете изучить как конвертировать Word в PowerPoint при подготовке презентационных материалов.
Метод 2: Конвертировать содержимое Word в Excel с помощью настольного программного обеспечения
Для документов, содержащих структурированные или полуструктурированные данные, настольное офисное программное обеспечение предлагает практичный способ перемещения содержимого из Word в Excel с высоким уровнем визуального контроля. Распространенные инструменты включают Microsoft Office и LibreOffice, которые позволяют пользователям копировать содержимое Word и вставлять его непосредственно в электронные таблицы Excel.
Хотя это настольное программное обеспечение не предоставляет встроенной функции «экспорта DOCX в XLSX», оно все же может давать надежные результаты, особенно когда документы Word содержат таблицы.
Почему таблицы конвертируются точнее
Большинство успешных преобразований DOCX в XLSX основаны на содержимом в виде таблиц. Таблицы в Word уже определяют строки и столбцы, что тесно совпадает с сеточной моделью данных Excel. При вставке в Excel таблицы Word обычно сохраняют свою структуру, выравнивание и границы ячеек с минимальной корректировкой.
Нетабличное содержимое также можно переносить. Абзацы, заголовки и списки можно вставлять в ячейки Excel, где каждая строка помещается в отдельные строки. Хотя может потребоваться дополнительное форматирование, этот подход часто достаточен для организации содержимого документа в формате электронной таблицы.
Пример: Копирование содержимого Word в Excel с помощью Microsoft Office
Ниже приведен типичный рабочий процесс с использованием Microsoft Office:
-
Откройте файл DOCX в Microsoft Word.

-
Выберите содержимое, которое хотите перенести:
- Только таблицы, для лучшей структурной точности
- Или весь документ, если необходимо
-
Скопируйте выделенное (Ctrl + C).
-
Откройте Microsoft Excel и выберите целевой лист.
-
Вставьте содержимое (Ctrl + V) в Excel.

-
При необходимости отрегулируйте ширину столбцов, выравнивание ячеек или перенос текста.
Этот метод особенно хорошо работает для документов Word, которые в основном содержат таблицы, формы или структурированные макеты. Если ваш документ содержит сложные таблицы, вам может быть полезно узнать, как извлекать таблицы из Word программно для большей точности и контроля.
Ограничения конвертации с помощью настольных приложений
Хотя настольные инструменты обеспечивают гибкость и визуальный контроль, у них есть несколько ограничений:
- Нет настоящего экспорта DOCX в XLSX или пакетного преобразования
- Для каждого документа требуются ручные действия
- Согласованность форматирования может быть трудно поддерживать между файлами
При работе с несколькими документами или повторяющимися задачами преобразования ручные рабочие процессы на настольных компьютерах могут быстро стать трудоемкими. В таких случаях автоматизированные или программные решения обычно более эффективны.
Метод 3: Конвертировать DOCX в XLSX с помощью Python (идеально для автоматизированных рабочих процессов)
Когда ручные методы становятся неэффективными, Python предлагает масштабируемый способ преобразования документов Word в файлы Excel. Этот подход особенно ценен для разработчиков, которым нужны последовательные, повторяемые результаты без использования настольных приложений.
Преобразование на основе Python хорошо подходит для:
- Пакетная обработка большого количества файлов DOCX
- Автоматизированные конвейеры данных
- Серверные рабочие процессы с документами
- Среды, в которых Microsoft Office недоступен
По сравнению с ручным экспортом, написание сценариев обеспечивает большую гибкость и значительно сокращает повторяющуюся работу.
Как Python конвертирует данные Word в Excel
Практическая стратегия заключается в извлечении структурированных данных из Word — особенно таблиц — и записи их непосредственно в рабочую книгу Excel. Поскольку таблицы уже организуют содержимое в строки и столбцы, они естественным образом преобразуются в формат электронной таблицы, сохраняя при этом логическую структуру.
В этом примере:
- Spire.Doc for Python загружает файл DOCX и извлекает данные таблиц.
- Spire.XLS for Python создает рабочую книгу Excel и записывает извлеченное содержимое на листы.
Объединение этих библиотек обеспечивает контролируемый программный процесс преобразования, подходящий для производственных сред.
Прежде чем использовать библиотеки в своем проекте, убедитесь, что вы установили необходимые пакеты. Вы можете установить их через pip:
Пошагово: Конвертация таблиц Word в Excel с помощью Python
Ниже приведен типичный рабочий процесс для преобразования таблиц DOCX в XLSX с помощью Python:
-
Загрузите файл DOCX Используйте Spire.Doc for Python, чтобы открыть документ Word.
-
Извлеките таблицы из документа Пройдитесь по структуре документа и извлеките данные таблиц.
-
Создайте рабочую книгу Excel Инициализируйте новую рабочую книгу с помощью Spire.XLS for Python.
-
Запишите данные таблиц на листы Сопоставьте строки и ячейки из таблиц Word со строками и столбцами Excel.
-
Сохраните файл как XLSX Экспортируйте конечный результат в виде электронной таблицы Excel.
Код Python: Конвертация таблиц DOCX в XLSX
Следующий пример демонстрирует, как извлечь таблицы из документа Word и экспортировать их на лист Excel.
from spire.doc import Document
from spire.xls import Workbook, Color
# Load the Word document
doc = Document()
doc.LoadFromFile("Sample.docx")
# Create a new Excel workbook
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.Worksheets.Clear()
# Iterate through all sections in the Word document
for sec_index in range(len(doc.Sections)):
section = doc.Sections.get_Item(sec_index)
# Iterate through all tables in the current section
for table_index in range(len(section.Tables)):
table = section.Tables.get_Item(table_index)
# Create a worksheet for each Word table
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add(f"Table-{table_index + 1}")
# Iterate through rows in the Word table
for row_index in range(len(table.Rows)):
row = table.Rows.get_Item(row_index)
# Iterate through cells in the current row
for cell_index in range(len(row.Cells)):
table_cell = row.Cells.get_Item(cell_index)
# Collect all paragraph text inside the Word table cell
cell_data = ""
for para_index in range(len(table_cell.Paragraphs)):
para = table_cell.Paragraphs.get_Item(para_index)
cell_data += para.Text + "\n"
# Write text to the corresponding Excel cell
cell = sheet.Range.get_Item(row_index + 1, cell_index + 1)
cell.Value = cell_data
# Copy the Word table cell background color to Excel
# Note: Color must be assigned directly to the Style to take effect
table_cell_color = table_cell.CellFormat.BackColor
cell.Style.Color = Color.FromRgb(
table_cell_color.R,
table_cell_color.G,
table_cell_color.B
)
# Auto-fit columns after writing the table
sheet.AllocatedRange.AutoFitColumns()
# Save the Excel file
workbook.SaveToFile("WordTableToExcel.xlsx")
Ниже приведен предварительный просмотр файла XLSX, преобразованного из документа Word:

Этот подход особенно полезен для структурированных документов, отчетов и файлов Word на основе форм, где таблицы представляют основные данные.
Для более продвинутых техник Python, включая сохранение форматирования и стилей таблиц при преобразовании Word в Excel, ознакомьтесь с нашим подробным руководством по преобразованию таблиц Word в Excel с помощью Python.
Сравнение методов конвертации DOCX в XLSX
Выбор правильного метода зависит от таких факторов, как объем документов, потребности в автоматизации и конфиденциальность данных. Таблица ниже предоставляет краткий обзор, который поможет вам оценить каждый вариант.
| Метод | Лучше всего для | Уровень автоматизации | Преимущества | Ограничения |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Онлайн-конвертер | Одноразовые задачи | Нет | Быстро и легко | Риски конфиденциальности, ограниченная точность |
| Настольное ПО | Небольшие объемы работ | Низкий | Визуальный контроль | Трудоемко, не масштабируемо |
| Автоматизация на Python | Большие рабочие процессы | Высокий | Гибко, повторяемо | Требует программирования |
Как выбрать правильный метод
- Используйте онлайн-конвертеры, когда важна скорость, а файлы не являются конфиденциальными.
- Выбирайте настольное программное обеспечение, если вы предпочитаете ручной контроль для небольшого количества документов.
- Выбирайте автоматизацию на Python при работе с большими наборами данных или создании повторяемых рабочих процессов.
Для текущих или критически важных для бизнеса процессов автоматизированные решения обычно обеспечивают большую долгосрочную эффективность и последовательность.
FAQ: Конвертация DOCX в XLSX
Могу ли я конвертировать любой документ Word в Excel?
Большинство файлов Word можно конвертировать, но документы с таблицами или структурированными данными работают лучше всего. Текст в свободной форме и сложные макеты могут потребовать корректировки после преобразования.
Сохранится ли форматирование после конвертации?
Не всегда. Word и Excel по-разному обрабатывают макеты, поэтому некоторые интервалы, объединенные ячейки или поток текста могут измениться. Обычно требуются незначительные корректировки в Excel.
Могу ли я конвертировать только таблицы из Word в Excel?
Да. Если ваш документ Word содержит таблицы, вы можете извлечь только таблицы для более точного и надежного преобразования.
Какой самый простой способ конвертировать несколько файлов DOCX?
Для нескольких файлов автоматизированные решения или пакетные инструменты, такие как библиотеки Python, могут сэкономить время и обеспечить согласованные результаты, особенно для больших документов.
Заключение
Преобразование DOCX в XLSX — это не универсальная задача. Хотя онлайн- и настольные инструменты полезны для простых сценариев, они часто не справляются, когда требуется точность, масштабируемость или автоматизация.
Понимая структуру ваших документов Word и выбирая правильный подход к преобразованию, вы можете достичь надежных результатов. Для разработчиков и опытных пользователей Python предлагает мощный и гибкий способ эффективного преобразования таблиц Word в электронные таблицы Excel.
Смотрите также
Markdown을 PDF로 변환하는 방법: 3가지 쉽고 확실한 방법

마크다운(MD)은 문서, 기술 블로그, README 파일 및 보고서 작성에 가장 널리 사용되는 형식 중 하나가 되었습니다. 그러나 최종 문서를 공유하거나, 보고서를 인쇄하거나, 전문 자료를 배포할 때 마크다운 파일이 항상 이상적인 것은 아닙니다. 이것이 많은 사용자가 마크다운을 PDF로 변환해야 하는 이유입니다. PDF는 레이아웃을 보존하고, 여러 장치에서 일관된 표시를 보장하며, 보편적으로 허용되는 형식입니다.
이 가이드에서는 콘텐츠의 구조와 서식을 유지하면서 마크다운 파일을 PDF로 변환하는 방법을 살펴봅니다. 개발자, 기술 작가, 연구원 또는 콘텐츠 제작자이든 관계없이 필요에 맞는 적절한 마크다운-PDF 변환 방법을 찾을 수 있습니다.
다룰 내용:
마크다운이란 무엇인가?
마크다운은 2004년 존 그루버가 만든 경량 마크업 언어입니다. 복잡한 서식 도구 대신 간단한 기호를 사용하여 일반 텍스트의 서식을 지정할 수 있습니다. 이로 인해 문서, 메모, 블로그 게시물, 심지어 학술 논문 작성에 이상적입니다.
몇 가지 기본적인 마크다운 요소는 다음과 같습니다:
- # 제목은 제목을 만듭니다
- _기울임꼴_은 기울임꼴 텍스트를 생성합니다
- - 목록 항목은 글머리 기호 목록을 생성합니다
마크다운 파일은 일반적으로 .md 또는 .markdown 확장자를 사용하며 HTML, PDF, Word 문서, 심지어 전자책과 같은 다른 형식으로 변환할 수 있습니다.
마크다운을 PDF로 변환하는 이유
마크다운은 콘텐츠 초안 작성 및 편집에 이상적이지만, PDF는 공유, 인쇄 및 전문 배포에 선호되는 형식입니다. 마크다운 파일을 PDF로 변환하면 다음과 같은 몇 가지 주요 이점이 있습니다:
- 전문적인 프레젠테이션: PDF는 보고서, 가이드 및 기술 문서에 완벽한 깔끔하고 세련된 형식을 제공합니다.
- 원활한 공유 및 인쇄: PDF는 보편적으로 지원되며 공유하거나 인쇄할 때 서식 무결성을 유지합니다.
- 일관된 서식: 일반 텍스트와 달리 PDF는 마크다운 파일의 구조, 제목, 글머리 기호 및 기타 요소를 유지하여 모든 장치에서 콘텐츠가 동일하게 보이도록 보장합니다.
마크다운을 PDF로 변환함으로써 콘텐츠가 전문적이고 더 넓은 청중에게 접근 가능하도록 보장할 수 있습니다.
마크다운을 PDF로 변환하는 방법
마크다운을 PDF로 변환하는 다양한 방법이 있으며, 각각 다른 요구에 부응합니다. 이 섹션에서는 온라인 도구에서 데스크톱 응용 프로그램 및 자동화된 파이썬 스크립트에 이르기까지 세 가지 신뢰할 수 있는 방법을 살펴보고, 장단점 및 이상적인 사용 사례를 비교하여 최상의 솔루션을 선택하는 데 도움을 드립니다.
1. 무료 온라인 도구를 사용하여 마크다운을 PDF로 변환
온라인 마크다운-PDF 변환기는 마크다운 파일을 PDF로 변환하는 가장 빠르고 편리한 방법을 제공합니다. 이러한 도구를 사용하면 마크다운 콘텐츠를 간단히 붙여넣거나 업로드하고 몇 분 안에 PDF를 생성할 수 있습니다. 빠른 변환, 가끔 사용하는 사용자 또는 로컬 소프트웨어를 설치할 수 없는 경우에 이상적입니다.
인기 있는 온라인 마크다운-PDF 변환기:
- MarkdowntoPDF: 마크다운 콘텐츠를 붙여넣고 PDF 버전을 즉시 다운로드할 수 있는 간단한 온라인 도구입니다.
- CloudConvert: 마크다운-PDF를 포함한 다양한 파일 변환을 지원하는 다용도 플랫폼입니다.
온라인에서 마크다운을 PDF로 변환하는 단계 (MarkdowntoPDF를 예로 사용):
-
온라인 마크다운-PDF 변환기를 엽니다.
-
웹페이지 왼쪽의 지정된 영역에 마크다운 콘텐츠를 붙여넣습니다.
-
오른쪽 상단의 다운로드 버튼을 클릭하여 PDF 파일을 다운로드합니다.
장점:
- 빠르고 간단함: 소프트웨어 설치나 복잡한 설정이 필요 없어 이동 중 변환에 적합합니다.
- 장치 친화적: 인터넷 연결이 있는 모든 장치에서 접근할 수 있어 어디서든 편리함을 제공합니다.
- 무료: 대부분의 온라인 도구는 숨겨진 비용이나 구독 없이 무료 변환을 제공합니다.
단점:
- 제한된 사용자 정의: 이러한 도구는 일반적으로 최소한의 서식 옵션을 제공하므로 최종 PDF 모양에 대한 제어가 제한될 수 있습니다.
- 개인 정보 보호 위험: 민감하거나 기밀 문서를 타사 웹사이트에 업로드하면 잠재적인 보안 및 개인 정보 보호 문제가 발생할 수 있습니다.
가장 적합한 경우:
- 고급 서식이 필요 없는 빠르고 작은 문서 변환.
- 추가 소프트웨어 없이 간단한 브라우저 기반 솔루션을 찾는 사용자.
2. 데스크톱 마크다운 편집기를 사용하여 마크다운을 PDF로 변환
문서 서식에 대한 더 많은 제어가 필요하거나 오프라인 작업을 선호하는 경우 Typora 및 Visual Studio Code(VS Code)와 같은 데스크톱 마크다운 편집기가 훌륭한 선택입니다. 이러한 도구는 더 많은 사용자 정의를 허용하며 크거나 복잡한 문서에 이상적입니다.
a. Typora 사용
Typora는 깔끔한 인터페이스와 실시간 미리보기 기능을 갖춘 잘 알려진 마크다운 편집기입니다. 사용자가 마크다운 콘텐츠를 쉽게 편집하고 PDF로 내보낼 수 있습니다. Typora는 복잡한 설정 없이 간단하고 방해 없는 쓰기 환경을 찾는 개발자, 기술 작가 및 콘텐츠 제작자에게 훌륭한 선택입니다.
Typora로 마크다운을 PDF로 변환하는 단계:
-
Typora 설치: 공식 웹사이트(Windows, macOS 및 Linux에서 사용 가능)에서 Typora를 다운로드하여 설치합니다.
-
마크다운 파일 열기: Typora를 실행하고 파일 → 열기를 선택하거나 .md 파일을 편집기 창으로 끌어다 놓아 마크다운 파일을 엽니다.
-
PDF로 내보내기: 문서가 준비되면 파일 → 내보내기 → PDF로 이동한 다음 대상 폴더를 선택하고 PDF를 저장합니다.
장점:
- 실시간 미리보기: 최종 PDF가 어떻게 보일지 즉시 미리 볼 수 있습니다.
- 간단한 인터페이스: 방해 없고 간단한 디자인으로 글쓰기에 적합합니다.
- 오프라인 사용: 인터넷 연결 없이 작동합니다.
단점:
- 일괄 지원 없음: 한 번에 하나의 파일만 변환할 수 있습니다.
가장 적합한 경우:
- 빠른 단일 파일 변환.
- 간단하고 방해 없는 쓰기 경험을 찾는 사용자.
- 인터넷 연결이 필요 없는 오프라인 작업.
b. Visual Studio Code (VS Code) 사용
VS Code는 Markdown PDF와 같은 확장의 도움으로 마크다운 편집 및 변환에도 사용할 수 있는 매우 다재다능한 코드 편집기입니다. 변환 프로세스에 대한 더 많은 제어가 필요한 개발자나 고급 사용자에게 특히 적합합니다.
VS Code를 사용하여 마크다운을 PDF로 내보내는 단계:
-
VS Code 설치: 아직 설치하지 않았다면 Visual Studio Code를 다운로드하여 설치합니다.
-
Markdown PDF 확장 설치: 확장 마켓플레이스로 이동하여 Markdown PDF 확장을 검색하고 설치합니다.
-
마크다운 파일 열기: VS Code에서 마크다운 파일을 엽니다.
-
PDF로 내보내기: 편집기 창 내부를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭한 다음 컨텍스트 메뉴에서 Markdown PDF: 내보내기(pdf)를 선택합니다. PDF가 생성되어 마크다운 파일과 동일한 폴더에 저장됩니다.
장점:
- 고도로 사용자 정의 가능: 추가 설정 및 템플릿을 포함하여 PDF 출력 형식에 대한 세부적인 제어를 제공합니다.
- 다양한 형식 지원: PDF 외에도 VS Code는 마크다운을 HTML, PNG 및 JPEG 이미지와 같은 다른 형식으로 변환할 수 있어 다양한 콘텐츠 요구에 맞는 다재다능한 도구입니다.
- 개발자에게 이상적: 이미 개발에 VS Code를 사용하고 있다면 도구를 전환할 필요 없이 마크다운 변환을 원활하게 통합합니다.
단점:
- 확장 필요: Markdown PDF 확장을 설치하고 추가 설정을 구성해야 할 수 있습니다.
- 초보자에게 복잡함: VS Code는 주로 개발 도구이므로 마크다운-PDF 변환에만 사용하는 경우 부담스러울 수 있습니다.
- 내장된 일괄 처리 없음: Typora와 마찬가지로 VS Code는 기본적으로 일괄 변환을 지원하지 않지만 사용자 정의 스크립팅으로 이를 수행할 수 있습니다.
가장 적합한 경우:
- 이미 VS Code를 사용하고 있는 개발자 또는 빈번한 마크다운 사용자.
- PDF 출력에 대한 고급 사용자 정의 및 제어가 필요한 사용자.
3. 파이썬을 사용하여 대량 마크다운-PDF 변환 자동화
대량의 마크다운 파일을 다루는 개발자나 팀의 경우 각 문서를 수동으로 변환하는 것은 비효율적일 수 있습니다. 이 프로세스를 파이썬으로 자동화하면 시간을 절약할 뿐만 아니라 문서 전반에 걸쳐 일관성을 보장할 수 있습니다. Spire.Doc for Python과 같은 파이썬 라이브러리를 사용하면 마크다운 파일을 PDF로 일괄 변환할 수 있어 자동화된 문서 파이프라인이나 보고서 생성에 이상적입니다.
파이썬을 사용하여 마크다운을 PDF로 일괄 변환하는 단계:
-
필요한 라이브러리 설치:
먼저 pip를 사용하여 PyPI에서 spire.doc를 설치합니다:
pip install spire.doc -
파이썬 스크립트 작성:
여러 마크다운 파일을 변환하는 파이썬 스크립트를 만듭니다. 다음은 특정 디렉토리 아래의 모든 MD 파일을 PDF로 변환하는 간단한 예입니다:
import os from spire.doc import * # Document 클래스의 객체 생성 doc = Document() # 마크다운 파일이 저장된 디렉토리 정의 input_directory = "input_directory_path" # 입력 폴더 경로로 바꾸세요 output_directory = "output_directory_path" # 출력 폴더 경로로 바꾸세요 # 출력 디렉토리가 존재하는지 확인 if not os.path.exists(output_directory): os.makedirs(output_directory) # 입력 디렉토리의 모든 파일을 반복 for filename in os.listdir(input_directory): if filename.endswith(".md"): # 파일이 마크다운 파일인지 확인 input_file_path = os.path.join(input_directory, filename) # .pdf 확장자로 출력 파일 경로 생성 output_file_path = os.path.join(output_directory, f"{os.path.splitext(filename)[0]}.pdf") # 마크다운 파일 로드 doc.LoadFromFile(input_file_path, FileFormat.Markdown) # 파일을 PDF 문서로 저장 doc.SaveToFile(output_file_path, FileFormat.PDF) # Document 객체 해제 doc.Dispose() print("일괄 변환이 성공적으로 완료되었습니다!") -
스크립트 실행:
파이썬 환경에서 스크립트를 실행합니다. 마크다운 파일이 PDF로 변환되어 지정된 출력 위치에 저장됩니다.
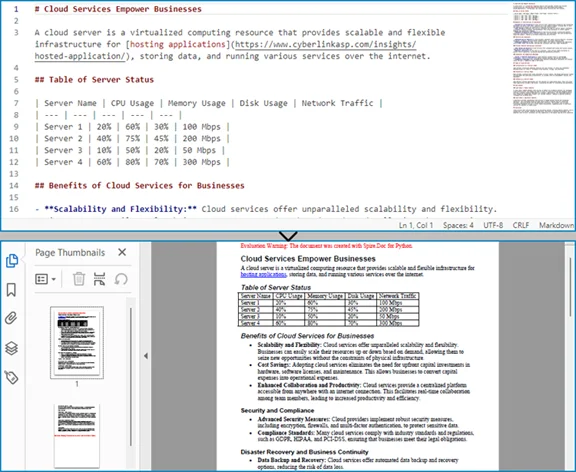
장점:
- 일괄 처리: 여러 파일의 변환을 한 번에 자동화하여 시간과 노력을 절약합니다.
- 고급 기능: 더 복잡한 문서 처리를 위해 더 큰 워크플로우나 자동화된 시스템에 쉽게 통합할 수 있습니다.
단점:
- 기술적 능력 필요: 파이썬 및 관련 라이브러리에 대한 지식이 필요합니다.
- 설치 시간: 종속성을 설치하고 변환 스크립트를 작성하는 데 시간이 걸립니다.
- GUI 없음: 그래픽 사용자 인터페이스가 없어 비개발자에게는 덜 사용자 친화적입니다.
가장 적합한 경우:
- 수동 작업 없이 대량의 마크다운 파일을 PDF로 변환해야 하는 개발자 또는 기업.
고품질 마크다운-PDF 변환을 위한 모범 사례
마크다운-PDF 변환이 원활하고 최종 PDF가 전문적으로 보이도록 하려면 다음 모범 사례를 고려하십시오:
- 깨끗한 마크다운 구문 사용: 모든 제목, 목록 및 코드 블록이 올바르게 서식 지정되었는지 확인하여 변환 중 문제를 방지합니다.
- 출력 미리보기: 변환을 최종 확정하기 전에 항상 PDF 미리보기를 확인하여 문서가 원하는 대로 보이는지 확인합니다.
- 이미지 최적화: 문서에 이미지가 포함된 경우 인쇄에 적합한 크기와 해상도인지 확인합니다.
- 페이지 나누기 고려: 긴 문서에서는 페이지 나누기를 사용하여 PDF 버전에서 레이아웃이 깔끔하게 유지되도록 합니다.
마크다운-PDF 변환의 실제 사용 사례
마크다운-PDF 변환은 다음을 포함한 다양한 시나리오에서 널리 사용됩니다:
- 기술 문서: 개발자와 엔지니어는 종종 매뉴얼 및 가이드를 위해 마크다운 파일을 PDF로 변환합니다.
- 보고서 및 학술 논문: 많은 연구원과 학생들이 논문 작성을 위해 마크다운을 사용한 다음 제출을 위해 PDF로 변환합니다.
- 책 및 전자책: 저자는 마크다운으로 콘텐츠 초안을 작성하고 나중에 인쇄 또는 배포를 위해 PDF로 변환할 수 있습니다.
최종 생각 및 권장 사항
이제 마크다운을 PDF로 변환하는 방법을 이해했으므로 필요에 맞는 올바른 방법을 선택하는 데 도움이 되는 빠른 가이드는 다음과 같습니다:
- 온라인 도구: 소프트웨어를 설치하지 않고 빠르고 쉬운 솔루션이 필요할 때 빠른 일회성 변환에 가장 적합합니다.
- 데스크톱 편집기: 서식에 대한 더 많은 제어가 필요하거나 더 크거나 복잡한 문서를 사용하는 사용자에게 이상적입니다.
- 파이썬 자동화: 한 번에 여러 파일을 변환하거나 변환 프로세스를 더 큰 자동화된 워크플로우에 통합해야 하는 사람들에게 적합합니다.
필요에 맞는 방법을 선택하여 시간을 절약하고 효율성을 높이며 마크다운-PDF 프로세스를 간소화하십시오.
마크다운-PDF 변환에 대한 FAQ
Q1: 마크다운을 PDF로 어떻게 변환합니까?
A1: 마크다운을 PDF로 변환하려면 MarkdowntoPDF와 같은 온라인 도구, Typora와 같은 데스크톱 편집기를 사용하거나 파이썬 스크립트로 프로세스를 자동화할 수 있습니다.
Q2: 마크다운을 PDF로 변환하는 가장 쉬운 방법은 무엇입니까?
A2: 가장 쉬운 방법은 MarkdowntoPDF와 같은 무료 온라인 변환기를 사용하는 것입니다. 마크다운을 붙여넣고 즉시 PDF를 다운로드할 수 있습니다.
Q3: 여러 마크다운 파일을 한 번에 PDF로 변환할 수 있습니까?
A3: 예, Spire.Doc과 같은 라이브러리와 함께 파이썬을 사용하면 간단한 스크립트로 마크다운 파일의 PDF로의 일괄 변환을 자동화할 수 있습니다.
Q4: 왜 마크다운을 PDF로 변환해야 합니까?
A4: 마크다운을 PDF로 변환하면 콘텐츠가 여러 장치에서 일관되게 표시되므로 공유, 인쇄 및 전문 배포에 이상적입니다.
참고 항목
Come convertire Markdown in PDF: 3 modi semplici e affidabili

Markdown (MD) è diventato uno dei formati più utilizzati per scrivere documentazione, blog tecnici, file README e report. Tuttavia, quando si tratta di condividere documenti finalizzati, stampare report o distribuire materiali professionali, i file Markdown non sono sempre ideali. Ecco perché molti utenti hanno bisogno di convertire Markdown in PDF - un formato che preserva il layout, garantisce una visualizzazione coerente su tutti i dispositivi ed è universalmente accettato.
Questa guida esplorerà come convertire i file Markdown in PDF mantenendo la struttura e la formattazione dei tuoi contenuti. Che tu sia uno sviluppatore, un redattore tecnico, un ricercatore o un creatore di contenuti, troverai il metodo di conversione da Markdown a PDF adatto alle tue esigenze.
Tratteremo:
- Cos'è Markdown
- Perché Convertire Markdown in PDF
- Come Convertire Markdown in PDF: 3 Metodi Affidabili
- Migliori Pratiche per un Risultato di Conversione di Alta Qualità
Cos'è Markdown?
Markdown è un linguaggio di markup leggero creato da John Gruber nel 2004. Consente di formattare testo semplice utilizzando simboli semplici anziché complessi strumenti di formattazione. Questo lo rende ideale per scrivere documentazione, note, post di blog e persino articoli accademici.
Alcuni elementi di base di Markdown includono:
- # Intestazione crea un titolo
- _corsivo_ produce testo in corsivo
- - elementi di elenco generano elenchi puntati
I file Markdown utilizzano in genere le estensioni .md o .markdown e possono essere convertiti in altri formati come HTML, PDF, documenti Word e persino eBook.
Perché Convertire Markdown in PDF
Mentre Markdown è ideale per la stesura e la modifica dei contenuti, il PDF è il formato preferito per la condivisione, la stampa e la distribuzione professionale. La conversione dei file Markdown in PDF offre diversi vantaggi chiave:
- Presentazione Professionale: i PDF offrono un formato pulito e raffinato, perfetto per report, guide e documentazione tecnica.
- Condivisione e Stampa Senza Interruzioni: i PDF sono universalmente supportati e mantengono l'integrità della formattazione quando vengono condivisi o stampati.
- Formattazione Coerente: a differenza del testo semplice, i PDF mantengono la struttura, le intestazioni, gli elenchi puntati e altri elementi del tuo file Markdown, garantendo che il contenuto appaia identico su tutti i dispositivi.
Convertendo Markdown in PDF, ti assicuri che i tuoi contenuti siano sia professionali che accessibili a un pubblico più ampio.
Come Convertire Markdown in PDF
Esistono vari modi per convertire Markdown in PDF, ognuno adatto a esigenze diverse. In questa sezione, esploreremo tre metodi affidabili, che vanno dagli strumenti online alle applicazioni desktop e agli script Python automatizzati, confrontandone pro, contro e casi d'uso ideali per aiutarti a scegliere la soluzione migliore.
1. Convertire Markdown in PDF Utilizzando Strumenti Online Gratuiti
I convertitori online da Markdown a PDF offrono il modo più rapido e conveniente per convertire un file Markdown in PDF. Questi strumenti ti consentono di incollare o caricare semplicemente i tuoi contenuti Markdown e generare un PDF in pochi istanti. Sono ideali per conversioni rapide, utenti occasionali o quando l'installazione di software locale non è un'opzione.
Convertitori Online Popolari da Markdown a PDF:
- MarkdowntoPDF: uno strumento online semplice che ti consente di incollare i tuoi contenuti Markdown e scaricare immediatamente la versione PDF.
- CloudConvert: una piattaforma versatile che supporta una varietà di conversioni di file, inclusa quella da Markdown a PDF.
Passaggi per Convertire Markdown in PDF Online (Usando MarkdowntoPDF come Esempio):
-
Incolla il tuo contenuto markdown nell'area designata sul lato sinistro della pagina web.

-
Fai clic sul pulsante Download in alto a destra per scaricare il file PDF.
Pro:
- Veloce & Semplice: nessuna installazione di software o configurazione complicata richiesta, perfetto per conversioni al volo.
- Compatibile con i Dispositivi: accessibile da qualsiasi dispositivo con una connessione Internet, offrendo comodità ovunque tu sia.
- Gratuito: la maggior parte degli strumenti online offre conversioni gratuite senza costi nascosti o abbonamenti.
Contro:
- Personalizzazione Limitata: questi strumenti offrono generalmente opzioni di formattazione minime, che possono limitare il controllo sull'aspetto finale del PDF.
- Rischi per la Privacy: il caricamento di documenti sensibili o riservati su siti Web di terze parti può comportare potenziali problemi di sicurezza e privacy.
Ideale Per:
- Conversioni rapide di piccoli documenti che non richiedono una formattazione avanzata.
- Utenti che cercano una soluzione semplice basata su browser senza la necessità di software aggiuntivo.
2. Convertire Markdown in PDF Utilizzando Editor Markdown Desktop
Se hai bisogno di un maggiore controllo sulla formattazione del tuo documento o preferisci lavorare offline, gli editor Markdown desktop come Typora e Visual Studio Code (VS Code) sono scelte eccellenti. Questi strumenti consentono una maggiore personalizzazione e sono ideali per documenti più grandi o complessi.
a. Usando Typora
Typora è un noto editor Markdown con un'interfaccia pulita e una funzione di anteprima in tempo reale. Consente agli utenti di modificare ed esportare facilmente i contenuti Markdown in PDF. Typora è una scelta eccellente per sviluppatori, redattori tecnici e creatori di contenuti che cercano un ambiente di scrittura semplice e senza distrazioni, senza configurazioni complicate.
Passaggi per Convertire Markdown in PDF con Typora:
-
Installa Typora: scarica Typora dal suo sito Web ufficiale (disponibile per Windows, macOS e Linux) e installalo.
-
Apri il Tuo File Markdown: avvia Typora e apri il tuo file Markdown selezionando File → Apri o trascinando e rilasciando il file .md nella finestra dell'editor.
-
Esporta in PDF: una volta che il tuo documento è pronto, vai su File → Esporta → PDF, quindi scegli una cartella di destinazione e salva il PDF.

Pro:
- Anteprima dal Vivo: anteprima istantanea di come apparirà il PDF finale.
- Interfaccia Semplice: design semplice e senza distrazioni, perfetto per la scrittura.
- Uso Offline: funziona senza una connessione Internet.
Contro:
- Nessun Supporto Batch: puoi convertire solo un file alla volta.
Ideale per:
- Conversioni rapide di un singolo file.
- Utenti che cercano un'esperienza di scrittura semplice e senza distrazioni.
- Lavoro offline senza bisogno di una connessione Internet.
b. Usando Visual Studio Code (VS Code)
VS Code è un editor di codice altamente versatile che può essere utilizzato anche per la modifica e la conversione di Markdown con l'aiuto di estensioni come Markdown PDF. È particolarmente adatto per sviluppatori o utenti avanzati che necessitano di un maggiore controllo sul processo di conversione.
Passaggi per Esportare Markdown in PDF Utilizzando VS Code:
-
Installa VS Code: scarica e installa Visual Studio Code se non l'hai già fatto.
-
Installa l'Estensione Markdown PDF: vai al Marketplace delle Estensioni, cerca l'estensione Markdown PDF e installala.

-
Apri il Tuo File Markdown: apri il tuo file Markdown in VS Code.
-
Esporta in PDF: fai clic con il pulsante destro del mouse all'interno della finestra dell'editor, quindi seleziona Markdown PDF: Esporta (pdf) dal menu contestuale. Il PDF verrà generato e salvato nella stessa cartella del tuo file Markdown.

Pro:
- Altamente Personalizzabile: offre un controllo dettagliato sul formato di output del PDF, incluse impostazioni e modelli aggiuntivi.
- Supporta Più Formati: oltre al PDF, VS Code può convertire Markdown in altri formati come HTML, immagini PNG e JPEG, rendendolo uno strumento versatile per diverse esigenze di contenuto.
- Ideale per Sviluppatori: se stai già utilizzando VS Code per lo sviluppo, integra perfettamente la conversione di Markdown senza la necessità di cambiare strumento.
Contro:
- Estensione Richiesta: è necessario installare l'estensione Markdown PDF ed eventualmente configurare impostazioni aggiuntive.
- Complesso per i Principianti: VS Code può essere opprimente se lo si utilizza solo per la conversione da Markdown a PDF, poiché è principalmente uno strumento di sviluppo.
- Nessuna Elaborazione Batch Integrata: come Typora, VS Code non supporta nativamente le conversioni batch, sebbene ciò possa essere realizzato con script personalizzati.
Ideale Per:
- Sviluppatori o utenti frequenti di Markdown che utilizzano già VS Code.
- Utenti che necessitano di personalizzazione e controllo avanzati sull'output del PDF.
3. Automatizzare la Conversione Massiva da Markdown a PDF Utilizzando Python
Per sviluppatori o team che gestiscono grandi volumi di file Markdown, la conversione manuale di ogni documento può essere inefficiente. Automatizzare questo processo con Python non solo fa risparmiare tempo, ma garantisce anche coerenza tra i documenti. Librerie Python come Spire.Doc for Python consentono di convertire in batch i file Markdown in PDF, rendendolo ideale per pipeline di documentazione automatizzate o generazione di report.
Passaggi per Convertire in Batch Markdown in PDF Utilizzando Python:
-
Installa la Libreria Richiesta:
Innanzitutto, installa spire.doc da PyPI usando pip:
pip install spire.doc -
Scrivi uno Script Python:
Crea uno script Python per convertire più file markdown. Ecco un semplice esempio che converte tutti i file MD in una directory specifica in PDF:
import os from spire.doc import * # Create an object of the Document class doc = Document() # Define the directory where your Markdown files are stored input_directory = "input_directory_path" # Replace with your input folder path output_directory = "output_directory_path" # Replace with your output folder path # Ensure output directory exists if not os.path.exists(output_directory): os.makedirs(output_directory) # Loop through all files in the input directory for filename in os.listdir(input_directory): if filename.endswith(".md"): # Check if the file is a Markdown file input_file_path = os.path.join(input_directory, filename) # Create output file path with .pdf extension output_file_path = os.path.join(output_directory, f"{os.path.splitext(filename)[0]}.pdf") # Load the Markdown file doc.LoadFromFile(input_file_path, FileFormat.Markdown) # Save the file to a PDF document doc.SaveToFile(output_file_path, FileFormat.PDF) # Dispose of the Document object doc.Dispose() print("Batch conversion completed successfully!") -
Esegui lo Script:
Esegui il tuo script nel tuo ambiente Python. Il file Markdown verrà convertito in PDF e salvato nella posizione di output specificata.

Pro:
- Elaborazione Batch: automatizza la conversione di più file contemporaneamente, risparmiando tempo e fatica.
- Funzionalità Avanzate: si integra facilmente in flussi di lavoro più ampi o sistemi automatizzati per un'elaborazione di documenti più complessa.
Contro:
- Competenze Tecniche Richieste: richiede la conoscenza di Python e della libreria coinvolta.
- Tempo di Configurazione: richiede un po' di tempo per installare le dipendenze e scrivere lo script di conversione.
- Nessuna GUI: manca di un'interfaccia utente grafica, rendendolo meno intuitivo per i non sviluppatori.
Ideale Per:
- Sviluppatori o aziende che necessitano di convertire un gran numero di file Markdown in PDF senza sforzo manuale.
Migliori Pratiche per una Conversione di Alta Qualità da Markdown a PDF
Per garantire che la conversione da Markdown a PDF sia fluida e che il PDF finale abbia un aspetto professionale, considera le seguenti migliori pratiche:
- Usa una sintassi Markdown pulita: assicurati che tutte le intestazioni, gli elenchi e i blocchi di codice siano formattati correttamente per prevenire problemi durante la conversione.
- Visualizza l'anteprima dell'output: controlla sempre l'anteprima del PDF per assicurarti che il documento abbia l'aspetto desiderato prima di finalizzare la conversione.
- Ottimizza le immagini: se il tuo documento include immagini, assicurati che abbiano le dimensioni e la risoluzione giuste per la stampa.
- Considera le interruzioni di pagina: nei documenti più lunghi, utilizza le interruzioni di pagina per garantire che il layout rimanga ordinato nella versione PDF.
Casi d'Uso Reali della Conversione da Markdown a PDF
La conversione da Markdown a PDF è ampiamente utilizzata in vari scenari, tra cui:
- Documentazione Tecnica: sviluppatori e ingegneri convertono spesso i file Markdown in PDF per manuali e guide.
- Report e Articoli Accademici: molti ricercatori e studenti usano Markdown per scrivere articoli, quindi li convertono in PDF per la sottomissione.
- Libri ed eBook: gli autori possono redigere i contenuti in Markdown e successivamente convertirli in PDF per la stampa o la distribuzione.
Considerazioni Finali e Raccomandazioni
Ora che hai capito come convertire Markdown in PDF, ecco una guida rapida per aiutarti a scegliere il metodo giusto per le tue esigenze:
- Strumenti online: ideali per conversioni rapide e occasionali quando hai bisogno di una soluzione veloce e facile senza installare software.
- Editor desktop: ideali per gli utenti che necessitano di un maggiore controllo sulla formattazione o che lavorano con documenti più grandi o complessi.
- Automazione con Python: perfetta per coloro che necessitano di convertire più file contemporaneamente o di integrare il processo di conversione in un flusso di lavoro automatizzato più ampio.
Seleziona il metodo che si allinea alle tue esigenze per risparmiare tempo, migliorare l'efficienza e ottimizzare il tuo processo da Markdown a PDF.
Domande Frequenti sulla Conversione da Markdown a PDF
D1: Come converto Markdown in PDF?
R1: Per convertire Markdown in PDF, puoi utilizzare strumenti online come MarkdowntoPDF, editor desktop come Typora o automatizzare il processo con script Python.
D2: Qual è il modo più semplice per convertire Markdown in PDF?
R2: Il modo più semplice è utilizzare convertitori online gratuiti come MarkdowntoPDF, dove incolli il tuo Markdown e scarichi immediatamente il PDF.
D3: Posso convertire più file Markdown in PDF contemporaneamente?
R3: Sì, utilizzando Python con librerie come Spire.Doc, puoi automatizzare la conversione batch di file Markdown in PDF con un semplice script.
D4: Perché dovrei convertire Markdown in PDF?
R4: La conversione da Markdown a PDF garantisce che i tuoi contenuti vengano visualizzati in modo coerente su tutti i dispositivi, rendendolo ideale per la condivisione, la stampa e la distribuzione professionale.
Vedi Anche
Comment convertir Markdown en PDF : 3 méthodes faciles et fiables

Le Markdown (MD) est devenu l'un des formats les plus utilisés pour la rédaction de documentation, de blogs techniques, de fichiers README et de rapports. Cependant, lorsqu'il s'agit de partager des documents finalisés, d'imprimer des rapports ou de distribuer des documents professionnels, les fichiers Markdown ne sont pas toujours idéaux. C'est pourquoi de nombreux utilisateurs ont besoin de convertir le Markdown en PDF - un format qui préserve la mise en page, garantit un affichage cohérent sur tous les appareils et est universellement accepté.
Ce guide explorera comment convertir des fichiers Markdown en PDF tout en conservant la structure et le formatage de votre contenu. Que vous soyez développeur, rédacteur technique, chercheur ou créateur de contenu, vous trouverez la méthode de conversion Markdown en PDF adaptée à vos besoins.
Nous aborderons :
- Qu'est-ce que le Markdown
- Pourquoi convertir le Markdown en PDF
- Comment convertir le Markdown en PDF : 3 méthodes fiables
- Meilleures pratiques pour un résultat de conversion de haute qualité
Qu'est-ce que le Markdown ?
Le Markdown est un langage de balisage léger créé par John Gruber en 2004. Il vous permet de formater du texte brut à l'aide de symboles simples plutôt que d'outils de formatage complexes. Cela le rend idéal pour la rédaction de documentation, de notes, de billets de blog et même d'articles universitaires.
Certains éléments de base du Markdown incluent :
- # Titre crée un titre
- _italique_ produit du texte en italique
- - éléments de liste génèrent des listes à puces
Les fichiers Markdown utilisent généralement les extensions .md ou .markdown et peuvent être convertis vers d'autres formats comme HTML, PDF, documents Word, et même des eBooks.
Pourquoi convertir le Markdown en PDF
Alors que le Markdown est idéal pour la rédaction et l'édition de contenu, le PDF est le format préféré pour le partage, l'impression et la distribution professionnelle. La conversion de vos fichiers Markdown en PDF offre plusieurs avantages clés :
- Présentation professionnelle : Les PDF offrent un format propre et soigné, parfait pour les rapports, les guides et la documentation technique.
- Partage et impression fluides : Les PDF sont universellement pris en charge et conservent l'intégrité du formatage lors du partage ou de l'impression.
- Formatage cohérent : Contrairement au texte brut, les PDF conservent la structure, les titres, les listes à puces et les autres éléments de votre fichier Markdown, garantissant que le contenu s'affiche de la même manière sur tous les appareils.
En convertissant le Markdown en PDF, vous vous assurez que votre contenu est à la fois professionnel et accessible à un public plus large.
Comment convertir le Markdown en PDF
Il existe différentes manières de convertir le Markdown en PDF, chacune répondant à des besoins différents. Dans cette section, nous explorerons trois méthodes fiables - allant des outils en ligne aux applications de bureau et aux scripts Python automatisés - en comparant leurs avantages, leurs inconvénients et leurs cas d'utilisation idéaux pour vous aider à choisir la meilleure solution.
1. Convertir le Markdown en PDF à l'aide d'outils en ligne gratuits
Les convertisseurs Markdown en PDF en ligne offrent le moyen le plus rapide et le plus pratique de convertir un fichier Markdown en PDF. Ces outils vous permettent de simplement coller ou de télécharger votre contenu Markdown et de générer un PDF en quelques instants. Ils sont idéaux pour les conversions rapides, les utilisateurs occasionnels ou lorsque l'installation d'un logiciel local n'est pas une option.
Convertisseurs Markdown en PDF en ligne populaires :
- MarkdowntoPDF : Un outil en ligne simple qui vous permet de coller votre contenu Markdown et de télécharger instantanément la version PDF.
- CloudConvert : Une plateforme polyvalente prenant en charge une variété de conversions de fichiers, y compris Markdown en PDF.
Étapes pour convertir le Markdown en PDF en ligne (en utilisant MarkdowntoPDF comme exemple) :
-
Ouvrez le convertisseur Markdown en PDF en ligne.
-
Collez votre contenu markdown dans la zone désignée sur le côté gauche de la page Web.

-
Cliquez sur le bouton Télécharger en haut à droite pour télécharger le fichier PDF.
Avantages :
- Rapide et simple : Aucune installation de logiciel ou configuration compliquée requise - parfait pour les conversions en déplacement.
- Compatible avec les appareils : Accessible depuis n'importe quel appareil avec une connexion Internet, offrant une commodité où que vous soyez.
- Gratuit : La plupart des outils en ligne proposent des conversions gratuites sans frais cachés ni abonnements.
Inconvénients :
- Personnalisation limitée : Ces outils offrent généralement des options de formatage minimales, ce qui peut restreindre le contrôle sur l'apparence finale du PDF.
- Risques de confidentialité : Le téléchargement de documents sensibles ou confidentiels sur des sites Web tiers peut poser des problèmes de sécurité et de confidentialité potentiels.
Idéal pour :
- Conversions rapides de petits documents qui ne nécessitent pas de formatage avancé.
- Utilisateurs à la recherche d'une solution simple, basée sur un navigateur, sans avoir besoin de logiciel supplémentaire.
2. Convertir le Markdown en PDF à l'aide d'éditeurs Markdown de bureau
Si vous avez besoin de plus de contrôle sur le formatage de votre document ou si vous préférez travailler hors ligne, les éditeurs Markdown de bureau comme Typora et Visual Studio Code (VS Code) sont d'excellents choix. Ces outils permettent une plus grande personnalisation et sont idéaux pour les documents plus volumineux ou plus complexes.
a. Utilisation de Typora
Typora est un éditeur Markdown bien connu avec une interface épurée et une fonction de prévisualisation en temps réel. Il permet aux utilisateurs d'éditer et d'exporter facilement du contenu Markdown en PDF. Typora est un excellent choix pour les développeurs, les rédacteurs techniques et les créateurs de contenu qui recherchent un environnement d'écriture simple et sans distraction, sans configurations compliquées.
Étapes pour convertir le Markdown en PDF avec Typora :
-
Installer Typora : Téléchargez Typora depuis son site officiel (disponible pour Windows, macOS et Linux) et installez-le.
-
Ouvrir votre fichier Markdown : Lancez Typora et ouvrez votre fichier Markdown en sélectionnant Fichier → Ouvrir ou en faisant glisser et en déposant le fichier .md dans la fenêtre de l'éditeur.
-
Exporter en PDF : Une fois votre document prêt, allez dans Fichier → Exporter → PDF, puis choisissez un dossier de destination et enregistrez le PDF.

Avantages :
- Aperçu en direct : Aperçu instantané de l'apparence finale du PDF.
- Interface simple : Conception simple et sans distraction, parfaite pour l'écriture.
- Utilisation hors ligne : Fonctionne sans connexion Internet.
Inconvénients :
- Pas de prise en charge par lots : Vous ne pouvez convertir qu'un seul fichier à la fois.
Idéal pour :
- Conversions rapides d'un seul fichier.
- Utilisateurs à la recherche d'une expérience d'écriture simple et sans distraction.
- Travail hors ligne sans besoin de connexion Internet.
b. Utilisation de Visual Studio Code (VS Code)
VS Code est un éditeur de code très polyvalent qui peut également être utilisé pour l'édition et la conversion de Markdown à l'aide d'extensions comme Markdown PDF. Il est particulièrement adapté aux développeurs ou aux utilisateurs avancés qui ont besoin de plus de contrôle sur le processus de conversion.
Étapes pour exporter le Markdown en PDF à l'aide de VS Code :
-
Installer VS Code : Téléchargez et installez Visual Studio Code si ce n'est pas déjà fait.
-
Installer l'extension Markdown PDF : Allez sur la Place de marché des extensions, recherchez l'extension Markdown PDF et installez-la.

-
Ouvrir votre fichier Markdown : Ouvrez votre fichier Markdown dans VS Code.
-
Exporter en PDF : Faites un clic droit dans la fenêtre de l'éditeur, puis sélectionnez Markdown PDF : Exporter (pdf) dans le menu contextuel. Le PDF sera généré et enregistré dans le même dossier que votre fichier Markdown.

Avantages :
- Hautement personnalisable : Offre un contrôle détaillé sur le format de sortie PDF, y compris des paramètres et des modèles supplémentaires.
- Prend en charge plusieurs formats : En plus du PDF, VS Code peut convertir le Markdown en d'autres formats comme HTML, images PNG et JPEG, ce qui en fait un outil polyvalent pour différents besoins de contenu.
- Idéal pour les développeurs : Si vous utilisez déjà VS Code pour le développement, il intègre de manière transparente la conversion Markdown sans avoir à changer d'outils.
Inconvénients :
- Extension requise : Vous devez installer l'extension Markdown PDF et éventuellement configurer des paramètres supplémentaires.
- Complexe pour les débutants : VS Code peut être intimidant si vous ne l'utilisez que pour la conversion de Markdown en PDF, car il s'agit principalement d'un outil de développement.
- Pas de traitement par lots intégré : Comme Typora, VS Code ne prend pas en charge nativement les conversions par lots, bien que cela puisse être accompli avec des scripts personnalisés.
Idéal pour :
- Développeurs ou utilisateurs fréquents de Markdown qui utilisent déjà VS Code.
- Utilisateurs ayant besoin d'une personnalisation et d'un contrôle avancés sur la sortie PDF.
3. Automatiser la conversion en masse de Markdown en PDF à l'aide de Python
Pour les développeurs ou les équipes traitant de gros volumes de fichiers Markdown, la conversion manuelle de chaque document peut être inefficace. L'automatisation de ce processus avec Python permet non seulement de gagner du temps, mais garantit également la cohérence de vos documents. Des bibliothèques Python comme Spire.Doc for Python vous permettent de convertir par lots des fichiers Markdown en PDF, ce qui le rend idéal pour les pipelines de documentation automatisés ou la génération de rapports.
Étapes pour convertir par lots le Markdown en PDF à l'aide de Python :
-
Installer la bibliothèque requise :
Tout d'abord, installez spire.doc depuis PyPI en utilisant pip :
pip install spire.doc -
Écrire un script Python :
Créez un script Python pour convertir plusieurs fichiers markdown. Voici un exemple simple qui convertit tous les fichiers MD d'un répertoire spécifique en PDF :
import os from spire.doc import * # Créer un objet de la classe Document doc = Document() # Définir le répertoire où vos fichiers Markdown sont stockés input_directory = "chemin_de_votre_dossier_d_entree" # Remplacer par le chemin de votre dossier d'entrée output_directory = "chemin_de_votre_dossier_de_sortie" # Remplacer par le chemin de votre dossier de sortie # S'assurer que le répertoire de sortie existe if not os.path.exists(output_directory): os.makedirs(output_directory) # Parcourir tous les fichiers du répertoire d'entrée for filename in os.listdir(input_directory): if filename.endswith(".md"): # Vérifier si le fichier est un fichier Markdown input_file_path = os.path.join(input_directory, filename) # Créer le chemin du fichier de sortie avec l'extension .pdf output_file_path = os.path.join(output_directory, f"{os.path.splitext(filename)[0]}.pdf") # Charger le fichier Markdown doc.LoadFromFile(input_file_path, FileFormat.Markdown) # Enregistrer le fichier dans un document PDF doc.SaveToFile(output_file_path, FileFormat.PDF) # Libérer l'objet Document doc.Dispose() print("La conversion par lots s'est terminée avec succès !") -
Exécuter le script :
Exécutez votre script dans votre environnement Python. Le fichier Markdown sera converti en PDF et enregistré à l'emplacement de sortie spécifié.

Avantages :
- Traitement par lots : Automatisez la conversion de plusieurs fichiers à la fois, ce qui permet d'économiser du temps et des efforts.
- Fonctionnalités avancées : Intégrez facilement dans des flux de travail plus importants ou des systèmes automatisés pour un traitement de documents plus complexe.
Inconvénients :
- Compétences techniques requises : Nécessite une connaissance de Python et de la bibliothèque impliquée.
- Temps de configuration : Prend un certain temps pour installer les dépendances et écrire le script de conversion.
- Pas d'interface graphique : Manque d'une interface utilisateur graphique, ce qui le rend moins convivial pour les non-développeurs.
Idéal pour :
- Développeurs ou entreprises qui ont besoin de convertir un grand nombre de fichiers Markdown en PDF sans effort manuel.
Meilleures pratiques pour une conversion de haute qualité de Markdown en PDF
Pour garantir que votre conversion de Markdown en PDF se déroule sans problème et que le PDF final ait un aspect professionnel, tenez compte des meilleures pratiques suivantes :
- Utilisez une syntaxe Markdown propre : Assurez-vous que tous les titres, listes et blocs de code sont correctement formatés pour éviter les problèmes lors de la conversion.
- Prévisualisez la sortie : Vérifiez toujours l'aperçu du PDF pour vous assurer que le document a l'apparence souhaitée avant de finaliser la conversion.
- Optimisez les images : Si votre document contient des images, assurez-vous qu'elles ont la bonne taille et la bonne résolution pour l'impression.
- Envisagez les sauts de page : Dans les documents plus longs, utilisez des sauts de page pour garantir que la mise en page reste soignée dans la version PDF.
Cas d'utilisation réels de la conversion de Markdown en PDF
La conversion de Markdown en PDF est largement utilisée dans divers scénarios, notamment :
- Documentation technique : Les développeurs et les ingénieurs convertissent souvent les fichiers Markdown en PDF pour les manuels et les guides.
- Rapports et articles universitaires : De nombreux chercheurs et étudiants utilisent le Markdown pour rédiger des articles, puis les convertissent en PDF pour les soumettre.
- Livres et eBooks : Les auteurs peuvent rédiger du contenu en Markdown et le convertir ultérieurement en PDF pour l'impression ou la distribution.
Réflexions finales et recommandations
Maintenant que vous comprenez comment convertir le Markdown en PDF, voici un guide rapide pour vous aider à choisir la bonne méthode pour vos besoins :
- Outils en ligne : Idéal pour les conversions rapides et uniques lorsque vous avez besoin d'une solution rapide et facile sans installer de logiciel.
- Éditeurs de bureau : Idéal pour les utilisateurs qui ont besoin de plus de contrôle sur le formatage ou qui travaillent avec des documents plus volumineux ou plus complexes.
- Automatisation Python : Parfait pour ceux qui ont besoin de convertir plusieurs fichiers à la fois ou d'intégrer le processus de conversion dans un flux de travail automatisé plus large.
Sélectionnez la méthode qui correspond à vos besoins pour gagner du temps, améliorer l'efficacité et rationaliser votre processus de conversion de Markdown en PDF.
FAQ sur la conversion de Markdown en PDF
Q1 : Comment puis-je convertir le Markdown en PDF ?
R1 : Pour convertir le Markdown en PDF, vous pouvez utiliser des outils en ligne comme MarkdowntoPDF, des éditeurs de bureau comme Typora, ou automatiser le processus avec des scripts Python.
Q2 : Quelle est la manière la plus simple de convertir le Markdown en PDF ?
R2 : La manière la plus simple est d'utiliser des convertisseurs en ligne gratuits comme MarkdowntoPDF, où vous collez votre Markdown et téléchargez instantanément le PDF.
Q3 : Puis-je convertir plusieurs fichiers Markdown en PDF à la fois ?
R3 : Oui, en utilisant Python avec des bibliothèques comme Spire.Doc, vous pouvez automatiser la conversion par lots de fichiers Markdown en PDF avec un script simple.
Q4 : Pourquoi devrais-je convertir le Markdown en PDF ?
R4 : La conversion de Markdown en PDF garantit que votre contenu est affiché de manière cohérente sur tous les appareils, ce qui le rend idéal pour le partage, l'impression et la distribution professionnelle.
Voir aussi
Cómo convertir Markdown a PDF: 3 formas fáciles y fiables
Tabla de Contenidos

Markdown (MD) se ha convertido en uno de los formatos más utilizados para escribir documentación, blogs técnicos, archivos README e informes. Sin embargo, cuando se trata de compartir documentos finalizados, imprimir informes o distribuir materiales profesionales, los archivos Markdown no siempre son ideales. Es por eso que muchos usuarios necesitan convertir de Markdown a PDF, un formato que preserva el diseño, garantiza una visualización coherente en todos los dispositivos y es universalmente aceptado.
Esta guía explorará cómo convertir archivos Markdown a PDF manteniendo la estructura y el formato de su contenido. Ya sea que sea un desarrollador, escritor técnico, investigador o creador de contenido, encontrará el método de conversión de Markdown a PDF adecuado para sus necesidades.
Cubriremos:
- ¿Qué es Markdown?
- ¿Por qué convertir de Markdown a PDF?
- Cómo convertir de Markdown a PDF: 3 métodos fiables
- Mejores prácticas para un resultado de conversión de alta calidad
¿Qué es Markdown?
Markdown es un lenguaje de marcado ligero creado por John Gruber en 2004. Le permite formatear texto sin formato utilizando símbolos simples en lugar de herramientas de formato complejas. Esto lo hace ideal para escribir documentación, notas, publicaciones de blog e incluso trabajos académicos.
Algunos elementos básicos de Markdown incluyen:
- # Encabezado crea un título
- _cursiva_ produce texto en cursiva
- - elementos de lista generan listas con viñetas
Los archivos Markdown suelen utilizar las extensiones .md o .markdown y se pueden convertir a otros formatos como HTML, PDF, documentos de Word e incluso libros electrónicos.
¿Por qué convertir de Markdown a PDF?
Si bien Markdown es ideal para redactar y editar contenido, PDF es el formato preferido para compartir, imprimir y distribuir profesionalmente. Convertir sus archivos Markdown a PDF ofrece varios beneficios clave:
- Presentación profesional: los PDF proporcionan un formato limpio y pulido que es perfecto para informes, guías y documentación técnica.
- Compartir e imprimir sin problemas: los PDF son universalmente compatibles y mantienen la integridad del formato cuando se comparten o imprimen.
- Formato coherente: a diferencia del texto sin formato, los PDF mantienen la estructura, los encabezados, las viñetas y otros elementos de su archivo Markdown, lo que garantiza que el contenido se vea igual en todos los dispositivos.
Al convertir de Markdown a PDF, se asegura de que su contenido sea profesional y accesible para un público más amplio.
Cómo convertir de Markdown a PDF
Existen varias formas de convertir Markdown a PDF, cada una para satisfacer diferentes necesidades. En esta sección, exploraremos tres métodos fiables, que van desde herramientas en línea hasta aplicaciones de escritorio y scripts de Python automatizados, comparando sus pros, sus contras y sus casos de uso ideales para ayudarle a elegir la mejor solución.
1. Convertir de Markdown a PDF usando herramientas en línea gratuitas
Los convertidores de Markdown a PDF en línea ofrecen la forma más rápida y conveniente de convertir un archivo Markdown a PDF. Estas herramientas le permiten simplemente pegar o cargar su contenido de Markdown y generar un PDF en momentos. Son ideales para conversiones rápidas, usuarios ocasionales o cuando no es posible instalar software local.
Convertidores populares de Markdown a PDF en línea:
- MarkdowntoPDF: una herramienta en línea sencilla que le permite pegar su contenido de Markdown y descargar la versión en PDF al instante.
- CloudConvert: una plataforma versátil que admite una variedad de conversiones de archivos, incluida la de Markdown a PDF.
Pasos para convertir de Markdown a PDF en línea (usando MarkdowntoPDF como ejemplo):
-
Pegue su contenido de Markdown en el área designada en el lado izquierdo de la página web.

-
Haga clic en el botón Descargar en la parte superior derecha para descargar el archivo PDF.
Pros:
- Rápido y sencillo: no se requiere instalación de software ni configuración complicada, perfecto para conversiones sobre la marcha.
- Compatible con dispositivos: accesible desde cualquier dispositivo con conexión a Internet, lo que ofrece comodidad dondequiera que esté.
- Gratuito: la mayoría de las herramientas en línea ofrecen conversiones gratuitas sin tarifas ocultas ni suscripciones.
Contras:
- Personalización limitada: estas herramientas generalmente ofrecen opciones de formato mínimas, lo que puede restringir el control sobre la apariencia final del PDF.
- Riesgos de privacidad: la carga de documentos confidenciales o sensibles a sitios web de terceros puede plantear posibles problemas de seguridad y privacidad.
Ideal para:
- Conversiones rápidas de documentos pequeños que no requieren formato avanzado.
- Usuarios que buscan una solución sencilla basada en navegador sin necesidad de software adicional.
2. Convertir de Markdown a PDF usando editores de Markdown de escritorio
Si necesita más control sobre el formato de su documento o prefiere trabajar sin conexión, los editores de Markdown de escritorio como Typora y Visual Studio Code (VS Code) son excelentes opciones. Estas herramientas permiten una mayor personalización y son ideales para documentos más grandes o complejos.
a. Usando Typora
Typora es un conocido editor de Markdown con una interfaz limpia y una función de vista previa en tiempo real. Permite a los usuarios editar y exportar fácilmente contenido de Markdown a PDF. Typora es una excelente opción para desarrolladores, escritores técnicos y creadores de contenido que buscan un entorno de escritura simple y sin distracciones sin configuraciones complicadas.
Pasos para convertir de Markdown a PDF con Typora:
-
Instalar Typora: descargue Typora de su sitio web oficial (disponible para Windows, macOS y Linux) e instálelo.
-
Abra su archivo Markdown: inicie Typora y abra su archivo Markdown seleccionando Archivo → Abrir o arrastrando y soltando el archivo .md en la ventana del editor.
-
Exportar a PDF: una vez que su documento esté listo, vaya a Archivo → Exportar → PDF, luego elija una carpeta de destino y guarde el PDF.

Pros:
- Vista previa en vivo: vista previa instantánea de cómo se verá el PDF final.
- Interfaz simple: diseño simple y sin distracciones, perfecto para escribir.
- Uso sin conexión: funciona sin conexión a Internet.
Contras:
- Sin soporte por lotes: solo puede convertir un archivo a la vez.
Ideal para:
- Conversiones rápidas de un solo archivo.
- Usuarios que buscan una experiencia de escritura simple y sin distracciones.
- Trabajo sin conexión sin necesidad de conexión a Internet.
b. Usando Visual Studio Code (VS Code)
VS Code es un editor de código muy versátil que también se puede utilizar para la edición y conversión de Markdown con la ayuda de extensiones como Markdown PDF. Es especialmente adecuado para desarrolladores o usuarios avanzados que necesitan más control sobre el proceso de conversión.
Pasos para exportar de Markdown a PDF usando VS Code:
-
Instalar VS Code: descargue e instale Visual Studio Code si aún no lo ha hecho.
-
Instale la extensión Markdown PDF: vaya al Mercado de extensiones, busque la extensión Markdown PDF e instálela.

-
Abra su archivo Markdown: abra su archivo Markdown en VS Code.
-
Exportar a PDF: haga clic con el botón derecho dentro de la ventana del editor, luego seleccione Markdown PDF: Exportar (pdf) en el menú contextual. El PDF se generará y guardará en la misma carpeta que su archivo Markdown.

Pros:
- Altamente personalizable: ofrece un control detallado sobre el formato de salida del PDF, incluidas configuraciones y plantillas adicionales.
- Admite múltiples formatos: además de PDF, VS Code puede convertir Markdown a otros formatos como HTML, imágenes PNG y JPEG, lo que lo convierte en una herramienta versátil para diferentes necesidades de contenido.
- Ideal para desarrolladores: si ya está utilizando VS Code para el desarrollo, integra a la perfección la conversión de Markdown sin necesidad de cambiar de herramienta.
Contras:
- Se requiere extensión: debe instalar la extensión Markdown PDF y posiblemente configurar ajustes adicionales.
- Complejo para principiantes: VS Code puede ser abrumador si solo lo está utilizando para la conversión de Markdown a PDF, ya que es principalmente una herramienta de desarrollo.
- Sin procesamiento por lotes integrado: al igual que Typora, VS Code no admite de forma nativa las conversiones por lotes, aunque esto se puede lograr con secuencias de comandos personalizadas.
Ideal para:
- Desarrolladores o usuarios frecuentes de Markdown que ya utilizan VS Code.
- Usuarios que necesitan personalización avanzada y control sobre la salida del PDF.
3. Automatizar la conversión masiva de Markdown a PDF usando Python
Para los desarrolladores o equipos que manejan grandes volúmenes de archivos Markdown, la conversión manual de cada documento puede ser ineficiente. La automatización de este proceso con Python no solo ahorra tiempo, sino que también garantiza la coherencia en todos sus documentos. Las bibliotecas de Python como Spire.Doc for Python le permiten convertir por lotes archivos Markdown a PDF, lo que lo hace ideal para canalizaciones de documentación automatizadas o generación de informes.
Pasos para convertir por lotes de Markdown a PDF usando Python:
-
Instale la biblioteca requerida:
Primero, instale spire.doc desde PyPI usando pip:
pip install spire.doc -
Escriba un script de Python:
Cree un script de Python para convertir varios archivos Markdown. Aquí hay un ejemplo simple que convierte todos los archivos MD en un directorio específico a PDF:
import os from spire.doc import * # Cree un objeto de la clase Document doc = Document() # Defina el directorio donde se almacenan sus archivos Markdown input_directory = "ruta_de_la_carpeta_de_entrada" # Reemplace con la ruta de su carpeta de entrada output_directory = "ruta_de_la_carpeta_de_salida" # Reemplace con la ruta de su carpeta de salida # Asegúrese de que el directorio de salida exista if not os.path.exists(output_directory): os.makedirs(output_directory) # Recorra todos los archivos en el directorio de entrada for filename in os.listdir(input_directory): if filename.endswith(".md"): # Compruebe si el archivo es un archivo Markdown input_file_path = os.path.join(input_directory, filename) # Cree la ruta del archivo de salida con la extensión .pdf output_file_path = os.path.join(output_directory, f"{os.path.splitext(filename)[0]}.pdf") # Cargue el archivo Markdown doc.LoadFromFile(input_file_path, FileFormat.Markdown) # Guarde el archivo en un documento PDF doc.SaveToFile(output_file_path, FileFormat.PDF) # Deseche el objeto Document doc.Dispose() print("¡La conversión por lotes se completó con éxito!") -
Ejecute el script:
Ejecute su script en su entorno de Python. El archivo Markdown se convertirá a PDF y se guardará en la ubicación de salida especificada.

Pros:
- Procesamiento por lotes: automatice la conversión de varios archivos a la vez, ahorrando tiempo y esfuerzo.
- Funciones avanzadas: integre fácilmente en flujos de trabajo más grandes o sistemas automatizados para un procesamiento de documentos más complejo.
Contras:
- Se requieren habilidades técnicas: requiere conocimientos de Python y de la biblioteca involucrada.
- Tiempo de configuración: lleva algún tiempo instalar las dependencias y escribir el script de conversión.
- Sin GUI: carece de una interfaz gráfica de usuario, lo que lo hace menos fácil de usar para los no desarrolladores.
Ideal para:
- Desarrolladores o empresas que necesitan convertir grandes cantidades de archivos Markdown a PDF sin esfuerzo manual.
Mejores prácticas para una conversión de Markdown a PDF de alta calidad
Para garantizar que su conversión de Markdown a PDF sea fluida y que el PDF final se vea profesional, considere las siguientes mejores prácticas:
- Use una sintaxis de Markdown limpia: asegúrese de que todos los encabezados, listas y bloques de código estén formateados correctamente para evitar problemas durante la conversión.
- Obtenga una vista previa del resultado: siempre verifique la vista previa del PDF para asegurarse de que el documento se vea como desea antes de finalizar la conversión.
- Optimice las imágenes: si su documento incluye imágenes, asegúrese de que tengan el tamaño y la resolución adecuados para la impresión.
- Considere los saltos de página: en documentos más largos, use saltos de página para garantizar que el diseño se mantenga ordenado en la versión PDF.
Casos de uso del mundo real de la conversión de Markdown a PDF
La conversión de Markdown a PDF se utiliza ampliamente en varios escenarios, que incluyen:
- Documentación técnica: los desarrolladores e ingenieros a menudo convierten archivos Markdown en PDF para manuales y guías.
- Informes y trabajos académicos: muchos investigadores y estudiantes usan Markdown para escribir trabajos y luego los convierten a PDF para su envío.
- Libros y libros electrónicos: los autores pueden redactar contenido en Markdown y luego convertirlo a PDF para su impresión o distribución.
Reflexiones finales y recomendaciones
Ahora que comprende cómo convertir de Markdown a PDF, aquí tiene una guía rápida para ayudarle a elegir el método adecuado para sus necesidades:
- Herramientas en línea: ideales para conversiones rápidas y únicas cuando necesita una solución rápida y fácil sin instalar software.
- Editores de escritorio: ideales para usuarios que necesitan más control sobre el formato o que trabajan con documentos más grandes o complejos.
- Automatización de Python: perfecta para aquellos que necesitan convertir varios archivos a la vez o integrar el proceso de conversión en un flujo de trabajo automatizado más grande.
Seleccione el método que se alinee con sus necesidades para ahorrar tiempo, mejorar la eficiencia y optimizar su proceso de Markdown a PDF.
Preguntas frecuentes sobre la conversión de Markdown a PDF
P1: ¿Cómo convierto de Markdown a PDF?
R1: Para convertir de Markdown a PDF, puede usar herramientas en línea como MarkdowntoPDF, editores de escritorio como Typora o automatizar el proceso con scripts de Python.
P2: ¿Cuál es la forma más fácil de convertir de Markdown a PDF?
R2: La forma más fácil es usar convertidores en línea gratuitos como MarkdowntoPDF, donde pega su Markdown y descarga el PDF al instante.
P3: ¿Puedo convertir varios archivos Markdown a PDF a la vez?
R3: Sí, usando Python con bibliotecas como Spire.Doc, puede automatizar la conversión por lotes de archivos Markdown a PDF con un script simple.
P4: ¿Por qué debería convertir de Markdown a PDF?
R4: La conversión de Markdown a PDF garantiza que su contenido se muestre de manera consistente en todos los dispositivos, lo que lo hace ideal para compartir, imprimir y distribuir profesionalmente.